Abstract
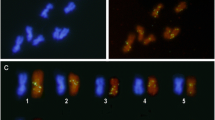
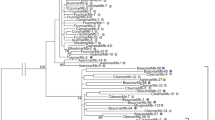
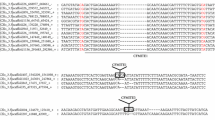
To date, only three types of full-length mariner elements have been described in ants, each one in a different genus of the Myrmicinae subfamily: Sinvmar was isolated from various Solenopsis species, Myrmar from Myrmica ruginodis, and Mboumar from Messor bouvieri. In this study, we report the coexistence of three mariner elements (Tnigmar-Si, Tnigmar-Mr, and Tnigmar-Mb) in the genome of a single species, Tapinoma nigerrimum (subfamily Dolichoderinae). Molecular evolutionary analyses of the nucleotide sequence data revealed a general agreement between the evolutionary history of most the elements and the ant species that harbour them, and suggest that they are at the vertical inactivation stage of the so-called Mariner Life Cycle. In contrast, significantly reduced levels of synonymous divergence between Mboumar and Tnigmar-Mb and between Myrmar and Botmar (a mariner element isolated from Bombus terrestris), relative to those observed between their hosts, suggest that these elements arrived to the species that host them by horizontal transfer, long after the species’ split. The horizontal transfer events for the two pairs of elements could be roughly dated within the last 2 million years and about 14 million years, respectively. As would be expected under this scenario, the coding sequences of the youngest elements, Tnigmar-Mb and Mboumar, are intact and, thus, potentially functional. Each mariner element has a different chromosomal distribution pattern according to their stage within the Mariner Life Cycle. Finally, a new defective transposable element (Azteca) has also been found inserted into the Tnigmar-Mr sequences showing that the ant genomes have been invaded by at least four different types of mariner elements.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abouheif E, Wray GA (2002) Evolution of the gene network underlying wing polyphenism in ants. Science 297:249–252
Augé-Gouillou C, Brillet B, Germon S, Hamelin MH, Bigot Y (2005) Mariner Mos 1transposase dimerizes prior to ITR binding. J Mol Biol 351:117–130
Barry EG, Witherspoon DJ, Lampe DJ (2004) A bacterial genetic screen identifies functional coding sequences of the insect mariner transposable element Famar1 amplified from the genome of the earwig, Forficula auricularia. Genetics 166:823–833
Bartolomé C, Maside X, Charlesworth B (2002) On the abundance and distribution of transposable elements in the genome of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Biol Evol 19:926–937
Bartolomé C, Bello X, Maside X (2009) Widespread evidence for horizontal transfer of transposable elements across Drosophila genomes. Genome Biol 10:R22
Bigot Y, Hamelin MH, Capy P, Periquet G (1994) Mariner-like elements in hymenopteran species, insertion site and distribution. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:3408–3412
Boratyn GM, Schaffer AA, Agarwala R, Altschul SF, Lipman DJ, Madden TL (2012) Domain enhanced lookup time accelerated BLAST. Biol Direct 17:12
Brady SG, Schultz TR, Fisher BL, Ward PS (2006) Evaluating alternative hypotheses for the early evolution and diversification of ants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:18172–18177
Brunet F, Giraud T, Godin F, Capy P (2002) Do deletions of Mos1-like elements occur randomly in the Drosophilidae family? J Mol Evol 54:227–234
Bouuaert C, Chalmers R (2010) Transposition of the human Hsmar1 transposon: rate-limiting steps and the importance of the flanking TA dinucleotide in second strand cleavage. Nucleic Acids Res 38:190–202
Bui QT, Casse N, Leignel V, Nicolas V, Chénais B (2008) Widespread occurence of mariner transposons in coastal crabs. Mol Phylogenet Evol 47:1181–1189
Charlesworth B, Jarne P, Assimacopoulos S (1994) The distribution of transposable elements within and between chromosomes in a population of Drosophila melanogaster. Drosophila melanogaster: III. Genet Res 64:183–197
De Menten L, Niculita H, Gilbert M, Delneste D, Aron S (2003) Fluorescence in situ hybridization: a new method for determining primary sex ratio in ants. Mol Ecol 12:1637–1648
Diao Y, Qi Y, Ma Y, Xia A, Sharakhov I, Chen X, Biedler J, Ling E, Tu ZJ (2011) Next-generation sequencing reveals recent horizontal transfer of a DNA transposon between divergent mosquitoes. PLoS One 6:e16743
Edgar RC (2004) MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res 32:1792–1797
Fontanillas P, Hartl DL, Reuter M (2007) Genome organization and gene expression shape the transposable element distribution in the Drosophila melanogaster euchromatin. PLoS Genet 3:e210
Haine ER, Kabat P, Cook JM (2007) Diverse mariner-like elements in fig wasps. Insect Mol Biol 16:743–752
Hartl DL (2001) Discovery of the transposable element mariner. Genetics 157:471–476
Hartl DL, Lohe AR, Lozovskaya ER (1997) Modern thoughts on an ancyent marinere: function, evolution, regulation. Annu Rev Genet 31:337–358
Heinze J, Gadau J, Hölldobler B, Nanda I, Schmid M, Scheller K (1994) Genetic variability in the ant Camponotus floridanus detected by multilocus fingerprinting. Naturwissenschaften 81:34–36
Hua-Van A, Le Rouzic A, Boutin TS, Filée J, Capy P (2011) The struggle for life of the genome's selfish architects. Biol Direct 6:19
Hurst GDD, Werren JH (2001) The role of selfish genetic elements in eukaryotic evolution. Nat Rev Genet 2:597–606
Jacobson JW, Medhora MM, Hartl DL (1986) Molecular structure of a somatically unstable transposable element in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:8684–8688
Kumaresan GS, Mathavan S (2004) Molecular diversity and phylogenetic analysis of mariner-like transposons in the genome of the silkworm Bombyx mori. Insect Mol Biol 13:259–271
Krieger MJB, Ross KG (2003) Molecular evolutionary analyses of mariners and other transposable elements in fire ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Insect Mol Biol 12:155–165
Langin T, Capy P, Daboussi MJ (1995) The transposable element Impala, a fungal member of the Tc1-mariner superfamily. Mol Gen Genet 246:19–28
Lampe DJ, Walden KKO, Robertson HM (2001) Loss of transposase-DNA interaction may underlie the divergence of mariner family transposable elements and the ability of more than one mariner to occupy the same genome. Mol Biol Evol 18:954–961
Lampe DJ, Witherspoon DJ, Soto-Adames FN, Robertson HM (2003) Recent horizontal transfer of mellifera subfamily mariner transposons into insect lineages representing four different orders shows that selection acts only during horizontal transfer. Mol Biol Evol 20:554–562
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG (2007) Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23:2947–2948
Leroy H, Castagnone-Sereno P, Renault S, Augé-Gouillou C, Bigot Y, Abad P (2003) Characterization of Mcmar1, a mariner-like element with large inverted terminal repeats (ITRs) from the phytoparasitic nematode Meloidogyne chitwoodi. Gene 304:35–41
Li WS (1997) Molecular evolution. Chapters 7 and 8. Sinauer Associates, Inc, Sunderland
Lohe AR, De Aguiar D, Hartl DL (1997) Mutations in the mariner transposase, the “D, D(35)E” consensus sequence is nonfunctional. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:1293–1297
Loreto EL, Carareto CM, Capy P (2008) Revisiting horizontal transfer of transposable elements in Drosophila. Heredity 100:545–554
Lorite P, Aránega AE, Luque F, Palomeque T (1997) Analysis of the nucleolar organizing regions in the ant Tapinoma nigerrimum (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Heredity 78:578–582
Lorite P, Carrillo JA, Garneria I, Petitpierre E, Palomeque T (2002) Satellite DNA in the elm leaf beetle Xanthogaleruca luteola (Coleoptera, Chrysomelidae): characterization, interpopulation analysis and chromosome location. Cytogenet Genome Res 98:302–307
Lorite P, Palomeque T (2010) Karyotype evolution in ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) with a review of the known ant chromosome numbers. Myrmecol News 13:89–102
McClean P (1998). DNA — basics of structure and analysis. Nucleic acid hybridizations. Retrieved from http://www.ndsu.nodak.edu/instruct/mcclean/plsc731/dna/dna6.htm 12/7/2012
Miskey C, Izsvák Z, Kawakami K, Ivics Z (2005) DNA transposons in vertebrate functional genomics. Cell Mol Life Sci 62:629–641
Meznar ER, Gadau J, Koeniger N, Rueppell OJ (2010) Comparative linkage mapping suggests a high recombination rate in all honeybees. J Hered 101(Suppl 1):S118–S126
Medhora M, Maruyama K, Hartl DL (1991) Molecular and functional analysis of the mariner mutator element Mos1 in Drosophila. Genetics 128:311–318
Moreau CS, Bell CD, Vila R, Archibald SB, Pierce NE (2006) Phylogeny of the ants: diversification in the age of Angiosperms. Science 312:101–104
Muñoz-López M, Siddique A, Bischerour J, Lorite P, Chalmers R, Palomeque T (2008) Transposition of Mboumar-9: identification of a new naturally-active mariner-family transposón. J Mol Biol 382:567–572
Nei M (1987) Molecular evolutionary genetics. Columbia Univ, Press, New York
Nei M, Kumar S (2000) Molecular evolutionary and phylogenetics. Chapter 10. Oxford University Press, New York
Niehuis O, Gibson JD, Rosenberg MS, Pannebakker BA, Koevoets T, Judson AK, Desjardins CA, Kennedy K, Duggan D, Beukeboom LW, van de Zande L, Shuker DM, Werren JH, Gadau J (2010) Recombination and its impact on the genome of the haplodiploid parasitoid wasp Nasonia. PLoS One 5:e8597
Palomeque T, Chica E, Cano MA, Díaz de la Guardia R (1988) Karyotypes, C-banding, and chromosomal location of active nucleolar organizing regions in Tapinoma (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Genome 30:277–280
Palomeque T, Muñoz-López M, Carrillo JA, Lorite P (2005) Characterization and evolutionary dynamics of a complex family of satellite DNA in the leaf beetle Chrysolina carnifex (Coleoptera, Chrysomelidae). Chromosome Res 13:795–807
Palomeque T, Carrillo JA, Muñoz-López M, Lorite P (2006) Detection of a mariner-like element and a miniature inverted-repeat transposable element (MITE) associated with the heterochromatin from ants of the genus Messor and their possible involvement for satellite DNA evolution. Gene 371:194–205
Plasterk RH, Izsvák Z, Ivics Z (1999) Resident aliens, the Tc1/mariner superfamily of transposable elements. Trends Genet 15:326–332
Rezende-Teixeira P, Lauand C, Siviero F, Machado-Santelli GM (2010) Normal and defective mariner-like elements in Rhynchosciara species (Sciaridae, Diptera). Genet Mol Res 9:849–857
Robertson HM (1996) Members of the pogo superfamily of DNA-mediated transposons in the human genome. Mol Gen Genet 252:761–766
Robertson HM, MacLeod EG (1993) Five major subfamilies of mariner transposable elements in insects, including the Mediterranean fruit fly, and related arthropods. Insect Mol Biol 2:125–139
Robertson HM, Asplund KL (1996) Bmmar1, a basal lineage of the mariner family of transposable elements in the silkworm moth, Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 26:945–954
Rouleux-Bonnin F, Petit A, Demattei MV, Bigot Y (2005) Evolution of full-length and deleted forms of the mariner-like element, Botmar1, in the genome of the bumble bee, Bombus terrestris (Hymenoptera: Apidae). J Mol Evol 60:736–747
Rouault JD, Casse N, Chénais B, Hua-Van A, Filée J, Capy P (2009) Automatic classification within families of transposable elements: application to the mariner family. Gene 448:227–232
Sánchez-Gracia A, Maside X, Charlesworth B (2005) High rate of horizontal transfer of transposable elements in Drosophila. Trends Genet 21:200–203
Schaack S, Gilbert C, Feschotte C (2010) Promiscuous DNA: horizontal transfer of transposable elements and why it matters for eukaryotic evolution. Trends Ecol Evol 25:537–546
Sela N, Kim E, Ast G (2010) The role of transposable elements in the evolution of non-mammalian vertebrates and invertebrates. Genome Biol 11:R59
Shao H, Tu Z (2001) Expanding the diversity of the IS630-Tc1-mariner superfamily: discovery of a unique DD37E transposon and reclassification of the DD37D and DD39D transposons. Genetics 159:1103–1115
Silva JC, Bastida F, Bidwell SL, Johnson PJ, Carlton JM (2005) A potentially functional mariner transposable element in the protist Trichomonas vaginalis. Mol Biol Evol 22:126–134
Sironi M, Menozzi G, Comi GP, Cereda M, Cagliani R, Bresolin N, Pozzoli U (2006) Gene function and expression level influence the insertion/fixation dynamics of distinct transposon families in mammalian introns. Genome Biol 7:R120
Sirviö A, Gadau J, Rueppell O, Lamatsch D, Boomsma JJ, Pamilo P, Page RE Jr (2006) High recombination frequency creates genotypic diversity in colonies of the leaf-cutting ant Acromyrmex echinatior. J Evol Biol 19:1475–1485
Sirviö A, Johnston JS, Wenseleers T, Pamilo P (2011) A high recombination rate in eusocial Hymenoptera: evidence from the common wasp Vespula vulgaris. BMC Genet 12:95
Tamura K, Subramanian S, Kumar S (2004) Temporal patterns of fruit fly (Drosophila) evolution revealed by mutation clocks. Mol Biol Evol 21:36–44
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using Maximum Likelihood, Evolutionary Distance, and Maximum Parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Viginier B, Peeters C, Brazier L, Doums C (2004) Very low genetic variability in the Indian queenless ant Diacamma indicum. Mol Ecol 13:2095–2100
Ward PS, Downie DA (2005) The ant subfamily Pseudomyrmecinae (Hymenoptera: Formicidae): phylogeny and evolution of big-eyed arboreal ants. Syst Entomol 30:310–335
Ward PS, Brady SG, Fisher BL, Schultz TR (2010) Phylogeny and biogeography of dolichoderine ants: effects of data partitioning and relict taxa on historical inference. Syst Biol 59:342–362
Wicker T, Sabot F, Hua-Van A, Bennetzen JL, Capy P, Chalhoub B, Flavell A, Leroy P, Morgante M, Panaud O, Paux E, SanMiguel P, Schulman AH (2007) A unified classification system for eukaryotic transposable elements. Nat Rev Genet 8:973–982
Wilfert L, Gadau J, Schmid-Hempel P (2007) Variation in genomic recombination rates among animal taxa and the case of social insects. Heredity 98:189–197
Wysocka A, Krzysztofiak L, Krzysztofiak A, Zołnierkiewicz O, Ojdowska E, Sell J (2011) Low genetic diversity in Polish populations of sibling ant species: Lasius niger (L.) and Lasius platythorax Seifert (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Insec Soc 58:191–195
Zhou MB, Zhong H, Tang DQ (2011) Isolation and characterization of seventy-nine full-length mariner-like transposase genes in the Bambusoideae subfamily. J Plant Res 124:607–617
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Dale K. Pollet (Louisiana State University Agricultural Center, Baton Rouge, LA, USA) for providing us samples of Solenopsis invicta. We are also grateful to Alain Lenoir (Université François Rabelais, Tours, France) for providing us samples of Myrmica ruginodis. This work was supported by the Spanish Junta de Andalucía (through the programs “Ayudas a Grupos de Investigación”, Group BIO220 and “Incentivos a proyectos de investigación de excelencia”, project CVI-6807, co-funded by the European Regional Development Fund), by the Spanish Ministerio de Educación e Innovación (through project CGL2011-23841, co-funded by the European Regional Development Fund) and by the University of Jaén (through the program “Programa propio de ayudas para la realización de proyectos de investigación”, UJA-08-16-03).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by: Sven Thatje
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 6186 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lorite, P., Maside, X., Sanllorente, O. et al. The ant genomes have been invaded by several types of mariner transposable elements. Naturwissenschaften 99, 1007–1020 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00114-012-0982-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00114-012-0982-5