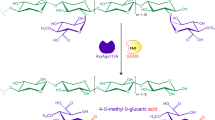
Abstract
Lignocellulosic biomass from various types of wood has become a renewable resource for production of biofuels and biobased chemicals. Because xylan is the major component of wood hemicelluloses, highly efficient enzymes to enhance xylan hydrolysis can improve the use of lignocellulosic biomass. In this study, a xylanolytic gene cluster was identified from the crude oil-degrading thermophilic strain Geobacillus thermodenitrificans NG80-2. The enzymes involved in xylan hydrolysis, which include two xylanases (XynA1, XynA2), three β-xylosidases (XynB1, XynB2, XynB3), and one α-l-arabinofuranosidase (AbfA), have many unique features, such as high pH tolerance, high thermostability, and a broad substrate range. The three β-xylosidases were highly resistant to inhibition by product (xylose) accumulation. Moreover, the combination of xylanase, β-xylosidase, and α-l-arabinofuranosidase exhibited the largest synergistic action on xylan degradation (XynA2, XynB1, and AbfA on oat spelt or beechwood xylan; XynA2, XynB3, and AbfA on birchwood xylan). We have demonstrated that the proposed enzymatic cocktail almost completely converts complex xylan to xylose and arabinofuranose and has great potential for use in the conversion of plant biomass into biofuels and biochemicals.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Rahman MA, Tashiro Y, Zendo T, Hanada K, Shibata K, Sonomoto K (2011) Efficient homofermentative L-(+)-lactic acid production from xylose by a novel lactic acid bacterium, Enterococcus mundtii QU 25. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:1892–1895. doi:10.1128/aem.02076-10
Ali MK, Rudolph FB, Bennett GN (2004) Thermostable xylanase10B from Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC824. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 31:229–234. doi:10.1007/s10295-004-0143-8
Anand A, Kumar V, Satyanarayana T (2013) Characteristics of thermostable endoxylanase and β-xylosidase of the extremely thermophilic bacterium Geobacillus thermodenitrificans TSAA1 and its applicability in generating xylooligosaccharides and xylose from agro-residues. Extremophiles 17:357–366. doi:10.1007/s00792-013-0524-x
Bajpai P (1997) Microbial xylanolytic enzyme system: properties and applications. Adv Appl Microbiol 43:141–194
Beg QK, Kapoor M, Mahajan L, Hoondal GS (2001) Microbial xylanases and their industrial applications: a review. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 56:326–338
Biely P (1993) Biochemical aspects of the production of microbial hemicellulases. In: Cougland MP, Hazlewood GP (eds) Hemicellulose and hemicellulases. Portland Press, London, pp 29–52
Bokinsky G, Peralta-Yahya PP, George A, Holmes BM, Steen EJ, Dietrich J, Soon Lee T, Tullman-Ercek D, Voigt CA, Simmons BA, Keasling JD (2011) Synthesis of three advanced biofuels from ionic liquid-pretreated switchgrass using engineered Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:19949–19954. doi:10.1073/pnas.1106958108
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Canakci S, Kacagan M, Inan K, Belduz AO, Saha BC (2008) Cloning, purification, and characterization of a thermostable α-L-arabinofuranosidase from Anoxybacillus kestanbolensis AC26Sari. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 81:61–68. doi:10.1007/s00253-008-1584-1
Chapla D, Pandit P, Shah A (2012) Production of xylooligosaccharides from corncob xylan by fungal xylanase and their utilization by probiotics. Bioresour Technol 115:215–221. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2011.10.083
Christov LP, Myburgh J, O’Neill FH, Van Tonder A, Prior BA (1999) Modification of the carbohydrate composition of sulfite pulp by purified and characterized β-xylanase and β-xylosidase of Aureobasidium pullulans. Biotechnol Prog 15:196–200. doi:10.1021/bp9900054
Cirino PC, Chin JW, Ingram LO (2006) Engineering Escherichia coli for xylitol production from glucose-xylose mixtures. Biotechnol Bioeng 95:1167–1176. doi:10.1002/bit.21082
Collins T, Gerday C, Feller G (2005) Xylanases, xylanase families and extremophilic xylanases. FEMS Microbiol Rev 29:3–23. doi:10.1016/j.femsre.2004.06.005
Dobberstein J, Emeis CC (1991) Purification and characterization of β-xylosidase from Aureobasidium pullulans. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 35:210–215. doi:10.1007/bf00184688
Emanuelsson O, Brunak S, von Heijne G, Nielsen H (2007) Locating proteins in the cell using TargetP, SignalP and related tools. Nat Protoc 2:953–971. doi:10.1038/nprot.2007.131
Feng L, Wang W, Cheng J, Ren Y, Zhao G, Gao C, Tang Y, Liu X, Han W, Peng X, Liu R, Wang L (2007) Genome and proteome of long-chain alkane degrading Geobacillus thermodenitrificans NG80-2 isolated from a deep-subsurface oil reservoir. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:5602–5607. doi:10.1073/pnas.0609650104
Gírio FM, Fonseca C, Carvalheiro F, Duarte LC, Marques S, Bogel-Łukasik R (2010) Hemicelluloses for fuel ethanol: a review. Bioresour Technol 101:4775–4800. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2010.01.088
Jiang ZQ, Yang SQ, Tan SS, Li LT, Li XT (2005) Characterization of a xylanase from the newly isolated thermophilic Thermomyces lanuginosus CAU44 and its application in bread making. Lett Appl Microbiol 41:69–76. doi:10.1111/j.1472-765X.2005.01725.x
Kambourova M, Mandeva R, Fiume I, Maurelli L, Rossi M, Morana A (2007) Hydrolysis of xylan at high temperature by co-action of the xylanase from Anoxybacillus flavithermus BC and the β-xylosidase/α-arabinosidase from Sulfolobus solfataricus Oα. J Appl Microbiol 102:1586–1593. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2672.2006.03197.x
Khasin A, Alchanati I, Shoham Y (1993) Purification and characterization of a thermostable xylanase from Bacillus stearothermophilus T-6. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:1725–1730
Klibanov AM (2001) Improving enzymes by using them in organic solvents. Nature 409:241–246. doi:10.1038/35051719
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Lama L, Calandrelli V, Gambacorta A, Nicolaus B (2004) Purification and characterization of thermostable xylanase and β-xylosidase by the thermophilic bacterium Bacillus thermantarcticus. Res Microbiol 155:283–289. doi:10.1016/j.resmic.2004.02.001
Lee RC, Hrmova M, Burton RA, Lahnstein J, Fincher GB (2003) Bifunctional family 3 glycoside hydrolases from barley with α-L-arabinofuranosidase and β-D-xylosidase activity: characterization, primary structures, and COOH-terminal processing. J Biol Chem 278:5377–5387. doi:10.1074/jbc.M210627200
Manin C, Shareek F, Morosoli R, Kluepfel D (1994) Purification and characterization of an α-L-arabinofuranosidase from Streptomyces lividans 66 and DNA sequence of the gene (abfA). Biochem J 302:443–449. doi:10.1042/bj3020443
Margolles A, de los Reyes-Gavilán CG (2003) Purification and functional characterization of a novel α-L-arabinofuranosidase from Bifidobacterium longum B667. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:5096–5103. doi:10.1128/AEM.69.9.5096-5103.2003
Matsushika A, Inoue H, Kodaki T, Sawayama S (2009) Ethanol production from xylose in engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains: current state and perspectives. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 84:37–53. doi:10.1007/s00253-009-2101-x
Mattéotti C, Haubruge E, Thonart P, Francis F, De Pauw E, Portetelle D, Vandenbol M (2011) Characterization of a new β-glucosidase/β-xylosidase from the gut microbiota of the termite (Reticulitermes santonensis). FEMS Microbiol Lett 314:147–157. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.2010.02161.x
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31:426–428. doi:10.1021/ac60147a030
Mohana S, Shah A, Divecha J, Madamwar D (2008) Xylanase production by Burkholderia sp. DMAX strain under solid state fermentation using distillery spent wash. Bioresour Technol 99:7553–7564. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2008.02.009
Morana A, Paris O, Maurelli L, Rossi M, Cannio R (2007) Gene cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of a bi-functional β-D-xylosidase/α-L-arabinosidase from Sulfolobus solfataricus involved in xylan degradation. Extremophiles 11:123–132. doi:10.1007/s00792-006-0020-7
Nanmori T, Watanabe T, Shinke R, Kohno A, Kawamura Y (1990) Purification and properties of thermostable xylanase and β-xylosidase produced by a newly isolated Bacillus stearothermophilus strain. J Bacteriol 172:6669–6672
Polizeli ML, Rizzatti AC, Monti R, Terenzi HF, Jorge JA, Amorim DS (2005) Xylanases from fungi: properties and industrial applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 67:577–591. doi:10.1007/s00253-005-1904-7
Poutanen K, Puls J (1988) Characteristics of Trichoderma reesei β-xylosidase and its use in the hydrolysis of solubilized xylans. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 28:425–432. doi:10.1007/bf00268208
Rasmussen LE, Sorensen HR, Vind J, Vikso-Nielsen A (2006) Mode of action and properties of the β-xylosidases from Talaromyces emersonii and Trichoderma reesei. Biotechnol Bioeng 94:869–876. doi:10.1002/bit.20908
Rastall RA (2010) Functional oligosaccharides: application and manufacture. Annu Rev Food Sci Technol 1:305–339. doi:10.1146/annurev.food.080708.100746
Raweesri P, Riangrungrojana P, Pinphanichakarn P (2008) α-L-Arabinofuranosidase from Streptomyces sp. PC22: purification, characterization and its synergistic action with xylanolytic enzymes in the degradation of xylan and agricultural residues. Bioresour Technol 99:8981–8986. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2008.05.016
Saha B (2003a) Hemicellulose bioconversion. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 30:279–291. doi:10.1007/s10295-003-0049-x
Saha BC (2003b) Purification and properties of an extracellular β-xylosidase from a newly isolated Fusarium proliferatum. Bioresour Technol 90:33–38. doi:10.1016/S0960-8524(03)00098-1
Sampaio FC, Chaves-Alves VM, Converti A, Lopes Passos FM, Cavalcante Coelho JL (2008) Influence of cultivation conditions on xylose-to-xylitol bioconversion by a new isolate of Debaryomyces hansenii. Bioresour Technol 99:502–508. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2007.01.017
Shallom D, Belakhov V, Solomon D, Gilead-Gropper S, Baasov T, Shoham G, Shoham Y (2002) The identification of the acid–base catalyst of α-arabinofuranosidase from Geobacillus stearothermophilus T-6, a family 51 glycoside hydrolase. FEBS Lett 514:163–167. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(02)02343-8
Shallom D, Leon M, Bravman T, Ben-David A, Zaide G, Belakhov V, Shoham G, Schomburg D, Baasov T, Shoham Y (2005) Biochemical characterization and identification of the catalytic residues of a family 43 β-D-xylosidase from Geobacillus stearothermophilus T-6. Biochemistry 44:387–397. doi:10.1021/bi048059w
Shi H, Li X, Gu H, Zhang Y, Huang Y, Wang L, Wang F (2013a) Biochemical properties of a novel thermostable and highly xylose-tolerant β-xylosidase/α-arabinosidase from Thermotoga thermarum. Biotechnol Biofuels 6:1–10. doi:10.1186/1754-6834-6-27
Shi P, Chen X, Meng K, Huang H, Bai Y, Luo H, Yang P, Yao B (2013b) Distinct actions by Paenibacillus sp. strain E18 α-L-arabinofuranosidases and xylanase in xylan degradation. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:1990–1995. doi:10.1128/aem.03276-12
Shinkawa S, Okano K, Yoshida S, Tanaka T, Ogino C, Fukuda H, Kondo A (2011) Improved homo L-lactic acid fermentation from xylose by abolishment of the phosphoketolase pathway and enhancement of the pentose phosphate pathway in genetically modified xylose-assimilating Lactococcus lactis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 91:1537–1544. doi:10.1007/s00253-011-3342-z
Shulami S, Gat O, Sonenshein AL, Shoham Y (1999) The glucuronic acid utilization gene cluster from Bacillus stearothermophilus T-6. J Bacteriol 181:3695–3704
Subramaniyan S, Prema P (2002) Biotechnology of microbial xylanases: enzymology, molecular biology, and application. Crit Rev Biotechnol 22:33–64. doi:10.1080/07388550290789450
Sullivan MJ, Petty NK, Beatson SA (2011) Easyfig: a genome comparison visualizer. Bioinformatics 27:1009–1010. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btr039
Suzuki S, Fukuoka M, Ookuchi H, Sano M, Ozeki K, Nagayoshi E, Takii Y, Matsushita M, Tada S, Kusumoto K-I, Kashiwagi Y (2010) Characterization of Aspergillus oryzae glycoside hydrolase family 43 β-xylosidase expressed in Escherichia coli. J Biosci Bioeng 109:115–117. doi:10.1016/j.jbiosc.2009.07.018
Tulchin N, Ornstein L, Davis BJ (1976) A microgel system for disc electrophoresis. Anal Biochem 72:485–490
Tuncer M, Ball AS (2003) Co-operative actions and degradation analysis of purified xylan-degrading enzymes from Thermomonospora fusca BD25 on oat-spelt xylan. J Appl Microbiol 94:1030–1035. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2672.2003.01943.x
Van Dyk JS, Pletschke BI (2012) A review of lignocellulose bioconversion using enzymatic hydrolysis and synergistic cooperation between enzymes—factors affecting enzymes, conversion and synergy. Biotechnol Adv 30:1458–1480. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2012.03.002
Vázquez MJ, Alonso JL, Domínguez H, Parajó JC (2000) Xylooligosaccharides: manufacture and applications. Trends Food Sci Technol 11:387–393. doi:10.1016/S0924-2244(01)00031-0
Waino M, Ingvorsen K (2003) Production of β-xylanase and β-xylosidase by the extremely halophilic archaeon Halorhabdus utahensis. Extremophiles 7:87–93. doi:10.1007/s00792-002-0299-y
Wang L, Tang Y, Wang S, Liu RL, Liu MZ, Zhang Y, Liang FL, Feng L (2006) Isolation and characterization of a novel thermophilic Bacillus strain degrading long-chain n-alkanes. Extremophiles 10:347–356. doi:10.1007/s00792-006-0505-4
Yan QJ, Wang L, Jiang ZQ, Yang SQ, Zhu HF, Li LT (2008) A xylose-tolerant β-xylosidase from Paecilomyces thermophila: characterization and its co-action with the endogenous xylanase. Bioresour Technol 99:5402–5410. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2007.11.033
Yang X, Shi P, Huang H, Luo H, Wang Y, Zhang W, Yao B (2014) Two xylose-tolerant GH43 bifunctional β-xylosidase/α-arabinosidases and one GH11 xylanase from Humicola insolens and their synergy in the degradation of xylan. Food Chem 148:381–387. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.10.062
Yang W, Bai Y, Yang P, Luo H, Huang H, Meng K, Shi P, Wang Y, Yao B (2015) A novel bifunctional GH51 exo-α-L-arabinofuranosidase/endo-xylanase from Alicyclobacillus sp. A4 with significant biomass-degrading capacity. Biotechnol Biofuels 8:1–11. doi:10.1186/s13068-015-0366-0
Zha J, Shen M, Hu M, Song H, Yuan Y (2014) Enhanced expression of genes involved in initial xylose metabolism and the oxidative pentose phosphate pathway in the improved xylose-utilizing Saccharomyces cerevisiae through evolutionary engineering. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 41:27–39. doi:10.1007/s10295-013-1350-y
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program) (Nos. 2013CB733904, 2012CB721001, and 2012CB721101), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 31270133, 31470194, 31371259, 81471904, 31270003 and 31400081), the Tianjin Research Program of Application Foundation and Advanced Technology (15JCQNJC09700) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 65141028).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 267 kb).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, D., Liu, J., Qi, Y. et al. Synergistic hydrolysis of xylan using novel xylanases, β-xylosidases, and an α-l-arabinofuranosidase from Geobacillus thermodenitrificans NG80-2. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101, 6023–6037 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8341-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8341-2