Abstract
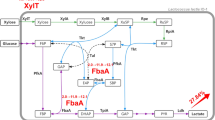
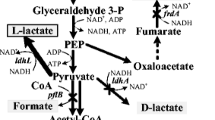
In order to achieve efficient homo L-lactic acid fermentation from xylose, we first carried out addition of xylose assimilation ability to Lactococcus lactis IL 1403 by introducing a plasmid carrying the xylRAB genes from L. lactis IO-1 (pXylRAB). Then modification of xylose assimilation pathway was carried out. L. lactis has two pathways for xylose assimilation called the phosphoketolase pathway (PK pathway) that produces both lactic acid and acetic acid and the pentose phosphate pathway (PP pathway) that produces only lactic acid as a final product. Thus a mutant strain that disrupted its phosphokeolase gene (ptk) was constructed. The Δptk mutant harboring pXylRAB lacked the PK pathway and produced predominantly lactic acid from xylose via the PP pathway, although its fermentation rate slightly decreased. Further introduction of the transketolase gene (tkt) to disrupted ptk locus led restoration of fermentation rate and this was attributed to enhancement of the PP pathway. As a result, ptk::tkt strain harboring pXylRAB produced 50.1 g/l of L-lactic acid from xylose with a high optical purity of 99.6% and a high yield of 1.58 (moles per mole xylose consumed) that is close to theoretical value of 1.67 from xylose.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Biswas I, Gruss A, Ehrlich SD, Maguin E (1993) High-efficiency gene inactivation and replacement system for gram-positive bacteria. J Bacteriol 175:3628–3635
Bolotin A, Wincker P, Mauger S, Jaillon O, Malarme K, Weissenbach J, Ehrlich SD, Sorokin A (2001) The complete genome sequence of the lactic acid bacterium Lactococcus lactis ssp. lactis IL 1403. Genome Res 11:731–753
Bustos G, Moldes AB, Cruz JM, Domínguez JM (2005) Influence of the metabolism pathway on lactic acid production from hemicellulosic trimming vine shoots hydrolyzates using Lactobacillus pentosus. Biotechnol Prog 21:793–798
Chaillou S, Bor YC, Batt CA, Postma PW, Pouwels PH (1998) Molecular cloning and functional expression in Lactobacillus plantarum 80 of xylT, encoding the D-xylose-H+ symporter of Lactobacillus brevis. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:4720–4728
Erlandson KA, Park JH, Wissam EK, Kao HH, Basaran P, Brydges S, Batt CA (2000) Dissolution of xylose metabolism in Lactococcus lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:3974–3980
Helanto M, Kiviharju K, Leisola M, Nyyssölä A (2007) Metabolic engineering of Lactobacillus plantarum for production of L-ribulose. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:7083–7091
Holo H, Nes IF (1989) High-frequency transformation, by electroporation, of Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris grown with glycine in osmotically stabilized media. Appl Environ Microbiol 55:3119–3123
Ikada Y, Jamshidi K, Tsuji H, Hyon SH (1987) Stereocomplex formation between enantiomeric poly (lactides). Macromolecules 20:904–906
Ishizaki A, Osajima K, Nakamura K, Kimura K, Hara T, Ezaki T (1990) Biochemical characterization of Lactococcus latis IO-1 whose optimal temperature is as high as 37C. J Gen Appl Microbiol 36:1–6
Lokman BC, Heerikhuisen M, Leer RJ, van den Broek A, Borsboom Y, Chaillou S, Postma PW, Pouwels PH (1997) Regulation of expression of the Lactobacillus pentosus xylAB operon. J Bacteriol 179:5391–5397
Maguin E, Prévost H, Ehrlich SD, Gruss A (1996) Efficient insertional mutagenesis in Lactococci and other gram-positive bacteria. J Bacteriol 178:931–935
Mora D, Maguin E, Masiero M, Parini C, Ricci G, Manachini PL, Daffonchio D (2004) Characterization of urease genes cluster of Streptococcus thermophilus. J Appl Microbiol 96:209–219
Narita J, Okano K, Kitao T, Ishida S, Sewaki T, Sung MH, Fukuda H, Kondo A (2006) Display of α-amylase on the surface of Lactobacillus casei cells by use of the PgsA anchor protein, and production of lactic acid from starch. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:269–275
Ohara H, Owaki M, Sonomoto K (2006) Xylooligosaccharide fermentation with Leuconostoc lactis. J Biosci Bioeng 101:415–420
Ohara H, Owaki M, Sonomoto K (2007) Calculation of metabolic flow of xylose in Lactococcus lactis. J Biosci Bioeng 103:92–94
Okano K, Kimura S, Narita J, Fukuda H, Kondo A (2007) Improvement in lactic acid production from starch using α-amylase-secreting Lactococcus lactis cells adapted to maltose or starch. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 75:1007–1013
Okano K, Yoshida S, Tanaka T, Ogino C, Fukuda H, Kondo A (2009a) Homo-D-lactic acid fermentation from arabinose by redirection of the phosphoketolase pathway to the pentose phosphate pathway in L-lactate dehydrogenase gene-deficient Lactobacillus plantarum. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:5175–5178
Okano K, Yoshida S, Yamada R, Tanaka T, Ogino C, Fukuda H, Kondo A (2009b) Improved production of homo-D-lactic acid via xylose fermentation by introduction of xylose assimilation genes and redirection of the phosphoketolase pathway to the pentose phosphate pathway in L-lactate dehydrogenase gene-deficient Lactobacillus plantarum. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:7858–7861
Okano K, Zhang Q, Shinkawa S, Yoshida S, Tanaka T, Fukuda H, Kondo A (2009c) Efficient production of optically pure D-lactic acid from raw corn starch by using genetically modified L-lactate dehydrogenase gene-deficient and α-amylase-secreting Lactobacillus plantarum strain. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:462–467
Park JH, Batt CA (2004) Restoration of a defective Lactococcus lactis xylose isomerase. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:4318–4325
Posthuma CC, Bader R, Engelmann R, Postma PW, Hengstenberg W, Pouwelsv PH (2002) Expression of the xylulose 5-phosphate phosphoketolase gene, xpkA, from Lactobacillus pentosus MD363 is induced by sugars that are fermented via the phosphoketolase pathway and is repressed by glucose mediated by CcpA and the mannose phosphoenolpyruvate phosphotransferase system. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:831–837
Satoh E, Ito Y, Sasaki Y, Sasaki T (1997) Application of the extracellular α-amylase gene from Streptococcus bovis 148 to construction of a secretion vector for yogurt starter strains. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:4593–4596
Tanaka K, Komiyama A, Sonomoto K, Ishizaki A, Hall SJ, Stanbury PF (2002) Two different pathways for D-xylose metabolism and the effect of xylose concentration on the yield coefficient of L-lactate in mixed-acid fermentation by the lactic acid bacterium Lactococcus lactis IO-1. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 60:160–167
Yasui K, Kano Y, Tanaka K, Watanabe K, Shimizu-Kadota M, Yoshikawa H, Suzuki T (2009) Improvement of bacterial transformation efficiency using plasmid artificial modification. Nucleic Acids Res 37:e3
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Dr. Emmanuelle Maguin for supplying the E. coli VE7108 and VE6838 (VE7108 containing pG+host9 plasmid) strains and to Meiji Dairies Corporation for supplying the pSECE1 plasmid. We are grateful to Dr. Eiichi Satoh for supplying the L. lactis IL1403 wild type strain. This work was supported in part by a Special Coordination Funds for Promoting Science and Technology, Creation of Innovation Centers for Advanced Interdisciplinary Research Areas (Innovative Bioproduction Kobe), MEXT, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shinkawa, S., Okano, K., Yoshida, S. et al. Improved homo l-lactic acid fermentation from xylose by abolishment of the phosphoketolase pathway and enhancement of the pentose phosphate pathway in genetically modified xylose-assimilating Lactococcus lactis . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 91, 1537–1544 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3342-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3342-z