Abstract
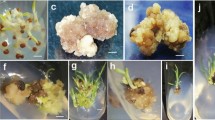
The crop species Olea europaea L. (olive tree) is of great economic importance in the Mediterranean region. Hence, many efforts have been done in the last decades to propagate this commercially valuable species by in vitro methods. On the other hand, the lesser known Olea maderensis (Lowe) Rivas Mart. & Del Arco which is a native species of the Madeira Archipelago has only been the subject of micropropagation from nodal stem cuttings. Therefore, in this work we analysed the stability of ten nuclear simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers at successive stages of the somatic embryogenesis process in two adult trees belonging to these two species from the Madeira Archipelago. For the induction of somatic embryogenesis, petiole and leaf explants were cultivated on solid Murashige and Skoog medium (MS) with 12.25 μM indole-3-butyric acid (IBA) and 4.56 μM of zeatin, in the dark. After 3 months, different callus tissues (non-embryogenic, pre-embryogenic and embryogenic) developed from leaf explants and petioles were later transferred to MS medium without growth regulators in the dark. All ten SSR markers were able to distinguish between species. However, no mutations were found at the SSR loci at any of the successive developmental stages from PEMs (pre-embryogenic masses) to somatic embryos. This genetic uniformity was observed within material derived from each genotype/species and its respective donor plant. Therefore, we conclude that the genomic integrities of both O. europaea and O. maderensis were maintained throughout the stages of the embryogenic processes in study suggesting the absence of somaclonal variation.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baali-Cherif D, Besnard G (2005) High genetic diversity and clonal growth in relict populations of Olea europaea subsp laperrinei (Oleaceae) from Hoggar, Algeria. Ann Bot (Lond) 96:823–830. doi:10.1093/aob/mci232
Benelli C, Fabbri A, Grassi S, Lambardi M, Rugini E (2001) Histology of somatic embryogenesis in mature tissues of olive (Olea europaea L.). J Hortic Sci Biotechnol 76:112–119
Belaj A, Satoviæ Z, Cipriani G, Baldoni L, Testolin R, Rallo L, Trujillo I (2003) Comparative study of the discriminating capacity of RAPD, AFLP and SSR markers and their effectiveness in establishing genetic relationship in olive. Theor Appl Genet 107:736–744
Brito G, Jardim R, Santos C, Coelho C (2007a) Micropropagação de uma espécie autóctone de Porto Santo como estratégia de combate à desertificação: exemplo da Oliveira-brava. Silva Lusitana 15:229–247
Brito G, Loureiro J, Lopes T, Rodriguez E, Santos C (2007b) Genetic characterization of olive trees from Madeira Archipelago using flow cytometry and microsatellite markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol. doi:10.1007/s10722-007-9268-8
Burg K, Bozhkov P, Helmersson A, von Arnold S (2007) Correlation of nuclear microsatellite instability and somatic embryogenesis in Pine. J Exp Bot 58:687–698. doi:10.1093/jxb/erl241
Canas LA, Benbadis A (1988) In vitro plant-regeneration from cotyledon fragments of the olive tree (Olea europaea L.). Plant Sci 54:65–74. doi:10.1016/0168-9452(88)90056-8
Canas LA, Carramolino L, Vicente M (1987) Vegetative propagation of the olive tree from in vitro cultured embryos. Plant Sci 50:85–90. doi:10.1016/0168-9452(87)90034-3
Capelo A, Brito G, Costa A, Santos C (2003) Micropropagation of the native Porto Santo Olea europaea: a contribution to combat desertification. I Simpósio sobre Biodiversidade em Ecossistemas Insulares. Book of Abstracts. Porto Santo, Portugal
Capelo J, Sequeira M, Jardim R, Mesquita S (2007) Biologia e Ecologia das florestas das Ilhas–Madeira. In: Silva JS (ed) Árvores e Florestas de Portugal–Açores e Madeira, a floresta das ilhas. Público, Comunicação Social, SA Lisboa, Portugal, pp 81–135
Cipriani G, Marrazzo MT, Marconi R, Cimato A, Testolin R (2002) Microsatellite markers isolated in olive (Olea europaea L.) are suitable for individual fingerprinting and reveal polymorphism within ancient cultivars. Theor Appl Genet 104:223–228. doi:10.1007/s001220100685
Conde P, Loureiro J, Santos C (2004) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from leaves of Ulmus minor Mill. Plant Cell Rep 22:632–639. doi:10.1007/s00299-003-0735-1
Doveri S, Gil FS, Díaz A, Reale S, Busconi M, Machado AC et al (2008) Standardization of a set of microsatellite markers for use in cultivar identification studies in olive (Olea europaea L.). Sci Hortic (Amsterdam) 116:367–373. doi:10.1016/j.scienta.2008.02.005
Endemann M, Hristoforoglu K, Stauber T, Wilhelm E (2001) Assessment of age-related polyploidy in Quercus robur L. somatic embryos and regenerated plants using DNA flow cytometry. Biol Plant 44:339–345. doi:10.1023/A:1012426306493
Fourré JL, Berger P, Niquet L, André P (1997) Somatic embryogenesis and somaclonal variation in Norway spruce: morphogenetic, cytogenetic and molecular approaches. Theor Appl Genet 94:159–169. doi:10.1007/s001220050395
Gallego FJ, Martinez I, Celestino C, Toribio M (1997) Testing somaclonal variation using RAPDs in Quercus suber L. somatic embryos. Int J Plant Sci 158:563–567. doi:10.1086/297468
García-Férriz L, Ghorbel R, Ybarra M, Marì A, Belaj A, Trujillo I (2002) Micropropagation from adult olive trees. IV international symposium on olive growing. Acta Hortic 586:879–882
Giri CC, Shyamkumar B, Anjaneyulu C (2004) Progress in tissue culture, genetic transformation and applications of biotechnology to trees: an overview. Trees (Berl West) 18:115–135. doi:10.1007/s00468-003-0287-6
Goto S, Thakur RC, Ishii K (1998) Determination of genetic stability in long-term micropropagated shoots of Pinus thunbergii Parl. using RAPD markers. Plant Cell Rep 18:193–197. doi:10.1007/s002990050555
Hajeer A, Worthington J, John S (eds) (2000) SNP and Microsatellite Genotyping. biotechniques books
Harvengt L, Trontin JF, Reymond I, Canlet F, Paques M (2001) Molecular evidence of true-to-type propagation of a 3-year-old Norway spruce through somatic embryogenesis. Planta 213:828–832. doi:10.1007/s004250100628
Hashmi G, Huettel R, Meyer R, Krusberg L, Hammerschlag F (1997) RAPD analysis of somaclonal variants derived from embryo callus cultures of peach. Plant Cell Rep 16:624–627. doi:10.1007/BF01275503
Hornero J, Martinez I, Celestino C, Gallego FJ, Torres V, Toribio M (2001) Early checking of genetic stability of cork oak somatic embryos by AFLP analysis. Int J Plant Sci 162:827–833. doi:10.1086/320784
Jones CJ, Edwards KJ, Castaglione S, Winfield MO, Sala F, van de Wiel C et al (1997) Reproducibility testing of RAPD, AFLP and SSR markers in plants by a network of European laboratories. Mol Breed 3:381–390. doi:10.1023/A:1009612517139
Leroy X, Leon K, Branchard M (2000) Plant genomic instability detected by microsatellite-primers. Electron J Biotechnol 3:1–9
Leva A, Muleo R, Petruccelli R (1995) Long-term somatic embryogenesis from immature olive cotyledons. J Hortic Sci 70:417–421
Lopes T, Pinto G, Loureiro J, Costa A, Santos C (2006) Determination of genetic stability in long-term somatic embryogenic cultures and derived plantlets of cork oak using microsatellite markers. Tree Physiol 26:1145–1152
Loureiro J, Pinto G, Lopes T, Dolezel J, Santos C (2005) Assessment of genetic stability of Quercus suber L. somatic embryogenesis process using flow cytometry. Planta 221:815–822. doi:10.1007/s00425-005-1492-x
Mencuccini M, Rugini E (1993) In vitro shoot regeneration from olive cultivar tissues. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 32:283–288. doi:10.1007/BF00042290
Meudt HM, Clarke AC (2007) Almost forgotten or latest practice? AFLP applications, analyses and advances. Trends Plant Sci 12:106–117. doi:10.1016/j.tplants.2007.02.001
Mitrakos K, Alexaki A, Papadimitriou P (1992) Dependence of olive morphogenesis on callus origin and age. J Plant Physiol 139:269–273
Mo LH, von Arnold S (1991) Origin and development of embryogenic cultures from seedlings of Norway spruce (Picea abies). J Plant Physiol 138:223–230
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bio assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3054.1962.tb08052.x
Omrani-Sabbaghi A, Shahriari M, Falahati-Anbaran M, Mohammadi SA, Nankali A, Mardi M et al (2007) Microsatellite markers based assessment of genetic diversity in Iranian olive (Olea europaea L.) collections. Sci Hortic (Amsterdam) 112:439–447. doi:10.1016/j.scienta.2006.12.051
Orinos T, Mitrakos K (1991) Rhizogenesis and somatic embryogenesis in calli from wild olive (Olea europaea var. sylvestris (Miller) Lehr) mature zygotic embryos. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 27:183–187. doi:10.1007/BF00041288
Otero ML, do Campo DM (1996) Micropropagation of olive (Olea europaea L.), clone Oblonga, by in vitro embryo culture. Phyton-int. J Exp Bot 59(1–2):201–206
Pinto G, Loureiro J, Lopes T, Santos C (2004) Analysis of the genetic stability of Eucalyptus globulus Labill. somatic embryos by flow cytometry. Theor Appl Genet 109:580–587. doi:10.1007/s00122-004-1655-3
Powell W, Gordon C, Machray J, Provan J (1996) Polymorphism revealed by simple sequence repeats. Trends Plant Sci 1:215–222
Revilla MA, Pacheco J, Casares A, Rodriguez R (1996) In vitro reinvigoration of mature olive trees (Olea europaea L.) through micrografting. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 32:257–261. doi:10.1007/BF02822697
de la Rosa R, James CM, Tobutt KR (2002) Isolation and characterization of polymorphic microsatellites in olive (Olea europaea L.) and their transferability to other genera in the Oleaceae. Mol Ecol Notes 2:265–267. doi:10.1046/j.1471-8286.2002.00217.x
Roussos PA, Pontikis CA (2002) In vitro propagation of olive (Olea europaea L.) cv. Koroneiki. Plant Growth Regul 37:295–304. doi:10.1023/A:1020824330589
Rugini E (1984) In vitro-propagation of some olive (Olea europaea sativa L.) cultivars with different root-ability, and medium development using analytical data from developing shoots and embryos. Sci Hortic (Amsterdam) 24:123–134. doi:10.1016/0304-4238(84)90143-2
Rugini E (1988) Somatic embryogenesis and plant-regeneration in olive (Olea europaea L.). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 14:207–214. doi:10.1007/BF00043411
Rugini E (1995) Somatic embryogenesis in olive (Olea europaea L.). In: Jain SM, Gupta PK, Newton RJ (eds) Somatic embryogenesis in woody plants. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrect, pp 171–189
Rugini E, Caricato G (1995) Somatic embryogenesis and plant-recovery from mature tissues of olive cultivars (Olea europaea L.). Canino Moraiolo. Plant Cell Rep 14:257–260
Santos CV, Brito G, Pinto G, Fonseca H (2003) In vitro plantlet regeneration of Olea europaea ssp. maderensis. Sci Hortic (Amsterdam) 97:83–87. doi:10.1016/S0304-4238(02)00148-6
Sarri V, Baldoni L, Porceddu A, Cultrera NGM, Contento A, Frediani M et al (2006) Microsatellite markers are powerful tools for discriminating among olive cultivars and assigning them to geographically defined populations. Genome 49:606–1615. doi:10.1139/G06-126
Sefc KM, Lopes MS, Mendonça D, Rodrigues dos Santos M, a Machado ML, a Machado A (2000) Identification of microsatellite loci in olive (Olea europaea L.) and their characterization in Italian and Iberian olive trees. Mol Ecol 9:1171–1173. doi:10.1046/j.1365-294x.2000.00954.x
Sensi E, Vignani R, Scali M, Masi E, Cresti M (2003) DNA fingerprinting and genetic relatedness among cultivated varieties of Olea europaea L. estimated by AFLP analysis. Sci Hortic (Amsterdam) 97:379–388. doi:10.1016/S0304-4238(02)00163-2
Shibli RA, Shatnawi M, Abu E, Al-Juboory KH (2001) Somatic embryogenesis and plant recovery from callus of ‘Nabali’ olive (Olea europaea L.). Sci Hortic (Amsterdam) 88:243–256. doi:10.1016/S0304-4238(00)00241-7
Terzopoulos PJ, Kolano B, Bebeli PJ, Kaltsikes PJ, Metzidakis I (2005) Identification of Olea europaea L. cultivars using inter-simple sequence repeat markers. Sci Hortic (Amsterdam) 105:45–51. doi:10.1016/j.scienta.2005.01.011
Thakur R, Goto S, Ishii K, Jain S (1999) Monitoring genetic stability in Quercus serrata Thunb. somatic embryogenesis using RAPD markers. J For Res 4:157–160. doi:10.1007/BF02762241
Trabelsi EB, Bouzid S, Bouzid M, Elloumi N, Belfeleh Z, Benabdallah A et al (2003) In-vitro regeneration of olive tree by somatic embryogenesis. J Plant Biol 46:173–180
Vendrame WA, Kochert GD, Wetzstein HY (1999) AFLP analysis of variation in Pecan somatic embryos. Plant Cell Rep 18:853–857. doi:10.1007/s002990050673
Vicente MC, Fulton T (2003) Using molecular marker technology in studies on plant genetic diversity: DNA-based technologies. IPGRI and Cornell University
Wilhelm E, Hristoforoglu K, Fluch S, Burg K (2005) Detection of microsatellite instability during somatic embryogenesis of oak (Quercus robur L.). Plant Cell Rep 23:790–795. doi:10.1007/s00299-004-0891-y
Zacchini M, de Agazio M (2004) Micropropagation of a local olive cultivar for germplasm preservation. Biol Plant 48:589–592. doi:10.1023/B:BIOP.0000047156.57328.27
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Eduardo Ferreira and Luis Souto for technical assistance in the analyses of fragments. Thanks are also due to Armando Costa, Raquel Santos and Ricardo Cruz. This work was supported by the FCT/MCTES project POCI/AGR/60672/2004. FCT also supported the fellowship of Tina Lopes (FCT/SFRH/BPD/6012/2001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by M. Canovas.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lopes, T., Capelo, A., Brito, G. et al. Genetic variability analyses of the somatic embryogenesis induction process in Olea spp. using nuclear microsatellites. Trees 23, 29–36 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-008-0251-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-008-0251-6