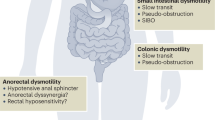
Abstract
The gastrointestinal tract is the most common organ system affected by systemic sclerosis (SSc) other than the skin. Greater than 90 % of SSc patients have esophageal involvement, and this primarily manifests as reflux and dysphagia. In addition to symptoms, complications include stricture, candidal esophagitis, and Barrett’s esophagus. There is an association between esophageal dysmotility and pulmonary disease, although causality has not been established. Gastric involvement is less common and can manifest as dysmotility or bleeding. Dysmotility often presents with impaired gastric emptying and associated symptoms, including nausea, postprandial fullness, bloating, and weight loss. Bleeding is often due to gastric antral vascular ectasia. While this affects a minority of SSc patients, consequences can be significant. This chapter will review the data regarding foregut manifestations and specifically will focus on diagnostic modalities and treatment options – including lifestyle modification, medical therapy, alternative therapy, endoscopic options, and surgical approaches where appropriate. Unfortunately, treatment remains supportive at present, and there is a lack of disease-modifying therapeutic options.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
LeRoy EC, Black C, Fleischmajer R, et al. Scleroderma (systemic sclerosis): classification, subsets and pathogenesis. J Rheumatol. 1988;15:202–5.
Clements PJ, Becvar R, Drosos AA, Ghattas L, Gabrielli A. Assessment of gastrointestinal involvement. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2003;21:S15–8.
Forbes A, Marie I. Gastrointestinal complications: the most frequent internal complications of systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2009;48 Suppl 3:iii36–9.
Steen VD, Medsger TA. Changes in causes of death in systemic sclerosis, 1972–2002. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007;66:940–4.
Vitali C, Borghi E, Napoletano A, et al. Oropharyngolaryngeal disorders in scleroderma: development and validation of the SLS scale. Dysphagia. 2010;25:127–38.
Scardina GA, Mazzullo M, Messina P. Early diagnosis of progressive systemic sclerosis: the role of oro-facial phenomena. Minerva Stomatol. 2002;51:311–7.
Domsic R, Fasanella K, Bielefeldt K. Gastrointestinal manifestations of systemic sclerosis. Dig Dis Sci. 2008;53:1163–74.
Roberts CG, Hummers LK, Ravich WJ, Wigley FM, Hutchins GM. A case-control study of the pathology of oesophageal disease in systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). Gut. 2006;55:1697–703.
Thoua NM, Bunce C, Brough G, Forbes A, Emmanuel AV, Denton CP. Assessment of gastrointestinal symptoms in patients with systemic sclerosis in a UK tertiary referral centre. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2010;49:1770–5.
Sjogren RW. Gastrointestinal motility disorders in scleroderma. Arthritis Rheum. 1994;37:1265–82.
Howe S, Eaker EY, Sallustio JE, Peebles C, Tan EM, Williams Jr RC. Antimyenteric neuronal antibodies in scleroderma. J Clin Invest. 1994;94:761–70.
Goldblatt F, Gordon TP, Waterman SA. Antibody-mediated gastrointestinal dysmotility in scleroderma. Gastroenterology. 2002;123:1144–50.
Cohen S, Fisher R, Lipshutz W, Turner R, Myers A, Schumacher R. The pathogenesis of esophageal dysfunction in scleroderma and Raynaud’s disease. J Clin Invest. 1972;51:2663–8.
Dessein PH, Joffe BI, Metz RM, Millar DL, Lawson M, Stanwix AE. Autonomic dysfunction in systemic sclerosis: sympathetic overactivity and instability. Am J Med. 1992;93:143–50.
Zuber-Jerger I, Muller A, Kullmann F, et al. Gastrointestinal manifestation of systemic sclerosis – thickening of the upper gastrointestinal wall detected by endoscopic ultrasound is a valid sign. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2010;49:368–72.
Thoua NM, Derrett-Smith EC, Khan K, Dooley A, Shi-Wen X, Denton CP. Gut fibrosis with altered colonic contractility in a mouse model of scleroderma. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2012;51:1989–98.
Taroni JN, Martyanov V, Huang CC, et al. Molecular characterization of systemic sclerosis esophageal pathology identifies inflammatory and proliferative signatures. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015;17:194.
Ostojic P, Damjanov N. Different clinical features in patients with limited and diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis. Clin Rheumatol. 2006;25:453–7.
Ebert EC. Esophageal disease in scleroderma. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2006;40:769–75.
Ebert EC. Esophageal disease in progressive systemic sclerosis. Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol. 2008;11:64–9.
Arif T, Masood Q, Singh J, Hassan I. Assessment of esophageal involvement in systemic sclerosis and morphea (localized scleroderma) by clinical, endoscopic, manometric and pH metric features: a prospective comparative hospital based study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2015;15:24.
Abu-Shakra M, Guillemin F, Lee P. Gastrointestinal manifestations of systemic sclerosis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1994;24:29–39.
Ling TC, Johnston BT. Esophageal investigations in connective tissue disease: which tests are most appropriate? J Clin Gastroenterol. 2001;32:33–6.
Kaye SA, Siraj QH, Agnew J, Hilson A, Black CM. Detection of early asymptomatic esophageal dysfunction in systemic sclerosis using a new scintigraphic grading method. J Rheumatol. 1996;23:297–301.
Harper RA, Jackson DC. Progressive systemic sclerosis. Br J Radiol. 1965;38:825–34.
Weston S, Thumshirn M, Wiste J, Camilleri M. Clinical and upper gastrointestinal motility features in systemic sclerosis and related disorders. Am J Gastroenterol. 1998;93:1085–9.
El-Serag HB, Sonnenberg A. Association of esophagitis and esophageal strictures with diseases treated with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Am J Gastroenterol. 1997;92:52–6.
Zamost BJ, Hirschberg J, Ippoliti AF, Furst DE, Clements PJ, Weinstein WM. Esophagitis in scleroderma. Prevalence and risk factors. Gastroenterology. 1987;92:421–8.
Katzka DA, Reynolds JC, Saul SH, et al. Barrett’s metaplasia and adenocarcinoma of the esophagus in scleroderma. Am J Med. 1987;82:46–52.
Segel MC, Campbell WL, Medsger Jr TA, Roumm AD. Systemic sclerosis (scleroderma) and esophageal adenocarcinoma: is increased patient screening necessary? Gastroenterology. 1985;89:485–8.
Vischio J, Saeed F, Karimeddini M, et al. Progression of esophageal dysmotility in systemic sclerosis. J Rheumatol. 2012;39:986–91.
Denis P, Ducrotte P, Pasquis P, Lefrancois R. Esophageal motility and pulmonary function in progressive systemic sclerosis. Respiration. 1981;42:21–4.
Johnson DA, Drane WE, Curran J, et al. Pulmonary disease in progressive systemic sclerosis. A complication of gastroesophageal reflux and occult aspiration? Arch Intern Med. 1989;149:589–93.
Lock G, Pfeifer M, Straub RH, et al. Association of esophageal dysfunction and pulmonary function impairment in systemic sclerosis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1998;93:341–5.
Marie I, Dominique S, Levesque H, et al. Esophageal involvement and pulmonary manifestations in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;45:346–54.
Kinuya K, Nakajima K, Kinuya S, Michigishi T, Tonami N, Takehara K. Esophageal hypomotility in systemic sclerosis: close relationship with pulmonary involvement. Ann Nucl Med. 2001;15:97–101.
Troshinsky MB, Kane GC, Varga J, et al. Pulmonary function and gastroesophageal reflux in systemic sclerosis. Ann Intern Med. 1994;121:6–10.
Savarino E, Bazzica M, Zentilin P, et al. Gastroesophageal reflux and pulmonary fibrosis in scleroderma: a study using pH-impedance monitoring. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009;179:408–13.
Zhang XJ, Bonner A, Hudson M, Canadian Scleroderma Research G, Baron M, Pope J. Association of gastroesophageal factors and worsening of forced vital capacity in systemic sclerosis. J Rheumatol. 2013;40:850–8.
Christmann RB, Wells AU, Capelozzi VL, Silver RM. Gastroesophageal reflux incites interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis: clinical, radiologic, histopathologic, and treatment evidence. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2010;40:241–9.
Olive A, Juncosa S, Evison G, Maddison PJ. Air in the oesophagus: a sign of oesophageal involvement in systemic sclerosis. Clin Rheumatol. 1995;14:319–21.
Madani G, Katz RD, Haddock JA, Denton CP, Bell JR. The role of radiology in the management of systemic sclerosis. Clin Radiol. 2008;63:959–67.
Clements PJ, Kadell B, Ippoliti A, Ross M. Esophageal motility in progressive systemic sclerosis (PSS). Comparison of cine-radiographic and manometric evaluation. Dig Dis Sci. 1979;24:639–44.
Weihrauch TR, Korting GW. Manometric assessment of oesophageal involvement in progressive systemic sclerosis, morphea and Raynaud’s disease. Br J Dermatol. 1982;107:325–32.
Jayanthi V, Srinivasan V, Nayak VM, Krishnamurthi V, Victor S. Comparative evaluation of cine-esophagogram with esophageal manometry in assessing esophageal motility in progressive systemic sclerosis. Indian J Gastroenterol. 1996;15:129–31.
Klein HA, Wald A, Graham TO, Campbell WL, Steen VD. Comparative studies of esophageal function in systemic sclerosis. Gastroenterology. 1992;102:1551–6.
Lock G, Zeuner M, Straub RH, et al. Esophageal manometry in systemic sclerosis: screening procedure or confined to symptomatic patients? Rheumatol Int. 1997;17:61–6.
Bassotti G, Battaglia E, Debernardi V, et al. Esophageal dysfunction in scleroderma: relationship with disease subsets. Arthritis Rheum. 1997;40:2252–9.
Thonhofer R, Siegel C, Trummer M, Graninger W. Early endoscopy in systemic sclerosis without gastrointestinal symptoms. Rheumatol Int. 2012;32(1):165–8.
Marie I, Ducrotte P, Denis P, Hellot MF, Levesque H. Oesophageal mucosal involvement in patients with systemic sclerosis receiving proton pump inhibitor therapy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006;24:1593–601.
Wegener M, Adamek RJ, Wedmann B, Jergas M, Altmeyer P. Gastrointestinal transit through esophagus, stomach, small and large intestine in patients with progressive systemic sclerosis. Dig Dis Sci. 1994;39:2209–15.
Savarino E, Mei F, Parodi A, et al. Gastrointestinal motility disorder assessment in systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2013;52:1095–100.
Rajapakse CN, Bancewicz J, Jones CJ, Jayson MI. Pharyngo-oesophageal dysphagia in systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1981;40:612–4.
Mainie I, Tutuian R, Patel A, Castell DO. Regional esophageal dysfunction in scleroderma and achalasia using multichannel intraluminal impedance and manometry. Dig Dis Sci. 2008;53:210–6.
Hirano I, Richter JE. ACG practice guidelines: esophageal reflux testing. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007;102:668–85.
Carlo-Stella N, Belloli L, Barbera R, et al. Gastroesophageal reflux and lung disease in systemic sclerosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009;179:1167; author reply -8.
Carlson DA, Hinchcliff M, Pandolfino JE. Advances in the evaluation and management of esophageal disease of systemic sclerosis. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2015;17:475.
Kahan A, Bour B, Couturier D, Amor B, Menkes CJ. Nifedipine and esophageal dysfunction in progressive systemic sclerosis. A controlled manometric study. Arthritis Rheum. 1985;28:490–5.
Jean F, Aubert A, Bloch F, et al. Effects of diltiazem versus nifedipine on lower esophageal sphincter pressure in patients with progressive systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1986;29:1054–5.
Kowal-Bielecka O, Landewe R, Avouac J, et al. EULAR recommendations for the treatment of systemic sclerosis: a report from the EULAR Scleroderma Trials and Research group (EUSTAR). Ann Rheum Dis. 2009;68:620–8.
Hansi N, Thoua N, Carulli M, et al. Consensus best practice pathway of the UK scleroderma study group: gastrointestinal manifestations of systemic sclerosis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2014;32:S-214–21.
Olive A, Maddison PJ, Davis M. Treatment of oesophagitis in scleroderma with omeprazole. Br J Rheumatol. 1989;28:553.
Hendel L. Hydroxyproline in the oesophageal mucosa of patients with progressive systemic sclerosis during omeprazole-induced healing of reflux oesophagitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1991;5:471–80.
Shoenut JP, Wieler JA, Micflikier AB. The extent and pattern of gastro-oesophageal reflux in patients with scleroderma oesophagus: the effect of low-dose omeprazole. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1993;7:509–13.
Gough A, Andrews D, Bacon PA, Emery P. Evidence of omeprazole-induced small bowel bacterial overgrowth in patients with scleroderma. Br J Rheumatol. 1995;34:976–7.
Reimer C. Safety of long-term PPI therapy. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2013;27:443–54.
Hendel L, Aggestrup S, Stentoft P. Long-term ranitidine in progressive systemic sclerosis (scleroderma) with gastroesophageal reflux. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1986;21:799–805.
Petrokubi RJ, Jeffries GH. Cimetidine versus antacid in scleroderma with reflux esophagitis. A randomized double-blind controlled study. Gastroenterology. 1979;77:691–5.
Janiak P, Thumshirn M, Menne D, et al. Clinical trial: the effects of adding ranitidine at night to twice daily omeprazole therapy on nocturnal acid breakthrough and acid reflux in patients with systemic sclerosis – a randomized controlled, cross-over trial. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2007;26:1259–65.
Horowitz M, Maddern GJ, Maddox A, Wishart J, Chatterton BE, Shearman DJ. Effects of cisapride on gastric and esophageal emptying in progressive systemic sclerosis. Gastroenterology. 1987;93:311–5.
Wehrmann T, Caspary WF. Effect of cisapride on esophageal motility in healthy probands and patients with progressive systemic scleroderma. Klin Wochenschr. 1990;68:602–7.
Kahan A, Chaussade S, Gaudric M, et al. The effect of cisapride on gastro-oesophageal dysfunction in systemic sclerosis: a controlled manometric study. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1991;31:683–7.
Limburg AJ, Smit AJ, Kleibeuker JH. Effects of cisapride on the esophageal motor function of patients with progressive systemic sclerosis or mixed connective tissue disease. Digestion. 1991;49:156–60.
Wang SJ, La JL, Chen DY, Chen YH, Hsieh TY, Lin WY. Effects of cisapride on oesophageal transit of solids in patients with progressive systemic sclerosis. Clin Rheumatol. 2002;21:43–5.
Ramirez-Mata M, Ibanez G, Alarcon-Segovia D. Stimulatory effect of metoclopramide on the esophagus and lower esophageal sphincter of patients of patients with PSS. Arthritis Rheum. 1977;20:30–4.
Johnson DA, Drane WE, Curran J, et al. Metoclopramide response in patients with progressive systemic sclerosis. Effect on esophageal and gastric motility abnormalities. Arch Intern Med. 1987;147:1597–601.
Drane WE, Karvelis K, Johnson DA, Curran JJ, Silverman ED. Scintigraphic detection of metoclopramide esophageal stimulation in progressive systemic sclerosis. J Nucl Med. 1987;28:810–5.
Sridhar KR, Lange RC, Magyar L, Soykan I, McCallum RW. Prevalence of impaired gastric emptying of solids in systemic sclerosis: diagnostic and therapeutic implications. J Lab Clin Med. 1998;132:541–6.
Mercado U, Arroyo de Anda R, Avendano L, Araiza-Casillas R, Avendano-Reyes M. Metoclopramide response in patients with early diffuse systemic sclerosis. Effects on esophageal motility abnormalities. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2005;23:685–8.
Fiorucci S, Distrutti E, Bassotti G, et al. Effect of erythromycin administration on upper gastrointestinal motility in scleroderma patients. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1994;29:807–13.
Folwaczny C, Laritz M, Meurer M, Endres SP, Konig A, Schindlbeck N. Effects of various prokinetic drugs on gastrointestinal transit times in patients with progressive systemic scleroderma. Z Gastroenterol. 1997;35:905–12.
Sjogren RW. Gastrointestinal features of scleroderma. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 1996;8:569–75.
Tack J, Janssen P, Masaoka T, Farre R, Van Oudenhove L. Efficacy of buspirone, a fundus-relaxing drug, in patients with functional dyspepsia. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;10:1239–45.
Di Stefano M, Papathanasopoulos A, Blondeau K, et al. Effect of buspirone, a 5-HT1A receptor agonist, on esophageal motility in healthy volunteers. Dis Esophagus. 2012;25:470–6.
Karamanolis GP, Panopoulos S, Karlaftis A, et al. Beneficial effect of the 5-HT1A receptor agonist buspirone on esophageal dysfunction associated with systemic sclerosis: a pilot study. U Eur Gastroenterol J. 2015;3:266–71.
Henderson RD, Pearson FG. Surgical management of esophageal scleroderma. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1973;66:686–92.
Orringer MB, Orringer JS, Dabich L, Zarafonetis CJ. Combined collis gastroplasty – fundoplication operations for scleroderma reflux esophagitis. Surgery. 1981;90:624–30.
Mansour KA. Surgery for scleroderma of the esophagus: a 12-year experience. Updated in 1995. Ann Thorac Surg. 1995;60:227.
Poirier NC, Taillefer R, Topart P, Duranceau A. Antireflux operations in patients with scleroderma. Ann Thorac Surg. 1994;58:66–72; discussion -3.
Kent MS, Luketich JD, Irshad K, et al. Comparison of surgical approaches to recalcitrant gastroesophageal reflux disease in the patient with scleroderma. Ann Thorac Surg. 2007;84:1710–5; discussion 5-6.
Szamosi S, Szekanecz Z, Szucs G. Gastrointestinal manifestations in Hungarian scleroderma patients. Rheumatol Int. 2006;26:1120–4.
Sallam H, McNearney TA, Chen JD. Systematic review: pathophysiology and management of gastrointestinal dysmotility in systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006;23:691–712.
Marie I, Ducrotte P, Antonietti M, Herve S, Levesque H. Watermelon stomach in systemic sclerosis: its incidence and management. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2008;28:412–21.
Ingraham KM, O’Brien MS, Shenin M, Derk CT, Steen VD. Gastric antral vascular ectasia in systemic sclerosis: demographics and disease predictors. J Rheumatol. 2010;37:603–7.
Maddern GJ, Horowitz M, Jamieson GG, Chatterton BE, Collins PJ, Roberts-Thomson P. Abnormalities of esophageal and gastric emptying in progressive systemic sclerosis. Gastroenterology. 1984;87:922–6.
Marie I, Levesque H, Ducrotte P, et al. Gastric involvement in systemic sclerosis: a prospective study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001;96:77–83.
Fiorucci S, Distrutti E, Gerli R, Morelli A. Effect of erythromycin on gastric and gallbladder emptying and gastrointestinal symptoms in scleroderma patients is maintained medium term. Am J Gastroenterol. 1994;89:550–5.
Pfaffenbach B, Adamek RJ, Hagemann D, et al. Effect of progressive systemic sclerosis on antral myoelectrical activity and gastric emptying. Z Gastroenterol. 1996;34:517–21.
Franck-Larsson K, Hedenstrom H, Dahl R, Ronnblom A. Delayed gastric emptying in patients with diffuse versus limited systemic sclerosis, unrelated to gastrointestinal symptoms and myoelectric gastric activity. Scand J Rheumatol. 2003;32:348–55.
Marycz T, Muehldorfer SM, Gruschwitz MS, et al. Gastric involvement in progressive systemic sclerosis: electrogastrographic and sonographic findings. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1999;11:1151–6.
Mittal BR, Wanchu A, Das BK, Ghosh PP, Sewatkar AB, Misra RN. Pattern of gastric emptying in patients with systemic sclerosis. Clin Nucl Med. 1996;21:379–82.
Wedmann B, Wegener M, Adamek RJ, el Gammal S. Gastrobiliary motility after liquid fatty meal in progressive systemic sclerosis. A sonographic study. Dig Dis Sci. 1994;39:565–70.
Abell TL, Camilleri M, Donohoe K, et al. Consensus recommendations for gastric emptying scintigraphy: a joint report of the American Neurogastroenterology and Motility Society and the Society of Nuclear Medicine. Am J Gastroenterol. 2008;103:753–63.
Talley NJ. Diabetic gastropathy and prokinetics. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003;98:264–71.
Bortolotti M, Bolondi L, Santi V, Sarti P, Brunelli F, Barbara L. Patterns of gastric emptying in dysmotility-like dyspepsia. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1995;30:408–10.
Tang DM, Friedenberg FK. Gastroparesis: approach, diagnostic evaluation, and management. Dis Mon. 2011;57:74–101.
Cassilly D, Kantor S, Knight LC, et al. Gastric emptying of a non-digestible solid: assessment with simultaneous SmartPill pH and pressure capsule, antroduodenal manometry, gastric emptying scintigraphy. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2008;20:311–9.
Kuo B, McCallum RW, Koch KL, et al. Comparison of gastric emptying of a nondigestible capsule to a radio-labelled meal in healthy and gastroparetic subjects. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2008;27:186–96.
Parkman HP. Assessment of gastric emptying and small-bowel motility: scintigraphy, breath tests, manometry, and SmartPill. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2009;19:49–55, vi.
Rees WD, Leigh RJ, Christofides ND, Bloom SR, Turnberg LA. Interdigestive motor activity in patients with systemic sclerosis. Gastroenterology. 1982;83:575–80.
Marie I, Levesque H, Ducrotte P, et al. Manometry of the upper intestinal tract in patients with systemic sclerosis: a prospective study. Arthritis Rheum. 1998;41:1874–83.
McNearney TA, Sallam HS, Hunnicutt SE, et al. Gastric slow waves, gastrointestinal symptoms and peptides in systemic sclerosis patients. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2009;21:1269–e120.
Tung A, Sweitzer B, Cutter T. Cardiac arrest after labetalol and metoclopramide administration in a patient with scleroderma. Anesth Analg. 2002;95:1667–8, table of contents.
Patterson D, Abell T, Rothstein R, Koch K, Barnett J. A double-blind multicenter comparison of domperidone and metoclopramide in the treatment of diabetic patients with symptoms of gastroparesis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1999;94:1230–4.
Parkman HP, Jacobs MR, Mishra A, et al. Domperidone treatment for gastroparesis: demographic and pharmacogenetic characterization of clinical efficacy and side-effects. Dig Dis Sci. 2011;56:115–24.
Buffery PJ, Strother RM. Domperidone safety: a mini-review of the science of QT prolongation and clinical implications of recent global regulatory recommendations. N Z Med J. 2015;128:66–74.
Verne GN, Eaker EY, Hardy E, Sninsky CA. Effect of octreotide and erythromycin on idiopathic and scleroderma-associated intestinal pseudoobstruction. Dig Dis Sci. 1995;40:1892–901.
Masaoka T, Tack J. Gastroparesis: current concepts and management. Gut Liver. 2009;3:166–73.
Maganti K, Onyemere K, Jones MP. Oral erythromycin and symptomatic relief of gastroparesis: a systematic review. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003;98:259–63.
Linke R, Meier M, Muenzing W, Folwaczny C, Schnell O, Tatsch K. Prokinetic therapy: what can be measured by gastric scintigraphy? Nucl Med Commun. 2005;26:527–33.
Wu KL, Rayner CK, Chuah SK, et al. Effects of ginger on gastric emptying and motility in healthy humans. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;20:436–40.
Chaiyakunapruk N, Kitikannakorn N, Nathisuwan S, Leeprakobboon K, Leelasettagool C. The efficacy of ginger for the prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting: a meta-analysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2006;194:95–9.
Sallam HS, McNearney TA, Chen JD. Acupuncture-based modalities: novel alternative approaches in the treatment of gastrointestinal dysmotility in patients with systemic sclerosis. Explore (NY). 2014;10:44–52.
Wollaston DE, Xu X, Tokumaru O, Chen JD, McNearney TA. Patients with systemic sclerosis have unique and persistent alterations in gastric myoelectrical activity with acupressure to Neiguan point PC6. J Rheumatol. 2005;32:494–501.
Sallam H, McNearney TA, Doshi D, Chen JD. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) improves upper GI symptoms and balances the sympathovagal activity in scleroderma patients. Dig Dis Sci. 2007;52:1329–37.
McNearney TA, Sallam HS, Hunnicutt SE, Doshi D, Chen JD. Prolonged treatment with transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) modulates neuro-gastric motility and plasma levels of vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP), motilin and interleukin-6 (IL-6) in systemic sclerosis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2013;31:140–50.
Friedenberg FK, Palit A, Parkman HP, Hanlon A, Nelson DB. Botulinum toxin A for the treatment of delayed gastric emptying. Am J Gastroenterol. 2008;103:416–23.
Duchini A, Sessoms SL. Gastrointestinal hemorrhage in patients with systemic sclerosis and CREST syndrome. Am J Gastroenterol. 1998;93:1453–6.
Jabbari M, Cherry R, Lough JO, Daly DS, Kinnear DG, Goresky CA. Gastric antral vascular ectasia: the watermelon stomach. Gastroenterology. 1984;87:1165–70.
Ghrenassia E, Avouac J, Khanna D, et al. Prevalence, correlates and outcomes of gastric antral vascular ectasia in systemic sclerosis: a EUSTAR case-control study. J Rheumatol. 2014;41:99–105.
Gostout CJ, Viggiano TR, Ahlquist DA, Wang KK, Larson MV, Balm R. The clinical and endoscopic spectrum of the watermelon stomach. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1992;15:256–63.
Suit PF, Petras RE, Bauer TW, Petrini Jr JL. Gastric antral vascular ectasia. A histologic and morphometric study of “the watermelon stomach”. Am J Surg Pathol. 1987;11:750–7.
Chawla SK, Ramani K, Lo Presti P. The honeycomb stomach: coalesced gastric angiodysplasia. Gastrointest Endosc. 1990;36:516–8.
Sebastian S, O’Morain CA, Buckley MJ. Review article: current therapeutic options for gastric antral vascular ectasia. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2003;18:157–65.
Dulai GS, Jensen DM. Treatment of watermelon stomach. Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol. 2006;9:175–80.
Lorenzi AR, Johnson AH, Davies G, Gough A. Gastric antral vascular ectasia in systemic sclerosis: complete resolution with methylprednisolone and cyclophosphamide. Ann Rheum Dis. 2001;60:796–8.
Schulz SW, O’Brien M, Maqsood M, Sandorfi N, Del Galdo F, Jimenez SA. Improvement of severe systemic sclerosis-associated gastric antral vascular ectasia following immunosuppressive treatment with intravenous cyclophosphamide. J Rheumatol. 2009;36:1653–6.
Tran A, Villeneuve JP, Bilodeau M, et al. Treatment of chronic bleeding from gastric antral vascular ectasia (GAVE) with estrogen-progesterone in cirrhotic patients: an open pilot study. Am J Gastroenterol. 1999;94:2909–11.
Kantsevoy SV, Cruz-Correa MR, Vaughn CA, Jagannath SB, Pasricha PJ, Kalloo AN. Endoscopic cryotherapy for the treatment of bleeding mucosal vascular lesions of the GI tract: a pilot study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003;57:403–6.
Cho S, Zanati S, Yong E, et al. Endoscopic cryotherapy for the management of gastric antral vascular ectasia. Gastrointest Endosc. 2008;68:895–902.
Shaheen NJ, Sharma P, Overholt BF, et al. Radiofrequency ablation in Barrett’s esophagus with dysplasia. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:2277–88.
Gross SA, Al-Haddad M, Gill KR, Schore AN, Wallace MB. Endoscopic mucosal ablation for the treatment of gastric antral vascular ectasia with the HALO90 system: a pilot study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2008;67:324–7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Clarke, J.O., Pandolfino, J.E. (2017). Upper Gastrointestinal Tract: Manifestations of Systemic Sclerosis. In: Varga, J., Denton, C., Wigley, F., Allanore, Y., Kuwana, M. (eds) Scleroderma. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-31407-5_30
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-31407-5_30
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-31405-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-31407-5
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)