Summary
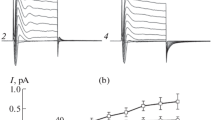
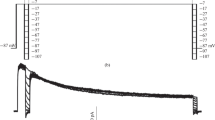
Patch-clamp techniques were used to study a K channel in the cell membrane of MDCK cells. This cell line derives from the kidney of a normal dog, presumably from the distal nephron, a region involved in potassium secretion. The cells were cultured in confluent monolayers and approached from the apical side. The K channel we describe is Ca2+ and voltage activated, has a conductance of 221±7 pS, and can be inhibited by 10mm tetraethylammonium and by 1mm quinidine, but not by 4-aminopyridine, nor by 1mm Ba2+ added to the outer side. Using the whole-cell configuration, we find that most of the cationic conductance of the membrane is constituted by a K-specific one (maximum K conductance 32.1±3.9 nSvs. a leak conductance of 1.01±0.17 nS). Comparisons of the maximum K conductance with that of a single K channel indicates that an MDCK cell has an average of 145 such channels. The membrane capacity is 24.5±1.4 pF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atwater, I., Rosario, L., Rojas, E. 1983. Properties of the Ca-activated K+ channel in pancreatic β-cells.Cell Calcium 4:451–4561
Barker, G., Simmons, N.L. 1981. Identification of two strains of cultured canine renal epithelial cells (MDCK cells) which display entirely different physiological properties.Q. J. Exp. Physiol. 66:61–72
Brown, C.D.A., Simmons, N.L. 1982. K+ transport in ‘tight’ epithelial monolayers of MDCK cells. Evidence for a calcium-activated K+ channel.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 690:95–105
Cereijido, M., Ehrenfeld, J., Fernandez-Castelo, S., Meza, I. 1981. Fluxes, junctions and blister in cultured monolayers of epithelioid cells (MDCK).Ann N. Y. Acad. Sci. 372:422–441
Cereijido, M., Robbins, E.S., Dolan, W.J., Rotunno, C.A., Sabatini, D.D. 1978. Polarized monolayer formed by epithelial cells on a permeable and translucent support.J. Cell. Biol. 77:853–880
Cereijido, M., Robbins, E. S., Sabatini, D.D., Stefani, E. 1984. Cell-to-cell communication in monolayers of epithelioid cell (MDCK) as a function of the age of the monolayers.J. Membrane Biol. 81:41–48
Fenwick, E.M., Marty, A., Neher, E. 1982. A patch-clamp study of bovine chromaffin cells and of their sensitivity to acetylcholine.J. Physiol. (London) 331:577–598
Fernandez-Castelo, S., Bolivar, J.J., Lopez-Vancell, R., Beaty, G., Cereijido, M.. 1985. Ion transport in MDCK cells.In: Tissue Culture of Epithelial Cells. M. Taub, editor. pp. 37–50. Plenum, London
Findlay, I. 1984. A patch-clamp study of potassium channels and whole-cell currents in acinar cells of the mouse lacrimal gland.J. Physiol. (London) 350:179–195
Garcia-Perez, A., Smith, W.L. 1983. Use of monoclonal antibodies to isolate cortical collecting tubule cells: AVP induces PGE release.Am. J. Physiol. 244:C211-C220
Guggino, S.E., Suarez-Isla, B.A., Guggino, W.B., Sacktor, B. 1985. Forskolin and antidiuretic hormones stimulate a Ca2+-activated K+ channel in cultured kidney cells.Am. J. Physiol. 249:F448-F455
Hamill, O.P., Marty, A., Neher, E., Sakmann, B., Sigworth, F.J. 1981. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches.Pfluegers Arch. 391:85–100
Hassid, A. 1983. Modulation of cyclic 3′5′-adenosin monophosphate in cultured renal (MDCK) cells by endogenous protaglandins.J. Cell Physiol. 116:297–302
Herzlinger, D.A., Easton, T.G., Ojakian, G.K. 1982. The MDCK epithelial cell line expresses a cell surface antigen of the kidney distal tubule.J. Cell. Biol. 93:269–277
Hunter, M., Lopes, A.G., Boulpaep, E.L., Giebisch, G.H. 1984. Single channel recordings of calcium-activated potassium channels in the apical membrane of rabbit cortical tubules.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 81:4237–4239
Koeppen, B.M., Beyenbach, K.W., Helman, S.I. 1984. Single-channel currents in renal tubules.Am. J. Physiol. 247:F380-F384
Kolb, H.A., Brown, C.D.A., Murer, H. 1985. Identification of a voltage-dependent anion channel in the apical membrane of a Cl− secretory epithelium (MDCK).Pfluegers Arch. 402:262–265
Latorre, R., Miller, C. 1983. Conduction and selectivity in potassium channels.J. Membrane Biol. 71:11–30
Lewis, M.G., Spector, A.A. 1981. Differences in types of protaglandins produced by two MDCK canine kidney cell sublines.Prostaglandins 21:1025–1032
Madin, S.H., Darby, N.B. 1958. As catalogued in: American type Culture Collection Catalog of Strains.2:574–576
Marty, A. 1981. Ca2+-dependent K+ channels with large unitary conductance in chromaffin cell membranes.Nature (London) 291:497–500
Maruyama, Y., Gallacher, D.V., Petersen, O.H. 1983. Voltage and Ca2+-activated K+ channel in baso-lateral acinar cell membranes of mammalian salivary glands.Nature (London) 302:827–829
Meza, I., Sabanero, M., Stefani, E., Cereijido, M. 1982. Occluding junctions in MDCK cells: Modulation of transepithelial permeability by the cytoskeleton.J. Cell Biochem. 18:407–421
Palmer, L.G. 1986. Patch-clamp technique in renal physiology.Am. J. Physiol. 29:F379-F385
Paulmichl, M., Gstraunthaler, G., Lang, F. 1985. Electrical properties of Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. Effects of extracellular potassium and bicarbonate.Pfluegers Arch. 405:102–107
Petersen, O.H., Maruyama, Y. 1984. Calcium-activated potassium channels and their role in secretion.Nature (London) 307:693–696
Richardson, J.C.W., Scalera, V., Simmons, N.L. 1981. Identification of two strains of MDCK cells whichresemble separate nephron tubule segments.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 673:26–36
Stefani, E., Cereijido, M. 1983. Electrical properties of cultured epithelioid cells (MDCK).J. Membrane Biol. 73:177–184
Valentich, J.D. 1981. Morphological similarities between the dog kidney cell line MDCK and the mammalian cortical collecting tubule.Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 372:384–405
Wong, S., Lecar, H., Adler, M. 1982. Single calcium-dependent potassium channels in clonal anterior pituitary cells.Biophys. J. 39:313–317
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bolívar, J.J., Cereijido, M. Voltage and Ca2+-Activated K+ channel in cultured epithelial cells (MDCK). J. Membrain Biol. 97, 43–51 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01869613
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01869613