Abstract
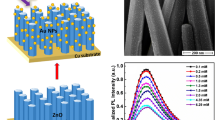
We report on an indirect optical method for the determination of glucose via the detection of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) that is generated during the glucose oxidase (GOx) catalyzed oxidation of glucose. It is based on the finding that the ultraviolet (~374 nm) and visible (~525 nm) photoluminescence of pristine zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles strongly depends on the concentration of H2O2 in water solution. Photoluminescence is quenched by up to 90 % at a 100 mM level of H2O2. The sensor constructed by immobilizing GOx on ZnO nanoparticles enabled glucose to be continuously monitored in the 10 mM to 130 mM concentration range, and the limit of detection is 10 mM. This enzymatic sensing scheme is supposed to be applicable to monitoring glucose in the food, beverage and fermentation industries. It has a wide scope in that it may be extended to numerous other substrate or enzyme activity assays based on the formation of H2O2, and of assays based on the consumption of H2O2 by peroxidases.

We report the application of ZnO nanoparticles (NPs) in a biosensor for monitoring glucose at a large concentration range. The biosensor is based on the indirect detection of hydrogen peroxide via the respective change of the UV and visible PL of ZnO NPs.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kirsch J, Siltanen C, Zhou Q, Revzin A, Simonian A (2013) Biosensor technology: recent advances in threat agent detection and medicine. Chem Soc Rev 42:8733–8768
Clark LC, Lyons C (1962) Electrode systems for continuous monitoring in cardiovascular surgery. Ann N Y Acad Sci 102:29–45
Cass AEG, Davis G, Francis GD, Hill HAO, Aston WJ, Higgins IJ, Plotkin EV, Scott LDL, Turner APF (1984) Ferrocene-mediated enzyme electrode for amperometric determination of glucose. Anal Chem 56:667–671
Turner APF (2013) Biosensors: sense and sensibility. Chem Soc Rev 42:3184–3196
Li J, Li H, Xue Y, Fang H, Wang W (2014) Facile electrodeposition of environment-friendly Cu2O/ZnO heterojunction for robust photoelectrochemical biosensing. Sensors Actuators B Chem 191:619–624
Xi X, Li J, Wang H, Zhao Q, Li H (2015) Non-enzymatic photoelectrochemical sensing of hydrogen peroxide using hierarchically structured zinc oxide hybridized with graphite-like carbon nitride. Microchim Acta, 1–7
Steiner M-S, Duerkop A, Wolfbeis OS (2011) Optical methods for sensing glucose. Chem Soc Rev 40:4805–4839
Wilhelm S, del Barrio M, Heiland J, Himmelstoß SF, Galbán J, Wolfbeis OS, Hirsch T (2014) Spectrally matched upconverting luminescent nanoparticles for monitoring enzymatic reactions. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:15427–15433
Yakimova R, Selegard L, Khranovskyy V, Pearce R, Spetz AL, Uvdal K (2012) ZnO materials and surface tailoring for biosensing. Frontiers in bioscience (Elite edition) 4:254–78
SelegÅrd L, Khranovskyy V, Söderlind F, Vahlberg C, Ahrén M, Käll P-O, Yakimova R, Uvdal K (2010) Biotinylation of ZnO nanoparticles and thin films: a Two-step surface functionalization study. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2:2128–2135
Shi X, Gu W, Li B, Chen N, Zhao K, Xian Y (2014) Enzymatic biosensors based on the use of metal oxide nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 181:1–22
Khranovskyy V, Tsiaoussis I, Yazdi GR, Hultman L, Yakimova R (2010) Heteroepitaxial ZnO nano hexagons on p-type SiC. J Cryst Growth 312:327–332
Khranovskyy V, Lazorenko V, Lashkarev G, Yakimova R (2012) Luminescence anisotropy of ZnO microrods. J Lumin 132:2643–2647
Wei Y, Li Y, Liu X, Xian Y, Shi G, Jin L (2010) ZnO nanorods/Au hybrid nanocomposites for glucose biosensor. Biosens Bioelectron 26:275–278
Khranovskyy V, Yakimova R, Karlsson F, Syed AS, Holtz P-O, Urgessa ZN, Oluwafemi OS, Botha JR (2012) Comparative PL study of individual ZnO nanorods, grown by APMOCVD and CBD techniques. Phys B Condens Matter 407:1538–1542
Raghavan R, Bechelany M, Parlinska M, Frey D, Mook WM, Beyer A, Michler J, Utke I (2012) Nanocrystalline-to-amorphous transition in nanolaminates grown by low temperature atomic layer deposition and related mechanical properties. Appl Phys Lett 100, 191912
Elias J, Bechelany M, Utke I, Erni R, Hosseini D, Michler J, Philippe L (2012) Urchin-inspired zinc oxide as building blocks for nanostructured solar cells. Nano Energy 1:696–705
Chaaya AA, Bechelany M, Balme S, Miele P (2014) ZnO 1D nanostructures designed by combining atomic layer deposition and electrospinning for UV sensor applications. J Mater Chem A 2:20650–20658
Abou Chaaya A, Viter R, Baleviciute I, Bechelany M, Ramanavicius A, Gertnere Z, Erts D, Smyntyna V, Miele P (2014) Tuning optical properties of Al2O3/ZnO nanolaminates synthesized by atomic layer deposition. J Phys Chem C 118:3811–3819
Dorfman A, Kumar N, Hahm J (2006) Highly sensitive biomolecular fluorescence detection using nanoscale ZnO platforms. Langmuir 22:4890–4895
Hong X, Chu X, Zou P, Liu Y, Yang G (2010) Magnetic-field-assisted rapid ultrasensitive immunoassays using Fe3O4/ZnO/Au nanorices as Raman probes. Biosens Bioelectron 26:918–922
Gu B, Xu C, Yang C, Liu S, Wang M (2011) ZnO quantum dot labeled immunosensor for carbohydrate antigen 19–9. Biosens Bioelectron 26:2720–2723
Somers RC, Bawendi MG, Nocera DG (2007) CdSe nanocrystal based chem-/bio- sensors. Chem Soc Rev 36:579–591
Gill R, Zayats M, Willner I (2008) Semiconductor quantum dots for bioanalysis. Angew Chem Int Ed 47:7602–7625
Wang L, Sun Y, Wang J, Wang J, Yu A, Zhang H, Song D (2010) Water-soluble ZnO–Au nanocomposite-based probe for enhanced protein detection in a SPR biosensor system. J Colloid Interface Sci 351:392–397
Khranovskyy V, Ekblad T, Yakimova R, Hultman L (2012) Surface morphology effects on the light-controlled wettability of ZnO nanostructures. Appl Surf Sci 258:8146–8152
Ferez L, Thami T, Akpalo E, Flaud V, Tauk L, Janot J-M, Déjardin P (2011) Interface of covalently bonded phospholipids with a phosphorylcholine head: characterization, protein nonadsorption, and further functionalization. Langmuir 27:11536–11544
Balme S, Janot J-M, Déjardin P, Vasina EN, Seta P (2006) Potentialities of confocal fluorescence for investigating protein adsorption on mica and in ultrafiltration membranes. J Membr Sci 284:198–204
Abou Chaaya A, Viter R, Bechelany M, Alute Z, Erts D, Zalesskaya A, Kovalevskis K, Rouessac V, Smyntyna V, Miele P (2013) Evolution of microstructure and related optical properties of ZnO grown by atomic layer deposition. Beilstein J Nanotechnol 4:690–698
Liao Z-M, Zhang H-Z, Zhou Y-B, Xu J, Zhang J-M, Yu D-P (2008) Surface effects on photoluminescence of single ZnO nanowires. Phys Lett A 372:4505–4509
Arya SK, Saha S, Ramirez-Vick JE, Gupta V, Bhansali S, Singh SP (2012) Recent advances in ZnO nanostructures and thin films for biosensor applications: Review. Anal Chim Acta 737:1–21
Yi Y, Deng J, Zhang Y, Li H, Yao S (2013) Label-free Si quantum dots as photoluminescence probes for glucose detection. Chem Commun 49:612–614
Rodriguez-Saona L E, Allendorf M E (2011) Use of FTIR for Rapid Authentication and Detection of Adulteration of Food. In Annual Review of Food Science and Technology, Vol 2, Doyle M P, Klaenhammer T R, Vol. 2, pp 467–483
Scampicchio M, Arecchi A, Lawrence NS, Mannino S (2010) Nylon nanofibrous membrane for mediated glucose biosensing. Sensors Actuators B Chem 145:394–397
Schäferling M, Wu M, Wolfbeis O (2004) Time-resolved fluorescent imaging of glucose. J Fluoresc 14:561–568
Wolfbeis OS, Schäferling M, Dürkop A (2003) Reversible optical sensor membrane for hydrogen peroxide using an immobilized fluorescent probe, and its application to a glucose biosensor. Microchim Acta 143:221–227
Wolfbeis OS, Dürkop A, Wu M, Lin Z (2002) A europium-Ion-based luminescent sensing probe for hydrogen peroxide. Angew Chem Int Ed 41:4495–4498
Wu M, Lin Z, Wolfbeis OS (2003) Determination of the activity of catalase using a europium (III)–tetracycline-derived fluorescent substrate. Anal Biochem 320:129–135
Lin Z, Wu M, Wolfbeis OS, Schäferling M (2006) A novel method for time-resolved fluorimetric determination and imaging of the activity of peroxidase, and its application to an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Chem Eur J 12:2730–2738
Wu M, Lin Z, Schäferling M, Dürkop A, Wolfbeis OS (2005) Fluorescence imaging of the activity of glucose oxidase using a hydrogen-peroxide-sensitive europium probe. Anal Biochem 340:66–73
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by EC FP-7 IRSES Grant #318520 “Development of nanotechnology based biosensors for agriculture” 2013–2016. Also, the support from the Swedish Research Council (VR) is acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sodzel, D., Khranovskyy, V., Beni, V. et al. Continuous sensing of hydrogen peroxide and glucose via quenching of the UV and visible luminescence of ZnO nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 182, 1819–1826 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1493-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1493-9