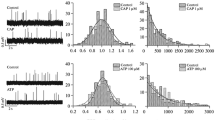
Abstract—The effects of ATP and adenosine on the parameters of the end plate currents of the frog’s Rana ridibunda neuromuscular synapse in the presence of cesium ions that modulate synaptic transmission were studied to identify the involvement of K+ channels in the mechanism of inhibitory presynaptic action of purine derivatives in the neuromuscular synapse of cold-blooded animals. There was a difference between the effects caused by a half-hour and one-hour action of cesium ions on the amplitude of the terminal plate currents; similar difference we noted previously in the effects of barium ions, which are blockers of some subtypes of potassium channels. In the case of exposure to cesium for 1 h, the inhibitory effect of adenosine on the amplitude of the terminal plate currents remained stable; while the inhibitory effect of ATP on the amplitude of postsynaptic responses decreased by approximately 2.5 times. The data obtained may indicate that the presynaptic inhibitory effect of ATP on the secretion of the transmitter from nerve endings can be realized through Cs+-sensitive potassium channels of the nerve terminals.

Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
S. N. Grishin and A. U. Ziganshin, Biochemistry (Moscow) Suppl. Ser. A: Membr. Cell Biol. 9 (1), 13 (2015).
R. A. Cunha and J. A. Ribeiro, Life Sci. 68 (2), 119 (2000).
K. J. Todd and R. Robitaille, Pflugers Arch. 452 (5), 608 (2006).
G. Burnstock, T. R. Arnett, and I. R. Orriss, Purinergic Signal. 9 (4), 541 (2013).
A. U. Ziganshin, C. H. V. Hoyle, A. E. Khairullin, and S. N. Grishin, Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21 (17), 6423 (2020).
S. N. Grishin and A. U. Ziganshin, Biol. Membrany 30 (4), 243 (2013).
N. A. Castle, D. G. Haylett, and D.H. Jenkinson, Trends Neurosci. 12 (2), 59 (1989).
A. Meir, S. Ginsburg, A. Butkevitch, et al., Physiol. Rev. 79 (3), 1019 (1999).
P. A. Fuchs, J. G. Nicholls, A. R. Martin, and B. G. Wallace, From Neuron to Brain, 4 th ed. (Sinauer Assoc., 2001).
S. Grishin, A. Shakirzyanova, A. Giniatullin, et al., Eur. J. Neurosci. 21, 1271 (2005).
G. Russo, S. Masetto, and I. Prigioni, Neuroreport 6 (3), 425 (1995).
S. Zhang, Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 290 (3), 1038 (2006).
E. V. Ponomareva, E. V. Kachaeva, E. G. Altaeva, et al., Biophysics 53 (6), 615 (2008).
S. N. Grishin, Biochemistry (Moscow) Suppl. Ser. A: Membrane and Cell Biology 10 (2), 99 (2016).
B. Katz and R. Miledi, Proc. Roy. Soc. Lond. B: Biol Sci. 205 (1160), 369 (1979).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest. The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Statement on the welfare of animals. The conducted experiments fully comply with the current national and international standards in the field of ethics.
Additional information
Translated by E. Puchkov
Abbreviation: EPC, end plate currents.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khairullin, A.E., Valiullin, V.V., Teplov, A.Y. et al. The Effect of Cesium Ions on the Inhibitory Action of Purines in the Neuromuscular Synapse. BIOPHYSICS 66, 965–967 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006350921060051
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006350921060051