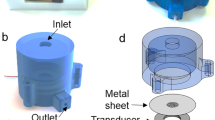
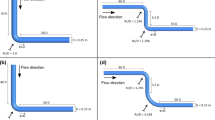
Abstract
Controlled drug delivery in medical application plays a prominent role, that can be achieved by micro-drug delivery devices. The efficient working of the controlled drug delivery system depends on the micropump in it. This paper presents theoretical, design and simulated analysis of piezoelectrically actuated micropump constructed using PZT-5H material, quartz channel, and a PDMS membrane. The designed micro pump is analyzed for different structural, material changes by considering turbulent and laminar flows. The turbulent flow model is having a flow rate of 0.039 µ3m/s, while laminar flow is having 0.029 µ3m/s at a less operating voltage of 5 V.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aoyagi S, Izumi H, Fukuda M (2008) Biodegradable polymer needle with various tip angles and consideration on insertion mechanism of mosquito’s proboscis. Sens Actuators A 143:20–28
Ashraf MW, Tayyaba S, Afzulpurkar N (2010) MEMS based polymeric drug delivery system. In: IEEE conference 978-1-4244-5449-5/10
Atul S, Takalkar, MC Lenin Babu (2016) Characterization of valveless micro pump for drug delivery by using piezoelectric effect. 978-1-5090-2029-4/16
Cao L, Mantell S, Polla D (2001) Design and simulation of an implantable medical drug delivery system using microelectromechanical systems technology. Sens Actuators A 94:117–125
Chung AJ, Kim D, Erickson D (2008) Electrokinetic micro fluidic device for rapid, low power drug delivery in autonomous micro systems. Lab Chip 8:330–338
Cui Q, Liu C, Zha XF (2007) Study on piezoelectric micro pump for the controlled drug delivery system. Microfluid Nanofluid 3:377–390
Dardano P, Caliò A, Politi J, Rea I, Rendina I, De Stefano L (2016) Optically monitored drug delivery patch based on porous silicon and polymer microneedles. Biomedical Opt Exp 7(5):1645–1655
Davis SP, Landis BJ, Adams ZH, Allen MG, Prausnitz MR (2004) Insertion of microneedle into skin measurement and prediction of insertion force and needle fracture force. J Bio-Mech 37:1155–1163
Donnelly RF, Caffarel-Salvador E (2016) Transdermal drug delivery mediated by microneedle array: innovations and barriers to success. Curr Pharm Design 22(9):1105–1117
Elman NM, Ho Duc HL, Cima MJ (2009) An implantable MEMS drug delivery device for rapid delivery in ambulatory emergency care. Biomed Microdevices. doi:10.1007/s10544-008-9272-6
Han X, Cao Q, Li L (2012) Design and evaluation of three-dimensional electromagnetic guide system for magnetic drug delivery. IEEE Trans Appl Supercond 22(3):4401404–4401404
Herrlich S, Spieth S, Messner S, Zengerle R (2012) Osmotic micro pumps for drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 64:1617–1627
Jeong OC, Yang SS (2000) Fabrication and test of a thermopneumatic micropump with a corrugated p + diaphragm. Sens Actuators A 83(1):249–255
Junwu K, Zhigang Y, Taijiang P, Cheng Guangming W, Boda W (2005) Design and test of a high-performance piezoelectric micro pump for drug delivery. Sens Actuators A 121:156–161
Kumar N, George D, Sajeesh P, Manivannan PV, Sen AK (2016) Development of solenoid actuated planar valveless micro pump with single and multiple inlet-outlet arrangements. J Micromech Microeng 26:75013
Lhernould MS, Delchambre A (2011) Innovative design of hallow polymeric microneedles for transdermal drug delivery. Microsyst Technol 17:1675–1682. doi:10.1007/s00542-011-1355-2
Makino E, Mitsuya T, Shibata T (2001) Fabrication of TiNi shape memory micropump. Sens Actuators A 88:256–262
Maruo S, Inoue H (2006) Optically driven micropump produced by three-dimensional two-photon microfabrication. Appl Phys Lett 89:144101
Meng E, Wang X, Mak H, Tai Y (2000) A check-valved silicone diaphragm pump. In: Proceedings MEMS T00, Miyazaki, Japan; pp 62–67
Ogawa J, Kanno I, Kotera H, Wasa K, Suzuki K (2009) Development of liquid pumping devices using vibrating microchannel walls. Sens Actuators A Phys 152:211–218
Paik SJ, Byun S, Lim JM, Park Y, Lee A, Chung S, Chang J, Chun K, Dan Cho D (2004) In-plane single-crystal–silicon microneedles for minimally invasive microfluid systems. Sens Actuators A 114:276–284
Mukerjee EV, Collins SD, Isseroff RR, Smith RL (2004) Microneedle array of transdermal biological fluid extraction and in situ analysis. Sens Actuators A 114:267–275
Reynaerts D, Peris J, Van Brussel H (1997) An implantable drug-delivery system based on shape memory alloy micro-actuation. Sens Actuators A 61:455–462
Sayar E, Farouk B (2015) Bulk acoustic wave piezoelectric micro pumps with stationary flow rectifiers: a three-dimensional structural/fluid dynamic investigation. Microfluid Nanofluid 18:433–445. doi:10.1007/s10404-014-1441-8
Sheikhlou M, Shabani R, Rezazadeh G (2016) Nonlinear analysis of electrostatically actuated diaphragm-type micropumps. Nonlinear Dyn 83:951–961
Sim WY, Yoon HJ, Jeong OC, Yang SS (2003) A phase change type micro pump with aluminum flap valves. J Micromech Microeng 13:286
Teymoori MM, Abbaspour-Sani E (2005) Design and simulation of a novel electrostatic peristaltic micro machined pump for drug delivery applications. Sens Actuators A 117:222–229
Zhan G, Lo T, Liu L, Tsien P (1996) A silicon membrane micropump with integrated bimetallic actuator. Chin J Electron 5:29–35
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank NPMASS, Govt. of India for providing the necessary tools through NMDC Center throughout India. The author(Dr. K. Srinivasa Rao) would like to thank Science Engineering Research Board (SERB), Govt. of India for providing partial financial support to carry out this research work.(File no: ECR/2016/000757).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sateesh, J., Girija Sravani, K., Akshay Kumar, R. et al. Design and Flow Analysis of MEMS based Piezo-electric Micro Pump. Microsyst Technol 24, 1609–1614 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-017-3563-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-017-3563-x