Abstract
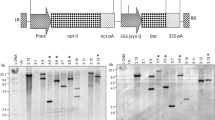
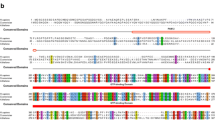
The functional and biological significance of translation initiation context sequence in determining high-level expression of modified synthetic human α1-proteinase inhibitor (α1-PI) gene was documented in stable transgenic tomato plants. Context sequence of initiator ATG codon derived from statistical analysis of databases was identified as taaA(A/C)aATGGCt in highly expressed dicot plant genes. Removal of initiator ATG context sequence reduced the expression of recombinant α1-PI protein to fourfolds. The mutation of consensus base at +4 position to a pyrimidine either alone or with substitution at −3 position eliminated most of the α1-PI expression, while mutation at −3 alone resulted in about sevenfold reduction. The presence of steady-state levels of α1-PI transcript in transgenic plants indicated that the variation in expression is entirely due to the point mutations incorporated in translation initiation context. These results indicated the significance of conserved nucleotide sequence around initiator ATG codon in augmenting post-transcriptional events and high-level expression of heterologous genes in transgenic plants.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- TIC:
-
Translation initiation context
- ELISA:
-
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- TSP:
-
Total soluble protein
- α1-PI:
-
α1-proteinase inhibitor
- AMV:
-
Alfalfa mosaic virus
- ER:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum
References
Agarwal S, Singh R, Sanyal I, Amla DV (2008) Expression of modified gene encoding functional human alpha-1-antitrypsin protein in transgenic tomato plants. Transgenic Res 17:881–896
Ashraf S, Singh PK, Yadav DK, Shahnawaz M, Mishra S, Sawant SV, Tuli R (2005) High-level expression of surface glycoprotein of rabies virus in tobacco leaves and its immunoprotective activity in mice. J Biotechnol 119:1–14
Boyd L, Thummel CS (1993) Selection of CUG and AUG initiator codons for Drosophila E74A translation depends on downstream sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:9164–9167
Cavener DR (1987) Comparison of the consensus sequence flanking translational start sites in Drosophila and vertebrates. Nucleic Acids Res 15:1353–1361
Guerineau F, Lucy A, Mullineaux P (1992) Effect of two consensus sequences preceding the translation initiator codon on gene expression in plant protoplasts. Plant Mol Biol 18:815–818
Iida Y, Kanagu D (2000) Quantification analysis of translation initiation signal in vertebrate mRNAs: effect of nucleotides at positions +4~+6 upon efficiency of translation initiation. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser 44:77–78
Johnston JC, Rochon DM (1996) Both codon context and leader length contribute to efficient expression of two overlapping open reading frames of a cucumber necrosis virus bifunctional sub-genomic mRNA. Virology 221:232–239
Joshi CP, Zhou H, Huang X, Chiang VL (1997) Context sequences of translation initiation codon in plants. Plant Mol Biol 35:993–1001
Kozak M (1986) Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell 44:283–292
Kozak M (1987) An analysis of 5′-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res 15:8125–8148
Kozak M (1990) Downstream secondary structure facilitates recognition of initiator codons by eukaryotic ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:8301–8305
Kozak M (1999) Initiation of translation in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Gene 234:187–208
Kozak M (2002) Pushing the limits of the scanning mechanism for initiation of translation. Gene 299:1–34
Liu Q, Xue Q (2005) Comparative studies on sequence characteristics around translation initiation codon in four eukaryotes. J Genet 84:317–322
Luehrsen KR, Walbot V (1994) The impact of AUG start codon context on maize gene expression in vivo. Plant Cell Rep 13:454–458
Lukaszewicz M, Feuermann M, Je′rouville B, Stas A, Boutry M (2000) In vivo evaluation of the context sequence of the translation initiation codon in plants. Plant Sci 154:89–98
Lutcke HA, Chow KC, Mickel FS, Moss KA, Kern HF, Scheele GA (1987) Selection of AUG initiation codons differs in plants and animals. EMBO J 6:43–48
McCormick S, Niedermeyer J, Fry J, Branason A, Horsch R, Fraley R (1986) Leaf disc transformation of cultivated tomato (L. esculentum) using Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Plant Cell Rep 5:81–84
Mishra S, Yadav DK, Tuli R (2006) Ubiquitin fusion enhances cholera toxin B subunit expression in transgenic plants and the plant-expressed protein binds GM1 receptors more efficiently. J Biotechnol 127:95–108
Miyasaka H, Kanai S, Tanaka S, Akiyama H, Hirano M (2002) Statistical analysis of the relationship between translation initiation AUG context and gene expression level in humans. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 66:667–669
Nakagawa S, Niimura Y, Gojobori T, Tanaka H, Miura KI (2008) Diversity of preferred nucleotide sequences around the translation initiation codon in eukaryote genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 36:861–871
Peach C, Velten J (1991) Transgene expression variability (position effect) of CAT and GUS reporter genes driven by linked divergent T-DNA promoters. Plant Mol Biol 17:49–60
Ruan Y, Gilmore J, Conner T (1998) Towards Arabidopsis genome analysis: monitoring expression profiles of 1400 genes using DNA microarrays. Plant J 15:821–833
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: A laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Sawant SV, Singh PK, Gupta SK, Madanala R, Tuli R (1999) Conserved nucleotide sequence in highly expressed genes in plants. J Genet 78:123–131
Sawant SV, Kiran K, Singh PK, Tuli R (2001) Sequence architecture downstream of the initiator codon enhances gene expression and protein stability in plants. Plant Physiol 126:1630–1636
Smit De MH, van Duin J (1990) Secondary structure of the ribosome binding site determines translational efficiency: a quantitative analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:7668–7672
Sullivan ML, Green PJ (1993) Post-transcriptional regulation of nuclear-encoded genes in higher plants: the roles of mRNA stability and translation. Plant Mol Biol 23:1091–1104
Taylor JL, Jones JDG, Sandler S, Mueller GM, Bedbrook J, Dunsmuir P (1987) Optimizing the expression of chimeric genes in plant cells. Mol Gen Genet 210:572–577
Wilde CD, Houdt HV, Buck SD, Angenon G, Jaeger GD, Depicker A (2000) Plant as bioreactors for protein production: avoiding the problem of transgene silencing. Plant Mol Biol 43:347–359
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Director, NBRI, Lucknow for infrastructural support, encouragement and valuable suggestions. We thankfully acknowledge Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), India for providing funds and senior research fellowships to SA and SJ. This work was carried out under the CSIR Network Project CMM0004 and OLP 0031.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by P. Kumar.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Agarwal, S., Jha, S., Sanyal, I. et al. Effect of point mutations in translation initiation context on the expression of recombinant human α1-proteinase inhibitor in transgenic tomato plants. Plant Cell Rep 28, 1791–1798 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-009-0779-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-009-0779-y