Summary
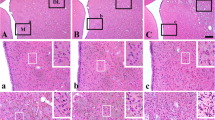
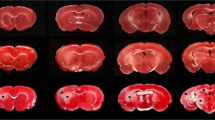
Male Fisher rats (n=61) underwent permanent focal cerebral ischemia induced by left middle cerebral artery (MCA) occlusion, in conjunction with ipsilateral common carotid artery ligation. The experiments were terminated at time points ranging from immediately following occlusion to 30 days post MCA occlusion. A coronal histological section, in close proximity to the site of the arterial occlusion, was taken from each brain and divided into six areas encompassing the affected cortex and caudate putamen. Each area was analyzed for ischemic damage according to a grading scale that reflects changes in neuronal morphology. Differential neuronal counts were also made on a 0.5-mm2 field in each of the six areas. The areas closest to the occluded vessel showed accelerated ischemic damage between 8 and 12 h after occlusion, leaving open the possibility that before 8 h, therapeutic intervention may be effective. After 12 h, changes in these areas progressed to complete necrosis and eventual cavitation with a complete loss of neurons after 10 days. The areas more peripheral to the occluded vessel exhibited mild ischemic damage, with an apparent reversal of damage grading at later time points and no loss of neurons. This reversal of ischemic damage in the peripheral areas is suggestive of a histological equivalent of the penumbra.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Astrup J, Siesjö BK, Symon L (1981) Thresholds in cerebral ischemia: the ischemic penumbra. Stroke 12:723–725
Bose B, Jones SC, Lorig R, Friel HT, Weinstein M, Little JR (1988) Evolving focal cerebral ischemia in cats: spatial correlation of nuclear magnetic resonance imaging, cerebral blood flow, tetrazolium staining, and histopathology. Stroke 19:28–37
Brierley JB (1976) Cerebral hypoxia. In: Adams JH, Corsellis JAN, Duchen LW (eds) Greenfield's neuropathology. Wiley and Sons, New York, pp 43–85
Brint S, Jacewicz M, Kiessling M, Tanabe J, Pulsinelli W (1988) Focal brain ischemia in the rat: methods for reproducible neocortical infarction using tandem occlusion of the distal middle cerebral and ipsilateral common carotid arteries. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 8:474–485
Brown AQ Brierley JB (1966) Evidence for early anoxicischemic cell damage in the rat brain. Experientia 22:546–547
Brown AW, Brierley JB (1968) The nature distribution and earliest stages of anoxic-ischemic nerve cell damage in the rat brain as defined by the optical microscope. Br J Exp Pathol 49:87–106
Cammermeyer J (1978) Is the solitary dark neuron a manifestation of postmortem trauma to the brain inadequately fixed by perfusion? Histochemistry 56:97–115
Chopp M, Li Y, Zhang ZG, Freytag SO (1992) p53 expression in brain after middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat. Biochem Biophysic Res Commun 182:1201–1207
Crowell RM, Marcoux FW, DeGirolami U (1981) Variability and reversibility of focal cerebral ischemia in unanesthetized monkeys. Neurology 31:1295–1302
DeGirolami U, Crowell RM, Marcoux FW (1984) Selective necrosis and total necrosis in focal cerebral ischemia: neuropathologic observations on experimental middle cerebral artery occlusion in the macaque monkey. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 43:57–71
Duverger D, Mackenzie ET (1988) The quantification of cerebral infarction following focal ischemia in the rat: influence of strain, arterial pressure, blood glucose concentration and age. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 8:449–461
Ebhardt G, Mies G, Auer LM, Traupe H, Heiss WD (1983) neuronal injury following permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion in cats. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 60:70–74
Eke A, Conger KA, Anderson M, Garcia JH (1990) Histologic assessment of neurons in rat models of cerebral ischemia. Stroke 21:299–304
Garcia JH, Kamijyo Y (1974) Cerebral infarction evolution of histopathologic changes after occlusion of a middle artery in primates. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 33:408–21
Garcia JH, Yoshida Y, Chen H, Li Y, Zhang Z, Lian J, Chen S, Chopp M (1992) Progression from ischemic injury to infarct following middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat. Am J Pathol (in press)
Hossmann KA, Schuier FJ (1980) Experimental brain infarcts in cats. I. Pathophysiological observations. Stroke 11:583–592
Iizuka H, Sakatani K, Young W (1989) Selective cortical neuronal damage after middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Stroke 20:1516–1523
Jacewicz M, Tanabe J, Pulsinelli W (1992) The CBF threshold and dynamics for focal cerebral infarction in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 12:359–370
Jakob A (1927) Normale und pathologische Anatomie und Histologie des Grosshirns. In: Deuticke F (ed) Normale Anatomie und Histologie und Allgemeine Histopathologie des Grosshirns, vol 1. Leipzig, Germany Deuticke pp 1–193
Jenkins LW, Povlishock JT, Lewelt W, Miller JD, Becker DP (1981) The role of postischemic recirculation in the development of ischemic neuronal injury following complete cerebral ischemia. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 55:205–220
Kirino T, Tamura A, Sano K (1984) Delayed neuronal death in the rat hippocampus following transient forebrain ischemia. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 64:139–147
Knight RA, Ordidge RJ, Helpern JA, Chopp M, Rodolosi LC, Peck D (1991) Temporal evolution of ischemic damage in rat brain measured by proton nuclear magnetic resonance imaging. Stroke 22:802–808
McGee-Russell SM, Brown AW, Brierley JB (1970) A combined light and electron microscope study of early anoxicischemic cell change in rat brain. Brain Res 20:193–200
Meier-Ruge W, Theodore D, Abraham J (1987) Enzyme histochemical investigation of the pathogenesis of ischemic brain lesions in primates and its clinical consequences. In: Cervós-Navarro J, Ferszt R (eds) Stroke and microcirculation. Raven Press, New York, pp 35–38
Meyer FB, Sundt TM, Yanagihara T, Anderson RE (1987) Focal cerebral ischemia: pathophysiologic mechanisms and rationale for future avenues of treatment. Mayo Clin Proc 62:35–55
Nedergaard M (1987) Neuronal injury in the infarct border: a neuropathological study in the rat. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 73:267–274
Nedergaard M (1988) Mechanisms of brain damage in focal cerebral ischemia. Acta Neurol Scand 77:81–101
Paxinos G, Watson C (1986) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, second edn. Academic Press, Orlando
Olsen TS (1986) Regional cerebral blood flow after occlusion of the middle cerebral artery. Acta Neurol Scand 73:321–337
Persson L, Hardemark HG, Bolander HG, Hillered L, Olsson Y (1989) Neurologic and neuropathologic outcome after middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Stroke 20:641–645
Petito CK, Lapinski RL (1986) Postischemic alterations in ultrastructural cytochemistry of neuronal golgi apparatus. Lab Invest 55:696–702
Petito CK, Pulsinelli WA (1984) Delayed neuronal recovery and neuronal death in rat hippocampus following severe cerebral ischemia: possible relationship to abnormalities in neuronal processes. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 4:194–205
Petito CK, Pulsinelli WA (1984) Sequential development of reversible and irreversible neuronal damage following cerebral ischemia. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 43:141–153
Pulsinelli WA, Brierley JB, Plum F (1982) Temporal profile of neuronal damage in a model of transient forebrain ischemia. Ann Neurol 11:491–498
Rubino GJ, Young W (1988) Ischemic cortical lesions after permanent occlusion of individual middle cerebral artery branches in rats. Stroke 19:870–877
Searle J, Kerr JFR, Bishop CJ (1992) Necrosis and Apoptosis: distinct modes of cell death with fundamentally different significance. Pathol Annu 17:229–259
Selman WR, Ricci AJ Crumrine RC, LaManna JC, Ratcheson RA, Lust WD (1990) The evolution of focal ischemic damage: a metabolic analysis. Metab Brain Dis 5:33–44
Shiino A, Harada K, Handa J, (1989) Focal brain ischemia model in rats. An experimental study. Surg Neurol 31:203–208
Smith ML, Auer RN, Siesjö BK (1984) The density and distribution of ischemic brain injury in the rat following 2–10 min of forebrain ischemia. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 64:319–332
Spielmeyer W (1922) Histopathologie des Nervensystems. Springer-Verlag, Berlin pp 74–79
Tyson GW, Teasdale GM, Graham DI, McCulloch J (1984) Focal cerebral ischemia in the rat: topography of hemodynamic and histopathological changes. Ann Neurol 15:559–567
Yamamoto K, Yoshimine T, Yanagihara T (1985) Cerebral ischemia in rabbit: a new experimental model with immunohistochemical investigation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 5:529–536
Yoshimine T, Yanagihara T (1983) Regional cerebral ischemia by occlusion of the posterior communicating artery and the middle cerebral in gerbils. T Neurosurg 58:362–367
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by NIH Grants NS23393 and NS29463
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dereski, M.O., Chopp, M., Knight, R.A. et al. The heterogeneous temporal evolution of focal ischemic neuronal damage in the rat. Acta Neuropathol 85, 327–333 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00227730
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00227730