Abstract
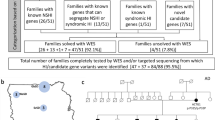
Hearing loss is the most common sensory deficit in humans with causative variants in over 140 genes. With few exceptions, however, the population-specific distribution for many of the identified variants/genes is unclear. Until recently, the extensive genetic and clinical heterogeneity of deafness precluded comprehensive genetic analysis. Here, using a custom capture panel (MiamiOtoGenes), we undertook a targeted sequencing of 180 genes in a multi-ethnic cohort of 342 GJB2 mutation-negative deaf probands from South Africa, Nigeria, Tunisia, Turkey, Iran, India, Guatemala, and the United States (South Florida). We detected causative DNA variants in 25 % of multiplex and 7 % of simplex families. The detection rate varied between 0 and 57 % based on ethnicity, with Guatemala and Iran at the lower and higher end of the spectrum, respectively. We detected causative variants within 27 genes without predominant recurring pathogenic variants. The most commonly implicated genes include MYO15A, SLC26A4, USH2A, MYO7A, MYO6, and TRIOBP. Overall, our study highlights the importance of family history and generation of databases for multiple ethnically discrete populations to improve our ability to detect and accurately interpret genetic variants for pathogenicity.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed ZM, Masmoudi S, Kalay E, Belyantseva IA, Mosrati MA, Collin RW, Riazuddin S, Hmani-Aifa M, Venselaar H, Kawar MN, Tlili A, van der Zwaag B, Khan SY, Ayadi L, Riazuddin SA, Morell RJ, Griffith AJ, Charfedine I, Caylan R, Oostrik J, Karaguzel A, Ghorbel A, Riazuddin S, Friedman TB, Ayadi H, Kremer H (2008) Mutations of LRTOMT, a fusion gene with alternative reading frames, cause nonsyndromic deafness in humans. Nat Genet 40:1335–1340. doi:10.1038/ng.245
Amendola LM, Jarvik GP, Leo MC, McLaughlin HM, Akkari Y, Amaral MD, Berg JS, Biswas S, Bowling KM, Conlin LK, Cooper GM, Dorschner MO, Dulik MC, Ghazani AA, Ghosh R, Green RC, Hart R, Horton C, Johnston JJ, Lebo MS, Milosavljevic A, Ou J, Pak CM, Patel RY, Punj S, Richards CS, Salama J, Strande NT, Yang Y, Plon SE, Biesecker LG, Rehm HL (2016) Performance of ACMG-AMP variant-interpretation guidelines among nine laboratories in the Clinical Sequencing Exploratory Research Consortium. Am J Hum Genet 98:1067–1076. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2016.03.024
Angeli S, Lin X, Liu XZ (2012) Genetics of hearing and deafness. Anat Rec (Hoboken) 295:1812–1829. doi:10.1002/ar.22579
Aronson SJ, Rehm HL (2015) Building the foundation for genomics in precision medicine. Nature 526:336–342. doi:10.1038/nature15816
Babanejad M, Fattahi Z, Bazazzadegan N, Nishimura C, Meyer N, Nikzat N, Sohrabi E, Najmabadi A, Jamali P, Habibi F, Smith RJ, Kahrizi K, Najmabadi H (2012) A comprehensive study to determine heterogeneity of autosomal recessive nonsyndromic hearing loss in Iran. Am J Med Genet A 158A:2485–2492. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.35572
Bademci G, Foster J 2nd, Mahdieh N, Bonyadi M, Duman D, Cengiz FB, Menendez I, Diaz-Horta O, Shirkavand A, Zeinali S, Subasioglu A, Tokgoz-Yilmaz S, Huesca-Hernandez F, de la Luz Arenas-Sordo M, Dominguez-Aburto J, Hernandez-Zamora E, Montenegro P, Paredes R, Moreta G, Vinueza R, Villegas F, Mendoza-Benitez S, Guo S, Bozan N, Tos T, Incesulu A, Sennaroglu G, Blanton SH, Ozturkmen-Akay H, Yildirim-Baylan M, Tekin M (2016) Comprehensive analysis via exome sequencing uncovers genetic etiology in autosomal recessive nonsyndromic deafness in a large multiethnic cohort. Genet Med 18:364–371. doi:10.1038/gim.2015.89
Baux D, Larrieu L, Blanchet C, Hamel C, Ben Salah S, Vielle A, Gilbert-Dussardier B, Holder M, Calvas P, Philip N, Edery P, Bonneau D, Claustres M, Malcolm S, Roux AF (2007) Molecular and in silico analyses of the full-length isoform of usherin identify new pathogenic alleles in Usher type II patients. Hum Mutat 28:781–789. doi:10.1002/humu.20513
Baux D, Blanchet C, Hamel C, Meunier I, Larrieu L, Faugere V, Vache C, Castorina P, Puech B, Bonneau D, Malcolm S, Claustres M, Roux AF (2014) Enrichment of LOVD-USHbases with 152 USH2A genotypes defines an extensive mutational spectrum and highlights missense hotspots. Hum Mutat 35:1179–1186. doi:10.1002/humu.22608
Borck G, Ur Rehman A, Lee K, Pogoda HM, Kakar N, von Ameln S, Grillet N, Hildebrand MS, Ahmed ZM, Nurnberg G, Ansar M, Basit S, Javed Q, Morell RJ, Nasreen N, Shearer AE, Ahmad A, Kahrizi K, Shaikh RS, Ali RA, Khan SN, Goebel I, Meyer NC, Kimberling WJ, Webster JA, Stephan DA, Schiller MR, Bahlo M, Najmabadi H, Gillespie PG, Nurnberg P, Wollnik B, Riazuddin S, Smith RJ, Ahmad W, Muller U, Hammerschmidt M, Friedman TB, Riazuddin S, Leal SM, Ahmad J, Kubisch C (2011) Loss-of-function mutations of ILDR1 cause autosomal-recessive hearing impairment DFNB42. Am J Hum Genet 88:127–137. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2010.12.011
Brownstein Z, Friedman LM, Shahin H, Oron-Karni V, Kol N, Abu Rayyan A, Parzefall T, Lev D, Shalev S, Frydman M, Davidov B, Shohat M, Rahile M, Lieberman S, Levy-Lahad E, Lee MK, Shomron N, King MC, Walsh T, Kanaan M, Avraham KB (2011) Targeted genomic capture and massively parallel sequencing to identify genes for hereditary hearing loss in Middle Eastern families. Genome Biol 12:R89. doi:10.1186/gb-2011-12-9-r89
Chu CW, Chen YJ, Lee YH, Jaung SJ, Lee FP, Huang HM (2015) Government-funded universal newborn hearing screening and genetic analyses of deafness predisposing genes in Taiwan. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 79:584–590. doi:10.1016/j.ijporl.2015.01.033
Davis A (1995) Hearing in adults: the prevalence and distribution of hearing impairment and reported hearing disability in the MRC Institute of Hearing Research’s National Study of Hearing. Whurr Publisher, London
Delmaghani S, del Castillo FJ, Michel V, Leibovici M, Aghaie A, Ron U, Van Laer L, Ben-Tal N, Van Camp G, Weil D, Langa F, Lathrop M, Avan P, Petit C (2006) Mutations in the gene encoding pejvakin, a newly identified protein of the afferent auditory pathway, cause DFNB59 auditory neuropathy. Nat Genet 38:770–778. doi:10.1038/ng1829
Eudy JD, Weston MD, Yao S, Hoover DM, Rehm HL, Ma-Edmonds M, Yan D, Ahmad I, Cheng JJ, Ayuso C, Cremers C, Davenport S, Moller C, Talmadge CB, Beisel KW, Tamayo M, Morton CC, Swaroop A, Kimberling WJ, Sumegi J (1998) Mutation of a gene encoding a protein with extracellular matrix motifs in Usher syndrome type IIa. Science 280:1753–1757
Fugazzola L, Cerutti N, Mannavola D, Crino A, Cassio A, Gasparoni P, Vannucchi G, Beck-Peccoz P (2002) Differential diagnosis between Pendred and pseudo-Pendred syndromes: clinical, radiologic, and molecular studies. Pediatr Res 51:479–484. doi:10.1203/00006450-200204000-00013
Garrison E, Marth G (2012) Haplotype-based variant detection from short-read sequencing. arXiv preprint arXiv:1207.3907
Gorlin RJ, Toriello HV, Cohen MM (1995) Hereditary hearing loss and its syndromes. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Gu X, Guo L, Ji H, Sun S, Chai R, Wang L, Li H (2015) Genetic testing for sporadic hearing loss using targeted massively parallel sequencing identifies 10 novel mutations. Clin Genet 87:588–593. doi:10.1111/cge.12431
Hutchin TP, Parker MJ, Young ID, Davis AC, Pulleyn LJ, Deeble J, Lench NJ, Markham AF, Mueller RF (2000) A novel mutation in the mitochondrial tRNA(Ser(UCN)) gene in a family with non-syndromic sensorineural hearing impairment. J Med Genet 37:692–694
King PJ, Ouyang X, Du L, Yan D, Angeli SI, Liu XZ (2012) Etiologic diagnosis of nonsyndromic genetic hearing loss in adult vs pediatric populations. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 147:932–936. doi:10.1177/0194599812453553
Kothiyal P, Cox S, Ebert J, Husami A, Kenna MA, Greinwald JH, Aronow BJ, Rehm HL (2010) High-throughput detection of mutations responsible for childhood hearing loss using resequencing microarrays. BMC Biotechnol 10:10. doi:10.1186/1472-6750-10-10
Lee HK, Song MH, Kang M, Lee JT, Kong KA, Choi SJ, Lee KY, Venselaar H, Vriend G, Lee WS, Park HJ, Kwon TK, Bok J, Kim UK (2009) Clinical and molecular characterizations of novel POU3F4 mutations reveal that DFN3 is due to null function of POU3F4 protein. Physiol Genomics 39:195–201. doi:10.1152/physiolgenomics.00100.2009
Li H, Durbin R (2010) Fast and accurate long-read alignment with Burrows–Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 26:589–595. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btp698
Maddalena A, Bale S, Das S, Grody W, Richards S, Committee ALQA (2005) Technical standards and guidelines: molecular genetic testing for ultra-rare disorders. Genet Med 7:571–583. doi:10.1097/01.GIM.0000182738.95726.ca
Mosrati MA, Hammami B, Rebeh IB, Ayadi L, Dhouib L, Ben Mahfoudh K, Hakim B, Charfeddine I, Mnif J, Ghorbel A, Masmoudi S (2011) A novel dominant mutation in SIX1, affecting a highly conserved residue, result in only auditory defects in humans. Eur J Med Genet 54:e484–e488. doi:10.1016/j.ejmg.2011.06.001
Nance WE (2003) The genetics of deafness. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev 9:109–119. doi:10.1002/mrdd.10067
Naz S, Giguere CM, Kohrman DC, Mitchem KL, Riazuddin S, Morell RJ, Ramesh A, Srisailpathy S, Deshmukh D, Riazuddin S, Griffith AJ, Friedman TB, Smith RJ, Wilcox ER (2002) Mutations in a novel gene, TMIE, are associated with hearing loss linked to the DFNB6 locus. Am J Hum Genet 71:632–636. doi:10.1086/342193
Naz S, Alasti F, Mowjoodi A, Riazuddin S, Sanati MH, Friedman TB, Griffith AJ, Wilcox ER, Riazuddin S (2003) Distinctive audiometric profile associated with DFNB21 alleles of TECTA. J Med Genet 40:360–363
Nord AS, Lee M, King MC, Walsh T (2011) Accurate and exact CNV identification from targeted high-throughput sequence data. BMC Genom 12:184. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-12-184
Rehman AU, Gul K, Morell RJ, Lee K, Ahmed ZM, Riazuddin S, Ali RA, Shahzad M, Jaleel AU, Andrade PB, Khan SN, Khan S, Brewer CC, Ahmad W, Leal SM, Riazuddin S, Friedman TB (2011) Mutations of GIPC3 cause nonsyndromic hearing loss DFNB72 but not DFNB81 that also maps to chromosome 19p. Hum Genet 130:759–765. doi:10.1007/s00439-011-1018-5
Riahi Z, Bonnet C, Zainine R, Louha M, Bouyacoub Y, Laroussi N, Chargui M, Kefi R, Jonard L, Dorboz I, Hardelin JP, Salah SB, Levilliers J, Weil D, McElreavey K, Boespflug OT, Besbes G, Abdelhak S, Petit C (2014) Whole exome sequencing identifies new causative mutations in Tunisian families with non-syndromic deafness. PLoS One 9:e99797. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0099797
Richards CS, Bale S, Bellissimo DB, Das S, Grody WW, Hegde MR, Lyon E, Ward BE, Molecular Subcommittee of the ALQAC (2008) ACMG recommendations for standards for interpretation and reporting of sequence variations: revisions 2007. Genet Med 10:294–300. doi:10.1097/GIM.0b013e31816b5cae
Richards S, Aziz N, Bale S, Bick D, Das S, Gastier-Foster J, Grody WW, Hegde M, Lyon E, Spector E, Voelkerding K, Rehm HL, Committee ALQA (2015) Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet Med 17:405–424. doi:10.1038/gim.2015.30
Schrauwen I, Sommen M, Corneveaux JJ, Reiman RA, Hackett NJ, Claes C, Claes K, Bitner-Glindzicz M, Coucke P, Van Camp G, Huentelman MJ (2013) A sensitive and specific diagnostic test for hearing loss using a microdroplet PCR-based approach and next generation sequencing. Am J Med Genet A 161A:145–152. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.35737
Shearer AE, Smith RJ (2015) Massively parallel sequencing for genetic diagnosis of hearing loss: the new standard of care. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 153:175–182. doi:10.1177/0194599815591156
Shearer AE, DeLuca AP, Hildebrand MS, Taylor KR, Gurrola J 2nd, Scherer S, Scheetz TE, Smith RJ (2010) Comprehensive genetic testing for hereditary hearing loss using massively parallel sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:21104–21109. doi:10.1073/pnas.1012989107
Shearer AE, Black-Ziegelbein EA, Hildebrand MS, Eppsteiner RW, Ravi H, Joshi S, Guiffre AC, Sloan CM, Happe S, Howard SD, Novak B, Deluca AP, Taylor KR, Scheetz TE, Braun TA, Casavant TL, Kimberling WJ, Leproust EM, Smith RJ (2013) Advancing genetic testing for deafness with genomic technology. J Med Genet 50:627–634. doi:10.1136/jmedgenet-2013-101749
Shearer AE, Eppsteiner RW, Booth KT, Ephraim SS, Gurrola J 2nd, Simpson A, Black-Ziegelbein EA, Joshi S, Ravi H, Giuffre AC, Happe S, Hildebrand MS, Azaiez H, Bayazit YA, Erdal ME, Lopez-Escamez JA, Gazquez I, Tamayo ML, Gelvez NY, Leal GL, Jalas C, Ekstein J, Yang T, Usami S, Kahrizi K, Bazazzadegan N, Najmabadi H, Scheetz TE, Braun TA, Casavant TL, LeProust EM, Smith RJ (2014) Utilizing ethnic-specific differences in minor allele frequency to recategorize reported pathogenic deafness variants. Am J Hum Genet 95:445–453. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2014.09.001
Sloan-Heggen CM, Babanejad M, Beheshtian M, Simpson AC, Booth KT, Ardalani F, Frees KL, Mohseni M, Mozafari R, Mehrjoo Z, Jamali L, Vaziri S, Akhtarkhavari T, Bazazzadegan N, Nikzat N, Arzhangi S, Sabbagh F, Otukesh H, Seifati SM, Khodaei H, Taghdiri M, Meyer NC, Daneshi A, Farhadi M, Kahrizi K, Smith RJ, Azaiez H, Najmabadi H (2015) Characterising the spectrum of autosomal recessive hereditary hearing loss in Iran. J Med Genet 52:823–829. doi:10.1136/jmedgenet-2015-103389
Tchernitchko D, Goossens M, Wajcman H (2004) In silico prediction of the deleterious effect of a mutation: proceed with caution in clinical genetics. Clin Chem 50:1974–1978. doi:10.1373/clinchem.2004.036053
Tekin D, Yan D, Bademci G, Feng Y, Guo S, Foster J 2nd, Blanton S, Tekin M, Liu X (2016) A next-generation sequencing gene panel (MiamiOtoGenes) for comprehensive analysis of deafness genes. Hear Res 333:179–184. doi:10.1016/j.heares.2016.01.018
Thusberg J, Vihinen M (2009) Pathogenic or not? And if so, then how? Studying the effects of missense mutations using bioinformatics methods. Hum Mutat 30:703–714. doi:10.1002/humu.20938
Tsai AC, Liu X (2014) Toward best practice in using molecular diagnosis to guide medical management, are we there yet? N Am J Med Sci (Boston) 7:199–200
Usami S, Abe S, Weston MD, Shinkawa H, Van Camp G, Kimberling WJ (1999) Non-syndromic hearing loss associated with enlarged vestibular aqueduct is caused by PDS mutations. Hum Genet 104:188–192
Weston MD, Kelley PM, Overbeck LD, Wagenaar M, Orten DJ, Hasson T, Chen ZY, Corey D, Mooseker M, Sumegi J, Cremers C, Moller C, Jacobson SG, Gorin MB, Kimberling WJ (1996) Myosin VIIA mutation screening in 189 Usher syndrome type 1 patients. Am J Hum Genet 59:1074–1083
Wu CC, Lu YC, Chen PJ, Yeh PL, Su YN, Hwu WL, Hsu CJ (2010) Phenotypic analyses and mutation screening of the SLC26A4 and FOXI1 genes in 101 Taiwanese families with bilateral nonsyndromic enlarged vestibular aqueduct (DFNB4) or Pendred syndrome. Audiol Neurootol 15:57–66. doi:10.1159/000231567
Yan D, Liu XZ (2008) Cochlear molecules and hereditary deafness. Front Biosci 13:4972–4983
Yan D, Tekin M, Blanton SH, Liu XZ (2013) Next-generation sequencing in genetic hearing loss. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers 17:581–587. doi:10.1089/gtmb.2012.0464
Yang T, Wei X, Chai Y, Li L, Wu H (2013) Genetic etiology study of the non-syndromic deafness in Chinese Hans by targeted next-generation sequencing. Orphanet J Rare Dis 8:85. doi:10.1186/1750-1172-8-85
Yoshimura H, Iwasaki S, Nishio SY, Kumakawa K, Tono T, Kobayashi Y, Sato H, Nagai K, Ishikawa K, Ikezono T, Naito Y, Fukushima K, Oshikawa C, Kimitsuki T, Nakanishi H, Usami S (2014) Massively parallel DNA sequencing facilitates diagnosis of patients with Usher syndrome type 1. PLoS One 9:e90688. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0090688
Yoshinaga-Itano C (2000) Successful outcomes for deaf and hard-of-hearing children. Semin Hear 21:309–326. doi:10.1055/s-2000-13462
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by R01 DC05575, R01 DC01246, 2P50DC000422-Sub-Project 6432, and R01 DC012115 from the National Institutes of Health/National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders to Xuezhong Liu and R01DC09645 and R01DC012836 to Mustafa Tekin; University of Pretoria RDP fund to RI Kabahuma.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, D., Tekin, D., Bademci, G. et al. Spectrum of DNA variants for non-syndromic deafness in a large cohort from multiple continents. Hum Genet 135, 953–961 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-016-1697-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-016-1697-z