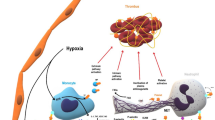
Abstract
Platelet activation and subsequent thrombus formation at sites of vascular injury is crucial for normal hemostasis, but it can also cause myocardial infarction and stroke. The initial capture of flowing platelets to the injured vessel wall is mediated by the interaction of the glycoprotein (GP) Ib-V-IX complex with von Willebrand factor immobilized on the exposed subendothelial extracellular matrix. Tethered platelets are then able to bind to collagens through the immunoglobulin-like receptor GPVI and to initiate cellular activation, a process that is reinforced by G protein-coupled receptors stimulated by locally produced thrombin and soluble mediators released from activated platelets. These signaling events lead to a rise in the cytosolic Ca2+ concentration, rearrangement of the cytoskeleton, release of granule content, and functional upregulation of integrin adhesion receptors allowing firm adhesion and thrombus growth. Fully activated platelets also undergo a procoagulant conversion thereby facilitating coagulation and thrombus stabilization. This review summarizes the most important receptor systems and signaling mechanisms involved in platelet activation and thrombus formation with special focus on recent discoveries.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ruggeri ZM (2002) Platelets in atherothrombosis. Nat Med 11:1227–1234
Gruner S, Prostredna M, Schulte V, Krieg T, Eckes B, Brakebusch C, Nieswandt B (2003) Multiple integrin–ligand interactions synergize in shear-resistant platelet adhesion at sites of arterial injury in vivo. Blood 12:4021–4027
Varga-Szabo D, Pleines I, Nieswandt B (2008) Cell adhesion mechanisms in platelets. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 3:403–412
Heemskerk JW, Kuijpers MJ, Munnix IC, Siljander PR (2005) Platelet collagen receptors and coagulation. A characteristic platelet response as possible target for antithrombotic treatment. Trends Cardiovasc Med 3:86–92
Whinna HC (2008) Overview of murine thrombosis models. Thromb Res 122:S64–S69
Braeuninger S, Kleinschnitz C (2009) Rodent models of focal cerebral ischemia: procedural pitfalls and translational problems. Exp Transl Stroke Med 1:8
Stoll G, Kleinschnitz C, Nieswandt B (2008) Molecular mechanisms of thrombus formation in ischemic stroke: novel insights and targets for treatment. Blood 9:3555–3562
Bluestein D, Niu L, Schoephoerster RT, Dewanjee MK (1997) Fluid mechanics of arterial stenosis: relationship to the development of mural thrombus. Ann Biomed Eng 2:344–356
Ruggeri ZM, Orje JN, Habermann R, Federici AB, Reininger AJ (2006) Activation-independent platelet adhesion and aggregation under elevated shear stress. Blood 6:1903–1910
Nesbitt WS, Westein E, Tovar-Lopez FJ, Tolouei E, Mitchell A, Fu J, Carberry J, Fouras A, Jackson SP (2009) A shear gradient-dependent platelet aggregation mechanism drives thrombus formation. Nat Med 6:665–673
Savage B, Saldivar E, Ruggeri ZM (1996) Initiation of platelet adhesion by arrest onto fibrinogen or translocation on von Willebrand factor. Cell 2:289–297
Canobbio I, Balduini C, Torti M (2004) Signalling through the platelet glycoprotein Ib-V-IX complex. Cell Signal 12:1329–1344
Ware J, Russell S, Ruggeri ZM (2000) Generation and rescue of a murine model of platelet dysfunction: the Bernard–Soulier syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 6:2803–2808
Kato K, Martinez C, Russell S, Nurden P, Nurden A, Fiering S, Ware J (2004) Genetic deletion of mouse platelet glycoprotein Ibbeta produces a Bernard–Soulier phenotype with increased alpha-granule size. Blood 8:2339–2344
Bergmeier W, Piffath CL, Goerge T, Cifuni SM, Ruggeri ZM, Ware J, Wagner DD (2006) The role of platelet adhesion receptor GPIbalpha far exceeds that of its main ligand, von Willebrand factor, in arterial thrombosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 45:16900–16905
Massberg S, Gawaz M, Gruner S, Schulte V, Konrad I, Zohlnhofer D, Heinzmann U, Nieswandt B (2003) A crucial role of glycoprotein VI for platelet recruitment to the injured arterial wall in vivo. J Exp Med 1:41–49
Wu D, Vanhoorelbeke K, Cauwenberghs N, Meiring M, Depraetere H, Kotze HF, Deckmyn H (2002) Inhibition of the von Willebrand (VWF)–collagen interaction by an antihuman VWF monoclonal antibody results in abolition of in vivo arterial platelet thrombus formation in baboons. Blood 10:3623–3628
Kleinschnitz C, De Meyer SF, Schwarz T, Austinat M, Vanhoorelbeke K, Nieswandt B, Deckmyn H, Stoll G (2009) Deficiency of von Willebrand factor protects mice from ischemic stroke. Blood 15:3600–3603
Kleinschnitz C, Pozgajova M, Pham M, Bendszus M, Nieswandt B, Stoll G (2007) Targeting platelets in acute experimental stroke: impact of glycoprotein Ib, VI, and IIb/IIIa blockade on infarct size, functional outcome, and intracranial bleeding. Circulation 17:2323–2330
Elvers M, Stegner D, Hagedorn I, Kleinschnitz C, Braun A, Kuijpers ME, Boesl M, Chen Q, Heemskerk JW, Stoll G, Frohman MA, Nieswandt B (2010) Impaired alpha(IIb)beta(3) integrin activation and shear-dependent thrombus formation in mice lacking phospholipase D1. Sci Signal 103:ra1
McDermott M, Wakelam MJ, Morris AJ (2004) Phospholipase D. Biochem Cell Biol 1:225–253
Vorland M, Holmsen H (2008) Phospholipase D in human platelets: presence of isoenzymes and participation of autocrine stimulation during thrombin activation. Platelets 3:211–224
Martinson EA, Scheible S, Greinacher A, Presek P (1995) Platelet phospholipase D is activated by protein kinase C via an integrin alpha IIb beta 3-independent mechanism. Biochem J 310:623–628
Offermanns S (2006) Activation of platelet function through G protein-coupled receptors. Circ Res 12:1293–1304
Offermanns S, Toombs CF, Hu YH, Simon MI (1997) Defective platelet activation in G alpha(q)-deficient mice. Nature 6647:183–186
Hart MJ, Jiang X, Kozasa T, Roscoe W, Singer WD, Gilman AG, Sternweis PC, Bollag G (1998) Direct stimulation of the guanine nucleotide exchange activity of p115 RhoGEF by Galpha13. Science 5372:2112–2114
Cantley LC (2002) The phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway. Science 5573:1655–1657
Nieswandt B, Watson SP (2003) Platelet–collagen interaction: is GPVI the central receptor? Blood 2:449–461
Watson SP, Herbert JM, Pollitt AY (2010) GPVI and CLEC-2 in haemostasis and vascular integrity. J Thromb Haemost 7:1456–1467
Dumont B, Lasne D, Rothschild C, Bouabdelli M, Ollivier V, Oudin C, Ajzenberg N, Grandchamp B, Jandrot-Perrus M (2009) Absence of collagen-induced platelet activation caused by compound heterozygous GPVI mutations. Blood 9:1900–1903
Hermans C, Wittevrongel C, Thys C, Smethurst PA, Van GC, Freson K (2009) A compound heterozygous mutation in glycoprotein VI in a patient with a bleeding disorder. J Thromb Haemost 8:1356–1363
Moroi M, Jung SM, Okuma M, Shinmyozu K (1989) A patient with platelets deficient in glycoprotein VI that lack both collagen-induced aggregation and adhesion. J Clin Invest 5:1440–1445
Boylan B, Chen H, Rathore V, Paddock C, Salacz M, Friedman KD, Curtis BR, Stapleton M, Newman DK, Kahn ML, Newman PJ (2004) Anti-GPVI-associated ITP: an acquired platelet disorder caused by autoantibody-mediated clearance of the GPVI/FcRgamma-chain complex from the human platelet surface. Blood 5:1350–1355
Nieswandt B, Schulte V, Bergmeier W, Mokhtari-Nejad R, Rackebrandt K, Cazenave JP, Ohlmann P, Gachet C, Zirngibl H (2001) Long-term antithrombotic protection by in vivo depletion of platelet glycoprotein VI in mice. J Exp Med 4:459–469
Schulte V, Rabie T, Prostredna M, Aktas B, Gruner S, Nieswandt B (2003) Targeting of the collagen-binding site on glycoprotein VI is not essential for in vivo depletion of the receptor. Blood 10:3948–3952
Lecut C, Schoolmeester A, Kuijpers MJ, Broers JL, van Zandvoort MA, Vanhoorelbeke K, Deckmyn H, Jandrot-Perrus M, Heemskerk JW (2004) Principal role of glycoprotein VI in alpha2beta1 and alphaIIbbeta3 activation during collagen-induced thrombus formation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 9:1727–1733
Konishi H, Katoh Y, Takaya N, Kashiwakura Y, Itoh S, Ra C, Daida H (2002) Platelets activated by collagen through immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif play pivotal role in initiation and generation of neointimal hyperplasia after vascular injury. Circulation 8:912–916
Konstantinides S, Ware J, Marchese P, mus-Jacobs F, Loskutoff DJ, Ruggeri ZM (2006) Distinct antithrombotic consequences of platelet glycoprotein Ibalpha and VI deficiency in a mouse model of arterial thrombosis. J Thromb Haemost 9:2014–2021
Holtkotter O, Nieswandt B, Smyth N, Muller W, Hafner M, Schulte V, Krieg T, Eckes B (2002) Integrin alpha 2-deficient mice develop normally, are fertile, but display partially defective platelet interaction with collagen. J Biol Chem 13:10789–10794
Gruner S, Prostredna M, Aktas B, Moers A, Schulte V, Krieg T, Offermanns S, Eckes B, Nieswandt B (2004) Anti-glycoprotein VI treatment severely compromises hemostasis in mice with reduced alpha2beta1 levels or concomitant aspirin therapy. Circulation 18:2946–2951
Suzuki-Inoue K, Fuller GL, Garcia A, Eble JA, Pohlmann S, Inoue O, Gartner TK, Hughan SC, Pearce AC, Laing GD, Theakston RD, Schweighoffer E, Zitzmann N, Morita T, Tybulewicz VL, Ozaki Y, Watson SP (2006) A novel Syk-dependent mechanism of platelet activation by the C-type lectin receptor CLEC-2. Blood 2:542–549
Uhrin P, Zaujec J, Breuss JM, Olcaydu D, Chrenek P, Stockinger H, Fuertbauer E, Moser M, Haiko P, Fassler R, Alitalo K, Binder BR, Kerjaschki D (2010) Novel function for blood platelets and podoplanin in developmental separation of blood and lymphatic circulation. Blood 19:3997–4005
Bertozzi CC, Schmaier AA, Mericko P, Hess PR, Zou Z, Chen M, Chen CY, Xu B, Lu MM, Zhou D, Sebzda E, Santore MT, Merianos DJ, Stadtfeld M, Flake AW, Graf T, Skoda R, Maltzman JS, Koretzky GA, Kahn ML (2010) Platelets regulate lymphatic vascular development through CLEC-2-SLP-76 signaling. Blood 4:661–670
May F, Hagedorn I, Pleines I, Bender M, Vogtle T, Eble J, Elvers M, Nieswandt B (2009) CLEC-2 is an essential platelet-activating receptor in hemostasis and thrombosis. Blood 16:3464–3472
Suzuki-Inoue K, Inoue O, Ding G, Nishimura S, Hokamura K, Eto K, Kashiwagi H, Tomiyama Y, Yatomi Y, Umemura K, Shin Y, Hirashima M, Ozaki Y (2010) Essential in vivo roles of the c-type lectin receptor CLEC-2: embryonic/neonatal lethality of CLEC-2-deficient mice by blood/lymphatic misconnections and impaired thrombus formation of CLEC-2-deficient platelets. J Biol Chem 32:24494–24507
Cicmil M, Thomas JM, Leduc M, Bon C, Gibbins JM (2002) Platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 signaling inhibits the activation of human platelets. Blood 1:137–144
Barrow AD, Trowsdale J (2006) You say ITAM and I say ITIM, let’s call the whole thing off: the ambiguity of immunoreceptor signalling. Eur J Immunol 7:1646–1653
Patil S, Newman DK, Newman PJ (2001) Platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 serves as an inhibitory receptor that modulates platelet responses to collagen. Blood 6:1727–1732
Wong C, Liu Y, Yip J, Chand R, Wee JL, Oates L, Nieswandt B, Reheman A, Ni H, Beauchemin N, Jackson DE (2009) CEACAM1 negatively regulates platelet–collagen interactions and thrombus growth in vitro and in vivo. Blood 8:1818–1828
Newland SA, Macaulay IC, Floto AR, de Vet EC, Ouwehand WH, Watkins NA, Lyons PA, Campbell DR (2007) The novel inhibitory receptor G6B is expressed on the surface of platelets and attenuates platelet function in vitro. Blood 11:4806–4809
Washington AV, Schubert RL, Quigley L, Disipio T, Feltz R, Cho EH, McVicar DW (2004) A TREM family member, TLT-1, is found exclusively in the alpha-granules of megakaryocytes and platelets. Blood 4:1042–1047
Lewandrowski U, Wortelkamp S, Lohrig K, Zahedi RP, Wolters DA, Walter U, Sickmann A (2009) Platelet membrane proteomics: a novel repository for functional research. Blood 1:e10–e19
Murugappa S, Kunapuli SP (2006) The role of ADP receptors in platelet function. Front Biosci 11:1977–1986
Hechler B, Leon C, Vial C, Vigne P, Frelin C, Cazenave JP, Gachet C (1998) The P2Y1 receptor is necessary for adenosine 5′-diphosphate-induced platelet aggregation. Blood 1:152–159
Leon C, Hechler B, Freund M, Eckly A, Vial C, Ohlmann P, Dierich A, LeMeur M, Cazenave JP, Gachet C (1999) Defective platelet aggregation and increased resistance to thrombosis in purinergic P2Y(1) receptor-null mice. J Clin Invest 12:1731–1737
Hechler B, Zhang Y, Eckly A, Cazenave JP, Gachet C, Ravid K (2003) Lineage-specific overexpression of the P2Y1 receptor induces platelet hyper-reactivity in transgenic mice. J Thromb Haemost 1:155–163
Porto I, Giubilato S, De Maria GL, Biasucci LM, Crea F (2009) Platelet P2Y12 receptor inhibition by thienopyridines: status and future. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 9:1317–1332
Hollopeter G, Jantzen HM, Vincent D, Li G, England L, Ramakrishnan V, Yang RB, Nurden P, Nurden A, Julius D, Conley PB (2001) Identification of the platelet ADP receptor targeted by antithrombotic drugs. Nature 6817:202–207
Cattaneo M, Zighetti ML, Lombardi R, Martinez C, Lecchi A, Conley PB, Ware J, Ruggeri ZM (2003) Molecular bases of defective signal transduction in the platelet P2Y12 receptor of a patient with congenital bleeding. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 4:1978–1983
Andre P, Prasad KS, Denis CV, He M, Papalia JM, Hynes RO, Phillips DR, Wagner DD (2002) CD40L stabilizes arterial thrombi by a beta3 integrin-dependent mechanism. Nat Med 3:247–252
Hechler B, Lenain N, Marchese P, Vial C, Heim V, Freund M, Cazenave JP, Cattaneo M, Ruggeri ZM, Evans R, Gachet C (2003) A role of the fast ATP-gated P2X1 cation channel in thrombosis of small arteries in vivo. J Exp Med 4:661–667
Oury C, Toth-Zsamboki E, Vermylen J, Hoylaerts MF (2002) P2X(1)-mediated activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2 contributes to platelet secretion and aggregation induced by collagen. Blood 7:2499–2505
Vane JR, Botting RM (1998) Anti-inflammatory drugs and their mechanism of action. Inflamm Res 47:S78–S87
Antithromobotic Trialists’ Collaboration (2002) Collaborative meta-analysis of randomised trials of antiplatelet therapy for prevention of death, myocardial infarction, and stroke in high risk patients. BMJ 324(7329):71–86
Thomas DW, Mannon RB, Mannon PJ, Latour A, Oliver JA, Hoffman M, Smithies O, Koller BH, Coffman TM (1998) Coagulation defects and altered hemodynamic responses in mice lacking receptors for thromboxane A2. J Clin Invest 11:1994–2001
Mackman N (2004) Role of tissue factor in hemostasis, thrombosis, and vascular development. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 6:1015–1022
Ahamed J, Versteeg HH, Kerver M, Chen VM, Mueller BM, Hogg PJ, Ruf W (2006) Disulfide isomerization switches tissue factor from coagulation to cell signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 38:13932–13937
Cho J, Furie BC, Coughlin SR, Furie B (2008) A critical role for extracellular protein disulfide isomerase during thrombus formation in mice. J Clin Invest 3:1123–1131
Pendurthi UR, Ghosh S, Mandal SK, Rao LV (2007) Tissue factor activation: is disulfide bond switching a regulatory mechanism? Blood 12:3900–3908
Siljander PR, Munnix IC, Smethurst PA, Deckmyn H, Lindhout T, Ouwehand WH, Farndale RW, Heemskerk JW (2004) Platelet receptor interplay regulates collagen-induced thrombus formation in flowing human blood. Blood 4:1333–1341
Muller F, Mutch NJ, Schenk WA, Smith SA, Esterl L, Spronk HM, Schmidbauer S, Gahl WA, Morrissey JH, Renne T (2009) Platelet polyphosphates are proinflammatory and procoagulant mediators in vivo. Cell 6:1143–1156
Kannemeier C, Shibamiya A, Nakazawa F, Trusheim H, Ruppert C, Markart P, Song Y, Tzima E, Kennerknecht E, Niepmann M, von Bruehl ML, Sedding D, Massberg S, Gunther A, Engelmann B, Preissner KT (2007) Extracellular RNA constitutes a natural procoagulant cofactor in blood coagulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 15:6388–6393
Wang T, Zhao H, Ren H, Guo J, Xu M, Yang R, Han ZC (2005) Type 1 and type 2 T-cell profiles in idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Haematologica 7:914–923
Renne T, Pozgajova M, Gruner S, Schuh K, Pauer HU, Burfeind P, Gailani D, Nieswandt B (2005) Defective thrombus formation in mice lacking coagulation factor XII. J Exp Med 2:271–281
Kleinschnitz C, Stoll G, Bendszus M, Schuh K, Pauer HU, Burfeind P, Renne C, Gailani D, Nieswandt B, Renne T (2006) Targeting coagulation factor XII provides protection from pathological thrombosis in cerebral ischemia without interfering with hemostasis. J Exp Med 3:513–518
Cheng Q, Tucker EI, Pine MS, Sisler I, Matafonov A, Sun MF, White-Adams TC, Smith SA, Hanson SR, McCarty OJ, Renne T, Gruber A, Gailani D (2010) A role for factor XIIa-mediated factor XI activation in thrombus formation in vivo. Blood. doi:10.1182/blood-2010-02-270918
Hagedorn I, Schmidbauer S, Pleines I, Kleinschnitz C, Kronthaler U, Stoll G, Dickneite G, Nieswandt B (2010) Factor XIIa inhibitor recombinant human albumin Infestin-4 abolishes occlusive arterial thrombus formation without affecting bleeding. Circulation 13:1510–1517
Salomon O, Steinberg DM, Koren-Morag N, Tanne D, Seligsohn U (2008) Reduced incidence of ischemic stroke in patients with severe factor XI deficiency. Blood 8:4113–4117
Perzborn E, Roehrig S, Straub A, Kubitza D, Mueck W, Laux V (2010) Rivaroxaban: a new oral factor Xa inhibitor. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 3:376–381
Roser-Jones C, Becker RC (2010) Apixaban: an emerging oral factor Xa inhibitor. J Thromb Thrombolysis 1:141–146
Smyth SS, Woulfe DS, Weitz JI, Gachet C, Conley PB, Goodman SG, Roe MT, Kuliopulos A, Moliterno DJ, French PA, Steinhubl SR, Becker RC (2009) G-protein-coupled receptors as signaling targets for antiplatelet therapy. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 4:449–457
Coughlin SR (2000) Thrombin signalling and protease-activated receptors. Nature 6801:258–264
Sambrano GR, Weiss EJ, Zheng YW, Huang W, Coughlin SR (2001) Role of thrombin signalling in platelets in haemostasis and thrombosis. Nature 6851:74–78
Nakanishi-Matsui M, Zheng YW, Sulciner DJ, Weiss EJ, Ludeman MJ, Coughlin SR (2000) PAR3 is a cofactor for PAR4 activation by thrombin. Nature 6778:609–613
Kahn ML, Zheng YW, Huang W, Bigornia V, Zeng D, Moff S, Farese RV Jr, Tam C, Coughlin SR (1998) A dual thrombin receptor system for platelet activation. Nature 6694:690–694
Kahn ML, Nakanishi-Matsui M, Shapiro MJ, Ishihara H, Coughlin SR (1999) Protease-activated receptors 1 and 4 mediate activation of human platelets by thrombin. J Clin Invest 6:879–887
Leger AJ, Jacques SL, Badar J, Kaneider NC, Derian CK, Andrade-Gordon P, Covic L, Kuliopulos A (2006) Blocking the protease-activated receptor 1–4 heterodimer in platelet-mediated thrombosis. Circulation 9:1244–1254
De ML, Mazzucato M, Masotti A, Ruggeri ZM (1994) Localization and characterization of an alpha-thrombin-binding site on platelet glycoprotein Ib alpha. J Biol Chem 9:6478–6484
Ramakrishnan V, Deguzman F, Bao M, Hall SW, Leung LL, Phillips DR (2001) A thrombin receptor function for platelet glycoprotein Ib-IX unmasked by cleavage of glycoprotein V. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 4:1823–1828
Hamilton JR, Cornelissen I, Coughlin SR (2004) Impaired hemostasis and protection against thrombosis in protease-activated receptor 4-deficient mice is due to lack of thrombin signaling in platelets. J Thromb Haemost 8:1429–1435
Yang J, Wu J, Kowalska MA, Dalvi A, Prevost N, O’Brien PJ, Manning D, Poncz M, Lucki I, Blendy JA, Brass LF (2000) Loss of signaling through the G protein, Gz, results in abnormal platelet activation and altered responses to psychoactive drugs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 18:9984–9989
Pozgajova M, Sachs UJ, Hein L, Nieswandt B (2006) Reduced thrombus stability in mice lacking the alpha2A-adrenergic receptor. Blood 2:510–514
Fabre JE, Nguyen M, Athirakul K, Coggins K, McNeish JD, Austin S, Parise LK, FitzGerald GA, Coffman TM, Koller BH (2001) Activation of the murine EP3 receptor for PGE2 inhibits cAMP production and promotes platelet aggregation. J Clin Invest 5:603–610
Ma H, Hara A, Xiao CY, Okada Y, Takahata O, Nakaya K, Sugimoto Y, Ichikawa A, Narumiya S, Ushikubi F (2001) Increased bleeding tendency and decreased susceptibility to thromboembolism in mice lacking the prostaglandin E receptor subtype EP(3). Circulation 10:1176–1180
Jackson SF, Schoenwaelder SM (2006) Type I phosphoinositide 3-kinases: potential antithrombotic targets? Cell Mol Life Sci 10:1085–1090
Schwarz UR, Walter U, Eigenthaler M (2001) Taming platelets with cyclic nucleotides. Biochem Pharmacol 9:1153–1161
Puri RN (1998) Phospholipase A2: its role in ADP- and thrombin-induced platelet activation mechanisms. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 10:1107–1122
Brass LF, Zhu L, Stalker TJ (2005) Minding the gaps to promote thrombus growth and stability. J Clin Invest 12:3385–3392
Varga-Szabo D, Braun A, Nieswandt B (2009) Calcium signaling in platelets. J Thromb Haemost 7:1057–1066
Liou J, Kim ML, Heo WD, Jones JT, Myers JW, Ferrell JE Jr, Meyer T (2005) STIM is a Ca2+ sensor essential for Ca2+ -store-depletion-triggered Ca2+ influx. Curr Biol 13:1235–1241
Roos J, DiGregorio PJ, Yeromin AV, Ohlsen K, Lioudyno M, Zhang S, Safrina O, Kozak JA, Wagner SL, Cahalan MD, Velicelebi G, Stauderman KA (2005) STIM1, an essential and conserved component of store-operated Ca2+ channel function. J Cell Biol 3:435–445
Grosse J, Braun A, Varga-Szabo D, Beyersdorf N, Schneider B, Zeitlmann L, Hanke P, Schropp P, Muhlstedt S, Zorn C, Huber M, Schmittwolf C, Jagla W, Yu P, Kerkau T, Schulze H, Nehls M, Nieswandt B (2007) An EF hand mutation in Stim1 causes premature platelet activation and bleeding in mice. J Clin Invest 11:3540–3550
Varga-Szabo D, Braun A, Kleinschnitz C, Bender M, Pleines I, Pham M, Renne T, Stoll G, Nieswandt B (2008) The calcium sensor STIM1 is an essential mediator of arterial thrombosis and ischemic brain infarction. J Exp Med 7:1583–1591
Braun A, Varga-Szabo D, Kleinschnitz C, Pleines I, Bender M, Austinat M, Bosl M, Stoll G, Nieswandt B (2009) Orai1 (CRACM1) is the platelet SOC channel and essential for pathological thrombus formation. Blood 9:2056–2063
Bergmeier W, Oh-Hora M, McCarl CA, Roden RC, Bray PF, Feske S (2009) R93W mutation in Orai1 causes impaired calcium influx in platelets. Blood 3:675–678
Rosado JA, Sage SO (2001) Activation of store-mediated calcium entry by secretion-like coupling between the inositol 1, 4, 5-trisphosphate receptor type II and human transient receptor potential (hTrp1) channels in human platelets. Biochem J Pt 1:191–198
Varga-Szabo D, Authi KS, Braun A, Bender M, Ambily A, Hassock SR, Gudermann T, Dietrich A, Nieswandt B (2008) Store-operated Ca(2+) entry in platelets occurs independently of transient receptor potential (TRP) C1. Pflugers Arch 2:377–387
Gilio K, van Kruchten R, Braun A, Berna-Erro A, Feijge MA, Stegner D, van der Meijden PE, Kuijpers MJ, Varga-Szabo D, Heemskerk JW, Nieswandt B (2010) Roles of platelet STIM1 and Orai1 in glycoprotein VI- and thrombin-dependent procoagulant activity and thrombus formation. J Biol Chem 31:23629–23638
Harper MT, Poole AW (2010) Diverse functions of protein kinase C isoforms in platelet activation and thrombus formation. J Thromb Haemost 3:454–462
Konopatskaya O, Gilio K, Harper MT, Zhao Y, Cosemans JM, Karim ZA, Whiteheart SW, Molkentin JD, Verkade P, Watson SP, Heemskerk JW, Poole AW (2009) PKCalpha regulates platelet granule secretion and thrombus formation in mice. J Clin Invest 2:399–407
Kawasaki H, Springett GM, Toki S, Canales JJ, Harlan P, Blumenstiel JP, Chen EJ, Bany IA, Mochizuki N, Ashbacher A, Matsuda M, Housman DE, Graybiel AM (1998) A Rap guanine nucleotide exchange factor enriched highly in the basal ganglia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 22:13278–13283
Stefanini L, Roden RC, Bergmeier W (2009) CalDAG-GEFI is at the nexus of calcium-dependent platelet activation. Blood 12:2506–2514
Cifuni SM, Wagner DD, Bergmeier W (2008) CalDAG-GEFI and protein kinase C represent alternative pathways leading to activation of integrin alphaIIbbeta3 in platelets. Blood 5:1696–1703
Chrzanowska-Wodnicka M, Smyth SS, Schoenwaelder SM, Fischer TH, White GC (2005) Rap1b is required for normal platelet function and hemostasis in mice. J Clin Invest 3:680–687
Lafuente EM, van Puijenbroek AA, Krause M, Carman CV, Freeman GJ, Berezovskaya A, Constantine E, Springer TA, Gertler FB, Boussiotis VA (2004) RIAM, an Ena/VASP and Profilin ligand, interacts with Rap1-GTP and mediates Rap1-induced adhesion. Dev Cell 4:585–595
Han J, Lim CJ, Watanabe N, Soriani A, Ratnikov B, Calderwood DA, Puzon-McLaughlin W, Lafuente EM, Boussiotis VA, Shattil SJ, Ginsberg MH (2006) Reconstructing and deconstructing agonist-induced activation of integrin alphaIIbbeta3. Curr Biol 18:1796–1806
Watanabe N, Bodin L, Pandey M, Krause M, Coughlin S, Boussiotis VA, Ginsberg MH, Shattil SJ (2008) Mechanisms and consequences of agonist-induced talin recruitment to platelet integrin alphaIIbbeta3. J Cell Biol 7:1211–1222
Crittenden JR, Bergmeier W, Zhang Y, Piffath CL, Liang Y, Wagner DD, Housman DE, Graybiel AM (2004) CalDAG-GEFI integrates signaling for platelet aggregation and thrombus formation. Nat Med 9:982–986
Santoro SA (1986) Identification of a 160, 000 dalton platelet membrane protein that mediates the initial divalent cation-dependent adhesion of platelets to collagen. Cell 6:913–920
Nieswandt B, Brakebusch C, Bergmeier W, Schulte V, Bouvard D, Mokhtari-Nejad R, Lindhout T, Heemskerk JW, Zirngibl H, Fassler R (2001) Glycoprotein VI but not alpha2beta1 integrin is essential for platelet interaction with collagen. EMBO J 9:2120–2130
Chen H, Locke D, Liu Y, Liu C, Kahn ML (2002) The platelet receptor GPVI mediates both adhesion and signaling responses to collagen in a receptor density-dependent fashion. J Biol Chem 4:3011–3019
Nurden AT (2006) Glanzmann thrombasthenia. Orphanet J Rare Dis 1:10
Tronik-Le RD, Roullot V, Poujol C, Kortulewski T, Nurden P, Marguerie G (2000) Thrombasthenic mice generated by replacement of the integrin alpha(IIb) gene: demonstration that transcriptional activation of this megakaryocytic locus precedes lineage commitment. Blood 4:1399–1408
Hodivala-Dilke KM, McHugh KP, Tsakiris DA, Rayburn H, Crowley D, Ullman-Cullere M, Ross FP, Coller BS, Teitelbaum S, Hynes RO (1999) Beta3-integrin-deficient mice are a model for Glanzmann thrombasthenia showing placental defects and reduced survival. J Clin Invest 2:229–238
Maia F, Sa FC, Feres F (2009) Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitors in clinical practice. Arq Bras Cardiol 1:68–76
Suh TT, Holmback K, Jensen NJ, Daugherty CC, Small K, Simon DI, Potter S, Degen JL (1995) Resolution of spontaneous bleeding events but failure of pregnancy in fibrinogen-deficient mice. Genes Dev 16:2020–2033
Ruggeri ZM, Dent JA, Saldivar E (1999) Contribution of distinct adhesive interactions to platelet aggregation in flowing blood. Blood 1:172–178
Ni H, Denis CV, Subbarao S, Degen JL, Sato TN, Hynes RO, Wagner DD (2000) Persistence of platelet thrombus formation in arterioles of mice lacking both von Willebrand factor and fibrinogen. J Clin Invest 3:385–392
Prasad KS, Andre P, He M, Bao M, Manganello J, Phillips DR (2003) Soluble CD40 ligand induces beta3 integrin tyrosine phosphorylation and triggers platelet activation by outside-in signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 21:12367–12371
Kasirer-Friede A, Ruggeri ZM, Shattil SJ (2010) Role for ADAP in shear flow-induced platelet mechanotransduction. Blood 11:2274–2282
Lee HS, Lim CJ, Puzon-McLaughlin W, Shattil SJ, Ginsberg MH (2009) RIAM activates integrins by linking talin to ras GTPase membrane-targeting sequences. J Biol Chem 8:5119–5127
Nieswandt B, Moser M, Pleines I, Varga-Szabo D, Monkley S, Critchley D, Fassler R (2007) Loss of talin1 in platelets abrogates integrin activation, platelet aggregation, and thrombus formation in vitro and in vivo. J Exp Med 13:3113–3118
Petrich BG, Marchese P, Ruggeri ZM, Spiess S, Weichert RA, Ye F, Tiedt R, Skoda RC, Monkley SJ, Critchley DR, Ginsberg MH (2007) Talin is required for integrin-mediated platelet function in hemostasis and thrombosis. J Exp Med 13:3103–3111
Tadokoro S, Shattil SJ, Eto K, Tai V, Liddington RC, de Pereda JM, Ginsberg MH, Calderwood DA (2003) Talin binding to integrin beta tails: a final common step in integrin activation. Science 5642:103–106
Martel V, Racaud-Sultan C, Dupe S, Marie C, Paulhe F, Galmiche A, Block MR, Albiges-Rizo C (2001) Conformation, localization, and integrin binding of talin depend on its interaction with phosphoinositides. J Biol Chem 24:21217–21227
Honda A, Nogami M, Yokozeki T, Yamazaki M, Nakamura H, Watanabe H, Kawamoto K, Nakayama K, Morris AJ, Frohman MA, Kanaho Y (1999) Phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate 5-kinase alpha is a downstream effector of the small G protein ARF6 in membrane ruffle formation. Cell 5:521–532
Powner DJ, Pettitt TR, Anderson R, Nash GB, Wakelam MJ (2007) Stable adhesion and migration of human neutrophils requires phospholipase D-mediated activation of the integrin CD11b/CD18. Mol Immunol 12:3211–3221
Holinstat M, Preininger AM, Milne SB, Hudson WJ, Brown HA, Hamm HE (2009) Irreversible platelet activation requires protease-activated receptor 1-mediated signaling to phosphatidylinositol phosphates. Mol Pharmacol 2:301–313
Moser M, Nieswandt B, Ussar S, Pozgajova M, Fassler R (2008) Kindlin-3 is essential for integrin activation and platelet aggregation. Nat Med 3:325–330
Malinin NL, Zhang L, Choi J, Ciocea A, Razorenova O, Ma YQ, Podrez EA, Tosi M, Lennon DP, Caplan AI, Shurin SB, Plow EF, Byzova TV (2009) A point mutation in KINDLIN3 ablates activation of three integrin subfamilies in humans. Nat Med 3:313–318
Svensson L, Howarth K, McDowall A, Patzak I, Evans R, Ussar S, Moser M, Metin A, Fried M, Tomlinson I, Hogg N (2009) Leukocyte adhesion deficiency-III is caused by mutations in KINDLIN3 affecting integrin activation. Nat Med 3:306–312
Moser M, Bauer M, Schmid S, Ruppert R, Schmidt S, Sixt M, Wang HV, Sperandio M, Fassler R (2009) Kindlin-3 is required for beta2 integrin-mediated leukocyte adhesion to endothelial cells. Nat Med 3:300–305
Acknowledgments
Our work cited in this review was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (SFB 688 and 487) and the Rudolf Virchow Center. D.S. was supported by a grant of the German Excellence Initiative to the Graduate School of Life Sciences, University of Würzburg. We thank Markus Bender and Ina Hagedorn for proofreading the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stegner, D., Nieswandt, B. Platelet receptor signaling in thrombus formation. J Mol Med 89, 109–121 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-010-0691-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-010-0691-5