Abstract
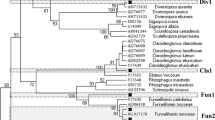
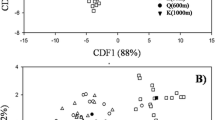
Community structure of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF), evaluated as spore samples and mycorrhizal roots of four herbaceous plant species, was investigated at different altitudes in a primary successional volcanic desert on Mount Fuji using molecular methods (fragment and sequence analysis of the large ribosomal subunit RNA gene). In total, 17 different AMF clades were identified, and most were members of the Glomaceae, Acaulosporaceae, and Gigasporaceae. The AMF community structures detected by spore sampling were inconsistent with those from plant roots. Of all AMF clades, six (35.3%) were detected only on the basis of spores, six (35.3%) only in roots, and five corresponded to both spores and roots (29.4%). Although an Acaulospora species was the most dominant among spores (67.1%), it accounted for only 6.8% in root samples. A species analysis of AMF communities at different altitudes demonstrated that AMF species diversity increased as altitude decreased and that the species enrichment at lower altitudes resulted from the addition of new species rather than species replacement. The inconsistencies in the species composition of spore communities with those in roots and the change in species diversity with altitude are discussed.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi N, Terashima I, Takahashi M (1996) Central die-back of monoclonal stands of Reynoutria japonica in an early stage of primary succession on Mount Fuji. Ann Bot 77:477–486
Allen MF (1987) Re-establishment of mycorrhizas on Mount St Helens: migration vectors. Trans Br Mycol Soc 88:413–417
Allen MF (1991) The ecology of mycorrhizae. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK
Allen MF, MacMahon JA (1988) Direct VA mycorrhizal inoculation of colonizing plants by pocket gophers (Thomomys talpoides) on Mount St. Helens. Mycologia 80:754–756
Bever JD (2003) Soil community feedback and the coexistence of competitors: conceptual frameworks and empirical tests. New Phytol 157:465–473
Bever JD, Morton JB, Antonovics J, Schultz PA (1996) Host-dependent sporulation and species diversity of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in a mown grassland. J Ecol 84:71–82
Brundrett M, Bougher N, Dell B, Grove T, Malajczuk N (1996) Working with mycorrhizas in forestry and agriculture. Pirie Printers, Canberra, Australia
Burrows RL, Pfleger FL (2002) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi respond to increasing plant diversity. Can J Bot 80:120–130
Chaurasia B, Pandey A, Palni LMS (2005) Distribution, colonization and diversity of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi associated with central Himalayan rhododendrons. For Ecol Manag 207:315–324
Clapp JP, Young JPW, Merryweather JW, Fitter AH (1995) Diversity of fungal symbionts in arbuscular mycorrhizas from a natural community. New Phytol 130:259–265
Daniell TL, Husband R, Fitter AH, Young JPW (2001) Molecular diversity of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi colonizing arable crops. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 36:203–209
Eom AH, Hartnett DC, Wilson GWT (2000) Host plant species effects on arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal communities in tallgrass prairie. Oecologia 122:435–444
Fujiyoshi M, Kagawa A, Nakatsubo T, Masuzawa T (2006) Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and soil developmental stages on herbaceous plants growing in the early stage of primary succession on Mount Fuji. Ecol Res 21:278–284
Gange AC, Brown VK, Sinclair GS (1993) Vesicular–arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi: a determinant of plant community structure in early succession. Funct Ecol 7:616–622
Gemma JN, Koske RE (1990) Mycorrhizae in recent volcanic substrates in Hawaii. Am J Bot 77:1193–1200
Gollotte A, van Tuinen D, Atkinson D (2004) Diversity of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi colonizing roots of the grass species Agrostis capillaris and Lolium perenne in a field experiment. Mycorrhiza 14:111–117
Grime JP, Mackey JML, Hillier SH, Read DJ (1987) Floristic diversity in a model system using experimental microcosms. Nature 328:420–422
Hartnett DC, Wilson GWT (1999) Mycorrhizae influence plant community structure and diversity in tallgrass prairie. Ecology 80:1187–1195
Helgason T, Daniell TJ, Husband R, Fitter AH, Young JPW (1998) Ploughing up the wood-wide web? Nature 394:431
Hijri M, Sanders IR (2005) Low gene copy number shows that arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi inherit genetically different nuclei. Nature 433:160–163
Husband R, Herre EA, Turner SL, Gallery R, Young JPW (2002) Molecular diversity of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and patterns of host association over time and space in a tropical forest. Mol Ecol 11:2669–2678
Janos DP (1980) Mycorrhizae influence tropical succession. Biotropica 12:56–64
Jansa J, Mozafar A, Anken T, Ruh R, Sanders IR, Frossard E (2002) Diversity and structure of AMF communities as affected by tillage in a temperate soil. Mycorrhiza 12:225–234
Johnson NC, Tilman D, Wedin D (1992) Plant and soil controls on mycorrhizal fungal communities. Ecology 73:2034–2042
Johnson D, Vandenkoornhuyse PJ, Leake JR, Gilbert L, Booth RE, Grime JP, Young JPW, Read DJ (2003) Plant communities affect arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal diversity and community composition in grassland microcosms. New Phytol 161:503–515
Kabir Z (2005) Tillage or no-tillage: impact on mycorrhizae. Can J Plant Sci 85:23–29
Landis FC, Gargas A, Givnish TJ (2004) Relationships among arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, vascular plants and environmental conditions in oak savannas. New Phytol 164:493–504
Massicotte HB, Melville LH, Peterson RL (1998) Anatomical aspects of field ectomycorrhizas on Polygonum viviparum (Polygonaceae) and Kobresia bellardii (Cyperaceae). Mycorrhiza 7:287–292
Masuzawa T (1997) Ecology of the Alpine Plants. University of Tokyo Press, Tokyo, Japan
Nara K, Nakaya H, Hogetsu T (2003) Ectomycorrhizal sporocarp succession and production during early primary succession on Mount Fuji. New Phytol 158:193–206
Oba H, Shinozaki N, Oyaizu H, Tawaraya K, Wagatsuma T, Barraquio WL, Saito M (2004) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal communities associated with some pioneer plants in the lahar area of Mt. Pinatubo, Philippines. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 50:1195–1203
Oehl F, Sieverding E, Ineichen K, Ris E-A, Boller T, Wiemken A (2005) Community structure of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi at different soil depths in extensively and intensively managed agroecosystems. New Phytol 165:273–283
Öpik M, Moora M, Liira J, Kõljalg U, Zobel M, Sen R (2003) Divergent arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal communities colonize roots of Pulsatilla spp. in boreal Scots pine forest and grassland soils. New Phytol 160:581–593
Öpik M, Moora M, Liira J, Zobel M (2006) Composition of root-colonizing arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal communities in different ecosystems around the globe. J Ecol 94:778–790
Pawlowska TE, Taylor JW (2004) Organization of genetic variation in individuals of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Nature 427:733–737
Renker C, Heinrichs J, Kaldorf M, Buscot F (2003) Combining nested PCR and restriction digest of the internal transcribed spacer region to characterize arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on roots from the field. Mycorrhiza 13:191–198
Rosendahl S, Stukenbrock EH (2004) Community structure of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in undisturbed vegetation revealed by analyses of LSU rDNA sequences. Mol Ecol 13:3179–3186
Sanders IR (2002) Ecology and evolution of multigenomic arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Am Nat 160:S128–S141
Sanders IR (2004) Plant and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal diversity—are we looking at the relevant levels of diversity and are we using the right techniques? New Phytol 164:415–418
Sanders IR, Fitter AH (1992) Evidence for differential responses between host fungus combinations of vesicular arbuscular mycorrhizas from a grassland. Mycol Res 96:415–419
Scheublin TR, Ridgway KP, Young JPW, van der Heijden MGA (2004) Nonlegumes, legumes, and root nodules harbor different arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:6240–6246
Stampe ED, Daehler CC (2003) Mycorrhizal species identity affects plant community structure and invasion: a microcosm study. Oikos 100:362–372
Titus JH, Tsuyuzaki S (2002) Arbuscular mycorrhizal distribution in relation to microsites on recent volcanic substrates of Mt. Koma, Hokkaido, Japan. Mycorrhiza 12:271–275
Trouvelot S, van Tuinen D, Hijri M, Gianinazzi-Pearson V (1999) Visualization of ribosomal DNA loci in spore interphasic nuclei of glomalean fungi by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Mycorrhiza 8:203–206
van der Heijden MGA, Klironomos JN, Ursic M, Moutoglis P, Streitwolf-Engel R, Boller T, Wiemken A, Sanders IR (1998) Mycorrhizal fungal diversity determines plant biodiversity, ecosystem variability and productivity. Nature 396:69–72
Vandenkoornhuyse P, Husband R, Daniell TJ, Watson IJ, Duck JM, Fitter AH, Young JPW (2002) Arbuscular mycorrhizal community composition associated with two plant species in a grassland ecosystem. Mol Ecol 11:1555–1564
Warner NJ, Allen MF, MacMahon JA (1987) Dispersal agents of vesicular arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in a disturbed arid ecosystem. Mycologia 79:721–730
Wu BY, Isobe K, Ishii R (2004) Arbuscular mycorrhizal colonization of the dominant plant species in primary successional volcanic deserts on the southeast slope of Mount Fuji. Mycorrhiza 14:391–395
Wu BY, Nara K, Hogetsu T (2005) Genetic structure of Cenococcum geophilum populations in primary successional volcanic deserts on Mount Fuji as revealed by microsatellite markers. New Phytol 165:285–293
Wubet T, Weiss M, Kottke I, Oberwinkler F (2003) Morphology and molecular diversity of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in wild and cultivated yew (Taxus baccata). Can J Bot 81:255–266
Yamato M (2004) Morphological types of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in roots of weeds on vacant land. Mycorrhiza 14:127–131
Zhou Z, Miwa M, Nara K, Wu BY, Nakaya H, Lian C, Miyashita N, Oishi R, Maruta E, Hogetsu T (2003) Patch establishment and development of a clonal plant, Polygonum cuspidatum, on Mount Fuji. Mol Ecol 12:1361–1373
Acknowledgement
We thank Takuro Urashima for assistance in the field. This work was supported in part by grants from the 21st Century Center of Excellence Programs and a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (No. 16101008) from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports, and Culture of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, B., Hogetsu, T., Isobe, K. et al. Community structure of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in a primary successional volcanic desert on the southeast slope of Mount Fuji. Mycorrhiza 17, 495–506 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00572-007-0114-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00572-007-0114-9