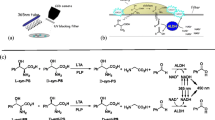
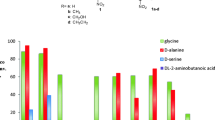
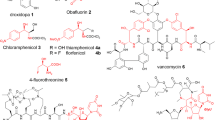
Abstract
Threonine aldolases (TAs) constitute a powerful tool for catalyzing carbon–carbon bond formations in synthetic organic chemistry, thus enabling an enantio- and diastereoselective synthesis of β-hydroxy-α-amino acids. Starting from the achiral precursors glycine and an aldehyde, two new stereogenic centres are formed in this catalytic step. The resulting chiral β-hydroxy-α-amino acid products are important precursors for pharmaceuticals such as thiamphenicol, a l-threo-phenylserine derivative or l-threo-3,4-dihydroxyphenylserine. TAs are pyridoxal-5-phosphate-dependent enzymes, which, in nature, catalyze the cleavage of l-threonine or l-allo-threonine to glycine and acetaldehyde in a glycine biosynthetic pathway. TAs from a broad number of species of bacteria and fungi have been isolated and characterised as biocatalysts for the synthesis of β-hydroxy-α-amino acids. In this review, screening methods to obtain novel TAs, their biological function, biochemical characterisation and preparative biotransformations with TAs are described.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alonso M, Riera A (2005) Improved preparation of β-hydroxy-alpha-amino acids: direct formation of sulfates by sulfuryl chloride. Tetrahedron Asymmetr 16:3908–3912
Aoyama Y, Motokawa Y (1981) L-Threonine dehydrogenase of chicken liver. Purification, characterization, and physiological significance. J Biol Chem 256:12367–12373
Baik SH, Yoshioka H (2009) Enhanced synthesis of l-threo-3,4-dihydroxyphenylserine by high-density whole-cell biocatalyst of recombinant l-threonine aldolase from Streptomyces avelmitilis. Biotechnol Lett 31:443–448
Baik SH, Yoshioka H, Yukawa H, Harayama S (2007) Synthesis of L-threo-3,4-dihydroxyphenylserine (L-threo-DOPS) with thermostabilized low-specific L-threonine aldolase from Streptomyces coelicolor A3. J Microbiol Biotechnol 17:721–727
Berkessel A, Gröger H (2005) Asymmetric organocatalysis. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, p 159
Blank S, Seebach D (1993) Preparation of (R,R)-2-amino-3-hydroxycarboxylic or (S,S)-2-amino-3-hydroxycarboxylic acids (allo-threonine analogs) by acylation reduction of t-butyl 2-t-butyl-3-methyl-4-oxoimidazolidine-1-carboxylate (Boc-Bmi). Liebigs Annalen Der Chemie 8:889–896
Contestabile R, Paiardini A, Pascarella S, di Salvo ML, D'Aguanno S, Bossa F (2001) L-Threonine aldolase, serine hydroxymethyltransferase and fungal alanine racemase—a subgroup of strictly related enzymes specialized for different functions. Eur J Biochem 268:6508–6525
Coppi L, Giordano C, Longoni A, Panossian S (1997) Thiamphenicol: a manufacturing process involving a double inversion of stereochemistry. In: Collins AN, Sheldrake GN, Crosby J (eds) Chirality in industry, vol 2, 2nd edn. Wiley, Chichester, pp 353–362
Dale RA (1978) Catabolism of threonine in mammals by coupling of L-threonine 3-dehydrogenase with 2-amino-3-oxobutyrate-CoA ligase. Biochim Biophys Acta 544:496–503
Dietz FR, Gröger H (2009) Asymmetric synthesis of all stereoisomers of α-methylthreonine using an organocatalytic Steglich rearrangement reaction as a key step. Synthesis-Stuttg 24:4208–4218
Edgar AJ (2002) Molecular cloning and tissue distribution of mammalian L-threonine 3-dehydrogenases. BMC Biochem 3:19
Edgar AJ (2005) Mice have a transcribed L-threonine aldolase/GLY1 gene, but the human GLY1 gene is a non-processed pseudogene. BMC Genomics 6:32. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-1186-1132
Eisenstein E (1995) Allosteric regulation of biosynthetic threonine deaminase from Escherichia coli: effects of isoleucine and valine on active-site ligand binding and catalysis. Arch Biochem Biophys 316:311–318
Fesko K, Giger L, Hilvert D (2008a) Synthesis of β-hydroxy-α-amino acids with a reengineered alanine racemase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 18:5987–5990
Fesko K, Reisinger C, Steinreiber J, Weber H, Schurmann M, Griengl H (2008b) Four types of threonine aldolases: similarities and differences in kinetics/thermodynamics. J Mol Catal B Enzym 52–3:19–26
Fesko K, Uhl M, Steinreiber J, Gruber K, Griengl H (2010) Biocatalytic access to α, α-dialkyl-alpha-amino acids by a mechanism-based approach. Angew Chem Int Ed 49:121–124
Fujii M, Miura T, Kajimoto T, Ida Y (2000) Facile synthesis of 3,4-dihydroxyprolines as an application of the L-threonine aldolase-catalyzed aldol reaction. Synlett 2000:1046–1048
Garbaccio RM, Wolkenberg SE (2006) Science of synthesis, vol 20b. Georg Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart, pp 1131–1202
Gasparski CM, Miller MJ (1991) Synthesis of β-hydroxy-α-amino acids by aldol condensation using a chiral phase-transfer catalyst. Tetrahedron 47:5367–5378
Gijsen H, Qiao L, Fitz W, Wong C-H (1996) Recent advances in the chemoenzymatic synthesis of carbohydrates and carbohydrate mimetics. Chem Rev 96:443–474
Gutierrez LM, Garrabou X, Agosta E, Servi S, Parella T, Joglar J, Clapés P (2008) Serine hydroxymethyl transferase from Streptococcus thermophilus and 2'-L-threonine aldolase from Escherichia coli as stereocomplementary biocatalysts for the synthesis of β-hydroxy-α, ω-diamino acid derivatives. Chem Eur J 14:4647–4656
Gwon H-J, Baik S-H (2010) Diastereoselective synthesis of l-threo-3, 4-dihydroxyphenylserine by low-specific l-threonine aldolase mutants. Biotechnol Lett 32:143–149
Herbert RB, Wilkinson B (1994) Preparation of (2R,3S)-β-hydroxy-α-amino acids by use of a novel Streptomyces aldolase as a resolving agent for racemic material. Can J Chem 72:114–117
Herbert RB, Wilkinson B, Ellames GJ, Kunec EK (1993) Stereospecific lysis of a range of β-hydroxy-α-amino acids catalyzed by a novel aldolase from Streptomyces amakusaensis. Chem Soc Chem Commun 1993:205–206
Horikawa M, Busch-Petersen J, Corey EJ (1999) Enantioselective synthesis of β-hydroxy-α-amino acid esters by aldol coupling using a chiral quaternary ammonium salt as catalyst. Tetrahedron Lett 40:3843–3846
Kataoka M, Ikemi M, Morikawa T, Miyoshi T, Nishi K, Wada M, Yamada H, Shimizu S (1997) Isolation and characterization of D-threonine aldolase, a pyridoxal-5'-phosphate-dependent enzyme from Arthrobacter sp. DK-38. Eur J Biochem 248:385–393
Kielkopf CL, Burley SK (2002) X-ray structures of threonine aldolase complexes: structural basis of substrate recognition. Biochemistry 41:11711–11720
Kimura T, Vassilev VP, Shen GJ, Wong CH (1997) Enzymatic synthesis of β-hydroxy-α-amino acids based on recombinant D- and L-threonine aldolases. J Am Chem Soc 119:11734–11742
Kumagai H, Yoshida H, Yamada H, Nagate T (1972) Threonine aldolase from Candida humicola 2. Purification, crystallization and properties. Biochim Biophys Acta 258:779–790
Kuroda S, Nozaki H, Watanabe K, Yokozeki K, Imabayashi Y (2008) Producing L-serine derivative e.g. α-methyl-L-serine which is useful as pharmaceutical intermediate, involves reacting L-alpha-amino acid with aldehyde, in presence of specific enzyme derived from Ralstonia genus. In: Pat Appl EP 1882737A1. Ajinomoto Co Inc.
Lee SJ, Kang HY, Lee Y (2003) High-throughput screening methods for selecting L-threonine aldolases with improved activity. J Mol Catal B Enzym 26:265–272
Liu JQ, Dairi T, Kataoka M, Shimizu S, Yamada H (1997) L-allo-threonine aldolase from Aeromonas jandaei DK-39: gene cloning, nucleotide sequencing, and identification of the pyridoxal 5'-phosphate-binding lysine residue by site-directed mutagenesis. J Bacteriol 179:3555–3560
Liu JQ, Ito S, Dairi T, Itoh N, Shimizu S, Yamada H (1998) Low-specificity L-threonine aldolase of Pseudomonas sp. NCIMB 10558: purification, characterization and its application to beta-hydroxy-alpha-amino acid synthesis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 49:702–708
Liu JQ, Dairi T, Itoh N, Kataoka M, Shimizu S, Yamada H (1998a) Gene cloning, biochemical characterization and physiological role of a thermostable low-specificity L-threonine aldolase from Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem 255:220–226
Liu JQ, Dairi T, Itoh N, Kataoka M, Shimizu S, Yamada H (1998b) A novel metal-activated pyridoxal enzyme with a unique primary structure, low specificity D-threonine aldolase from Arthrobacter sp. strain DK-38—molecular cloning and cofactor characterization. J Biol Chem 273:16678–16685
Liu JQ, Ito S, Dairi T, Itoh N, Kataoka M, Shimizu S, Yamada H (1998c) Gene cloning, nucleotide sequencing, and purification and characterization of the low-specificity L-threonine aldolase from Pseudomonas sp. strain NCIMB 10558. Appl Environm Microbiol 64:549–554
Liu JQ, Odani M, Dairi T, Itoh N, Shimizu S, Yamada H (1999) A new route to L-threo-3-[4-(methylthio)phenylserine], a key intermediate for the synthesis of antibiotics: recombinant low-specificity D-threonine aldolase-catalyzed stereospecific resolution. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 51:586–591
Liu JQ, Dairi T, Itoh N, Kataoka M, Shimizu S, Yamada H (2000a) Diversity of microbial threonine aldolases and their application. J Mol Catal B Enzym 10:107–115
Liu JQ, Odani M, Yasuoka T, Dairi T, Itoh N, Kataoka M, Shimizu S, Yamada H (2000b) Gene cloning and overproduction of low-specificity D-threonine aldolase from Alcaligenes xylosoxidans and its application for production of a key intermediate for parkinsonism drug. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 54:44–51
Makart S, Bechtold M, Panke S (2007) Towards preparative asymmetric synthesis of β-hydroxy-α-amino acids: L-allo-threonine formation from glycine and acetaldehyde using recombinant GlyA. J Biotechnol 130:402–410
Misono H, Maeda H, Tuda K, Ueshima S, Miyazaki N, Nagata S (2005) Characterization of an inducible phenylserine aldolase from Pseudomonas putida 24-1. Appl Environm Microbiol 71:4602–4609
Miura T, Fujii M, Shingu K, Koshimizu I, Naganoma J, Kajimoto T, Ida Y (1998) Application of L-threonine aldolase-catalyzed reaction for the preparation of a peptidic mimetic of RNA: a leading compound of Vero-toxin inhibitors. Tetrahedron Lett 39:7313–7316
Moon SH, Ohfune Y (1994) Efficient syntheses of the 4 enantiomers and diastereomers of α-methylthreonine and both enantiomers of α-methylserine. J Am Chem Soc 116:7405–7406
Nishiyama T, Mohile SS, Kajimoto T, Node M (2007) Synthesis of thymine polyoxin C by using L-threonine aldolase-catalyzed aldol reaction. Heterocycles 71:1397–1405
Nishiyama T, Kajimoto T, Mohile SS, Hayama N, Otsuda T, Ozeki M, Node M (2009) The first enantioselective synthesis of imino-deoxydigitoxose and protected imino-digitoxose by using L-threonine aldolase-catalyzed aldol condensation. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 30:230–234
Nozaki H, Kuroda S, Watanabe K, Yokozeki K (2008) Gene cloning of α-methylserine aldolase from Variovorax paradoxus and purification and characterization of the recombinant enzyme. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 72:2580–2588
Nozaki H, Kuroda S, Watanabe K, Yokozeki K (2009) Gene cloning, purification, and characterization of α-methylserine aldolase from Bosea sp AJ110407 and its applicability for the enzymatic synthesis of α-methyl-L-serine and α-ethyl-L-serine. J Mol Catal B Enzym 59:237–242
Ogawa H, Gomi T, Fujioka M (2000) Serine hydroxymethyltransferase and threonine aldolase: are they identical? Int J Biochem Cell Biol 32:289–301
Ooi T, Taniguchi M, Kameda M, Maruoka K (2002) Direct asymmetric aldol reactions of glycine Schiff base with aldehydes catalyzed by chiral quaternary ammonium salts. Angew Chem Int Ed 41:4542–4544
Riario-Sforza G, Pagani R, Marinello E (1969) Threonine aldolase and allothreonine aldolase in rat liver. Eur J Biochem 8:88–92
Sagui F, Conti P, Roda G, Contestabile R, Riva S (2008) Enzymatic synthesis of ω-carboxy-β-hydroxy-(L)-α-amino acids. Tetrahedron 64:5079–5084
Samach A, Hareven D, Gutfinger T, Ken-Dror S, Lifschitz E (1991) Biosynthetic threonine deaminase gene of tomato: isolation, structure, and upregulation in floral organs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:2678–2682
Schirch L (1982) Serine hydroxymethyltransferase. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol 53:83–112
Schirch LV, Gross T (1968) Serine transhydroxymethylase. J Biol Chem 243:5651–5655
Schöllkopf U, Hartwig W, Groth U (1980) Asymmetric syntheses via heterocyclic intermediates. 3. Enantioselective synthesis of α-methylserines. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 19:212–213
Seebeck FP, Hilvert D (2003) Conversion of a PLP-dependent racemase into an aldolase by a single active site mutation. J Am Chem Soc 125:10158–10159
Shao H, Rueter JK, Goodman M (1998) Novel enantioselective synthesis of α-methylthreonines and α, β-dimethylcysteines. J Org Chem 63:5240–5244
Steinreiber J, Fesko K, Mayer C, Reisinger C, Schürmann M, Griengl H (2007a) Synthesis of γ-halogenated and long-chain β-hydroxy-α-amino acids and 2-amino-1,3-diols using threonine aldolases. Tetrahedron 63:8088–8093
Steinreiber J, Fesko K, Reisinger C, Schürmann M, van Assema F, Wolberg M, Mink D, Griengl H (2007b) Threonine aldolases—an emerging tool for organic synthesis. Tetrahedron 63:918–926
Steinreiber J, Schürmann M, van Assema F, Wolberg M, Fesko K, Reisinger C, Mink D, Griengl H (2007c) Synthesis of aromatic 1, 2-amino alcohols utilizing a bienzymatic dynamic kinetic asymmetric transformation. Adv Synth Catal 349:1379–1386
Steinreiber J, Schürmann M, Wolberg M, van Assema F, Reisinger C, Tesko K, Mink D, Griengl H (2007d) Overcoming thermodynamic and kinetic limitations of aldolase-catalyzed reactions by applying multienzymatic dynamic kinetic asymmetric transformations. Angew Chem Int Ed 46:1624–1626
Stocklein W, Schmidt HL (1985) Evidence for L-threonine cleavage and allo-threonine formation by different enzymes from Clostridium pasteurianum—threonine aldolase and serine hydroxymethyltransferase. Biochem J 232:621–622
Tanaka T, Ozawa M, Miura T, Inazu T, Tsuji S, Kajimoto T (2002) Synthesis of novel mimetics of CMP-sialic acid as the inhibitors of sialyltransferases. Synlett 9:1487–1490
Tanaka T, Tsuda C, Miura T, Inazu T, Tsuji S, Nishihara S, Hisamatsu M, Kajimoto T (2004) Design and synthesis of peptide mimetics of GDP-fucose: targeting inhibitors of fucosyltransferases. Synlett 2:243–246
Vassilev VP, Uchiyama T, Kajimoto T, Wong CH (1995) L-Threonine aldolase in organic synthesis—preparation of novel β-hydroxy-α-amino acids. Tetrahedron Lett 36:4081–4084
Vidal L, Calveras J, Clapes P, Ferrer P, Caminal G (2005) Recombinant production of serine hydroxymethyl transferase from Streptococcus thermophilus and its preliminary evaluation as a biocatalyst. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 68:489–497
Wada M, Sakamoto M, Kataoka M, Liu JQ, Yamada H, Shimizu S (1998) Distribution of threonine aldolase activity with different stereospecificities in aerobic bacteria. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 62:1586–1588
Yamada H, Kumagai H, Nagate T, Yoshida H (1971) Formation of threonine aldolase by bacteria and yeasts. Agric Biol Chem 35:1340–1345
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dückers, N., Baer, K., Simon, S. et al. Threonine aldolases—screening, properties and applications in the synthesis of non-proteinogenic β-hydroxy-α-amino acids. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 88, 409–424 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2751-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2751-8