Summary
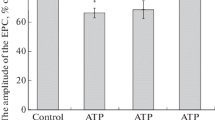
The ionic requirement for the action potentials recorded from the neurohaemal tissue on the lateral branch of the median nerve inCarausius morosus has been studied using extracellular electrodes. Sodium-free, magnesium-free, or calcium-free salines produce irreversible block of the action potentials following prolonged exposure to the nerves. Reducing the sodium concentration to 4 mM has little effect on the amplitude of the action potentials, whilst increasing the sodium concentration to 100 mM reduces the amplitude by 50%. Neither tetrodotoxin nor procaine has any effect on these action potentials.
Reducing the magnesium concentration to 1 mM increases the amplitude of the action potentials, whilst increasing the concentration of magnesium reduces the amplitude.
The amplitude of the action potentials is linearly related to the log of the external calcium concentration, and the action potentials are blocked by both cobalt ions and lanthanum ions.
It is concluded that calcium is the major charge carrier of the inward current in these neurosecretory axons which is the first report of calcium dependent action potentials in a nerve axon. Furthermore, small amounts of sodium and magnesium are necessary to maintain electrical activity. Magnesium is a competitive inhibitor of the calcium currents.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berlind, A., Cooke, I.M.: Effect of calcium omission on neurosecretion and electrical activity of crab pericardial organs. Gen. comp. Endocr.11, 458–463 (1968)
Berlind, A., Cooke, I.M.: The role of divalent cations in electrically elicited release of a neurohormone from crab pericardial organs. Gen. comp. Endocr.17, 60–72 (1971)
Brady, J., Maddrell, S.H.P.: Neurohaemal organs in the medial nervous system of insects. Z. Zellforsch.76, 389–404 (1967)
Dreifuss, J.J., Grau, J.D., Nordmann, J.J.: Release processes for neurohormones and the secretion of neurotransmitters. Experientia (Basel)27, 1110 (1971)
Finlayson, L.H., Osborne, M.P.: Peripheral neurosecretory cells in the stick insect (Carausius morosus) and the blowfly larva (Phormia terraenovae). J. Insect Physiol.14, 1793–1801 (1968)
Finlayson, L.H., Osborne, M.P.: Electrical activity of neurohaemal tissue in the stick insect,Carausius morosus. J. Insect. Physiol.16, 791–800 (1970)
Finlayson, L.H., Osborne, M.P.: Secretory activity of neurons and related electrical activity. Advanc. comp. Physiol. Biochem.6, 165–258 (1975)
Florkin, M., Jeuniaux, C.: Haemolymph: Composition. In: The Physiology of Insecta (ed. M. Rockstein), Vol. V, pp. 255–307. New York and London: Academic Press 1974
Geduldig, D., Junge, D.: Sodium and calcium components of action potentials in theAplysia giant neuron. J. Physiol. (Lond.)199, 342–365 (1968)
Hagiwara, S.: Ca Spike. In: Advances in Biophysics, Vol. 4 (ed. M. Kotani), pp. 71–102. Tokyo: University of Tokyo Press 1973
Iwasaki, S., Satow, Y.: Sodium- and Calcium-dependent spike potentials in the secretory neuron soma of the X-organ of the crayfish. J. Physiol. (Lond.)57, 216–238 (1971)
Kerkut, G.A., Gardner, D.R.: The role of calcium ions in the action potentials ofHelix aspersa neurones. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.20, 147–162 (1967)
Leslie, R.A.: The effects of ionic lanthanum and hypertonic physiological salines on the nervous systems of larval and adult stick insects. J. Cell. Sci.18, 271–286 (1975)
Narahashi, T., Moore, J.W., Scott, W.R.: Tetrodotoxin blockage of sodium conductance increase in lobster giant axons. J. gen. Physiol.47, 965–974 (1964)
Orchard, I.: Calcium dependent action potentials in a peripheral neurosecretory cell of the stick insect. J. comp. Physiol.112, 95–102 (1976)
Osborne, M.P.: Structure and function of neuromuscular junctions and stretch receptors. In: Insect Ultrastructure; Symposium Royal Entomological Society, Vol. 5 (ed. A.C. Neville), pp. 77–100. Oxford: Blackwell 1970
Osborne, M.P.: The ultrastructure of nerve muscle synapses. In: Insect Muscle (ed. P.N.R. Usherwood), pp. 151–205. New York and London: Academic Press 1975
Patlak, J.B.: The ionic basis for the action potential in the flight muscle of the fly,Sarcophaga bullata. J. comp. Physiol.107, 1–11 (1976)
Sattelle, D.B.: Electrophysiology of the giant nerve cell bodies ofLimnaea stagnalis (L) (Gastropoda: Pulmonata). J. exp. Biol.60, 653–671 (1974)
Standen, N.B.: Calcium and sodium ions as charge carriers of the action potential of an identified snail neuron. J. Physiol. (Lond.)249, 241–252 (1975)
Treherne, J.E.: Some preliminary observations on the effects of cations on conduction processes in the abdominal nerve cord of the stick insect,Carausius morosus. J. exp. Biol.42, 1–6 (1965)
Treherne, J.E.: A study of the function of the fat-body sheath in the stick insect,Carausius morosus. J. exp. Biol.56, 129–137 (1972)
Treherne, J.E., Maddrell, S.H.P.: Axonal function and ionic regulation in the central nervous system of a phytophagous insect (Carausius morosus). J. exp. Biol.47, 235–247 (1967)
Treherne, J.E., Moreton, R.B.: The environment and function of invertebrate nerve cells. Int. Rev. Cytol.28, 45–88 (1970)
Treherne, J.E., Pichon, Y.: The insect blood-brain barrier. In: Advances in Insect Physiology, Vol. 9 (ed. J.W.L. Beament, J.E. Treherne, V.B. Wigglesworth), pp. 257–313. New York and London: Academic Press 1972
Wald, F.: Ionic differences between somatic and axonal action potentials in snail giant neurones. J. Physiol. (Lond.)220, 267–281 (1972)
Washio, H.: The ionic requirements for the initiation of action potentials in insect muscle fibres. J. gen. Physiol.59, 121–134 (1972)
Wood, D.W.: The effects of ions upon neuromuscular transmission in a herbivorous insect. J. Physiol. (Lond.)138, 268–289 (1957)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
We are grateful to the Science Research Council for financial support, and to Mrs. J. Birch for the printing of the electron micrographs.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Orchard, I., Osborne, M.P. The effects of cations upon the action potentials recorded from neurohaemal tissue of the stick insect. J. Comp. Physiol. 118, 1–12 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00612333
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00612333