Abstract
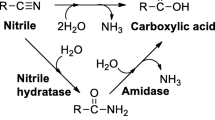
We found that ε-caprolactam is a new powerful inducer for the formation of Rhodococcus rhodochrous J1 nitrilase. When Rhodococcus rhodochrous J1 cells were cultivated at 28°C for 120 h in a nutrient medium supplemented with 0.5% (w/v) ε-caprolactam, an enormous amount of nitrilase was formed in the cells which corresponded to approximately 30% of all soluble protein. The level of ε-caprolactam in the culture broth barely decreased in the course of cultivation. γ-Butyrolactam and δ-valerolactam also caused effective induction. The induction of nitrilase formation by ε-caprolactam was also observed in some other Rhodococcus strains.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bandyopadhyay AK, Nagasawa T, Asano Y, Fujishiro K, Tani Y, Yamada H (1986) Purification and characterization of benzonitrilase from Arthrobacter sp. strain J-1. Appl Environ Microbiol 51:302–306
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein, utilizing the principle of protein dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Collins PA, Knowles CJ (1983) The utilization of nitriles and amides by Nocardia rhodochrous. J Gen Microbiol 129:711–718
Goldlust A, Bohak Z (1989) Induction, purification and characterization of the nitrilase of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. Melonis. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 11:581–601
Harper DB (1977a) Microbial metabolism of aromatic nitriles. Enzymology of C-n cleavage by Nocardia sp. (rhodochrous group) NCIB 11216. Biochen J 165:309–319
Harper DB (1977b) Fungal degradation of aromatic nitriles. Enzymology of C-N cleavage by Fusarium solani. Biochem J 167:685–692
Harper DB (1985) Characterization of a nitrilase from Nocardia sp. (rhodochrous group) NCIB 11215. Int J Biochem 17:677–683
Kobayashi M, Nagasawa T, Yamada H (1989) Nitrilase of Rhodococcus rhodochrous J1. Purification and characterization. Eur J Biochem 182:349–356
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Mathew CD, Nagasawa T, Kobayashi M, Yamada H (1988) Nitrilase-catalyzed production of nicotinic acid from 3-cyanopyridine in Rhodococcus rhodochrous J1. Appl Environ Microbiol 54:1030–1032
Nagasawa T, Yamada H (1989) Microbial transformation of nitriles. TIBTECH 7:153–158
Nagasawa T, Kobayashi M, Yamada H (1988a) Optimum culture conditions for the production of benzonitrilase by Rhodococcus rhodochrous J1. Arch Microbiol 150:89–94
Nagasawa T, Takeuchi K, Yamada H (1988b) Occurrence of a cobalt-induced and cobalt-containing nitrile hydratase in Rhodococcus rhodochrous J1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 155:1008–1016
Stalker DM, Malyj LD, McBride KE (1988) Purification and properties of a nitrilase specific for the herbicide bromoxynil and corresponding nucleotide sequence analysis of the bxn gene. J Biol Chem 263:6310–6314
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagasawa, T., Nakamura, T. & Yamada, H. ε-caprolactam, a new powerful inducer for the formation of Rhodococcus rhodochrous J1 nitrilase. Arch. Microbiol. 155, 13–17 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00291267
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00291267