Abstract
Objectives
To evaluate MR diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) as non-invasive diagnostic tool for detection of acute and chronic allograft dysfunction and changes of organ microstructure.
Methods
15 kidney transplanted patients with allograft dysfunction and 14 healthy volunteers were examined using a fat-saturated echo-planar DTI-sequence at 1.5 T (6 diffusion directions, b = 0, 600 s/mm²). Mean apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) and mean fractional anisotropy (FA) were calculated separately for the cortex and for the medulla and compared between healthy and transplanted kidneys. Furthermore, the correlation between diffusion parameters and estimated GFR was determined.
Results
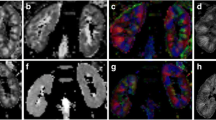
The ADC in the cortex and in the medulla were lower in transplanted than in healthy kidneys (p < 0.01). Differences were more distinct for FA, especially in the renal medulla, with a significant reduction in allografts (p < 0.001). Furthermore, in transplanted patients a correlation between mean FA in the medulla and estimated GFR was observed (r = 0.72, p < 0.01). Tractography visualized changes in renal microstructure in patients with impaired allograft function.
Conclusions
Changes in allograft function and microstructure can be detected and quantified using DTI. However, to prove the value of DTI for standard clinical application especially correlation of imaging findings and biopsy results is necessary.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schwarz A, Gwinner W, Hiss M, Radermacher J, Mengel M, Haller H (2005) Safety and adequacy of renal transplant protocol biopsies. Am J Transplant 5:1992–1996
Thoeny HC, Zumstein D, Simon-Zoula S et al (2006) Functional evaluation of transplanted kidneys with diffusion-weighted and BOLD MR imaging: initial experience. Radiology 241:812–821
Blondin D, Lanzman RS, Mathys C et al (2009) Functional MRI of transplanted kidneys using diffusion-weighted imaging. Rofo 181:1162–1167
Eisenberger U, Thoeny HC, Binser T et al (2010) Evaluation of renal allograft function early after transplantation with diffusion-weighted MR imaging. Eur Radiol 20:1374–1383. doi:10.1007/s00330-009-1679-9
Le Bihan D, Breton E, Lallemand D, Aubin ML, Vignaud J, Laval-Jeantet M (1988) Separation of diffusion and perfusion in intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging. Radiology 168:497–505
Hagmann P, Jonasson L, Maeder P, Thiran JP, Wedeen VJ, Meuli R (2006) Understanding diffusion MR imaging techniques: from scalar diffusion-weighted imaging to diffusion tensor imaging and beyond. Radiographics 26(Suppl 1):S205–23. doi:10.1148/rg.26si065510
Mukherjee P, Berman JI, Chung SW, Hess CP, Henry RG (2008) Diffusion tensor MR imaging and fiber tractography: theoretic underpinnings. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29:632–641. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A1051
Fukuda Y, Ohashi I, Hanafusa K et al (2000) Anisotropic diffusion in kidney: apparent diffusion coefficient measurements for clinical use. J Magn Reson Imaging 11:156–160
Ries M, Jones RA, Basseau F, Moonen CT, Grenier N (2001) Diffusion tensor MRI of the human kidney. J Magn Reson Imaging 14:42–49
Notohamiprodjo M, Dietrich O, Horger W et al (2010) Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) of the kidney at 3 tesla-feasibility, protocol evaluation and comparison to 1.5 tesla. Invest Radiol 45:245–254
Notohamiprodjo M, Glaser C, Herrmann KA et al (2008) Diffusion tensor imaging of the kidney with parallel imaging: initial clinical experience. Invest Radiol 43:677–685
Gurses B, Kilickesmez O, Tasdelen N, Firat Z, Gurmen N (2010) Diffusion tensor imaging of the kidney at 3 tesla: normative values and repeatability of measurements in healthy volunteers. Diagn Interv Radiol. doi:10.4261/1305-3825.DIR.3892-10.1;10.4261/1305-3825.DIR.3892-10.1
Cockcroft DW, Gault MH (1976) Prediction of creatinine clearance from serum creatinine. Nephron 16:31–41
Lanzman RS, Wittsack HJ, Martirosian P et al (2010) Quantification of renal allograft perfusion using arterial spin labeling MRI: initial results. Eur Radioll 20(6):1485–9
Mengel M, Gwinner W, Schwarz A et al (2007) Infiltrates in protocol biopsies from renal allografts. Am J Transplant 7:356–365
Seron D (2009) Interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy in renal allograft protocol biopsies as a surrogate of graft survival. Transplant Proc 41:769–770
Seron D, Moreso F (2007) Protocol biopsies in renal transplantation: prognostic value of structural monitoring. Kidney Int 72:690–697
Haller H, Richter N, Brocker V, Gwinner W, Gueler F, Schwarz A (2009) Current problems of kidney transplantation. Internist (Berl) 50:523–535
Kataoka M, Kido A, Yamamoto A et al (2009) Diffusion tensor imaging of kidneys with respiratory triggering: optimization of parameters to demonstrate anisotropic structures on fraction anisotropy maps. J Magn Reson Imaging 29:736–744
Vermathen P, Binser T, Thoeny HC, Boesch C, Frey FJ, Eisenberger U (2011) Longitudinal follow-up of kidneys from living donors to their recipients by DWI. Proc Intl Soc Magn Reson Med 19:2983
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hueper, K., Gutberlet, M., Rodt, T. et al. Diffusion tensor imaging and tractography for assessment of renal allograft dysfunction—initial results. Eur Radiol 21, 2427–2433 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-011-2189-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-011-2189-0