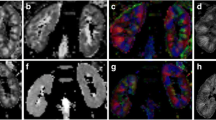
Abstract
Objective
To investigate the relationship of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) and fractional anisotropy (FA) values with renal function on 3T diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) in chronic kidney disease.
Materials and methods
Twenty healthy volunteers and 29 patients with CKD underwent DTI. The relationship among ADC, FA, and renal function was analyzed.
Results
Cortical and medullary ADC and FA values of patients with chronic kidney disease were lower than those of healthy volunteers (P = 0.000). Both the renal ADC and FA values correlated inversely with serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen (P < 0.05).
Conclusion
DTI is a feasible and non-invasive means to reflect the severity of renal function damaged.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang D, Ye Q, Williams DS, et al. (2004) Normal and transplanted rat kidneys: diffusion MR imaging at 7 T. Radiology 231:702–709
Eisenberger U, Thoeny HC, Binser T, et al. (2010) Evaluation of renal allograft function early after transplantation with diffusion-weighted MR imaging. Eur Radiol 20:1374–1383
Namimoto T, Yamashita Y, Mitsuzaki K, et al. (1999) Measurement of the apparent diffusion coefficient in diffuse renal disease by diffusion-weighted echo-planar MR imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 9:832–837
Ries M, Basseau F, Tyndal B, et al. (2003) Renal diffusion and BOLD MRI in experimental diabetic nephropathy. Blood oxygen level-dependent. J Magn Reson Imaging 17:104–113
Yildirim E, Kirbas I, Teksam M, et al. (2008) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of kidneys in renal artery stenosis. Eur J Radiol 65:148–153
Bozgeyik Z, Kocakoc E, Sonmezgoz F (2009) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging findings of kidneys in patients with early phase of obstruction. Eur J Radiol 70:138–141
Chan JH, Tsui EY, Luk SH, et al. (2001) MR diffusion-weighted imaging of kidney: differentiation between hydronephrosis and pyonephrosis. Clin Imaging 25:110–113
Karadeli E, Ulu EM, Yildirim E, et al. (2010) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of kidneys in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: initial experience. Rheumatol Int 30:1177–1181
Toya R, Naganawa S, Kawai H, et al. (2010) Correlation between estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values of the kidneys. Magn Reson Med Sci 9:59–64
Carbone SF, Gaggioli E, Ricci V, et al. (2007) Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of renal function: a preliminary study. Radiol Med 112(8):1201–1210
Xu Y, Wang X, Jiang X (2007) Relationship between the renal apparent diffusion coefficient and glomerular filtration rate: preliminary experience. J Magn Reson Imaging 26:678–681
Ries M, Jones RA, Basseau F, et al. (2001) Diffusion tensor MRI of the human kidney. J Magn Reson Imaging 14:42–49
Kataoka M, Kido A, Yamamoto A, et al. (2009) Diffusion tensor imaging of kidneys with respiratory triggering: optimization of parameters to demonstrate anisotropic structures on fraction anisotropy maps. J Magn Reson Imaging 29:736–744
Gurses B, Kilickesmez O, Tasdelen N, et al. (2011) Diffusion tensor imaging of the kidney at 3 Tesla: normative values and repeatability of measurements in healthy volunteers. Diagn Interv Radiol 17:317–322
Notohamiprodjo M, Dietrich O, Horger W, et al. (2010) Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) of the kidney at 3 Tesla—feasibility, protocol evaluation and comparison to 1.5 Tesla. Invest Radiol 45:245–254
Cutajar M, Clayden JD, Clark CA, Gordon I (2011) Test-retest reliability and repeatability of renal diffusion tensor MRI in healthy subjects. Eur J Radiol 80:e263–e268
Sigmund EE, Vivier PH, Sui D, et al. (2012) Intravoxel incoherent motion and diffusion-tensor imaging in renal tissue under hydration and furosemide flow challenges. Radiology 263:758–769
Cheung JS, Fan SJ, Chow AM, et al. (2010) Diffusion tensor imaging of renal ischemia reperfusion injury in an experimental model. NMR Biomed 23:496–502
Notohamiprodjo M, Glaser C, Herrmann KA, et al. (2008) Diffusion tensor imaging of the kidney with parallel imaging: initial clinical experience. Invest Radiol 43:677–685
Lu L, Sedor JR, Gulani V, et al. (2011) Use of diffusion tensor MRI to identify early changes in diabetic nephropathy. Am J Nephrol 34:476–482
National Kidney Foundation (2002) K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification, and stratification. Am J Kidney Dis 39(2 Suppl 1):S1–266
Xu X, Fang W, Ling H, et al. (2010) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of kidneys in patients with chronic kidney disease: initial study. Eur Radiol 20:978–983
Namimoto T, Yamashita Y, Mitsuzaki K, et al. (1999) Measurement of the apparent diffusion coefficient in diffuse renal disease by diffusion-weighted echo-planar MR imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 9:832–837
Hueper K, Gutberlet M, Rodt T, et al. (2011) Diffusion tensor imaging and tractography for assessment of renal allograft dysfunction-initial results. Eur Radiol 21:2427–2433
Acknowledgements
This study is supported by Guangdong Science and Technology Program Grant number 2010B080701067.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Wj., Pui, M.H., Guo, Y. et al. 3T magnetic resonance diffusion tensor imaging in chronic kidney disease. Abdom Imaging 39, 770–775 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-014-0116-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-014-0116-y