Abstract
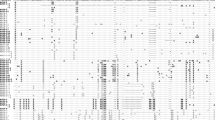
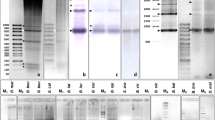
The present study characterizes the complex satellite DNA from the specialized phytophagous beetle species Chrysolina carnifex. The satellite DNA is formed by six monomer types, partially homologous but having diverged enough to be separate on the phylogenetic trees, since each monomer type is located on a different branch, having statistically significant bootstrap values. Its analysis suggests a common evolutionary origin of all monomers from the same 211-bp sequence mainly by means of base-substitution mutations evolutionarily fixed to each monomer type and duplications and/or deletions of pre-existing segments in the 211-bp sequence. The analysis of the sequences and Southern hybridizations suggest that the monomers are organized in three types of repeats: monomers (211-bp) and higher-order repeats in the form of dimers (477-bp) or even trimers (633-bp). These repetitive units are not isolated from others, and do not present the pattern characteristic for the regular tandem arrangement of satellite DNA. In-situ hybridization with biotinylated probes corresponding to the three types of repeats showed the pericentromeric location of these sequences in all meiotic bivalents, coinciding with the heterochromatic blocks revealed by C-banding, indicating in addition that each type of repeat is neither isolated from others nor located in specific chromosomes but rather that they are intermixed in the heterochromatic regions. The presence of this repetitive DNA in C. haemoptera, C. bankii and C. americana was also tested by Southern analysis. The results show that this satellite DNA sequence is specific to the C. carnifex genome but has not been found in three other species of Chrysolina occupying similar or different host plants.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers MW, Lipman DJ (1990) A basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215: 403–410.
Altschul SF, Stephen F, Thomas L et al. (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucl Acids Res 25: 3389–3402.
Daccordi M (1996) Notes on the distribution of the Crysomelinae and their possible origin. In: Jolivet PHA, Cox ML, eds. Chrysomelidae Biology, Vol. 1. Amsterdam: SPB Academic, pp 399–412.
Dover G (2002) Molecular drive. Trends Genet 18: 587–589.
Garin CF, Juan C, Petitpierre E (1999) Mitochondrial DNA phylogeny and the evolution of host-plant use in Palearctic, Chrysolina (Coleoptera, Chrysomelidae). J Mol Evol 48: 435–444.
Gómez-Zurita J, Garin CF, Juan C, Petitpierre E (1999) Mitochondrial 16S rDNA sequences and their use as phylogenetic markers in leaf-beetles with special reference to the subfamily Chrysomelidae. In: Cox ML, ed. Advances in Chrysomelidae Biology. Oegstgeest, The Netherlands: Backhuys Publ, pp 25–38.
Goméz-Zurita J, Juan C, Petitpierre E (2000) The evolutionary history of the genus Timarcha (Coleoptera, Chrysomelidae) inferred from mitochondrial COII gene and partial 16S rDNA sequences. Mol Phylogenet Evol 4: 433–447.
Heinze J, Gadau J, Hölldobler B, Nanda I, Schmid M, Scheller K (1994) Genetic variability in the ant Camponotus floridanus detected by multilocus fingerprinting. Naturwissenschaften 81: 34–36.
Jolivet P (1988) Food habits and food selection of Chrysomelidae. Bionomic and evolutionary perspectives. In: Jolivet P, Petitpierre E, Hsiao TS, eds. Biology of Chrysomelidae. Dordrecht, Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers, pp 1–24.
Jolley-Souders K (2001) Basic guide to in situ hybridization. Boekel Notes volume 1. Retrieved from http://www.grantlaboratory.com/pdf/guidehybrid.pdf 29/9/2005.
Juan C, Pons J, Petitpierre E (1993) Location of tandemly repeated DNA sequences in beetle chromosomes by fluorescent in situ hybridization. Chromosome Res 1: 167–174.
Jukes TH, Cantor CR (1969) Evolution of protein molecules. In: Munro HN, ed. Mammalian Protein Metabolism. New York: Academic Press, pp 21–132.
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of bases substitutions. J Mol Evol 16: 111–120.
Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M (1993) MEGA: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis. Version 1.01, University Park, PA: Pennsylvania State Univesity.
Lorite P, Palomeque T, Garnería I, Petitpierre E (2001) Characterization and chromosome location of satellite DNA in the leaf beetle Chrysolina americana (Coleoptera, Chrysomelidae). Genetica 110: 143–150.
Lorite P, Carrillo JA, Garnería I, Petitpierre E, Palomeque T (2002) Satellite DNA in the elm leaf beetle, Xanthogaleruca luteola (Coleoptera, Chrysomelidae): characterization, interpopulation analysis, and chromosome location. Cytogenet Genome Res 98: 302–307.
McClean P (1998). DNA — basics of structure and analysis. Nucleic acid hybridizations. Retrieved from http://www.ndsu.nodak.edu/instruct/mcclean/plsc731/dna/dna6.htm 29/9/2005.
Nei M (1987) Molecular Evolutionary Genetics. New York: Columbia University Press.
Pearson WR, Lipman DJ (1998) Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85: 2444–2448.
Petitpierre E (1975) Notes on chromosomes of ten species of the genus Chrysolina Mots. (Coleoptera, Chrysomelidae). Genetica 45: 349–354.
Petitpierre E (1981) New data on the cytology of Chrysolina Mots. and Oreina Chevr. (Coleoptera, Chrysomelidae). Genetica 54: 265–272.
Petitpierre E (1983) Karyometric differences among nine species of the genus Chrysolina Mots. (Coleoptera, Chrysomelidae). Can J Genet Cytol 25: 33–39.
Petitpierre E (1999) The cytogenetic and cytotaxonomy of Chrysolina Mots. and Oreina Chevr. (Coleoptera, Chrysomelidae, Chrysomelinae). Hereditas 131: 55–62.
Pinkel D, Straume T, Gray JM (1986) Cytogenetic analysis using quantitative, high sensitivity fluorescence hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83: 2934–2938.
Plohl M, Borstnik B, Lucijanic-Justic V, Ugarkovic Đ (1992) Evidence for random distribution of sequence variants in Tenebrio molitor satellite DNA. Genet Res 60: 7–13.
Pons J, Bruvo B, Juan C, Petitpierre E, Plohl M, Ugarkovic Đ (1997) Conservation of satellite DNA in species of the genus Pimelia (Tenebrionidae, Coleoptera). Gene 205: 183–190.
Pons J, Petitpierre E, Juan C (2002a) Evolutionary dynamic of satellite DNA family PIM357 in species of the genus Pimelia (Tenebrionidae, Coleoptera). Mol Biol Evol 19: 1329–1340.
Pons J, Juan C, Petitpierre E (2002b) Higher-order organization and compartmentalization of satellite DNA PIM357 in species of the coleopteran genus Pimelia. Chromosome Res 10: 597–606.
Pons J, Bucor R, Vogler AP (2003) Higher-order repeats in the satellite DNA of the cave beetle Pholeuon proserpinae glaciale (Coleoptera: Cholevidae). Hereditas 139: 28–34.
Rożek M, Lachowska D, Petitpierre E, Holecová M (2004) C-bands on chromosomes of 32 beetle species (Coleoptera: Elateridae, Cantharidae, Oedemeridae, Cerambycidae, Anthicidae, Chrysomelidae, Attelabidae and Curculionidae). Hereditas 150: 161–170.
Rozas J, Rozas R (1999) DnaSP version 3: and integrated program for molecular population genetics and molecular evolution analysis. Bioinformatics 15: 174–175.
Rudd KM, Willard HF (2004) Analysis of the centromeric regions of the human genome assembly. Trends Genet 20: 529–533.
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbour-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4: 406–425.
Smith GP (1976) Evolution of repeated DNA sequences by unequal crossover. Science 191: 528–535.
Smith SG, Virkki N (1978) Coleoptera. In: John B, ed. Animal Cytogenetics, vol. 3, Insecta 5. Berlin: G. Borntraeger.
Stephan W, Cho S (1994) Possible role of natural selection in the formation of tandem-repetitive noncoding DNA. Genetics 136: 333–341.
Strong DR, Lawton JL, Southwood TRE (1984) Insects on Plants: Community Patterns and Mechanisms. Cambridge: Harvard University Press.
Sumner AT (1972) A simple technique for demonstrating centromeric heterochromatin. Exp Cell Res 75: 304–306.
Sumner AT (1990) Banding with fluorochromes other than quinacrine. In: Hyman U, ed. Chromosome Banding. London: Unwin Hyman, pp 163–165.
Ugarković Đ, Plohl M (2002) Variation in satellite DNA profiles—causes and effects. EMBO J 21: 5955–5959.
Ugarkovic Đ, Petitpierre E, Juan C, Plohl M (1995) Satellite DNAs in Tenebrionid species: structure, organization and evolution. Croatica Chemica Acta 68: 627–638.
Virkki N (1984) Chromosomes in evolution of Coleoptera. In: Shama AK, Shama A, eds. Chromosomes in Evolution of Eukaryotic Groups, Vol. 2. Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press, pp 41–76.
Willard HF, Wayne JS (1987) Hierarchical order in chromosome-specific human alpha satellite DNA. Trends Genet 3: 192–198.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Palomeque, T., Muñoz-López, M., Carrillo, J.A. et al. Characterization and evolutionary dynamics of a complex family of satellite DNA in the leaf beetle Chrysolina carnifex (Coleoptera, Chrysomelidae). Chromosome Res 13, 795–807 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-005-1013-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-005-1013-6