Summary
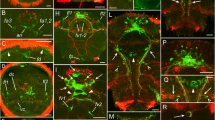
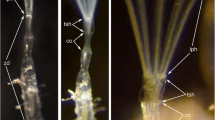
The nervous system (NS) of Bothriomolus balticus (Proseriata) was studied by the immunocytochemical (ICC) method with antisera to RFamide, SALMFamide and serotonin and with the histochemical GAIF method. The use of the ICC technique provided a much more precise morphological account of the nervous system than had previously been possible. The obtained data are discussed in connection with the comparative morphology of the nerve cords of the Plathelminthes. A similar position does not grant direct correspondence between nerve cords in the taxon Seriata. Marginal cords had probably an independent origin in the Monocelididae and Otoplanidae. The ventral (main) cords of B. balticus seem to correspond to the lateral (main) cords of the Monocelididae. It can be hypothesized that both: (1) a shift of the main cords accompanied by formation of new cords from the plexus and fusion of other cords and (2) a redistribution of nerve processes and perikarya between the cords, take part in the evolution of cords in the Plathelminthes. The first hypothesis seems to explain the difference in the position of main cords in proseriates, though, the second hypothesis might dominate, for example, in the Neorhabdocoela and the Neodermata. The correctness of the evolutionary analysis of the nerve cords in plathelminths can only be provided by neurons or neuron groups marking these structures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ax P (1956) Monographie der Otoplanidae (Turbellaria), Morphologie und Systematik. Acad Wiss Lit Mainz, Abh Mat.-Naturw Kl 13: 1–298
Böckerman I, Reuter M, Timoshkin O (1994) Ultrastructural study of the central nervous system of endemic Geocentrophora (Prorynchidae, Plathelminthes) from lake Baikal. Acta Zool (Stockholm) in press.
Ehlers U (1985) Das Phylogenetische System des Plathelminthes. Gustav Fischer, Stuttgart New York
Eriksson K, Timoschkin O, Reuter M (1990) Neuroactive substances in an endemic flatworm from lake Baikal. Acta Acad Aboensis Ser B 50 (7): 137–147
Fairweather I, Halton DW (1991) Neuropeptides in platyhelminths. Parasitology 102 (suppl): 77–92
Fairweather I, Maule AG, Mitchel SH, Johnston CF, Halton DW (1987) Immunocytochemical demonstration of 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) in the nervous system of the liver fluke, Fasciola hepatica (Trematoda Digenea). Parasitol Res 73: 255–258
Fairweather I, Mahendrasingam S, Johnston CF, Halton D, Shaw C (1990a) An ontogenetic study of the cholinergic and serotinergic nervous systems in Triocularia acanthiaevulgaris (Cestoda, Tetraphyllidea). Parasitol Res 76: 487–496
Fairweather I, Mahendrasingam S, Johnston CF, Halton D, Shaw C (1990b) Peptidergic nerve elements in three developmental stages of the tetraphyllidean tapeworm, Trilocularia acanthiaevulgaris. Parasitol Res 76: 497–508
Gelei J von (1909–12) Tanulmnyok a Dendrocoelum lacteum Oerstd. szöventtanárol. A Magyar Tudomanyos Akademia vitéz-dijaval jutalmazott palayamu, Budapest
Gustafsson MKS (1987) Immunocytochemical demonstration of neuropeptides and serotonin in the nervous system of adult Schistosoma mansoni. Parasitol Res 74: 168–174
Gustafsson MKS (1991) Skin the tapworms before you stain their nervous system! A new method for whole mount immunocytochemistry. Parasitol Res 77: 509–516
Gustafsson M, Reuter M (1992) The map of neuronal signal substances in flatworms. In: Singh RN (ed) Nervous systems principles of design and function. Goa, India, pp 165–188
Gustafsson MKS, Lehtonen MAI, Sundler F (1986) Immunocytochemical evidence for the presence of “mammalian” neurohormonal peptides in the neurons of the tapeworm Diphyllobothrium dendriticum. Cell Tissue Res 243: 41–49
Halton DW, Shaw C, Maule AG, Johnston CF, Fairweather I (1992) Peptidergic messengers: a new perspective of the nervous system of parasitic plathelminths. J Parasitol 78: 179–193
Hanström B (1926) Über den feineren Bau des Nervensystems der Tricladen Trubellarien auf Grund von Untersuchungen and Bdelloura candida. Acta Zool (Stockholm) 7: 101–115
Hauser M, Koopowitz H (1987) Age-dependent changes in fluorescent neurons in the brain of Notoplana acticola, a polycladid flatworm. J Exp Zool 241: 217–225
Joffe BI (1990) Morphological regularities in the evolution of the nervous system in the Plathelminthes: anatomicalvariants of orthogon and their dependence upon the body form (in Russian). Proc Zool Inst, Leningrad 221: 87–125
Joffe BI (1991) On the number and spatial distribution of catecholamine-containing (GA-positive) neurons in some higher and lower turbellarians: a comparison. Hydrobiologia 227: 201–209
Joffe BI, Kotikova EA (1988) On the possibility of homologization of neurons in Platyhelminthes (in Russian). In: Sakharov DA (ed) Simpler nervous systems. Nauka, Leningrad, pp 130–132
Joffe BI, Kotikova EA (1991) Distribution of catecholamines in turbellarians (with discussion of neuronal homologies in the Platyhelminthes). Stud Neurosci 13: 77–113
Johnston CF, Shaw C, Halton DW, Fairweather I (1990) Confocal scanning laser microscopy and helminth neuroanatomy. Parasitology Today 6: 248–290
Kabotyanski EA, Nezlin LP, Sakharov DA (1991) Serotonin neurons in the planarian pharynx. Stud Neurosci 13: 138–152
Kerschbaum HH, Treiblmayer K, Pohlhammer K (1988) Localization of 5-Ht and gastrin-cck-immunoreactivity in Crenobia alpina (Tricladida, Plathelminthes). Fortschr Zool 36: 177
Kotikova EA (1976) Some features of the nervous system in Proseriata (Turbellaria) (in Russian). Zool Zh 54: 508–514
Kotikova EA (1986) Comparative characterization of the nervous system of the Turbellaria. Hydrobiologia 132: 89–92
Kotikova EA, Timoschkin OA (1987) The structure of the nervous system of Lecithoepitheliata and Prolecithophora from the Baikal lake (Turbellaria) (in Russian). Proc Zool Inst, Leningrad 167: 97–110
Magee RM, Fairweather I, Johnston CF, Halton DW, Shaw C (1989) Immunocytochemical demonstration of neuropeptides in the nervous system of the liver fluke, Fasciola hepatica (Trematoda, Digenea). Parasitology 98: 227–238
Mamkaev YuV (1986) Initial morphological diversity as a criterion in deciphering turbellarian phylogeny. Hydrobiologia 132: 21–33
Mamkaev YuV, Kotikova EA (1972) On the morphologic characteristics of the nervous apparatus of acoel turbellarians (in Russian). Zool Zh 51: 477–489
Martens PM, Schockaert ER (1988) Phylogeny of the digonoporid Proseriata. Fortschr Zool 36: 399–403
Maule AG, Halton DW, Johnston CF, Fairweather I, Shaw C (1989a) Immunocytochemical demonstration of neuropeptides in the fish-gill parasite, Diclidophora merlangi (Monogenoidea). Int J Parasitol 19: 307–316
Maule AG, Shaw C, Halton DW, Johnston CF, Fairweather I (1989b) Localization, quantification and characterization of pancreatic polypeptide immunoreactivity in the parasitic flatworm Diclidophora merlangi and its fish host (Merlangius merlangus). Gen Comp Endocrinol 74: 50–56
Maule AG, Halton DW, Johnston CF, Shaw C, Fairweather I (1990a) A cytochemical study of the serotoninergic, cholinergic and peptidergic components of the reproductive system in the monogenean parasite, Diclidophora merlangi. Parasitol Res 76: 409–419
Maule AG, Halton DW, Johnston CF, Shaw C, Fairweather I (1990b) The serotoninergic, cholinergic and peptidergic components of the nervous system of the monogenean parasite, Diclidophora merlangi: a cytochemical study. Parasitology 100: 255–273
Maule AG, Shaw C, Halton DW, Thim L, Johnston CF, Fairweather I, Buchanan KD (1991) Neuropeptide F: a novell parasitic flatworm regulatory peptide from Moniezia expansa (Cestoda: Cyclophyllidae). Parasitology 102: 309–316
McKay DM, Halton DW, Johnston CF, Fairweather I, Shaw C (1990) Occurrence and distribution of putative neurotransmitters in the frog lung parasite, Haplometra cylindracea (Trematoda, Digenea). Parasitol Res 97: 509–517
McKay DM, Fairweather I, Johnston CF, Shaw C, Halton DW (1991a) Immunocytochemical and radioimmunometrical demonstration of serotonin- and neuropeptide-immunoreactivities in the adult rat tapeworm, Hymenolepis diminuta (Cestoda, Cyclophyllidea). Parasitology 103: 275–289
McKay DM, halton DW, Maule AG, Johnston CF, Fairweather I, Shaw C (1991b) Putative neurotransmitters in two monogeneans. Helminthologia 28: 75–81
McKay DM, Halton DW, Johnston CF, Fairweather I, Shaw C (1991c) Cytochemical demonstration of cholinergic, serotoninergic and peptidergic nerve elements in Gorgoderina vitelloba (Trematoda, Digenea). Int J Parasitol 21: 71–80
Palmberg I, Reuter M (1990) Neuronal subsets in regenerating Microstomum lineare. Immunocytochemistry of FMRF/RFamide and 5-HT. Acta Acad Abo Ser B 50:(7) 147–160
Reisinger E (1925) Untersuchungen am Nervensystem der Bothrioplana semperi Braun. Z Morphol Ökol Tiere 5: 119–149
Reisinger E (1968) Xenoprorhynchus — ein Modellfall für progressiven Funktionswechsel. Z Zool Syst Evolutionsforsch 6: 1–55
Reisinger E (1970) Zur Problematik der Evolution der Coelomaten. Z Zool Syst Evolutionsforsch 8: 81–109
Reisinger E (1972) Die Evolution des Orthogon der Spiralier und das Archicöelomatenproblem. Z Zool Syst Evolutionsforsch 10: 1–43
Reiter D, Wikgren M (1991) Immunoreactivity to a specific echinoderm neuropeptide in the nervous system of the flatworm Macrostomum hystricinum marinum (Turbellaria, Macrostomida). Hydrobiologia 227: 229
Reuter M (1987) Immunocytochemical demonstration of serotonin and neuropeptides in the nervous system of Gyrodactylus salaris (Monogenea). Acta Zool (Stockholm) 68: 187–193
Reuter M (1988) Development and organization of nervous system vizualized by immunocytochemistry in three flatworm species. Fortschr Zool 36: 181–184
Reuter M (1990) From innovation to intergration. Trends in the integrative system in microturbellarians. Acta Acad Abo Ser B 50:(70): 161–178
Reuter M, Eriksson K (1991) Cateochalmines demonstrated by glyoxylic-acid-induced fluorescence and HPLC in some microturbellarians. Hydrobiologia 229: 209–220
Reuter M, Palmberg I (1989) Development and differentiation of neuronal subsets in asexually reproducing Microstomum lineare. Immunocytochemistry of 5-HT, RFamide and SCPB. Histochemistry 91: 132–131
Reuter M, Wikgren M, Lehtonen M (1986) Immunocytochemical demonstration of 5-HT-like and FMRF-amide-like substances in whole mounts of Microstomum lineare (Turbellaria). Cell Tissue Res 246: 7–12
Reuter M, Lehtonen M, Wikgren M (1988) Immunocytochemical evidence of neuroactive substances in flatworms of different taxa — a comparison. Acta Zool (Stockholm) 69: 29–37
Rieger RM, Tyler S, Smith JPS III, Rieger GE (1990) Platyhelminthes: Turbellaria. In: Harrison FW, Bogitsh BJ (eds) Plathyhelminthes and Rhynchocoela, vol 3. In: Harrison FW (ed) Microscopic anatomy of invertebrates. Wiley-Liss, New York: 7–140
Sakharov DA (1974) The genealogy of neurons (in Russian). Nauka, Moscow
Sakharov DA, Golubev AI, Malyutina LV, Kabotyanski EA, Nezlin LP (1988) Serotoninergic control of ciliary locomotion in a turbellarian flatworm. Symp Biol Hungariae 36: 479–491
Schishov BA (1991) Aminergic elements in the nervous system of helminths. Stud Neurosci 13: 113–137
Skuce PJ, Johnston CF, Fairweather I, Halton DW, Shaw C (1990a) A confocal scanning laser microscope study of the peptidergic and serotoninergic components of the nervous system in larval Schistosoma mansoni. Parasitology 101: 227–234
Skuce PJ, Shaw C, Johnston CF, Fairweather I, Halton DW, Buchanan KD (1990b) Immunoreactivity to the pancreatic polypeptide family in the nervous system of the adult blood fluke, Schistosoma mansoni. Cell Tissue Res 261: 573–581
Sopott-Ehlers B (1985) The phylogenetic relationships within the Seriata (Platyhelminthes). In: Conway Morris S, George JD, Gibson R, Platt HM (eds) The origins and relationships of the lower invertebrates. Oxford University Press, Oxford, UK, pp 159–167
Stretton AOW, Cowden C, Sithigorngul P, Davis RE (1991) Neuropeptides in the nematode Ascaris suum. Parasitology 102, Suppl: 107–116
Timoshkin OA (1991) Turbellaria lecithoepitheliata: morphology, systematics, phylogeny. Hydrobiologia 227: 323–332
Welsh J, Williams LD (1970) Monoamine-containing nerves of Planaria. J Comp Neurol 138: 103–116
Wikgren M, Reuter M (1985) Neuropeptides in a microturbellarian — whole mount immunocytochemistry. Peptides 6, (Suppl 3): 471–475
Wikgren MC, Thorndyke MC (1990) An echinoderm neuropeptide in flatworms? Acta Acad Abo Ser B 50: 45–53
Wikgren M, Reuter M, Gustafsson M (1986) Neuropeptides in free-living and parasitic flatworms. Hydrobiologia 132: 93–99
Wigren M, Reuter M, Gustafsson MKS, Lindroos P (1990) Immunocytochemical localization of histamine in flatworms. Cell Tissue Res 260: 479–484
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Joffe, B.I., Reuter, M. The nervous system of Bothriomolus balticus (Proseriata) —a contribution to the knowledge of the orthogon in the Plathelminthes. Zoomorphology 113, 113–127 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00403089
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00403089