Abstract
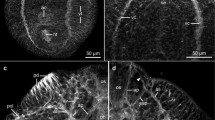
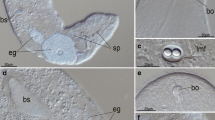
The nervous system (NS) ofDugesia tigrina has been studied by immunocytochemical double-staining, using the authentic flatworm neuropeptide, neuropeptide F (NPF), and serotonin (5-HT) on cryosections. This technique provides a precise morphological (descriptive) account of the NS. The results show that the central nervous system is shaped like a horseshoe. The brain is composed of two lateral lobes connected by three commissures, one antero-dorsal in front of the cerebral eyes and two, more ventral, behind the eyes. The pair of main nerve cords extend from the lateral lobes of the brain to the tail end of the worm. Cross sections reveal a very close contact between lateral branches from the main cords and the submuscular plexus. Thin cord-like lateral nerves are formed by longitudinal plexal fibres. No dorsal cords were observed. The patterns of immunoreactivity to NPF and 5-HT differ from each other in several respects. In the walls of gut diverticula only NPF immunoreactive (IR) cells and fibres were observed. Only NPF-immunoreactive cells occur in the parenchyma along dorso-ventral nerve fibres connecting the dorsal and ventral parts of the submuscular plexus. The number of 5-HT-immunoreactive cells associated with the main nerve cords (MCs) is greater than that of the NPF-immunoreactive cells, and the spongy structure of the MCs is more apparent following immunostaining for 5-HT. Thin 5-HT-immunoreactive fibres were observed in the subepithelial plexus, penetrating the basal lamina and innervating a rhabdite-free ventro-lateral sensory area along the body periphery. The correspondence between MCs in the lower flatworms (Catenulida and Macrostomida) and the Seriata (Tricladida and Proseriata) confirms the status of the MCs in flatworms as the most important and stable neuronal characteristic, and constitutes support for the hypothesized common origin of the MCs in flatworms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bagunà, J., and Ballester, R. (1978) The nervous system in planarians: peripheral and gastrodermal plexuses, pharynx innervation, and the relationship between central nervous system and the acoelomate organization.J. Morphol.,155, 237–252.
Ball, I. R. (1981) The phyletic status of the Paludicola.Hydrobiologia,84, 7–12
Bautz, A. and Schilt, J. (1986) Somatostatin-like peptide and regeneration capacities in planarians.Gen. Comp. Endocrinol.,64, 267–272.
Bullock, T. H., and Horridge, G. A. (1965)Structure and function in the nervous systems of invertebrates, Vol. I. San Francisco: W. H. Freeman and Co.
Coons, A. H., Leduc, E. H. and Conolly, J. M. (1955) Studies on antibody production I. A method for the histochemical demonstration of specific antibody and its application to a study of the hyperimmune rabbit.J. Exp. Med. 102, 49–60.
Cyr, D., Gruner, S. and Mettrick, D. F. (1983)Hymenolepis diminuta: uptake of 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin), glucose, and changes in worm glycogen levels.Can. J. Zool.,61, 1469–1474.
Ehlers, U. (1985) Das Phylogenetische System des Plathelminthes. Stuttgart/New York: Gustav Fischer.
Eriksson, K. S., and Panula, P. (1994) Gamma-aminobutyric acid in the nervous system of a planarian.J. Comp. Neurol.,345, 528–536.
Eriksson, K., Gustafsson, M. K. S. and Åkerlind, G. (1993) Highperformance liquid chromatographic analysis of monoamines in the cestodeDiphyllobothrium dendriticum.Parasitol. Res.,79, 699–702.
Eriksson, K., Panula, P. and Reuter, M. (1995) GABA in the nervous system of the planarianPolycelis nigra.Hydrobiologia,305, 285–289.
Gustafsson, M. K. S. (1987) Immunocytochemical demonstration of neuropeptides and serotonin in the nervous system of adultSchistosoma mansoni.Parasitol. Res.,74, 168–174.
Gustafsson, M.K.S. (1992) The neuroanatomy of parasitic flatworms.Adv. Neuroimmunol.,2, 267–286.
Gustafsson, M. K. S., Halton, D. W., Maule, A. G., Reuter, M. and Shaw, C. (1994) The gull-tapeworm,Diphyllobothrium dendriticum and neuropeptide F: an immunocytochemical study.Parasitology,109, 599–609.
Gustafsson, M. K. S., Fagerholm, H.-P., Halton, D. W., Hanzelova, V., Maule, A. G., Reuter M. and Shaw, C. (1995) Neuropeptides and serotonin in the cestodeProteocephalus exiguus: an immunocytochemical study.Int. J. Parasitol.,25, 673–682.
Halton, D. W., Shaw, C., Maule, A. G. and Smart, D. (1994) Regulatory peptides in helminth parasites.Adv. Parasitol.,34, 163–227.
Hanström, B. (1926) Über den feineren Bau des Nervensystems der Tricladen Turbellarien auf Grund von Untersuchungen anBdelloura Candida.Acta Zool. (Stockh.),7, 101–115.
Hyman, L. H. (1951)The Invertebrates. II. Platyhelminthes and Rhynchocoela.The acoelomate Bilateria. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Joffe, B. I. and Reuter, M. (1993) The nervous system ofBothriomolus balticus (Proseriata) — a contribution to the knowledge of the orthogon in the Plathelminthes.Zoomorphology,113, 113–127.
Kabotyanski, E. A., Nezlin, L. P. and Sakharov, D. A. (1991) Serotonin neurons in planarian pharynx.Stud. Neurosci.,13, 138–152.
Kotikova, E. A. (1986) Comparative characterization of the nervous system of the Turbellaria.Hydrobiologia.,132, 89–92.
Lentz, T. (1968) Histochemical localization of acetylcholinesterase activity in a planarian.Comp. Biochem. Physiol.,27, 713–718.
Maickel, R. P., Cox, R. H., Saillant, J. R. J. and Miller, F. P. (1968) A method for the determination of serotonin and norepinephrine in discrete areas of rat brain.Int. J. Neuropharm.,7, 272–281.
Mansour, T. E. (1979) Chemotherapy of parasitic worms: new biochemical strategies.Science,205, 462–469.
Mansour, T. E. (1984) Serotonin receptors in parasitic worms.Adv. Parasitol,23, 1–36.
Martelly, I., Moraczewski, J., Franquinet, R. and Castagna, M. (1987) Protein kinase C activity in a freshwater planarian (Dugesia gonocephala).Comp. Biochem. Physiol.,86B, 405–409.
Maule, A. G., Shaw, C., Halton, D. W., Thim, L., Johnston, C. F., Fairweather, I. and Buchanan, K. D. (1991) Neuropeptide F: a novel parasitic flatworm regulatory peptide fromMoniezia expansa (Cestoda: Cyclophyllidea).Parasitology,102, 309–316.
Maule, A. G., Shaw, C., Halton, D. W., Brennan, G. P., Johnston, C. F. and Moore, S. (1992) Neuropeptide F (Moniezia expansa): localization and characterization using specific antisera.Parasitology,105, 505–512.
Maule, A. G., Halton, D. W. and Shaw, C. (1995) Neuropeptide F: a ubiquitous invertebrate neuromediator?Hydrobiologia,305, 297–303.
Micoletzky, H. (1906) Beiträge zur Morphologie des Nervensystems und Exkretions-apparates der Süsswassertricladen.Zool. Anz.,30, 702–710.
Reisinger, E. (1972) Die Evolution des Orthogon der Spiralier und das Archicöelomatenproblem.Z. Zool. Syst. Evolutionsforsch.,10, 1–43.
Reuter, M. and Gustafsson, M. (1995) The flatworm nervous system—pattern and phylogeny. InThe Nervous Systems of Invertebrates — An Evolutionary and Comparative Approach, ed. O. Breidbach and W. Kutsch, pp. 25–59. Basel, Switzerland: Birkhäuser Verlag.
Reuter, M., Maule, A. G., Halton, D. W., Gustafsson, M. K. S. and Shaw, C. (1995a) The organization of the nervous system in Plathelminthes. The neuropeptide F-immunoreactive pattern in Catenulida, Macrostomida, Proseriata.Zoomorphology,115, 83–97.
Reuter, M., Gustafsson, M. K. S., Sahlgren, C., Halton, D. W., Maule, A. G. and Shaw, C. (1995b) The nervous system of Tricladida. I. Neuroanatomy ofProcerodes littoralis (Maricola, Procerodidae): An immunocytochemical study.Invertebrate Neurosci.,1, 113–122.
Rieger, R. M., Tyler, S., Smith, III J. P. S., and Rieger, G. (1991) Platyhelminthes: Turbellaria. InMicroscopic Anatomy of Invertebrates 3: Platyhelminthes and Nemertinea ed. F. W. Harrison and B. J. Bogitsch, pp. 7–140. New York: Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Sakharov, D. A. (1990) Integrative function of serotonin common to distantly related invertebrate animals.Acta Acad. Aboensis, Ser. B.,50, 73–88.
Sakharov, D. A., Gobulev, A. I., Malyutina, L. V., Kabotyanski, E. A. and Nezlin, P. L. (1988) Serotonergic control of ciliary locomotion in a turbellarian flatworm. InNeurobiology of Invertebrates, Modulators and Receptors ed. J. Salánki and K. S- Rozsa, pp. 479–491. Symp. Biol. Hung. v36. Budapest: Akadémiai Kladó.
Webb, R. A. (1988) Endocrinology of acoelomates. In:Endocrinology of selected invertebrate types, ed. H. Laufer and R. G. H. Downer, pp. 31–62. New York: Allen R. Liss.
Welsh, J. H., and Williams, L. D. (1970) Monoamine containing neurons in planaria.J. Comp. Neurol.,138, 103–116.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reuter, M., Gustafsson, M.K.S., Sheiman, I.M. et al. The nervous system of Tricladida. II. Neuroanatomy ofDugesia tigrina (Paludicola, Dugesiidae): An immunocytochemical study. Invertebrate Neuroscience 1, 133–143 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02331911
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02331911