Abstract
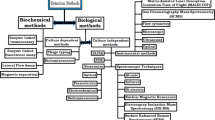
Foodborne illnesses caused by pathogenic bacteria represent a widespread and growing problem to public health, and there is an obvious need for rapid detection of food pathogens. Traditional culture-based techniques require tedious sample workup and are time-consuming. It is expected that new and more rapid methods can replace current techniques. To enable large scale screening procedures, new multiplex analytical formats are being developed, and these allow the detection and/or identification of more than one pathogen in a single analytical run, thus cutting assay times and costs. We review here recent advancements in the field of rapid multiplex analytical methods for foodborne pathogenic bacteria. A variety of strategies, such as multiplex polymerase chain reaction assays, microarray- or multichannel-based immunoassays, biosensors, and fingerprint-based approaches (such as mass spectrometry, electronic nose, or vibrational spectroscopic analysis of whole bacterial cells), have been explored. In addition, various technological solutions have been adopted to improve detectability and to eliminate interferences, although in most cases a brief pre-enrichment step is still required. This review also covers the progress, limitations and future challenges of these approaches and emphasizes the advantages of new separative techniques to selectively fractionate bacteria, thus increasing multiplexing capabilities and simplifying sample preparation procedures.

New analytical formats are under development to allow multiplexed detection of foodborne pathogens, thus cutting assay times and costs and enabling large scale screening procedures. A variety of analytical strategies are being explored to reach this goal. This review covers the recent progresses, limitations and future challenges of these approaches








Similar content being viewed by others
References
European Food Safety Authority, Tracing seeds, in particular fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum) seeds, in relation to the Shiga toxin-producing E. coli (STEC) O104:H4 2011 outbreaks in Germany and France, EFSA-Q-2011-00817
Nugen SR, Baeumner AJ (2008) Trends and opportunities in food pathogen detection. Anal Bioanal Chem 391:451–454
Pedrero M, Campuzano S, Pingarrón JM (2009) Electroanalytical Sensors and devices for multiplexed detection of foodborne pathogen microorganisms. Sensors 9:5503–5520
Byrne B, Stack E, Gilmartin N, O’Kennedy R (2009) Antibody-based sensors: principles, problems and potential for detection of pathogens and associated toxins. Sensors 9:4407–4445
Raz SR, Haasnoot W (2011) Multiplex bioanalytical methods for food and environmental monitoring. Trends Anal Chem 30:1526–1537
Gehring AG, Tu SI (2011) High-throughput biosensors for multiplexed food-borne pathogen detection. Annu Rev Anal Chem 4:151–172
Stevens KA, Jaykus LA (2004) Bacterial separation and concentration from complex sample matrices: A review. Crit Rev Microbiol 30:7–24
Cenciarini-Borde C, Courtois S, La Scola B (2009) Nucleic acids as viability markers for bacteria detection using molecular tools. Future Microbiol 4:45–64
Wang L, Mustapha A (2010) EMA-real-time PCR as a reliable method for detection of viable Salmonella in chicken and eggs. J Food Sci 75:134–139
He Y, Chen CY (2010) Quantitative analysis of viable, stressed and dead cells of Campylobacter jejuni strain 81–176. Food Microbiol 27:439–446
Espiñeira M, Atanassova M, Vieites JM, Santaclara FJ (2010) Validation of a method for the detection of five species, serogroups, biotypes and virulence factors of Vibrio by multiplex PCR in fish and seafood. Food Microbiol 27:122–131
Oliwa-Stasiak K, Molnar CI, Arshak K, Bartoszcze M, Adley CC (2010) Development of a PCR assay for identification of the Bacillus cereus group species. J Appl Microbiol 108:266–273
Kawasaki S, Fratamico PM, Horikoshi N, Okada Y, Takeshita K, Sameshima T, Kawamoto S (2009) Evaluation of a multiplex PCR system for simultaneous detection of Salmonella spp., Listeria monocytogenes, and Escherichia coli O157:H7 in foods and in food subjected to freezing. Foodborne Pathog Dis 6:81–89
Yuan Y, Xu W, Zhai Z, Shi H, Luo Y, Chen Z, Huang K (2009) Universal primer-multiplex PCR approach for simultaneous detection of Escherichia coli, Listeria monocytogenes, and Salmonella spp. in food samples. J Food Sci 74:446–452
Oh MH, Paek SH, Shin GW, Kim HY, Jung GY, Oh S (2009) Simultaneous identification of seven foodborne pathogens and Escherichia coli (pathogenic and nonpathogenic) using capillary electrophoresis-based single-strand conformation polymorphism coupled with multiplex PCR. J Food Prot 72:1262–1266
Li Y, Li Y, Zheng B, Qu L, Li C (2009) Determination of foodborne pathogenic bacteria by multiplex PCR-microchip capillary electrophoresis with genetic algorithm-support vector regression optimization. Anal Chim Acta 643:100–107
Chakravorty S, Helb D, Burday M, Connell N, Alland D (2007) A detailed analysis of 16S ribosomal RNA gene segments for the diagnosis of pathogenic bacteria. J Microbiol Methods 69:330–339
Gilbert C, Winters D, O’Leary A, Slavik M (2003) Development of a triplex PCR assay for the specific detection of Campylobacter jejuni, Salmonella spp., and Escherichia coli O157:H7. Mol Cell Probes 17:135–138
Kim JS, Lee GG, Park JS, Jung YH, Kwak HS, Kim SB, Nam YS, Kwon ST (2007) A novel multiplex PCR assay for rapid and simultaneous detection of five pathogenic bacteria: Escherichia coli O157:H7, Salmonella, Staphylococcus aureus, Listeria monocytogenes, and Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J Food Prot 70:1656–1662
Lei I, Roffey P, Blanchard C, Gu K (2008) Development of a multiplex PCR method for the detection of six common foodborne pathogens. J Food Drug Anal 16:37–43
Zhang C, Wang H, Xing D (2011) Multichannel oscillatory-flow multiplex PCR microfluidics for high-throughput and fast detection of foodborne bacterial pathogens. Biomed Microdevices 13:885–897
Wang H, Zhang C, Xing D (2011) Simultaneous detection of Salmonella enterica, Escherichia coli O157:H7, and Listeria monocytogenes using oscillatory-flow multiplex PCR. Microchim Acta 173:503–512
Kawasaki S, Fratamico PM, Horikoshi N, Okada Y, Takeshita K, Sameshima T, Kawamoto S (2010) Multiplex real-time polymerase chain reaction assay for simultaneous detection and quantification of Salmonella species, Listeria monocytogenes, and Escherichia coli O157:H7 in ground pork samples. Foodborne Pathog Dis 7:549–554
Suo B, He Y, Tu SI, Shi X (2010) A multiplex real-time polymerase chain reaction for simultaneous detection of Salmonella spp., Escherichia coli O157, and Listeria monocytogenes in meat products. Foodborne Pathog Dis 76:619–628
Amoako KK, Goji N, Macmillan T, Said KB, Druhan S, Tanaka E, Thomas EG (2010) Development of multitarget real-time PCR for the rapid, specific, and sensitive detection of Yersinia pestis in milk and ground beef. J Food Prot 73:18–25
He YP, Yao XM, Gunther NW, Xie YP, Tu SI, Shi XM (2010) Simultaneous detection and differentiation of Campylobacter jejuni, C. coli, and C. lari in chickens using a multiplex real-time PCR assay. Food Anal Methods 4:321–329
McCarthy N, Reen FJ, Buckley JF, Frye JG, Boyd EF, Gilroy D (2009) Sensitive and rapid molecular detection assays for Salmonella enterica serovars Typhimurium and Heidelberg. J Food Prot 72:2350–2357
Postollec F, Falentin H, Pavan S, Combrisson J, Sohier D (2011) Recent advances in quantitative PCR (qPCR) applications in food microbiology. Food Microbiol 28:848–861
Cheng JC, Huang CL, Lin CC, Chen CC, Chang YC, Chang SS et al (2006) Rapid detection and identification of clinically important bacteria by high-resolution melting analysis after broad-range ribosomal RNA real-time PCR. Clin Chem 52:1997–2004
Huang Q, Hu Q, Li Q (2007) Identification of 8 foodborne pathogens by multicolor combinational probe coding technology in a single real-time PCR. Clin Chem 53:1741–1748
Suo B, He Y, Paoli G, Gehring A, Tu SI, Shi X (2010) Development of an oligonucleotide-based microarray to detect multiple foodborne pathogens. Mol Cell Probes 24:77–86
Hu Y, Liu J, Xia D, Chen S (2011) Simultaneous analysis of foodborne pathogenic bacteria by an oligonucleotide microarray assay. J Basic Microbiol 52:27–34
Fang H, Xu J, Ding D, Jackson SA, Patel IR, Frye JG, Zou W, Nayak R, Foley S, Chen J, Su Z, Ye Y, Turner S, Harris S, Zhou G, Cerniglia C, Tong W (2011) An FDA bioinformatics tool for microbial genomics research on molecular characterization of bacterial foodborne pathogens using microarrays. BMC Bioinform 11(Suppl 6):S4
Zou W, Al-Khaldi SF, Branham WS, Han T, Fuscoe JC, Han J, Foley SL, Xu J, Fang H, Cerniglia CE, Nayak R (2011) Microarray analysis of virulence gene profiles in Salmonella serovars from food/food animal environment. J Infect Dev Ctries 5:94–105
Zeng X, Shen Z, Mernaugh R (2011) Recombinant antibodies and their use in biosensors. Anal Bioanal Chem 402:3027–3038
Hamula CLA, Zhang H, Li F, Wang Z, Le XC, Li XF (2011) Selection and analytical applications of aptamers binding microbial pathogens. Trends Anal Chem 30:1587–1597
Zhao Y, Ye M, Chao Q, Jia N, Ge Y, Shen H (2009) Simultaneous detection of multifood-borne pathogenic bacteria based on functionalized quantum dots coupled with immunomagnetic separation in food samples. J Agric Food Chem 57:517–524
Wang H, Li Y, Wang A, Slavik M (2011) Rapid, sensitive, and simultaneous detection of three foodborne pathogens using magnetic nanobead-based immunoseparation and quantum dot-based multiplex immunoassay. J Food Prot 74:2039–2047
Dudak FC, Boyaci IH (2009) Multiplex detection of Escherichia coli and Salmonella enteritidis by using quantum dot-labeled antibodies. J Rapid Meth Automat Microbiol 17:315–327
Miao T, Wang Z, Li S, Wang X (2011) Sensitive fluorescent detection of Staphylococcus aureus using nanogold linked CdTe nanocrystals as signal amplification labels. Microchim Acta 172:431–437
Wang L, Zhao W, O’Donoghue MB, Tan W (2007) Fluorescent nanoparticles for multiplexed bacteria monitoring. Bioconjug Chem 18:297–301
Magliulo M, Simoni P, Guardigli M, Michelini E, Luciani M, Lelli R, Roda A (2007) A rapid multiplexed chemiluminescent immunoassay for the detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7, Yersinia enterocolitica, Salmonella typhimurium, and Listeria monocytogenes pathogen bacteria. J Agric Food Chem 55:4933–4939
Roda A, Mirasoli M, Venturoli S, Cricca M, Bonvicini F, Baraldini M, Pasini P, Zerbini M, Musiani M (2002) Microtiter format for simultaneous multianalyte detection and development of a PCR chemiluminescent enzyme immunoassay for typing human papillomavirus DNAs. Clin Chem 48:1654–1660
Gehring AG, Albin DM, Reed SA, Tu S, Brewster JD (2008) An antibody microarray, in multiwell plate format, for multiplex screening of foodborne pathogenic bacteria and biomolecules. Anal Bioanal Chem 391:497–506
Leach KM, Stroot JM, Lim DV (2010) Same-day detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 from spinach by using electrochemiluminescent and cytometric bead array biosensors. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:8044–8052
Wolter A, Niessner R, Seidel M (2008) Detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7, Salmonella typhimurium, and Legionella pneumophila in water using a flow-through chemiluminescence microarray readout system. Anal Chem 80:5854–5863
Karsunke XYZ, Niessner R, Seidel M (2009) Development of a multichannel flow-through chemiluminescence microarray chip for parallel calibration and detection of pathogenic bacteria. Anal Bioanal Chem 395:1623–1630
Roda A, Mirasoli M, Dolci LS, Buragina A, Bonvicini F, Simoni P, Guardigli M (2011) Portable device based on chemiluminescence lensless imaging for personalized diagnostics through multiplex bioanalysis. Anal Chem 83:3178–3185
Park J, Park S, Kim Y-K (2010) Multiplex detection of pathogens using an immunochromatographic assay strip. Biochip J 4:305–312
Karoonuthaisiri N, Charlermroj R, Uawisetwathana U, Luxananil P, Kirtikara K, Gajanandana O (2009) Development of antibody array for simultaneous detection of foodborne pathogens. Biosens Bioelectron 24:1641–1648
Arora K, Chand S, Malhotra BD (2006) Recent developments in bio-molecular electronics techniques for food pathogens. Anal Chim Acta 568:259–274
Velusamy V, Arshak K, Korostynska O, Oliwa K, Adley C (2010) An overview of foodborne pathogen detection: in the perspective of biosensors. Biotechnol Adv 28:232–254
Lazcka O, Del Campo FJ, Muñoz FX (2007) Pathogen detection: a perspective of traditional methods and biosensors. Biosens Bioelectron 22:1205–1217
Nayak M, Kotian A, Marathe S, Chakravortty D (2009) Detection of microorganisms using biosensors-a smarter way towards detection techniques. Biosens Bioelectron 25:661–667
Farabullini F, Lucarelli F, Palchetti I, Marrazza G, Mascini M (2007) Disposable electrochemical genosensor for the simultaneous analysis of different bacterial food contaminants. Biosens Bioelectron 22:1544–1549
Taylor AD, Ladd J, Yu QM, Chen SF, Homola J, Jiang SY (2006) Quantitative and simultaneous detection of four foodborne bacterial pathogens with a multi-channel SPR sensor. Biosens Bioelectron 22:752–758
Zordan MD, Grafton MM, Acharya G, Reece LM, Cooper CL, Aronson AI, Park K, Leary JF (2009) Detection of pathogenic E. coli O157:H7 by a hybrid microfluidic SPR and molecular imaging cytometry device. Cytometry Part A 75:155–162
Kang T, Yoo SM, Yoon I, Lee SY, Kim B (2010) Patterned multiplex pathogen DNA detection by Au particle-on-wire SERS sensor. Nano Lett 10:1189–1193
Zelada-Guillén GA, Bhosale SV, Riu J, Rius FX (2010) Real-time potentiometric detection of bacteria in complex samples. Anal Chem 82:9254–9260
Bai S, Zhao J, Zhang Y, Huang W, Xu S, Chen H, Fan LM, Chen Y, Deng XW (2010) Rapid and reliable detection of 11 food-borne pathogens using thin-film biosensor chips. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 86:983–990
Elsholz B, Nitsche A, Achenbach J, Ellerbrok H, Blohm L, Albers J, Pauli G, Hintsche R, Wörl R (2009) Electrical microarrays for highly sensitive detection of multiplex PCR products from biological agents. Biosens Bioelectron 24:1737–1743
Pöhlman C, Wang Y, Humenik M, Heidenreich B, Gareis M, Sprinzl M (2009) Rapid, specific and sensitive electrochemical detection of foodborne bacteria. Biosens Bioelectron 24:2766–2771
Hee PC, Pyo KJ, Wook LS, Li JN, Pil JY, Jun SS (2009) A direct, multiplex biosensor platform for pathogen detection based on cross-linked polydiacetylene (PDA) supramolecules. Adv Funct Mater 19:3703–3710
Jin S-Q, Yin B-C, Ye B-C (2009) Multiplexed bead-based mesofluidic system for detection of food-borne pathogenic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:6647–6654
Goh YY, Ho B, Ding JL (2002) A novel fluorescent protein-based biosensor for gram-negative bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(12):6343–6352
Ye J, Liu Y, Li Y (2002) A chemiluminescence fiber-optic biosensor coupled with immunomagnetic separation for rapid detection of E. coli O15: H7. Trans ASAE 45:473–478
Ligler FS, Sapsford KE, Golden JP, Shriver-Lake LC, Taitt CR, Dyer MA, Barone S, Myatt CJ (2007) The array biosensor: portable, automated systems. Anal Sci 23:5–10
Massad-Ivanir N, Shtenberg G, Tzur A, Krepker M, Segal E (2001) Engineering nanostructured porous SiO2 surfaces for bacteria detection via direct-cell-capture. Anal Chem 83:3282–3289
Massad-Ivanir N, Shtenberg G, Segal E (2012) Advancing nanostructured porous si-based optical transducers for label free bacteria detection. Adv Exp Med Biol 733:37–45
Janshoff A, Galla HJ, Steinem C (2000) Piezoelectric mass-sensing devices as biosensors-an alternative to optical biosensors? Angew Chem Int Ed 39:4004–4032
Serra B, Gamella M, Reviejo AJ, Pingarrón JM (2008) Lectin-modified piezoelectric biosensors for bacteria recognition and quantification. Anal Bioanal Chem 391:1853–1860
Yang H, Li HP, Jiang XP (2008) Detection of foodborne pathogens using bioconjugated nanomaterials. Microfluidic Nanofluidic 5:571–583
Sanvicens N, Pastells C, Pascual N, Marco MP (2009) Nanoparticle-based biosensors for detection of pathogenic bacteria. Trends Anal Chem 28:1243–1252
Vinayaka AC, Thakur MS (2010) Focus on quantum dots as potential fluorescent probes for monitoring food toxicants and foodborne pathogens. Anal Bioanal Chem 397:1445–1455
Miranda OR, Li XN, Garcia-Gonzalez L, Zhu ZJ, Yan B, Bunz UHF, Rotello VM (2011) Colorimetric bacteria sensing using a supramolecular enzyme-nanoparticle biosensor. JACS 133:9650–9653
Valdés MG, Valdés Gonzáles AC, García Calzón JA, Díaz-García ME (2009) Analytical nanotechnology for food analysis. Microchim Acta 166:1–19
Chang HC (2007) Nanobead electrokinetics: the enabling microfluidic platform for rapid multi-target pathogen detection. AIChe J 53:2486–2492
Siangproh W, Dungchai W, Rattanarat P, Chailapakul O (2011) Nanoparticle-based electrochemical detection in conventional and miniaturized systems and their bioanalytical applications: a review. Anal Chim Acta 690:10–25
Petryayeva E, Krull UJ (2011) Localized surface plasmon resonance: nanostructures, bioassays and biosensing-A review. Anal Chim Acta 706:8–24
Chen SH, Wu VCH, Chuang YC, Lin CS (2008) Using oligonucleotide-functionalized Au nanoparticles to rapidly detect foodborne pathogens on a piezoelectric biosensor. J Microbiol Methods 73:7–17
Wang Y, Irudayaraj J (2010) Multifunctional magnetic–optical nanoparticle probes for simultaneous detection, separation, and thermal ablation of multiple pathogens. Small 6:283–289
Wang Y, Ravindranath SP, Irudayaraj J (2011) Separation and detection of multiple pathogens in a food matrix by magnetic SERS nanoprobes. Anal Bioanal Chem 399:1271–1278
Ravindranath SP, Wang Y, Irudayaraj J (2011) SERS driven cross-platform based multiplex pathogen detection. Sens Actuat B-Chem 152:183–190
Jung JH, Kim G-Y, Seo TS (2011) An integrated passive micromixer–magnetic separation–capillary electrophoresis microdevice for rapid and multiplex pathogen detection at the single-cell level. Lab Chip 11:3465–3470
Demirev PA, Fenselau C (2008) Mass spectrometry for rapid characterization of microorganisms. Annu Rev Anal Chem 1:71–93
Wensing A, Gernold M, Geider K (2011) Detection of Erwinia species from the apple and pear flora by mass spectroscopy of whole cells and with novel PCR primers. J Appl Microbiol 112:147–158
Sospedra I, Soler C, Mañes J, Soriano JM (2011) Analysis of staphylococcal Enterotoxin A in milk by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 400:1525–1531
Böhme K, Fernández-No IC, Barros-Velázquez J, Gallardo JM, Cañas B, Calo-Mata P (2011) Rapid species identification of seafood spoilage and pathogenic Gram-positive bacteria by MALDI-TOF mass fingerprinting. Electrophoresis 32:2951–2965
Dieckmann R, Helmuth R, Erhard M, Malorny B (2008) Rapid classification and identification of Salmonellae at the species and subspecies levels by whole-cell matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization–time of flight mass spectrometry. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:7767–7778
Mazzeo MF, Sorrentino A, Gaita M, Cacace G, Di Stasio M, Facchiano A, Comi G, Malorni A, Siciliano RA (2006) Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization–time of flight mass spectrometry for the discrimination of food-borne microorganisms. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:1180–1189
Mandrel RE, Wachtelt MR (1999) Novel detection techniques for human contaminate poultry. Curr Opin Biotechnol 10:273–278
Ochoa ML, Harrington PB (2005) Immunomagnetic isolation of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 from ground beef and identification by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry and database searches. Anal Chem 77:5258–5267
Sedo O, Sedlacek I, Zdrahal Z (2011) Sample preparation methods for MALDI-MS profiling of bacteria. Mass Spectrom Rev 30:417–434
Madonna AJ, Basile F, Furlong E, Voorhees KJ (2001) Detection of bacteria from biological mixtures using immunomagnetic separation combined with matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 15:1068–1074
Reschiglian P, Zattoni A, Cinque L, Roda B (2004) Hollow-fiber flow field-flow fractionation for whole bacteria analysis by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 76:2103–2111
Parisi D, Magliulo M, Nanni P, Casale M, Forina M, Roda A (2008) Analysis and classification of bacteria by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry and a chemometric approach. Anal Bioanal Chem 391:2127–2134
Casalinuovo IA, Di Pierro D, Coletta M, Di Francesco P (2006) Application of electronic noses for disease diagnosis and food spoilage detection. Sensors 6:1428–1439
Wilson AD, Baietto M (2011) Advances in electronic-nose technologies developed for biomedical applications. Sensors 11:1105–1176
Green GC, Chan AD, Goubran RA (2006) An investigation into the suitability of using three electronic nose instruments for the detection and discrimination of bacteria types. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 1:1850–1853
Green GC, Chan AD, Hanhong D, Min L (2011) Using a metal oxide sensor (MOS)-based electronic nose for discrimination of bacteria based on individual colonies in suspension. Sens Actuat B-Chem 152:21–28
McEntegart CM, Penrose WR, Strathmann S, Stetter JR (2000) Detection and discrimination of coliform bacteria with gas sensor arrays. Sens Actuat B-Chem 70:170–176
Walter A, März A, Schumacher W, Rösch P, Popp J (2011) Towards a fast, high specific and reliable discrimination of bacteria on strain level by means of SERS in a microfluidic device. Lab Chip 11:1013–1021
Davis R, Mauer LJ (2011) Subtyping of Listeria monocytogenes at the haplotype level by Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy and multivariate statistical analysis. Int J Food Microbiol 150:140–149
Davis R, Burgula Y, Deering A, Irudayaraj J, Reuhs BL, Mauer LJ (2010) Detection and differentiation of live and heat-treated Salmonella enterica serovars inoculated onto chicken breast using Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy. J Appl Microbiol 109:2019–2031
Nicolaou N, Xu Y, Goodacre R (2011) Fourier transform infrared and Raman spectroscopies for the rapid detection, enumeration, and growth interaction of the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus and Lactococcus lactis ssp. cremoris in milk. Anal Chem 83:5681–5687
Cheng S, Wang Z, Ge S, Wang H, He P, Fang Y, Wang Q (2012) Rapid separation of four probiotic bacteria in mixed samples using microchip electrophoresis with laser-induced fluorescence detection. Microchim Acta 176:295–301
Szumski M, Kłodzińska E, Buszewski B (2009) Application of a fluorescence stereomicroscope as an in-line detection unit for electrophoretic separation of bacteria. Microchim Acta 164:287–291
Buszewski B, Szumski M, Kłodzinska E, Dahm H (2003) Separation of bacteria by capillary electrophoresis. J Sep Sci 26:1045–1049
Armstrong DW, Schulte G, Schneiderheinze JM, Westenberg DJ (1999) Separating microbes in the manner of molecules. 1. Capillary electrokinetic approaches. Anal Chem 71:5465–5469
Armstrong DW, Schneiderheinze JM (2000) Rapid identification of the bacterial pathogens responsible for urinary tract infections using direct injection CE. Anal Chem 72:4474–4476
Gagnon ZR (2011) Cellular dielectrophoresis: applications to the characterization, manipulation, separation and patterning of cells. Electrophoresis 32:2466–2487
Karo O, Wahl A, Nicol SB, Brachert J, Lambrecht B, Spengler HP, Nauwelaers F, Schmidt M, Schneider CK, Müller TH, Montag T (2008) Bacteria detection by flow cytometry. Clin Chem Lab Med 46:947–953
Dunbar SA, Vander Zee CA, Oliver KG, Karem KL, Jacobson JW (2003) Quantitative, multiplexed detection of bacterial pathogens: DNA and protein applications of the Luminex LabMAP system. J Microbiol Methods 53:245–252
Dunbar SA (2006) Applications of Luminex xMAP technology for rapid, high-throughput multiplexed nucleic acid detection. Clin Chim Acta 363:71–82
Kim JS, Anderson GP, Erickson JS, Golden JP, Nasir M, Ligler FS (2009) Multiplexed detection of bacteria and toxins using a microflow cytometer. Anal Chem 81:5426–5432
Thangawng AL, Kim JS, Golden JP, Anderson GP, Robertson KL, Low V, Ligler FS (2010) A hard microflow cytometer using groove-generated sheath flow for multiplexed bead and cell assays their. Anal Bioanal Chem 398:1871–1881
Kim JS, Ligler FS (2010) Utilization of microparticles in next-generation assays for microflow cytometers. Anal Bioanal Chem 398:2373–2382
Giddings JC (1993) Field-flow fractionation: analysis of macromolecular, colloidal, and particulate materials. Science 260:1456–1465
Schimpf ME (2000) Field-flow fractionation handbook. In: Shimpf ME, Caldwell KC, Giddings JC (eds) Wiley-Interscience, New York
Saenton S, Lee H, Gao YS, Ranville JF, Williams SKR (2000) Evaluation of different field flow fractionation techniques for separating bacteria. Sep Sci Technol 35:1761–1775
Reschiglian P, Roda B, Zattoni A, Min BR, Moon MH (2002) High performance, disposable hollow fiber flow field-flow fractionation for bacteria and cells. First application to deactivated Vibrio cholerae. J Sep Sci 25:490–498
Reschiglian P, Zattoni A, Roda B, Cinque L, Melucci D, Min BR, Moon MH (2003) Hyperlayer hollow-fiber flow field-flow fractionation of cells. J Chromatogr A 985:519–529
Nilsson M, Birnbaum S, Wahlund KG (1996) Determination of relative amounts of ribosome and subunits in Escherichia coli using asymmetrical flow field-flow fractionation. J Biochem Biophys Methods 33:9–23
Janča J, Halabalová V, Růžička J (2010) Role of the shape of various bacteria in their separation by Microthermal Field-Flow Fractionation. J Chromatogr A 1217:8062–8071
Reschiglian P, Zattoni A, Roda B, Michelini E, Roda A (2005) Field-flow fractionation and biotechnology. Trends Biotechnol 23:475–483
Roda B, Zattoni A, Reschiglian P, Moon MH, Mirasoli M, Michelini E, Roda A (2009) Field-flow fractionation in bioanalysis: a review of recent trends. Anal Chim Acta 635:132–143
Reschiglian P, Zattoni A, Cinque L, Roda B, Dal Piaz F, Roda A, Moon MH, Min BR (2004) Hollow-fiber flow field-flow fractionation for whole bacteria analysis by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 76:2103–2111
Magliulo M, Roda B, Zattoni A, Michelini E, Luciani M, Lelli R, Reschiglian P, Roda A (2006) An innovative, flow-assisted, noncompetitive chemiluminescent immunoassay for the detection of pathogenic bacteria. Clin Chem 52:2151–2155
Roda A, Mirasoli M, Roda B, Reschiglian P (2010) Flow-assisted analysis. In: Roda A (ed) Chemiluminescence and bioluminescence: past, present and future. Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, pp 191–226
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The work was presented at the workshop of Biosensors for food safety and environmental monitoring, Ouarzazate, Morocco (October 06–08, 2011).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roda, A., Mirasoli, M., Roda, B. et al. Recent developments in rapid multiplexed bioanalytical methods for foodborne pathogenic bacteria detection. Microchim Acta 178, 7–28 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-012-0824-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-012-0824-3