Abstract
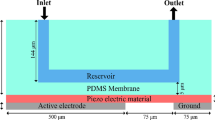
This paper presents the design and simulation of piezoelectric micro pump integrated with micro needle. The proposed micro pump adopted rectangular piezoelectric vibrator supplied with an external alternating current voltage. It has four primary components: electrodes, piezoelectric plate, PDMS (polydimethylsiloxane) membrane and channel with inlet and outlet bottom up and whole setup is constructed on a glass base. The simulations are carried out by subjecting the developed model to voltage changes, material changes which shows the satisfactory results. The micro pump possesses a flow rate of 4.1 ml/min at an input voltage 10 V with frequency 300 Hz while it is integrated with Micro Needle is having 4.67 ml/min. High pumping rates at low applied voltages making the proposed model significantly important for Transdermal controlled drug delivery applications.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashraf MW, Tayyaba S, Afzulpurkar N (2010) MEMS based polymeric drug delivery system. IEEE conference 978-1-4244-5449-5/10
Atul ST, Babu MCL (2016) Characterization of valve-less micro pump for drug delivery by using piezoelectric effect. 978-1-5090-2029-4/16
Cao L, Mantell S, Polla D (2001) Design and simulation of an implantable medical drug delivery system using microelectromechanical systems technology. Sens Actuators A 94:117–125
Chang HT, Lee CY, Wen CY (2007) Design and modeling of electromagnetic actuator in mems-based valveless impedance pump. Microsyst Technol 13:1615–1622
Cheng CH, Tseng YP (2013) Characteristic studies of the piezoelectrically actuated micro pump with check valve. Microsyst Technol 19:1707–1715
Cheng CH, Yang AS, Lin CJ, Huang WJ (2017) Characteristic studies of a novel piezoelectric impedance micro pump. Microsyst Technol 23:1709–1717
Cui Q, Liu C, Zha XF (2007) Study on piezoelectric micro pump for the controlled drug delivery system. Microfluid Nanofluid 3:377–390
Elman NM, Ho Duc HL, Cima MJ (2009) An implantable MEMS drug delivery device for rapid delivery in ambulatory emergency care. Biomed Micro Devices. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-008-9272-6
Farokhi H, Ghayesh MH (2015a) Thermo-mechanical dynamics of perfect and imperfect Timoshenko microbeams. Int J Eng Sci 91:12–33
Farokhi H, Ghayesh MH (2015b) Nonlinear dynamical behaviour of geometrically imperfect microplates based on modified couple stress theory. Int J Mech Sci 90:133–144
Farokhi H, Ghayesh MH (2015c) Nonlinear motion characteristics of microarches under axial loads based on modified couple stress theory. Arch Civil Mech Eng 15:401–411
Ghayesh MH (2014) Nonlinear size-dependent behaviour of single-walled carbon nanotubes. Appl Phys A 117:1393–1399
Ghayesh MH, Amabili M (2014) Coupled longitudinal-transverse behaviour of a geometrically imperfect microbeam. Compos Part B 60:371–377
Ghayesh MH, Farokhi H (2015) Coupled longitudinal-transverse-rotational behaviour of shear deformable microbeams. Compos B 77:319–328
Ghayesh MH, Farokhi H, Amabili Marco (2013) Coupled nonlinear size-dependent behaviour of microbeams. Appl Phys A 112:329–338
Ghayesh MH, Farokhi H, Amabili M (2014a) In-plane and out-of-plane motion characteristics of microbeams with modal interactions. Compos Part B 60:423–439
Ghayesh MH, Farokhi H, Alici G (2014b) Subcritical parametric dynamics of microbeams. Int J Eng Sci 95:36–48
Ghayesh MH, Farokhi H, Alici G (2016) Size-dependent performance of microgyroscopes. Int J Eng Sci 100:99–111
Gholipour Alireza, Farokhi Hamed, Ghayesh Mergen H (2015) In-plane and out-of-plane nonlinear size-dependent dynamics of microplates. Nonlinear Dyn 79:1771–1785
Han X, Cao Q, Li L (2012) Design and evaluation of Three-dimensional electromagnetic guide system for magnetic drug delivery. IEEE Trans Appl Superconduct 22:3
Heggers JP, Kossovsky P, Robert W, Robson MC, Pelley RP, Raine TJ (1983) Biocompatibility of silicone implants. Ann Plast Surg 11(1):38–45
Jeong OC, Yang SS (2000) Fabrication and test of a theromopneumatic micro pump with a corrugated p + diaphragm. Sens Actuators A 83:249–255
Judy JW (2000) Biomedical applications of MEMS. In: Measurement and science technology conference Anaheim. CA, pp 403–414
Junwu K, Zhigang Y, Taijiang P, Guangming C, Boda W (2005) Design and test of a high-performance piezoelectric micro pump for drug delivery. Sens Actuators A 121:156–161
Liu G, Yang Z, Liu J, Li X, Wang H, Zhao T, Yang X (2014) A low cost, high performance insulin delivery system. Microsyst Technol 20:2287–2294
Lo R, Li PY, Saati S, Agrawal R, Humayun MS, Meng E (2008) A refillable microfabricated drug delivery device for treatment of ocular diseases. Lab Chip 8(7):1027–1030
Makino E, Mitsuya T, Shibata T (2001) Fabrication of TiNi shape memory micro pump. Sens Actuators A 88:256–262
Rashvand K, Rezazadeh G, Mobki H, Ghayesh MH (2013) On the size-dependent behavior of a capacitive circular micro-plate considering the variable length-scale parameter. Int J Mech Sci 77:333–342
Reynaerts D, Peris J, Van Brussel H (1997) An implantable drug-delivery system based on shape memory alloy micro-actuation. Sens Actuators A 61:455–462
Sateesh J, Sravani KG, Akshay Kumar R et al (2017) Design and flow analysis of MEMS based piezo-electric micro pump. Microsyst Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-017-3563-x
Sommerfeld A (1883) Ein beitrag zur hydrodynamischen erklaerung der turbulenten fluessigkeitsbewegüngen. Phil Trans Lond R Soc 174:935 (und vol. 186 (1895) p. 123)
Song P, Tng DJH, Hu R, Lin G, Meng E, Yong K-T (2013) An electrochemically actuated MEMS device for individualized drug delivery: an in vitro study. Adv Healthc Mater 2(8):1170–1178
Song P, Hu R, Tng DJH, Yong K-T (2014) Moving towards individualized medicine with microfluidics technology. RSC Adv 4(22):11499–11511
Teymoori MM, Abbaspour-Sani E (2005) Design and simulation of a novel electrostatic peristaltic micro machined pump for drug delivery applications. Sens Actuators A 117:222–229
Zengerle R, Ulrich J, Kluge S, Richter M, Richter A (1995) A bidirectional silicon micro pump. Sens Actuators A 50:81–86
Zhang R, Jullien GA, Dalton C (2013) Study on an alternating current electrothermal micropump for microneedle based fluid delivery systems. J Appl Phys 114:024701
Acknowledgements
The Authors would like to thank to NMDC supported by NPMASS, National Institute of Technology, Silchar for providing the necessary computational tools. The corresponding author (Dr. K. Srinivasa Rao) would like to thank Science Engineering research Board (SERB), Govt. of India, New Delhi (Grant file no: ECRA/2016/000757) for providing partial financial assistance to carry out the work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rao, K.S., Sateesh, J., Guha, K. et al. Design and analysis of MEMS based piezoelectric micro pump integrated with micro needle. Microsyst Technol 26, 3153–3159 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-018-3807-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-018-3807-4