Abstract
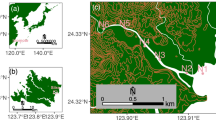
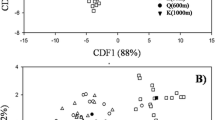
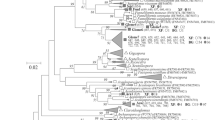
To better understand the diversity and species composition of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) in mangrove ecosystems, the AMF colonization and distribution in four semi-mangrove plant communities were investigated. Typical AMF hyphal, vesicle and arbuscular structures were commonly observed in all the root samples, indicating that AMF are important components on the landward fringe of mangrove habitats. AMF spores were extracted from the rhizospheric soils, and an SSU rDNA fragment from each spore morph-type was amplified and sequenced for species identification. AMF species composition and diversity in the roots of each semi-mangrove species were also analyzed based on an SSU-ITS-LSU fragment, which was amplified, cloned and sequenced from root samples. In total, 11 unique AMF sequences were obtained from spores and 172 from roots. Phylogenetic analyses indicated that the sequences from the soil and roots were grouped into 5 and 14 phylotypes, respectively. AMF from six genera including Acaulospora, Claroideoglomus, Diversispora, Funneliformis, Paraglomus, and Rhizophagus were identified, with a further six phylotypes from the Glomeraceae family that could not be identified to the genus level. The AMF genus composition in the investigated semi-mangrove communities was very similar to that in the intertidal zone of this mangrove ecosystem and other investigated mangrove ecosystems, implying possible fungal adaptation to mangrove conditions.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
An ZQ, Hendrix JW, Hershman DE, Henson GT (1990) Evaluation of the most probable number (MPN) and wet sieving methods for determining soil-borne populations of endogonaceous mycorrhizal fungi. Mycologia 82:516–518
Choudhury B, Kalita MC, Azad P (2010) Distribution of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in marshy and shoreline vegetation of Deepar Beel Ramsar Site of Assam, India. World J Microbial Biotechnol 26:1965–1971
D’souza J, Rodrigues BF (2013) Biodiversity of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal (AM) fungi in mangroves of Goa in West India. J For Res 24:515–523. doi:10.1007/s11676-013-0342-0
Gai JP, Tian H, Yang FY, Christie P, Li XL, Klironomos JN (2012) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal diversity along a Tibetan elevation gradient. Pedobiologia 55:145–151
Hodge A, Fitter AH (2010) Substantial nitrogen acquisition by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi from organic material has implications for N cycling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:13754–13759
Kumar T, Ghose M (2008) Status of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) in the Sundarbans of India in relation to tidal inundation and chemical properties of soil. Wetl Ecol Manag 16:471–483
Lee J, Lee S, Young JPW (2008) Improved PCR primers for the detection and identification of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 65:339–349
Leigh J, Hodge A, Fitter AH (2009) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi can transfer substantial amounts of nitrogen to their host plant from organic material. New Phytol 181:924–937
Liu YJ, Mao L, He XH, Cheng G, Ma XJ, An LZ, Feng HY (2012a) Rapid change of AM fungal community in a rain-fed wheat field with short-term plastic film mulching practice. Mycorrhiza 22:31–39
Liu YJ, Shi GX, Mao L, Cheng G, Jiang SJ, Ma XJ, An LZ, Du GZ, Johnson NC, Feng HY (2012b) Direct and indirect influences of 8 yr of nitrogen and phosphorus fertilization on Glomeromycota in an alpine meadow ecosystem. New Phytol 194:523–535
Liu RJ, Li Y, Diao ZK, Li M, Lin XG (2013) Effects of soil depth and season variation on community structure of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in greenhouse soils planted with watermelon. Pedosphere 23:350–358
McGonigle TP, Miller MH, Evans DG, Fairchild GL, Swan JL (1990) A new method which gives an objective measure of colonization of roots by vesicular arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. New Phytol 115:495–501
Miller SP (2000) Arbuscular mycorrhizal colonization of semi-aquatic grasses along a wide hydrologic gradient. New Phytol 145:145–155
Møller CL, Kjøller R, Sand-Jensen K (2013) Organic enrichment of sediments reduces arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in oligotrophic lake plants. Freshwater Biol 58:769–779. doi:10.1111/fwb.12083
Nagelkerken I, Blaber SJM, Bouillon S, Green P, Haywood M, Kirton LG, Meynecke JO, Pawlik PHM, Sasekumar A, Somerfield PJ (2008) The habitat function of mangroves for terrestrial and marine fauna: a review. Aquat Bot 89:155–185
Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney DR (1982) Methods of soil analysis. ASA and SSSA, Madison, WI
Parniske M (2008) Arbuscular mycorrhiza: the mother of plant root endosymbioses. Nat Rev Microbiol 6:763–775
Schenck NC, PérezY (1990) Manual for the identification of VA mycorrhizal fungi (3rd edn). Synergistic Publications, INVAM, University of Florida
Schloss PD, Westcott SL, Ryabin T, Hall JR, Hatmann M et al (2009) Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:7537–7541
Schwarzott D, Schüßler A (2001) A simple and reliable method for SSU rRNA gene DNA extraction, amplification, and cloning from single AM fungal spores. Mycorrhiza 10:203–207
Sengupta A, Chaudhuri S (2002) Arbuscular mycorrhizal relations of mangrove plant community at the Ganges river estuary in India. Mycorrhiza 12:169–174
Sivakumar N (2013) Effect of edaphic factors and seasonal variation on spore density and root colonization of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in sugarcane fields. Ann Microbiol 63:151–160
Smith SE, Read DJ (2008) Mycorrhizal symbiosis. Academic, Cambridge
Stockinger H, Krüger M, Schübler A (2010) DNA barcoding of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. New Phytol 187:461–476
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The ClustalX windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
van der Heijden MGA, Bardgett RD, van Straalen NM (2008) The unseen majority: soil microbes as drivers of plant diversity and productivity in terrestrial ecosystems. Ecol Lett 11:296–310
Wang YT, Huang YL, Qiu Q, Xin GR, Yang ZY, Shi SH (2011) Flooding greatly affects the diversity of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi communities in the roots of wetland plants. PLoS ONE 6:e24512
Wang YT, Qiu Q, Yang ZY, Hu ZJ, Tam NFY, Xin GR (2010) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in two mangroves in South China. Plant Soil 331:181–191
Wilde P, Manal A, Stodden M, Sieverding E, Hildebrandt U (2009) Biodiversity of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in roots and soils of two salt marshes. Environ Microbiol 11:1548–1546
Wirsel SGR (2004) Homogeneous stands of a wetland grass harbour diverse consortia of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 48:129–138
Wu J, Xiao Q, Xu J, Li MY, Pan JY, Yang MH (2008) Natural products from true mangrove flora: source, chemistry and bioactivities. Nat Prod Rep 25:955–981
Ypsilantis I, Sylvia DM (2007) Interactions of assemblages of mycorrhizal fungi with two Florida wetland plants. Appl Soil Ecol 35:261–271
Acknowledgments
This research was supported financially by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31371567), the Foundation for Distinguished Young Talents in Higher Education of Guangdong, China (2012LYM_0049), the Science Foundation on Cultivating Young Teachers from South China Normal University and the Research Fund Program of Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Environmental Pollution Control and Remediation Technology. The study sponsor had no role in the study design, data collection, data analysis, data interpretation, or the writing of the report.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Li, T., Li, Y. et al. Distribution of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in four semi-mangrove plant communities. Ann Microbiol 65, 603–610 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-014-0896-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-014-0896-x