Abstract
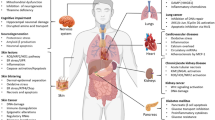
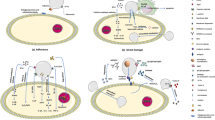
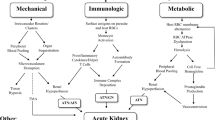
Amanita poisoning has a high mortality rate. The α-amanitin toxin in Amanita is the main lethal toxin. There is no specific detoxification drug for α-amanitin, and the clinical treatment mainly focuses on symptomatic and supportive therapy. The pathogenesis of α-amanitin mainly includes: α-amanitin can inhibit the activity of RNA polymeraseII in the nucleus, including the inhibition of the largest subunit of RNA polymeraseII, RNApb1, bridge helix, and trigger loop. In addition, α-amanitin acts in vivo through the enterohepatic circulation and transport system. α-Amanitin can cause the cell death. The existing mechanisms of cell damage mainly focus on apoptosis, oxidative stress, and autophagy. In addition to the pathogenic mechanism, α-amanitin also has a role in cancer treatment, which is the focus of current research. The mechanism of action of α-amanitin on the body is still being explored.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andera L, Wasylyk B (1997) Transcription abnormalities potentiate apoptosis of normal human fibroblasts. Mol Med 3(12):852–863
Arima Y, Nitta M, Kuninaka S et al (2005) Transcriptional blockade induces p53-dependent apoptosis associated with translocation of p53 to mitochondria. J Biol Chem 280(19):19166–19176. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M410691200
Beck A, Goetsch L, Dumontet C, Corvaïa N (2017) Strategies and challenges for the next generation of antibody-drug conjugates. Nat Rev Drug Discov 16(5):315–337. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd.2016.268
Bursch W, Ellinger A, Gerner C, Fröhwein U, Schulte-Hermann R (2000) Programmed cell death (PCD). Apoptosis, autophagic PCD, or others? Ann N Y Acad Sci 926:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.2000.tb05594.x
Bushnell DA, Cramer P, Kornberg RD (2002) Structural basis of transcription: α-amanitin-RNA polymerase II cocrystal at 2.8 A resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99(3):1218–1222. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.251664698
Chafin DR, Guo H, Price DH (1995) Action of α-amanitin during pyrophosphorolysis and elongation by RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem 270(32):19114–19119. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.270.32.19114
Chen X, Shao B, Yu C et al (2020) The cyclopeptide α-amatoxin induced hepatic injury via the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway associated with oxidative stress. Peptides 129:170314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2020.170314
Chen JZ, Fu WS, Xu F et al (2022) Acute mushroom poisoning of Amanita pseudosychnopyramis: A case report from Fujian, China with exact species identification and descriptive study. Toxicon 212:55–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxicon.2022.04.001
Cochet-Meilhac M, Chambon P (1974) Animal DNA-dependent RNA polymerases. 11. Mechanism of the inhibition of RNA polymerases B by amatoxins. Biochim Biophys Acta 353(2):160–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/0005-2787(74)90182-8
Dong Z, Ekins S, Polli JE (2013) Structure-activity relationship for FDA approved drugs as inhibitors of the human sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide (NTCP). Mol Pharm 10(3):1008–1019. https://doi.org/10.1021/mp300453k
Donkers JM, Kooijman S, Slijepcevic D et al (2019) NTCP deficiency in mice protects against obesity and hepatosteatosis. JCI Insight. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.127197
Duerr C, Friess W (2019) Antibody-drug conjugates-stability and formulation. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 139:168–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2019.03.021
El-Bahay C, Gerber E, Horbach M, Tran-Thi QH, Röhrdanz E, Kahl R (1999) Influence of tumor necrosis factor-α and silibin on the cytotoxic action of α-amanitin in rat hepatocyte culture. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 158(3):253–260. https://doi.org/10.1006/taap.1999.8705
Evans N, Hamilton A, Bello-Villalba MJ, Bingham C (2012) Irreversible renal damage from accidental mushroom poisoning. BMJ 345:e5262. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.e5262
Faulstich H, Fauser U (1973) Hemodialysis in Amanita phalloides poisoning. Serum levels and excretion of amanitine. Dtsch Med Wochenschr 98(47):2258–2259
Faulstich H, Talas A, Wellhöner HH (1985) Toxicokinetics of labeled amatoxins in the dog. Arch Toxicol 56(3):190–194. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00333425
Fehrenbach T, Cui Y, Faulstich H, Keppler D (2003) Characterization of the transport of the bicyclic peptide phalloidin by human hepatic transport proteins. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 368(5):415–420. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-003-0814-4
Feinfeld DA, Rosenberg JW, Winchester JF (2006) Three controversial issues in extracorporeal toxin removal. Semin Dial 19(5):358–362. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1525-139X.2006.00187_1.x
Floersheim GL (1972) Curative potencies against -amanitin poisoning by cytochrome c. Science 177(4051):808–809. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.177.4051.808
Floersheim GL (1987) Treatment of human amatoxin mushroom poisoning. myths and advances in therapy. Med Toxicol 2(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf03259857
French LK, Hendrickson RG, Horowitz BZ (2011) Amanita phalloides poisoning. Clin Toxicol (phila) 49(2):128–129. https://doi.org/10.3109/15563650.2011.557663
Fukano K, Tsukuda S, Watashi K, Wakita T (2019) Concept of viral inhibitors via NTCP. Semin Liver Dis 39(1):78–85. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0038-1676804
Ganzert M, Felgenhauer N, Schuster T, Eyer F, Gourdin C, Zilker T (2008) Amanita poisoning–comparison of silibinin with a combination of silibinin and penicillin. Dtsch Med Wochenschr 133(44):2261–2267. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0028-1091268
Garcia J, Carvalho AT, Dourado DF, Baptista P, de Lourdes BM, Carvalho F (2014) New in silico insights into the inhibition of RNAP II by α-amanitin and the protective effect mediated by effective antidotes. J Mol Graph Model 51:120–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmgm.2014.05.002
Garcia J, Costa VM, Carvalho AT et al (2015) A breakthrough on Amanita phalloides poisoning: an effective antidotal effect by polymyxin B. Arch Toxicol 89(12):2305–2323. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-015-1582-x
Garcia J, Costa VM, Bovolini A et al (2019) An effective antidotal combination of polymyxin B and methylprednisolone for α-amanitin intoxication. Arch Toxicol 93(5):1449–1463. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-019-02426-5
Garcia J, Carvalho A, das Neves RP et al (2022) Antidotal effect of cyclosporine A against α-amanitin toxicity in CD-1 mice, at clinical relevant doses. Food Chem Toxicol 166:113198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2022.113198
Gong XQ, Nedialkov YA, Burton ZF (2004) α-Amanitin blocks translocation by human RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem 279(26):27422–27427. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M402163200
Goulet DR, Atkins WM (2020) Considerations for the design of antibody-based therapeutics. J Pharm Sci 109(1):74–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xphs.2019.05.031
Gu X, Zhang L, Sun W et al (2022) Autophagy promotes α-amanitin-induced apoptosis of Hepa1-6 liver cells. Chem Res Toxicol 35(3):392–401. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrestox.1c00297
Gundala S, Wells LD, Milliano MT, Talkad V, Luxon BA, Neuschwander-Tetri BA (2004) The hepatocellular bile acid transporter Ntcp facilitates uptake of the lethal mushroom toxin α-amanitin. Arch Toxicol 78(2):68–73. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-003-0527-y
Hagenbuch B, Meier PJ (1994) Molecular cloning, chromosomal localization, and functional characterization of a human liver Na+/bile acid cotransporter. J Clin Invest 93(3):1326–1331. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci117091
Jiang S, Zhang H, Li X et al (2021) Vitamin D/VDR attenuate cisplatin-induced AKI by down-regulating NLRP3/Caspase-1/GSDMD pyroptosis pathway. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 206:105789. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105789
Karlson-Stiber C, Persson H (2003) Cytotoxic fungi—an overview. Toxicon 42(4):339–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0041-0101(03)00238-1
Kaya E, Surmen MG, Yaykasli KO et al (2014) Dermal absorption and toxicity of α amanitin in mice. Cutan Ocul Toxicol 33(2):154–160. https://doi.org/10.3109/15569527.2013.802697
Kostova V, Désos P, Starck JB, Kotschy A (2021) The chemistry behind ADCs. Pharmaceuticals (basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14050442
Kovtun YV, Goldmacher VS (2007) Cell killing by antibody-drug conjugates. Cancer Lett 255(2):232–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2007.04.010
Kröncke KD, Fricker G, Meier PJ, Gerok W, Wieland T, Kurz G (1986) α-Amanitin uptake into hepatocytes. Identification of hepatic membrane transport systems used by amatoxins. J Biol Chem 261(27):12562–12567
Kullak-Ublick GA, Stieger B, Meier PJ (2004) Enterohepatic bile salt transporters in normal physiology and liver disease. Gastroenterology 126(1):322–342. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2003.06.005
Le Daré B, Ferron PJ, Gicquel T (2021) Toxic effects of amanitins: repurposing toxicities toward new therapeutics. Toxins (basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13060417
Lee CH, Ling V (2003) Superinduction of P-glycoprotein messenger RNA in vivo in the presence of transcriptional inhibitors. J Exp Ther Oncol 3(1):14–26. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1359-4117.2003.01063.x
Lee KB, Wang D, Lippard SJ, Sharp PA (2002) Transcription-coupled and DNA damage-dependent ubiquitination of RNA polymerase II in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(7):4239–4244. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.072068399
Leist M, Gantner F, Naumann H et al (1997) Tumor necrosis factor-induced apoptosis during the poisoning of mice with hepatotoxins. Gastroenterology 112(3):923–934. https://doi.org/10.1053/gast.1997.v112.pm9041255
Letschert K, Faulstich H, Keller D, Keppler D (2006) Molecular characterization and inhibition of amanitin uptake into human hepatocytes. Toxicol Sci 91(1):140–149. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfj141
Leu JI, George DL (2007) Hepatic IGFBP1 is a prosurvival factor that binds to BAK, protects the liver from apoptosis, and antagonizes the proapoptotic actions of p53 at mitochondria. Genes Dev 21(23):3095–3109. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1567107
Li Y, Tan L, Li H, Xu Z, Zuo X, Tang Y (2014) An artificial receptor fabricated by target recognition determinant imprinting for selective capture of α-amanitin. J Chromatogr A 1324:190–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2013.11.042
Li WQ, Guo HF, Li LY, Zhang YF, Cui JW (2021a) The promising role of antibody drug conjugate in cancer therapy: Combining targeting ability with cytotoxicity effectively. Cancer Med 10(14):4677–4696. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.4052
Li Y, Qiu Z, Huang L, Cao C (2021b) Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation combined with sequential blood purification in the treatment of myocardial damage and cardiac arrest caused by mushroom poisoning. Toxicon 197:65–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxicon.2021.04.011
Lin LY, Tong YL, Lu YQ (2022) The characteristics of liver injury induced by Amanita and clinical value of α-amanitin detection. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int 21(3):257–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hbpd.2022.01.007
Lindell TJ, Weinberg F, Morris PW, Roeder RG, Rutter WJ (1970) Specific inhibition of nuclear RNA polymerase II by α-amanitin. Science 170(3956):447–449. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.170.3956.447
Liu X, Farnung L, Wigge C, Cramer P (2018) Cryo-EM structure of a mammalian RNA polymerase II elongation complex inhibited by α-amanitin. J Biol Chem 293(19):7189–7194. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA118.002545
Ljungman M, Zhang F, Chen F, Rainbow AJ, McKay BC (1999) Inhibition of RNA polymerase II as a trigger for the p53 response. Oncogene 18(3):583–592. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1202356
Lockshin RA, Osborne B, Zakeri Z (2000) Cell death in the third millennium. Cell Death Differ 7(1):2–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4400649
Lu H, Choudhuri S, Ogura K et al (2008) Characterization of organic anion transporting polypeptide 1b2-null mice: essential role in hepatic uptake/toxicity of phalloidin and microcystin-LR. Toxicol Sci 103(1):35–45. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfn038
Ma XY, Wang JF, Luo JB et al (2020) Successful treatment of liver failure caused by fatal amanita poisoning with percutaneous cholecystostomy: a case report. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi 28(12):1052–1054. https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20200515-00246
Magdalan J, Ostrowska A, Piotrowska A et al (2009) Failure of benzylpenicillin, N-acetylcysteine and silibinin to reduce α-amanitin hepatotoxicity. In Vivo 23(3):393–399
Magdalan J, Ostrowska A, Piotrowska A et al (2010) Benzylpenicillin, acetylcysteine and silibinin as antidotes in human hepatocytes intoxicated with α-amanitin. Exp Toxicol Pathol 62(4):367–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etp.2009.05.003
Magdalan J, Piotrowska A, Gomułkiewicz A et al (2011a) Benzylpenicyllin and acetylcysteine protection from α-amanitin-induced apoptosis in human hepatocyte cultures. Exp Toxicol Pathol 63(4):311–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etp.2010.02.004
Magdalan J, Piotrowska A, Gomułkiewicz A, Sozański T, Szeląg A, Dziegięl P (2011b) Influence of commonly used clinical antidotes on antioxidant systems in human hepatocyte culture intoxicated with α-amanitin. Hum Exp Toxicol 30(1):38–43. https://doi.org/10.1177/0960327110368418
McCombs JR, Owen SC (2015) Antibody drug conjugates: design and selection of linker, payload and conjugation chemistry. Aaps J 17(2):339–351. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12248-014-9710-8
Nguyen VT, Giannoni F, Dubois MF et al (1996) In vivo degradation of RNA polymerase II largest subunit triggered by α-amanitin. Nucleic Acids Res 24(15):2924–2929. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/24.15.2924
Nieminen P, Mustonen AM (2020) Toxic potential of traditionally consumed mushroom species-a controversial continuum with many unanswered questions. Toxins (basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12100639
Pahl A, Lutz C, Hechler T (2018) Amanitins and their development as a payload for antibody-drug conjugates. Drug Discov Today Technol 30:85–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ddtec.2018.08.005
Panowski S, Bhakta S, Raab H, Polakis P, Junutula JR (2014) Site-specific antibody drug conjugates for cancer therapy. Mabs 6(1):34–45. https://doi.org/10.4161/mabs.27022
Pond SM, Olson KR, Woo OF et al (1986) Amatoxin poisoning in northern California, 1982–1983. West J Med 145(2):204–209
Ponziani S, Di Vittorio G, Pitari G et al (2020) Antibody-drug conjugates: the new frontier of chemotherapy. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21155510
Popp T, Balszuweit F, Schmidt A, Eyer F, Thiermann H, Steinritz D (2020) Assessment of α-amanitin toxicity and effects of silibinin and penicillin in different in vitro models. Toxicol in Vitro 67:104921. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2020.104921
Poucheret P, Fons F, Doré JC, Michelot D, Rapior S (2010) Amatoxin poisoning treatment decision-making: pharmaco-therapeutic clinical strategy assessment using multidimensional multivariate statistic analysis. Toxicon 55(7):1338–1345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxicon.2010.02.005
Remijsen Q, Kuijpers TW, Wirawan E, Lippens S, Vandenabeele P, Vanden Berghe T (2011) Dying for a cause: NETosis, mechanisms behind an antimicrobial cell death modality. Cell Death Differ 18(4):581–588. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2011.1
Rodrigues DF, Pires da Neves R, Carvalho ATP, Lourdes Bastos M, Costa VM, Carvalho F (2020) In vitro mechanistic studies on α-amanitin and its putative antidotes. Arch Toxicol 94(6):2061–2078. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-020-02718-1
Rosenthal P (2002) Mushroom poisoning and auxiliary partial orthotopic liver transplantation. Am J Gastroenterol 97(5):1272–1273. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1572-0241.2002.05726.x
Scott AM, Wolchok JD, Old LJ (2012) Antibody therapy of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 12(4):278–287. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc3236
Seifart KH, Sekeris CE (1969) α-amanitin, a specific inhibitor of transcription by mammalian RNA-polymerase. Z Naturforsch B 24(12):1538–1544. https://doi.org/10.1515/znb-1969-1211
Shi Y, He J, Chen S et al (2002) MARS: optimistic therapy method in fulminant hepatic failure secondary to cytotoxic mushroom poisoning–a case report. Liver 22(Suppl 2):78–80. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0676.2002.00017.x
Shrestha A, Mehdizadeh Gohari I, McClane BA (2019) RIP1, RIP3, and MLKL contribute to cell death caused by clostridium perfringens enterotoxin. Mbio. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.02985-19
Stirpe F, Fiume L (1967) Effect of α-amanitin on ribonucleic acid synthesis and on ribonucleic acid polymerase in mouse liver. Biochem J 103(3):67p–68p
Sun J, Zhang YT, Niu YM et al (2018) Effect of biliary drainage on the toxicity and toxicokinetics of amanita exitialis in beagles. Toxins (basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10060215
Tan L, He R, Li Y, Liang Y, Li H, Tang Y (2016) Fabrication of a biomimetic adsorbent imprinted with a common specificity determinant for the removal of α- and β-amanitin from plasma. J Chromatogr A 1459:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2016.06.072
Thiel C, Thiel K, Klingert W et al (2011) The enterohepatic circulation of amanitin: kinetics and therapeutical implications. Toxicol Lett 203(2):142–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2011.03.016
Tian J, Li C, Li W (2021) Entry of hepatitis B virus: going beyond NTCP to the nucleus. Curr Opin Virol 50:97–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coviro.2021.08.001
Tong TC, Hernandez M, Richardson WH 3rd et al (2007) Comparative treatment of α-amanitin poisoning with N-acetylcysteine, benzylpenicillin, cimetidine, thioctic acid, and silybin in a murine model. Ann Emerg Med 50(3):282–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annemergmed.2006.12.015
Trabulus S, Altiparmak MR (2011) Clinical features and outcome of patients with amatoxin-containing mushroom poisoning. Clin Toxicol (phila) 49(4):303–310. https://doi.org/10.3109/15563650.2011.565772
Tsuchikama K, An Z (2018) Antibody-drug conjugates: recent advances in conjugation and linker chemistries. Protein Cell 9(1):33–46. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13238-016-0323-0
Tsurusaki S, Tsuchiya Y, Koumura T et al (2019) Hepatic ferroptosis plays an important role as the trigger for initiating inflammation in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Cell Death Dis 10(6):449. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-1678-y
Van der Jeught K, Xu HC, Li YJ, Lu XB, Ji G (2018) Drug resistance and new therapies in colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 24(34):3834–3848. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i34.3834
Wettengel JM, Burwitz BJ (2020) Innovative HBV animal models based on the entry receptor ntcp. Viruses. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12080828
Yan H, Zhong G, Xu G et al (2012) Sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide is a functional receptor for human hepatitis B and D virus. Elife 1:e00049. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.00049
Yan H, Liu Y, Sui J, Li W (2015) NTCP opens the door for hepatitis B virus infection. Antivir Res 121:24–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.antiviral.2015.06.002
Yang Y, Shao RF, Chen GB (2020) Research progress on the mechanism of mushroom poisoning. J Clin Emerg 21(8):675–678. https://doi.org/10.13201/j.issn.1009-5918.2020.08.016
Zhang J, Zhang Y, Peng Z et al (2014) Experience of treatments of amanita phalloides-induced fulminant liver failure with molecular adsorbent recirculating system and therapeutic plasma exchange. Asaio J 60(4):407–412. https://doi.org/10.1097/mat.0000000000000083
Zheleva A, Tolekova A, Zhelev M, Uzunova V, Platikanova M, Gadzheva V (2007) Free radical reactions might contribute to severe α amanitin hepatotoxicity—a hypothesis. Med Hypotheses 69(2):361–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2006.10.066
Funding
1. Yunnan Provincial Science and Technology Department Science and Technology Plan Kunming Medical University Joint Project; 202201AY070001-249. 2. Young and middle-aged academic and technical leaders in Yunnan Province; C098-2060499. Reserve talents.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, JX and GC; writing—original draft preparation, JX; writing—review and editing, JX, XL, DN, RS, and GC; supervision, GC; funding acquisition, GC. All the authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, J., Lou, X., Ning, D. et al. Mechanism and treatment of α-amanitin poisoning. Arch Toxicol 97, 121–131 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-022-03396-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-022-03396-x