Abstract
The authors describe a method for signal amplification of label-free voltammetric immunosensors. A glassy carbon electrode (GCE) was modified with Prussian Blue-platinum nanoparticles (PB-PtNPs) as a redox-active species that gives a strong amperometric signal at 0.18 V (vs. Ag/AgCl). Benefitting from the excellent electrical conductivity and the strong catalytic activity to H2O2, the modified GCE gives a strongly enhanced signal. The PB-PtNPs were incorporated into a polyaniline (PANI) hydrogel to further enhance the signal. The signal response of the PB-PtNP-PANI/GCE is larger by a factor of 7.6 than that of PB-PtNP/GCE. In order to further improve electrical conductivity and immobilize antibody, gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) were deposited on the surface of the PB-PtNP-PANI hydrogel. The AuNP-PB-PtNP-PANI hydrogel nanocomposite on the GCE was used in an immunosensor for the model analyte carcinoma antigen 125 (CA125), a biomarker for epithelial ovarian cancer, by immobilizing the respective antibody on the modified GCE. A linear response found for the 0.01 to 5000 U mL−1 CA125 concentration range, with a detection limit of 4.4 mU mL−1 (at an S/N ratio of 3). The electrochemical sensitivity is as high as 119.76 μA·(U/mL)−1·cm−2. The detection of CA125 in human serum showed satisfactory accuracy compared to a commercial chemiluminescent microparticle immunoassay (CMIA).

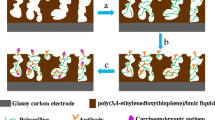
Schematic of a nanocomposites consisting of gold nanoparticles, Prussian Blue, platinum nanoparticles and polyaniline hydrogel as a signal multi-amplification sensing substrate for the ultrasensitive immuno detection of carcinoma antigen 125 (CA125).





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hipkins J, Whitworth M, Tarrier N, Jayson G (2004) Social support, anxiety and depression after chemotherapy for ovarian cancer: a prospective study. Br J Health Psychol 9:569–581
Bast RC, Siegal FP, Runowicz C, Klug TL, Knapp RC, Zurawski VR, Schonholz D, Cohen CJ (1985) Elevation of serum CA 125 prior to diagnosis of an epithelial ovarian carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol 22:115–120
Moore LE, Pfeiffer RM, Zhang Z, Lu KH, Fung ET, Bast RC (2012) Proteomic biomarkers in combination with CA 125 for detection of epithelial ovarian cancer using prediagnostic serum samples from the prostate, lung, colorectal, and ovarian (PLCO) cancer screening trial. Cancer 118:91–100
Sekiya S, Seki K, Nagai Y (1997) Rise of serum CA 125 in patients with pure ovarian yolk sac tumors. Int. J. Gynecol Obstet 58:323–324
Huh JJ, Montz FJ, Bristow RE (2002) Struma ovarii associated with pseudo-Meigs' syndrome and elevated serum CA 125. Gynecol Oncol 86:231–234
Wu J, Fu Z, Yan F, Ju H (2007) Biomedical and clinical applications of immunoassays and immunosensors for tumor markers. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 26:679–688
Mcquarrie SA, Baum RP, Niesen A, Madiyalakan R, Korz W, Sykes TR, Sykes CJ, Hör G, Mcewan AJ, Noujaim AA (1997) Pharmacokinetics and radiation dosimetry of 99Tcm-labelled monoclonal antibody B43.13 in ovarian cancer patients. Nucl Med Commun 18:878–886
He Z, Gao N, Jin W (2003) Determination of tumor marker CA125 by capillary electrophoretic enzyme immunoassay with electrochemical detection. Anal Chim Acta 497:75–81
Ryder KW, Oei TO, Hull MT, Sample MM (1988) An enzyme immunoassay procedure for cancer antigen 125 evaluated. Clin Chem 34:2513–2516
Lin J, Ju H (2005) Electrochemical and chemiluminescent immunosensors for tumor markers. Biosens Bioelectron 20:1461–1470
Hosu O, Ravalli A, Lo Piccolo GM, Cristea C, Sandulescu R, Marrazza G (2017) Smartphone-based immunosensor for CA125 detection. Talanta 166:234–240
Liu Y, Liu Y, Feng H, Wu Y, Joshi L, Zeng X, Li J (2012) Layer-by-layer assembly of chemical reduced graphene and carbon nanotubes for sensitive electrochemical immunoassay. Biosens Bioelectron 35:63–68
Chen Z, Liu Y, Wang Y, Zhao X, Li J (2013) Dynamic evaluation of cell surface N-glycan expression via an electrogenerated chemiluminescence biosensor based on concanavalin a-integrating gold-nanoparticle-modified Ru(bpy)3 2+-doped silica nanoprobe. Anal Chem 85:4431–4438
Liang RQ, Wang HZ, Wang HY, Ruan KC (2004) Detection of tumor marker CA125 in ovarian carcinoma using quantum dots. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 36:681–686
He M, Huang Z, Yan X, Liao X, Yin G, Duan A, Gu J (2013) Label-free detection of hepatocellular carcinoma markers based on photoluminescence of antibody-conjugated ZnO arrays. J Biomed Nanotechnol 9:2024–2033
Shan J, Ma Z (2016) Simultaneous detection of five biomarkers of lung cancer by electrochemical immunoassay. Microchim Acta 183:2889–2897
Torati SR, Kasturi KCSB, Lim B, Kim CG (2016) Hierarchical gold nanostructures modified electrode for electrochemical detection of cancer antigen CA125. Sensors Actuators B Chem 243:64–71
Zhang L, Li C, Zhao D, Wu T, Nie G (2014) An electrochemical immunosensor for the tumor marker α-fetoprotein using a glassy carbon electrode modified with a poly(5-formylindole), single-wall carbon nanotubes, and coated with gold nanoparticles and antibody. Microchim Acta 181:1601–1608
Niu Y, Yang T, Ma S, Peng F, Yi M, Wan M, Mao C, Shen J (2017) Label-free immunosensor based on hyperbranched polyester for specific detection of α-fetoprotein. Biosens Bioelectron 92:1–7
Jie G, Zhang J, Wang D, Cheng C, Chen HY, Zhu JJ (2008) Electrochemiluminescence immunosensor based on CdSe nanocomposites. Anal Chem 80:4033–4039
Lv P, Min L, Yuan R, Chai Y, Chen S (2010) A novel immunosensor for carcinoembryonic antigen based on poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride) protected prussian blue nanoparticles and double-layer nanometer-sized gold particles. Microchim Acta 171:297–304
Liang YR, Zhang ZM, Liu ZJ, Wang K, Wu XY, Zeng K, Meng H, Zhang Z (2017) A highly sensitive signal-amplified gold nanoparticle-based electrochemical immunosensor for dibutyl phthalate detection. Biosens Bioelectron 91:199–202
Tang Z, Fu Y, Ma Z (2017) Multiple signal amplification strategies for ultrasensitive label-free electrochemical immunoassay for carbohydrate antigen 24-2 based on redox hydrogel. Biosens Bioelectron 91:299–305
Neugebauer S, Stoica L, Guschin D, Schuhmann W (2008) Redox-amplified biosensors based on selective modification of nanopore electrode structures with enzymes entrapped within electrodeposition paints. Microchim Acta 163:33–40
Alizadeh N, Hallaj R, Salimi A (2017) A highly sensitive electrochemical immunosensor for hepatitis B virus surface antigen detection based on hemin/G-quadruplex horseradish peroxidase-mimicking DNAzyme-signal amplification. Biosens Bioelectron 94:184–192
He Y, Sun J, Wang X, Wang L (2015) Detection of human leptin in serum using chemiluminescence immunosensor: signal amplification by hemin/G-quadruplex DNAzymes and protein carriers by Fe3O4/polydopamine/Au nanocomposites. Sensors Actuators B Chem 221:792–798
Yang J, Xiang Y, Song C, Liu L, Jing X, Xie G, Xiang H (2015) Quadruple signal amplification strategy based on hybridization chain reaction and an immunoelectrode modified with graphene sheets, a hemin/G-quadruplex DNAzyme concatamer, and alcohol dehydrogenase: ultrasensitive determination of influenza virus. Microchim Acta 182:1–9
Lai G, Cheng H, Xin D, Zhang H, Yu A (2015) Amplified inhibition of the electrochemical signal of ferrocene by enzyme-functionalized graphene oxide nanoprobe for ultrasensitive immunoassay. Anal Chim Acta 902:189–195
Luo Y, Asiri AM, Zhang X, Yang G, Du D, Lin Y (2014) Magnetic electrochemical immunosensor for detection of phosphorylated p53 based on enzyme functionalized carbon nanospheres as signal amplification. RSC Adv 4:54066–54071
Wu H, Ohnuki H, Ota S, Murata M, Yoshiura Y, Endo H (2016) New approach for monitoring fish stress: a novel enzyme-functionalized label-free immunosensor system for detecting cortisol levels in fish. Biosens Bioelectron 93:57–64
Zhang L, Zhang Q, Lu X, Li J (2007) Direct electrochemistry and electrocatalysis based on film of horseradish peroxidase intercalated into layered titanate nano-sheets. Biosens Bioelectron 23:102–106
Tang J, Tang D (2015) Non-enzymatic electrochemical immunoassay using noble metal nanoparticles: a review. Microchim Acta 182:2077–2089
Liu Y, Ma H, Gao J, Wu D, Ren X, Yan T, Pang X, Wei Q (2016) Ultrasensitive electrochemical immunosensor for SCCA detection based on ternary Pt/PdCu nanocube anchored on three-dimensional graphene framework for signal amplification. Biosens Bioelectron 79:71–78
Zhang J, Wang J, Zhu J, Xu J, Chen H, Xu D (2008) An electrochemical impedimetric arrayed immunosensor based on indium tin oxide electrodes and silver-enhanced gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 163:63–70
Liu K, Zhang JJ, Wang C, Zhu JJ (2011) Graphene-assisted dual amplification strategy for the fabrication of sensitive amperometric immunosensor. Biosens Bioelectron 26:3627–3632
Jiang F, Zhang JJ, Zhang JR, Zhu JJ (2013) Ultrasensitive immunoassay based on dual signal amplification of the electrically heated carbon electrode and quantum dots functionalized labels for the detection of matrix metalloproteinase-9 †. Analyst 138:1962–1965
Liu ZH, Zhang GF, Chen Z, Qiu B, Tang D (2014) Prussian blue-doped nanogold microspheres for enzyme-free electrocatalytic immunoassay of p53 protein. Microchim Acta 181:581–588
Chen X, Wu G, Cai Z, Oyama M, Xi C (2014) Advances in enzyme-free electrochemical sensors for hydrogen peroxide, glucose, and uric acid. Microchim Acta 181:689–705
Zhu M, Tang Y, Wen Q, Li J, Yang P (2016) Dynamic evaluation of cell-secreted interferon gamma in response to drug stimulation via a sensitive electro-chemiluminescence immunosensor based on a glassy carbon electrode modified with graphene oxide, polyaniline nanofibers, magnetic beads, and gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 183:1739–1748
Gao P, Liu D (2015) Petal-like CuO nanostructures prepared by a simple wet chemical method, and their application to non-enzymatic amperometric determination of hydrogen peroxide. Microchim Acta 182:1231–1239
Dan W, Ma H, Yong Z, Jia H, Tao Y, Qin W (2015) Corallite-like magnetic Fe3O4@MnO2@Pt nanocomposites as multiple signal amplifiers for the detection of carcinoembryonic antigen. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:100–105
Liang RP, Yao GH, Fan LX, Qiu JD (2012) Magnetic Fe3O4@Au composite-enhanced surface plasmon resonance for ultrasensitive detection of magnetic nanoparticle-enriched α-fetoprotein. Anal Chim Acta 737:22–28
Zhang S, Shen Y, Shen G, Wang S, Shen G, Yu R (2016) Electrochemical immunosensor based on Pd-Au nanoparticles supported on functionalized PDDA-MWCNT nanocomposites for aflatoxin B1 detection. Anal Biochem 494:10–15
Li M, Wang P, Li F, Chu Q, Li Y, Dong Y (2017) An ultrasensitive sandwich-type electrochemical immunosensor based on the signal amplification strategy of mesoporous core-shell Pd@Pt nanoparticles/amino group functionalized graphene nanocomposite. Biosens Bioelectron 87:752–759
Zhang Y, Lu F, Yan Z, Wu D, Ma H, Du B, Wei Q (2015) Electrochemiluminescence immunosensing strategy based on the use of Au@Ag nanorods as a peroxidase mimic and NH4CoPO4 as a supercapacitive supporter: application to the determination of carcinoembryonic antigen. Microchim Acta 182:1421–1429
Wang J, Wang Y, Cui M, Xu S, Luo X (2016) Enzymeless voltammetric hydrogen peroxide sensor based on the use of PEDOT doped with Prussian blue nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 184:1–7
Yang J, Lin M, Cho MS, Lee Y (2015) Determination of hydrogen peroxide using a Prussian blue modified macroporous gold electrode. Microchim Acta 182:1089–1094
Doroftei F, Pinteala T, Arvinte A (2014) Enhanced stability of a Prussian blue/sol-gel composite for electrochemical determination of hydrogen peroxide. Microchim Acta 181:111–120
Pan L, Yu G, Zhai D, Lee HR, Zhao W, Liu N, Wang H, Tee BC, Shi Y, Cui Y (2012) Hierarchical nanostructured conducting polymer hydrogel with high electrochemical activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:9287–9292
Ravalli A, Santos GPD, Ferroni M, Faglia G, Yamanaka H, Marrazza G (2013) New label free CA125 detection based on gold nanostructured screen-printed electrode. Sensors Actuators B Chem 179:194–200
Büyüktiryaki S, Say R, Denizli A, Ersöz A (2017) Phosphoserine imprinted nanosensor for detection of cancer antigen 125. Talanta 167:172–180
Liu W, Ma C, Yang H, Zhang Y, Yan M, Ge S, Yu J, Song X (2014) Electrochemiluminescence immunoassay using a paper electrode incorporating porous silver and modified with mesoporous silica nanoparticles functionalized with blue-luminescent carbon dots. Microchim Acta 181:1415–1422
Viswanathan S, Rani C, Ribeiro S, Deleruematos C (2012) Molecular imprinted nanoelectrodes for ultrasensitive detection of ovarian cancer marker. Biosens Bioelectron 33:179–183
Chen S, Yuan R, Chai Y, Xu Y, Min L, Li N (2008) A new antibody immobilization technique based on organic polymers protected Prussian blue nanoparticles and gold colloidal nanoparticles for amperometric immunosensors. Sensors Actuators B Chem 135:236–244
Acknowledgements
This research was financed by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21673143, 21273153), Natural Science Foundation of Beijing Municipality (2172016, 2132008), and the Project of the Construction of Scientific Research Base by the Beijing Municipal Education Commission.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Yun Zheng and Huiqiang Wang contribute equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 5116 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, Y., Wang, H. & Ma, Z. A nanocomposite containing Prussian Blue, platinum nanoparticles and polyaniline for multi-amplification of the signal of voltammetric immunosensors: highly sensitive detection of carcinoma antigen 125. Microchim Acta 184, 4269–4277 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2470-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2470-2