Abstract
Purpose
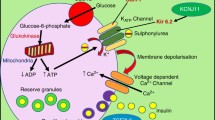
Sulphonylureas (SU) are widely used in the management of type 2 diabetes. We investigated the influence of CYP2C9, KCNJ11 and ABCC8 polymorphisms on the response to SU currently used in everyday clinical practice.
Methods
Patients treated for type 2 diabetes with sulphonylurea in monotherapy (n = 21) or in combination with metformin (n = 135) were provided with glucose-monitoring devices and instructed to measure fasting blood glucose levels once per week and additionally at any signs and symptoms suggesting low blood glucose for a period of three months. All patients were genotyped for CYP2C9 rs1799853 and rs1057910 (*2 and *3 allele, respectively), KCNJ11 rs5219 and rs5215, and ABCC8 rs757110.
Results
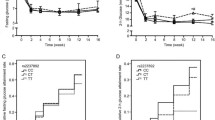
The average duration of diabetes in the study group was 10.6 ± 7.1 years. Most of the patients achieved relatively good blood glucose control (HbA1c 7.0 ± 0.9). In total, 76 hypoglycemia events were observed (mean 0.48 ± 1.3). No severe hypoglycemia was reported; the lowest blood glucose was 2.1 mmol/l. Although 124 (79.5 %) patients never experienced hypoglycemia, 32 (20.5 %) patients experienced from one to eight events. None of the investigated polymorphisms influenced HbA1c levels or risk for hypoglycemia episodes in the whole group of patients. CYP2C9 genotype significantly influenced the occurrence of hypoglycemia events among the elderly patients (aged 60 years and over; n = 103). Among them, carriers of two wild-type alleles suffered 0.36 ± 0.98 events, while patients with one or two polymorphic alleles had 0.79 ± 1.7 or 2.67 ± 4.6 events, respectively (p = 0.014).
Conclusions
Our results indicate that the CYP2C9 genotype may influence the risk for hypoglycemia events in elderly patients, but not in the overall population of type 2 diabetes patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belsey J, Krishnarajah G (2008) Glycaemic control and adverse events in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with metformin + sulphonylurea: a meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes Metab 10(Suppl 1):1–7
Best JD, Drury PL, Davis TM, Taskinen MR, Kesaniemi YA, Scott R, Pardy C, Voysey M, Keech AC (2012) Glycemic control over 5 years in 4,900 people with type 2 diabetes: real-world diabetes therapy in a clinical trial cohort. Diabetes Care 35(5):1165–1170
Drury PL, Cundy T (2012) Glycemic management of type 2 diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 367(2):182
Schernthaner G, Grimaldi A, Di Mario U, Drzewoski J, Kempler P, Kvapil M, Novials A, Rottiers R, Rutten GE, Shaw KM (2004) GUIDE study: double-blind comparison of once-daily gliclazide MR and glimepiride in type 2 diabetic patients. Eur J Clin Invest 34(8):535–542
Aquilante CL (2010) Sulfonylurea pharmacogenomics in Type 2 diabetes: the influence of drug target and diabetes risk polymorphisms. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther 8(3):359–372
Niemi M, Cascorbi I, Timm R, Kroemer HK, Neuvonen PJ, Kivisto KT (2002) Glyburide and glimepiride pharmacokinetics in subjects with different CYP2C9 genotypes. Clin Pharmacol Ther 72(3):326–332
Yoo HD, Kim MS, Cho HY, Lee YB (2011) Population pharmacokinetic analysis of glimepiride with CYP2C9 genetic polymorphism in healthy Korean subjects. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 67(9):889–898
Holstein A, Hahn M, Patzer O, Seeringer A, Kovacs P, Stingl J (2011) Impact of clinical factors and CYP2C9 variants for the risk of severe sulfonylurea-induced hypoglycemia. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 67(5):471–476
Holstein A, Hammer C, Hahn M, Kulamadayil NS, Kovacs P (2010) Severe sulfonylurea-induced hypoglycemia: a problem of uncritical prescription and deficiencies of diabetes care in geriatric patients. Expert Opin Drug Saf 9(5):675–681
Holstein A, Plaschke A, Ptak M, Egberts EH, El-Din J, Brockmoller J, Kirchheiner J (2005) Association between CYP2C9 slow metabolizer genotypes and severe hypoglycemia on medication with sulphonylurea hypoglycemic agents. Br J Clin Pharmacol 60(1):103–106
Becker ML, Visser LE, Trienekens PH, Hofman A, van Schaik RH, Stricker BH (2008) Cytochrome P450 2C9 *2 and *3 polymorphisms and the dose and effect of sulfonylurea in type II diabetes mellitus. Clin Pharmacol Ther 83(2):288–292
Gokalp O, Gunes A, Cam H, Cure E, Aydin O, Tamer MN, Scordo MG, Dahl ML (2011) Mild hypoglycemic attacks induced by sulphonylureas related to CYP2C9, CYP2C19 and CYP2C8 polymorphisms in routine clinical setting. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 67(12):1223–1229
Surendiran A, Pradhan SC, Agrawal A, Subrahmanyam DK, Rajan S, Anichavezhi D, Adithan C (2011) Influence of CYP2C9 gene polymorphisms on response to glibenclamide in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 67(8):797–801
Zhou K, Donnelly L, Burch L, Tavendale R, Doney AS, Leese G, Hattersley AT, McCarthy MI, Morris AD, Lang CC, Palmer CN, Pearson ER (2010) Loss-of-function CYP2C9 variants improve therapeutic response to sulfonylureas in type 2 diabetes: a Go-DARTS study. Clin Pharmacol Ther 87(1):52–56
Shao H, Ren XM, Liu NF, Chen GM, Li WL, Zhai ZH, Wang DW (2010) Influence of CYP2C9 and CYP2C19 genetic polymorphisms on pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of gliclazide in healthy Chinese Han volunteers. J Clin Pharm Ther 35(3):351–360
Tan B, Zhang YF, Chen XY, Zhao XH, Li GX, Zhong DF (2010) The effects of CYP2C9 and CYP2C19 genetic polymorphisms on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of glipizide in Chinese subjects. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 66(2):145–151
Zhang Y, Si D, Chen X, Lin N, Guo Y, Zhou H, Zhong D (2007) Influence of CYP2C9 and CYP2C19 genetic polymorphisms on pharmacokinetics of gliclazide MR in Chinese subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol 64(1):67–74
Suzuki K, Yanagawa T, Shibasaki T, Kaniwa N, Hasegawa R, Tohkin M (2006) Effect of CYP2C9 genetic polymorphisms on the efficacy and pharmacokinetics of glimepiride in subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 72(2):148–154
Gong B, Yu J, Li H, Li W, Tong X (2012) The effect of KCNJ11 polymorphism on the risk of type 2 diabetes: a global meta-analysis based on 49 case–control studies. DNA Cell Biol 31(5):801–81020
Qin LJ, Lv Y, Huang QY (2013) Meta-analysis of association of common variants in the KCNJ11-ABCC8 region with type 2 diabetes. Genet Mol Res 12(3):2990–3002
van Dam RM, Hoebee B, Seidell JC, Schaap MM, de Bruin TW, Feskens EJ (2005) Common variants in the ATP-sensitive K+ channel genes KCNJ11 (Kir6.2) and ABCC8 (SUR1) in relation to glucose intolerance: population-based studies and meta-analyses. Diabet Med 22(5):590–598
Javorsky M, Klimcakova L, Schroner Z, Zidzik J, Babjakova E, Fabianova M, Kozarova M, Tkacova R, Salagovic J, Tkac I (2012) KCNJ11 gene E23K variant and therapeutic response to sulfonylureas. Eur J Intern Med 23(3):245–249
Holstein A, Hahn M, Stumvoll M, Kovacs P (2009) The E23K variant of KCNJ11 and the risk for severe sulfonylurea-induced hypoglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes. Horm Metab Res 41(5):387–390
Ragia G, Tavridou A, Petridis I, Manolopoulos VG (2012) Association of KCNJ11 E23K gene polymorphism with hypoglycemia in sulfonylurea-treated type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 98(1):119–124
American Diabetes Association Workgroup on Hypoglycemia (2005) Defining and reporting hypoglycemia in diabetes. Diabetes Care 28(5):1245–1249
Seaquist ER, Anderson J, Childs B, Cryer P, Dagogo-Jack S, Fish L, Heller SR, Rodriguez H, Rosenzweig J, Vigersky R (2013) Hypoglycemia and diabetes: a report of a workgroup of the American Diabetes Association and the Endocrine Society. Diabetes Care 36(5):1384–1395
Herman D, Dolzan V, Breskvar K (2003) Genetic polymorphism of cytochromes P450 2C9 and 2C19 in Slovenian population (Genetski polimorfizem citokromov P450 2C9 in 2C19 v slovenski populaciji). Zdravniški vestnik - J Slovene Med Soc 72(6):347–351
Herman D, Locatelli I, Grabnar I, Peternel P, Stegnar M, Mrhar A, Breskvar K, Dolzan V (2005) Influence of CYP2C9 polymorphisms, demographic factors and concomitant drug therapy on warfarin metabolism and maintenance dose. Pharmacogenomics J 5(3):193–202
Holstein A, Plaschke A, Hammer C, Egberts EH (2003) Characteristics and time course of severe glimepiride- versus glibenclamide-induced hypoglycemia. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 59(2):91–97
McGavin JK, Perry CM, Goa KL (2002) Gliclazide modified release. Drugs 62(9):1357–1364, discussion 1365-1356
Gloyn AL, Hashim Y, Ashcroft SJ, Ashfield R, Wiltshire S, Turner RC (2001) Association studies of variants in promoter and coding regions of beta-cell ATP-sensitive K-channel genes SUR1 and Kir6.2 with Type 2 diabetes mellitus (UKPDS 53). Diabet Med 18(3):206–212
Sesti G, Laratta E, Cardellini M, Andreozzi F, Del Guerra S, Irace C, Gnasso A, Grupillo M, Lauro R, Hribal ML, Perticone F, Marchetti P (2006) The E23K variant of KCNJ11 encoding the pancreatic beta-cell adenosine 5′-triphosphate-sensitive potassium channel subunit Kir6.2 is associated with an increased risk of secondary failure to sulfonylurea in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91(6):2334–2339
Zhang H, Liu X, Kuang H, Yi R, Xing H (2007) Association of sulfonylurea receptor 1 genotype with therapeutic response to gliclazide in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 77(1):58–61
Feng Y, Mao G, Ren X, Xing H, Tang G, Li Q, Li X, Sun L, Yang J, Ma W, Wang X, Xu X (2008) Ser1369Ala variant in sulfonylurea receptor gene ABCC8 is associated with antidiabetic efficacy of gliclazide in Chinese type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 31(10):1939–1944
Sato R, Watanabe H, Genma R, Takeuchi M, Maekawa M, Nakamura H (2010) ABCC8 polymorphism (Ser1369Ala): influence on severe hypoglycemia due to sulfonylureas. Pharmacogenomics 11(12):1743–1750
Holstein A, Beil W, Kovacs P (2012) CYP2C metabolism of oral antidiabetic drugs–impact on pharmacokinetics, drug interactions and pharmacogenetic aspects. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 8(12):1549–1563
Ragia G, Petridis I, Tavridou A, Christakidis D, Manolopoulos VG (2009) Presence of CYP2C9*3 allele increases risk for hypoglycemia in Type 2 diabetic patients treated with sulfonylureas. Pharmacogenomics 10(11):1781–1787
Swen JJ, Wessels JA, Krabben A, Assendelft WJ, Guchelaar HJ (2010) Effect of CYP2C9 polymorphisms on prescribed dose and time-to-stable dose of sulfonylureas in primary care patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Pharmacogenomics 11(11):1517–1523
Hubbard RE, O’Mahony MS, Woodhouse KW (2013) Medication prescribing in frail older people. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 69(3):319–326
Woodhouse K (2013) Treating older people. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 69(Suppl 1):53–57
Dolzan V, Grabnar I (2005) Genetic polymorphism and drug dosing in elderly patients (Odmerjanje zdravil pri starostnikih glede na genetski polimorfizem). Farm Vestn 56(S1):83–88
Reitman ML, Schadt EE (2007) Pharmacogenetics of metformin response: a step in the path toward personalized medicine. J Clin Invest 117(5):1226–1229
Vidan-Jeras B, Jurca B, Dolzan V, Jeras M, Breskvar K, Bohinjec M (1998) Slovenian Caucasian normal. In: Terasaki PI, Gjerston DW (eds) HLA 1998. American Society for Histocompatibility and Immunogenetics, Lenexa, pp 180–181
Garte S, Gaspari L, Alexandrie AK, Ambrosone C, Autrup H, Autrup JL, Baranova H, Bathum L, Benhamou S, Boffetta P, Bouchardy C, Breskvar K, Brockmoller J, Cascorbi I, Clapper ML, Coutelle C, Daly A, Dell’Omo M, Dolzan V, Dresler CM, Fryer A, Haugen A, Hein DW, Hildesheim A, Hirvonen A, Hsieh LL, Ingelman-Sundberg M, Kalina I, Kang D, Kihara M, Kiyohara C, Kremers P, Lazarus P, Le Marchand L, Lechner MC, van Lieshout EM, London S, Manni JJ, Maugard CM, Morita S, Nazar-Stewart V, Noda K, Oda Y, Parl FF, Pastorelli R, Persson I, Peters WH, Rannug A, Rebbeck T, Risch A, Roelandt L, Romkes M, Ryberg D, Salagovic J, Schoket B, Seidegard J, Shields PG, Sim E, Sinnet D, Strange RC, Stucker I, Sugimura H, To-Figueras J, Vineis P, Yu MC, Taioli E (2001) Metabolic gene polymorphism frequencies in control populations. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 10(12):1239–1248
Acknowledgments
We wish to acknowledge the clinical nurse Mrs. Kirič Nevenka for her support with the clinical part of the study, Mrs. Savica Soldat BSc for her expert technical assistance and Miss Katja Goricar BSc for her support with the statistical analysis.
The study was financially supported by the Ministry of Education, Science, and Sport of the Republic of Slovenia (Grants Nos P1-0170 and P3-0298).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Table 1
(DOCX 12 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Klen, J., Dolžan, V. & Janež, A. CYP2C9, KCNJ11 and ABCC8 polymorphisms and the response to sulphonylurea treatment in type 2 diabetes patients. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 70, 421–428 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-014-1641-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-014-1641-x