Summary
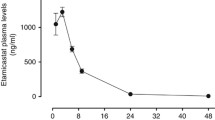
In borderline and permanent hypertensives after rapid i.v. injection of dl-propranolol 0.2 mg/kg plasma levels were measured and were fitted to a two-compartment open-model. In borderline patients, characterized by a high basal cardiac output (CO), plasma levels were always lower than in permanent hypertensives. The biological half-life was reduced and the central volume of distribution, volume of distribution at pseudo-equilibrium and total clearance (TC) were markedly increased. In the overall population, there was a significant positive correlation between CO and TC. Rapid achievement of a predetermined plateau in each group constituted experimental proof of the validity of the two-compartment open-model for kinetic analysis of propranolol i.v. If kinetic parameters from permanent hypertensives were applied to borderline hypertensives a lower plateau was obtained. Thus, in so far as β-blockade is related to plasma level of propranolol, an increased intravenous dose may be required in patients with high CO.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bello, S.T., Sevy, R.W., Harakal, C.: Varying hemodynamic patterns in essential hypertension. Amer. J. med. Sci.250, 24–35 (1965)
Branch, R.A., Shand, D.G., Nies, A.S.: Increase in hepatic blood flow and d-propranolol clearance by glucagon in the monkey. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther.187, 581–587 (1973)
Branch, R.A., Shand, D.G., Wilkinson, G.R., Nies, A.S.: Increased clearance of antipyrine and d-propranolol after phenobarbital treatment in the monkey. J. clin. Invest.53, 1101–1107 (1974)
Eich, R.H., Peters, R.J., Cuddy, R.P.: The hemodynamics in labile hypertension. Amer. Heart J.63, 188–195 (1962)
Evans, G.H., Nies, A.S., Shand, D.G.: The disposition of propranolol. III. Decreased half-life and volume of distribution as a result of plasma binding in man, monkey, dog and rat. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther.186, 114–122 (1973)
Gibaldi, M., Nagashima, R., Levy, G.: Relationship between drug concentration in plasma or serum and amount of drug in the body. J. Pharm. Sci.58, 193–197 (1969)
Julius, S., Pascual, A.V., London, R.: Role of parasympathetic inhibition in the hyperkinetic type of borderline hypertension. Circulation44, 413–417 (1971)
Julius, S., Conway, J.: Hemodynamic studies with borderline blood pressure elevation. Circulation38, 282–288 (1968)
Lowenthal, D.T., Briggs, W.A., Gibson, T.P., Nelson, H., Cirksena, W.J.: Pharmacokinetics of oral propranolol in chronic and renal disease. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.16, 761–769 (1974)
Lund-Johansen, P.: Hemodynamics in early essential hypertension. Acta med. scand.482, (Suppl.) 1–105 (1967)
Mitenko, P.A., Ogilvie, R.I.: Rapidly achieved plasma concentration plateaus, with observations on theophylline kinetics. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.13, 329–335 (1972)
Nies, A.S., Evans, G.H., Shand, D.G.: Regional hemodynamic effects of beta-adrenergic blockade with propranolol in the unanesthetized primate. Amer. Heart. J.85, 97–102 (1973)
Paterson, J.W., Conolly, M.E., Dollery, C.T.: The pharmacodynamics and metabolism of propranolol in man. Pharmacol. Clin.2, 127–133 (1970)
Prichard, B.N.C., Gillam, P.M.S.: Treatment of hypertension with propranolol. Brit. med. J.1969 I, 7–16
Safar, M., Milliez, P.: Hemodynamic findings in human arterial hypertension. Rev. Europ. Etud. Clin. Biol.17, 147–154 (1972)
Safar, M., London, G., Weiss, Y., Milliez, P.: Vascular reactivity to norepinephrine and hemodynamic parameters in borderline hypertension. Amer. Heart J.89, 480–486 (1975)
Shand, D.G., Evans, G.H., Nies, A.S.: The almost complete hepatic extraction of propranolol during intravenous administration in the dog. Life Sci.10, 1417–1421 (1971)
Shand, D.G., Nuckolls, E.M., Oates, J.A.: Plasma propranolol level in adults with observations in four children. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.11, 112–120 (1970)
Shand, D.G., Rangno, R.E.: The disposition of propranolol. I. Elimination during oral absorption in man. Pharmacology (Basel)7, 159–168 (1972)
Shand, D.G., Rangno, R.E., Evans, G.H.: The disposition of propranolol. II. Hepatic elimination in the rat. Pharmacology (Basel)8, 344–352 (1972)
Stenson, R.E., Constantino, R.T., Harrison, D.C.: Interrelationships of hepatic blood flow, cardiac output and blood levels of lidocaine in man. Circulation43, 205–211 (1971)
Wolfson, S., Gorlin, R.: Physiological and clinical aspects of beta-adrenergic blockade. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci.139, 1003–1009 (1967)
Zacharias, R.J., Cowen, K.J., Prestt, J., Vickers, J., Wall, B.G.: Propranolol in hypertension: A study of long-term therapy 1964–1970. Amer. Heart J.83, 755–761 (1972)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weiss, Y.A., Safar, M.E., Chevillard, C. et al. Comparison of the pharmacokinetics of intravenous dl-propranolol in borderline and permanent hypertension. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 10, 387–393 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00563074
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00563074