Abstract
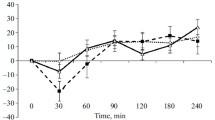
After intravenous administration of an analgesic dose of morphine into rat, the time course of morphine concentrations was followed in plasma, whole brain, and four discrete areas of the brain during 8 hr. These concentration curves indicated a three-exponential function which could be described by a mammillary system of three compartments. Maximal brain levels were obtained 15–20 min after injection, showing a fairly even distribution pattern of morphine. The plasma to whole brain ratio showed three-exponential characteristics, approaching a constant value of about 4.7–4.8 after 4 hr. By use of the SAAM-25 program, the experimental data from plasma and brain were simultaneously fitted to five separate sets of three-compartment models. Results obtained implied the uniqueness of the computed transfer constants of the three-compartment model.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. J. Mulé.Physiological disposition of narcotic agonists and antagonists. in D. H. Clouet (ed.),Narcotic Drugs, Biochemical Pharmacology, Plenum Press. New York, 1971, pp. 99–121.
L. Paalzow and G. Paalzow. Studies on the relationship between morphine analgesia and the brain catecholamines in mice.Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol. 30:104–114 (1971).
L. Paalzow and G. Paalzow. Blood and brain concentration of morphine in relation to the analgesic activity in mice.Acta Pharm. Suecica 8:329–336 (1971).
L. Paalzow. Studies on the relationship between the analgesic activity of salicylic acid and the brain catecholamines in mice.Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol. 32:11–21 (1973).
G. Paalzow, L. Paalzow, and B. Stalby. Pentazocine analgesia and regional rat brain catecholamines.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 27:78–88 (1974).
B. Dahlström and L. Paalzow. Quantitative determination of morphine by gas-liquid chromatography and electron-capture detection.J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 27:172–176 (1975).
J. Glowinski and L. L. Iversen. Regional studies of catecholamines in the rat brain. I.J. Neurochem. 13:655–669 (1966).
B. Dahlström, G. Paalzow, and L. Paalzow. Pharmacokinetical evaluation of morphine analgesia in the rat.Proc. Sec. Int. Congr. Pharmacol. Budapest (1974).
A. Rescigno and G. Segre. The precursor-product relationship.J. Theoret. Biol. 1:498 (1961).
A. Rescigno and G. Segre. In A. Rescigno and G. Segre (eds.),Drug and Tracer Kinetics, Blaisdell, Waltham, Mass., 1966.
S. Spector and E. S. Vesell. Disposition of morphine in man.Science 174:421–422 (1971).
S. Spector. Quantitative determination of morphine in serum by radioimmunoassay.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 178:253–258 (1971).
B. A. Berkowitz, K. V. Cerreta, and S. Spector. The influence of physiologic and pharmacologie factors on the disposition of morphine as determined by radioimmunoassay.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 191:527–534 (1974).
M. Berman. Compartmental analysis in kinetics. In R. W. Stacy and B. D. Waxman (eds.),Computers in Biomedical Research II, Academic Press, London. 1965, pp. 173–201.
A. E. Takemori and M. W. Stenwick. Studies on the uptake of morphine by the choroid plexusin vitro.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 154:586–594 (1966).
C. C. Hug, Jr. Transport of narcotic analgesics by choroid plexus and kidney tissuein vitro.Biochem. Pharmacol. 16:345–359 (1967).
J. H. Wang and A. E. Takemori. Studies on the transport of morphine into the cerebrospinal fluid of rabbits.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 183:41–48 (1972).
A. Herz and H.-J. Teschemacher. Activities and sites of antinociceptive action of morphinelike analgesics. In N. J. Harper and A. B. Simmonds (eds.),Advances in Drug Research, Vol. 6, Academic Press, London, 1971, pp. 79–121.
S. J. Mulé, L. A. Woods, and L. B. Mellett. Distribution of N-C14-methyl labelled morphine. II. Effect of nalorphine in the central nervous system of nontolerant dogs and observations on metabolism.J. Pharmacol. 136:242–249 (1962).
J. Jóhannesson and L. A. Woods. Analgesic action and brain and plasma levels of morphine and codeine in morphine tolerant, codeine tolerant and non-tolerant rats.Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol. 21:381–396 (1964).
E. Leong Way. Pharmacologie implications of some factors influencing brain uptake of morphine.Arch. Biol. Med. Exp. 4:92–104 (1967).
J. W. Miller and H. W. Elliott. Rat tissue levels of carbon-14 labelled analgesics as related to pharmacological activity.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 113:283–291 (1955).
S. J. Mulé and L. A. Woods. Distribution ofN-C 14-methyl labelled morphine. I. In central nervous system of non-tolerant and tolerant dogs.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 136:232–241 (1962).
P. Schubert, H. Teschemacher, G. W. Kreutzberg, and A. Herz. Intracerebral distribution pattern of radioactive morphine and morphine-like drugs after intraventricular and intrathecal injection.Histochemie 22:277–288 (1970).
L.-E. Appelgren and L. Terenius. Differences in the autoradiographic localization of labelled morphine-like analgesics in the mouse.Acta Physiol. Scand. 88:175–182 (1973).
G. Levy, M. Gibaldi, and W. J. Jusko. Multicompartment pharmacokinetic models and pharmacologie effects.J. Pharm. Sci. 58:422–424 (1969).
M. Gibaldi, G. Levy, and H. Weintraub. Drug distribution and pharmacologie effects.Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 12:734–742 (1971).
J. G. Wagner. Kinetics of the pharmacologie response. I.J. Theoret. Biol. 20:173–201 (1968).
J. G. Wagner. Relations between drug concentration and response.J. Mond. Pharm. 14: 279–310 (1971).
M. Rowland. Application of clearance concepts to some literature data on drug metabolism in the isolated perfused lever preparation andin vivo.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 17:352–356 (1972).
M. Berman, M. F. Weiss, and E. Shahn. Some formal approaches to the analysis of kinetic data in terms of linear compartmental systems.Biophys. J. 2:289–316 (1962).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dahlström, B.E., Paalzow, L.K. Pharmacokinetics of morphine in plasma and discrete areas of the rat brain. Journal of Pharmacokinetics and Biopharmaceutics 3, 293–302 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01082303
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01082303