Abstract
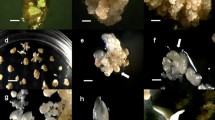
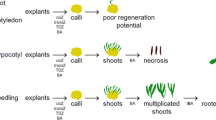
In calli from distal and proximal cotyledon segments and from radicles of mature wild olive zygotic embryos, rhizogenesis prevailed during the first and somatic embryogenesis during the second 30 day subculture period. Rhizogenesis was enhanced by low IBA (0.5 and 2.5 μM) and 5.0 μM 2iP. By reducing by half the media salt concentrations and by inserting a 21 day dark period rhizogenesis was also enhanced. Somatic embryogenesis was inhibited by both 2iP and IBA at concentrations higher than 5.0 μM, but was not influenced by lower salt concentrations or by inserting the dark period.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 2.4-D:
-
2.4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
- 2iP:
-
N6-[2-isopentenyl]adenine
- BA:
-
6-benzylaminopurine
- IBA:
-
indole-3-butyric acid
- MS:
-
Murashige & Skoog
- NAA:
-
naphthaleneacetic acid
- OM:
-
Olive medium [4]
- OMc:
-
OM medium in which OM macroelements were replaced with the ones proposed by Bourgin & Nitsch [2]
- OMe:
-
OM salts of quarter strength, with half strength vitamin mixture (except biotin which added in full strength), with 5 μM 2iP and 20 g l-1 sucrose [2]
- OMr:
-
OM salts half strength containing 5 μM IBA and 20 g l-1 sucrose [2]
References
Bao ZH, Ma YF, Liu JF, Wang KJ, Zhang PF, Ni DX & Yang WQ (1980) Induction of plantlets from the hypocotyl of Olea europaea L. in vitro. Acta Bot. Sin. 22: 96–97
Canas LA & Benbadis A (1988) In vitro plant regeneration from cotyledon fragments of the olive tree (Olea europaea L.) Plant Sci. 54: 65–74
Kapsali M, Mitrakos K & Diamantoglou S (1986) Olea europaea callus growth and differentiation. 5th Congress of the Federation of European Societies of Plant Physiology. 31 Aug-4 Sept, Hamburg, Abstracts pp 1–15
Rugini E (1984) In vitro propagation of some olive (Olea europea Sativa L.) cultivars with different root-ability, and medium development using analytical data from developing shoots and embryos. Scientia Hortic. 24: 123–134
Rugini E (1986) Olive (Olea europaea L.). In: Bajaj YPS (Ed) Biotechnology in Agriculture and Forestry, Vol I (pp 153–167). Springer Verlag, Berlin
Rugini E & Tarini P (1986) Somatic embryogenesis in olive (Olea europaea L.). Conf. Fruit Tree Biotechnol, October 14–15, Paris (abstract)
Rugini E (1988) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in olive (Olea europaea L.). Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 14: 207–214
Wang KJ, Zhang PF, Ni DX, Zhu XZ, Yang WQ & Bao ZH (1979) Cytohistological studies on the tissue culture of Olea europaea L. II. Histogenesis and organogenesis. Acta Bot. Sin. 21: 225–230
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Orinos, T., Mitrakos, K. Rhizogenesis and somatic embryogenesis in calli from wild olive (Olea europaea var. sylvestris (Miller) Lehr) mature zygotic embryos. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 27, 183–187 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00041288
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00041288