Abstract
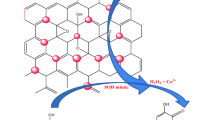
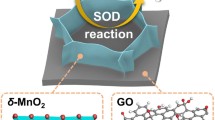
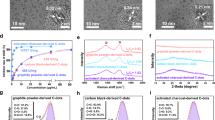
Although nanozyme has become an emerging area of research attracting extensive attention recently, the activity and specificity of currently reported nanozymes are generally lower than those of natural enzymes. Developing highly active and specific nanozymes is therefore extremely necessary and also remains a great challenge. Superoxide dismutase (SOD) catalyzes the disproportionation of cytotoxic O2− into hydrogen peroxide and oxygen, and plays an important role in reducing human oxidative stress. In this work, we prepare Cu single-atom catalysts (Cu/GO SACs, GO = graphene oxide) through a simple and low-cost strategy at room temperature using Cu foam and graphene oxide. Cu/GO SACs can maintain excellent catalytic activity under harsh environment. Compared with the natural enzyme, SOD-like Cu/GO SAC nanozyme has higher catalytic activity and meanwhile, it does not possess the common properties of other mimic enzymes often existing in nanomaterials. Based on the excellent SOD-like enzyme activity of Cu/GO SACs, it successfully eliminates the active oxygen in cigarette smoke. This work not only provides a new idea for the design and synthesis of nanozymes with excellent SOD mimetic properties, but also is promising in the treatment of lung injury and inflammatory diseases related to free radical production.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lincoln, K. M.; Gonzalez, P.; Richardson, T. E.; Julovich, D. A.; Saunders, R.; Simpkins, J. W.; Green, K. N. A potent antioxidant small molecule aimed at targeting metal-based oxidative stress in neurodegenerative disorders. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 2712–2714.
Perez, L. R.; Franz, K. J. Minding metals: Tailoring multifunctional chelating agents for neurodegenerative disease. Dalton Trans. 2010, 39, 2177–2187.
Hayyan, M.; Hashim, M. A.; AlNashef, I. M. Superoxide ion: Generation and chemical implications. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 3029–3085.
Halliwell, B. Reactive oxygen species in living systems: Source, biochemistry, and role in human disease. Am. J. Med. 1991, 91, S14–S22.
Bandyopadhyay, U.; Das, D.; Banerjee, R. K. Reactive oxygen species: Oxidative damage and pathogenesis. Curr. Sci. 1999, 77, 658–666.
Valentine, J. S.; Wertz, D. L.; Lyons, T. J.; Liou, L. L.; Goto, J. J.; Gralla, E. B. The dark side of dioxygen biochemistry. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 1998, 2, 253–262.
Martínez-Camarena, Á.; Sánchez-Murcia, P. A.; Blasco, S.; González, L.; García-España, E. Unveiling the reaction mechanism of novel copper N-alkylated tetra-azacyclophanes with outstanding superoxide dismutase activity. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 7511–7514.
Valko, M.; Leibfritz, D.; Moncol, J.; Cronin, M. T. D.; Mazur, M.; Telser, J. Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 39, 44–84.
Zhong, M. X.; Chi, M. Q.; Ma, F. Q.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, C.; Lu, X. F. Dual responsive enzyme mimicking of ternary polyaniline-MnO2-Pd nanowires and its application in colorimetric biosensing. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 16482–16492.
Fridovich, I. Superoxide dismutases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1975, 44, 147–159.
Iuchi, Y.; Roy, D.; Okada, F.; Kibe, N.; Tsunoda, S.; Suzuki, S.; Takahashi, M.; Yokoyama, H.; Yoshitake, J.; Kondo, S. et al. Spontaneous skin damage and delayed wound healing in SOD1-deficient mice. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2010, 341, 181–194.
Yasui, K.; Baba, A. Therapeutic potential of superoxide dismutase (SOD) for resolution of inflammation. Inflamm. Res. 2016, 55, 359–363.
McCord, J. M.; Edeas, M. A. SOD, oxidative stress and human pathologies: A brief history and a future vision. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2005, 59, 139–142.
Zhou, W. Q.; Li, H. F.; Xia, B.; Ji, W. L.; Ji, S. B.; Zhang, W. N.; Huang, W.; Huo, F. W.; Xu, H. P. Selenium-functionalized metal-organic frameworks as enzyme mimics. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 5761–5768.
Liang, M. M.; Yan, X. Y. Nanozymes: From new concepts, mechanisms, and standards to applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 2190–2200.
Jiang, D. W.; Ni, D. L.; Rosenkrans, Z. T.; Huang, P.; Yan, X. Y.; Cai, W. B. Nanozyme: New horizons for responsive biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 3683–3704.
Ding, H.; Hu, B.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, H.; Yan, X. Y.; Nie, G. H.; Liang, M. M. Carbon-based nanozymes for biomedical applications. Nano Res. 2021, 14, 570–583.
Wu, J. J. X.; Li, S. R.; Wei, H. Integrated nanozymes: Facile preparation and biomedical applications. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 6520–6530.
Zhang, X. J.; Lin, S. J.; Liu, S. W.; Tan, X. L.; Dai, Y.; Xia, F. Advances in organometallic/organic nanozymes and their applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2020, 429, 213652.
Lu, M. J.; Wang, C.; Ding, Y. Q.; Peng, M. H.; Zhang, W.; Li, K.; Wei, W.; Lin, Y. Q. Fe-N/C single-atom catalysts exhibiting multienzyme activity and ROS scavenging ability in cells. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 14534–14537.
Wu, J. J. X.; Wang, X. Y.; Wang, Q.; Lou, Z. P.; Li, S. R.; Zhu, Y. Y.; Qin, L.; Wei, H. Nanomaterials with enzyme-like characteristics (nanozymes): Next-generation artificial enzymes (II). Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 1004–1076.
Zhou, X.; Zeng, W. N.; Rong, S.; Lv, H.; Chen, Y. H.; Mao, Y. H.; Tan, W. L.; Li, H. Alendronate-modified nanoceria with multiantioxidant enzyme-mimetic activity for reactive oxygen species/reactive nitrogen species scavenging from cigarette smoke. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 47394–47406.
Zhang, D. Y.; Liu, H. K.; Li, C. Y.; Younis, M. R.; Lei, S.; Yang, C.; Lin, J.; Li, Z. M.; Huang, P. Ceria nanozymes with preferential renal uptake for acute kidney injury alleviation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 56830–56838.
Huang, Y. Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, C. Q.; Ju, E. G.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, J. S.; Qu, X. G. Self-assembly of multi-nanozymes to mimic an intracellular antioxidant defense system. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 6646–6650.
Liu, Y. F.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, M.; Yu, Y. J.; Lin, S. C.; Jiang, B.; Zhao, X. Z.; Miao, L. Y.; Wei, C. W. et al. Integrated cascade nanozyme catalyzes in vivo ROS scavenging for antiinflammatory therapy. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabb2695.
Lin, S. C.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X. Y.; Zhang, Y. Y.; Zhang, Y. J.; Miao, L. Y.; Zhao, X. Z.; Wei, H. Copper tannic acid coordination nanosheet: A potent nanozyme for scavenging ROS from cigarette smoke. Small 2020, 16, 1902123.
Wang, A. Q.; Li, J.; Zhang, T. Heterogeneous single-atom catalysis. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2018, 2, 65–81.
Zhang, H. B.; Liu, G. G.; Shi, L.; Ye, J. H. Single-atom catalysts: Emerging multifunctional materials in heterogeneous catalysis. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1701343.
Li, X. Y.; Rong, H. P.; Zhang, J. T.; Wang, D. S.; Li, Y. D. Modulating the local coordination environment of single-atom catalysts for enhanced catalytic performance. Nano Res. 2020, 13, 1842–1855.
Zhou, M.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, G.; Wu, W. J.; Chen, W. X.; Yu, P.; Lin, Y. Q.; Mao, J. J.; Mao, L. Q. Single-atom Ni-N4 provides a robust cellular NO sensor. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3188.
Zhang, N. Q.; Ye, C. L.; Yan, H.; Li, L. C.; He, H.; Wang, D. S.; Li, Y. D. Single-atom site catalysts for environmental catalysis. Nano Res. 2020, 13, 3165–3182.
Pei, J. H.; Zhao, R. L.; Mu, X. Y.; Wang, J. Y.; Liu, C. L.; Zhang, X. D. Single-atom nanozymes for biological applications. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 6428–6441.
Wu, K. L.; Chen, X.; Liu, S. J.; Pan, Y.; Cheong, W. C.; Zhu, W.; Cao, X.; Shen, R. G.; Chen, W. X.; Luo, J. et al. Porphyrin-like Fe-N4 sites with sulfur adjustment on hierarchical porous carbon for different rate-determining steps in oxygen reduction reaction. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 6260–6269.
Cao, F. F.; Zhang, L.; You, Y. W.; Zheng, L. R.; Ren, J. S.; Qu, X. G. An enzyme-mimicking single-atom catalyst as an efficient multiple reactive oxygen and nitrogen species scavenger for sepsis management. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 5108–5115.
Ma, W. J.; Mao, J. J.; Yang, X. T.; Pan, C.; Chen, W. X.; Wang, M.; Yu, P.; Mao, L. Q.; Li, Y. D. A single-atom Fe-N4 catalytic site mimicking bifunctional antioxidative enzymes for oxidative stress cytoprotection. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 159–162.
Li, Y. Q.; Liu, J. W. Nanozyme’s catching up: Activity, specificity, reaction conditions and reaction types. Mater. Horiz. 2021, 8, 336–350.
Liu, B. W.; Liu, J. W. Surface modification of nanozymes. Nano Res. 2017, 10, 1125–1148.
Dong, H. J.; Fan, Y. Y.; Zhang, W.; Gu, N.; Zhang, Y. Catalytic mechanisms of nanozymes and their applications in biomedicine. Bioconjug. Chem. 2019, 30, 1273–1296.
Wang, Q. Q.; Wei, H.; Zhang, Z. Q.; Wang, E. K.; Dong, S. J. Nanozyme: An emerging alternative to natural enzyme for biosensing and immunoassay. Trends Analyt. Chem. 2018, 105, 218–224.
Li, M. H.; Chen, J. X.; Wu, W. W.; Fang, Y. X.; Dong, S. J. Oxidase-like MOF-818 nanozyme with high specificity for catalysis of catechol oxidation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 15569–15574.
Chen, Y. J.; Wang, P. X.; Hao, H. G.; Hong, J. J.; Li, H. J.; Ji, S. F.; Li, A.; Gao, R.; Dong, J. C.; Han, X. D. et al. Thermal atomization of platinum nanoparticles into single atoms: An effective strategy for engineering high-performance nanozymes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 18643–18651.
Jiang, B.; Duan, D. M.; Gao, L. Z.; Zhou, M. J.; Fan, K. L.; Tang, Y.; Xi, J. Q.; Bi, Y. H.; Tong, Z.; Gao, G. F. et al. Standardized assays for determining the catalytic activity and kinetics of peroxidase-like nanozymes. Nat. Protoc. 2018, 13, 1506–1520.
Ji, S. F.; Jiang, B.; Hao, H. G.; Chen, Y. J.; Dong, J. C.; Mao, Y.; Zhang, Z. Z.; Gao, R.; Chen, W. X.; Zhang, R. F. et al. Matching the kinetics of natural enzymes with a single-atom iron nanozyme. Nat. Catal. 2021, 4, 407–417.
Bai, Y. H.; Zheng, Y. J.; Wang, Z.; Hong, Q.; Liu, S. Q.; Shen, Y. F.; Zhang, Y. J. Metal-doped carbon nitrides: Synthesis, structure and applications. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 11876–11892.
Qu, Y. T.; Wang, L. G.; Li, Z. J.; Li, P.; Zhang, Q. H.; Lin, Y.; Zhou, F. Y.; Wang, H. J.; Yang, Z. K.; Hu, Y. D. et al. Ambient synthesis of single-atom catalysts from bulk metal via trapping of atoms by surface dangling bonds. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1904496.
Lamberti, C.; Bordiga, S.; Salvalaggio, M.; Spoto, G.; Zecchina, A.; Geobaldo, F.; Vlaic, G.; Bellatreccia, M. XAFS, IR, and UV—vis study of the CuI environment in CuI-ZSM-5. J. Phys. Chem. B 1997, 101, 344–360.
Tang, X.; Wang, L.; Yang, B.; Fei, C.; Yao, T. Y.; Liu, W.; Lou, Y.; Dai, Q. G.; Cai, Y. F.; Cao, X. M. et al. Direct oxidation of methane to oxygenates on supported single Cu atom catalyst. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 285, 119827.
Zhang, J.; Zheng, C. Y.; Zhang, M. L.; Qiu, Y. J.; Xu, Q.; Cheong, W. C.; Chen, W. X.; Zheng, L. R.; Gu, L.; Hu, Z. P. et al. Controlling N-doping type in carbon to boost single-atom site Cu catalyzed transfer hydrogenation of quinoline. Nano Res. 2020, 13, 3082–3087.
Zhao, H. T.; Joseph, J.; Zhang, H.; Karoui, H.; Kalyanaraman, B. Synthesis and biochemical applications of a solid cyclic nitrone spin trap: A relatively superior trap for detecting superoxide anions and glutathiyl radicals. Free Radical Biol. Med. 2001, 31, 599–606.
Singh, N.; NaveenKumar, S. K.; Geethika, M.; Mugesh, G. A cerium vanadate nanozyme with specific superoxide dismutase activity regulates mitochondrial function and ATP synthesis in neuronal cells. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 3121–3130.
Zhao, H. Q.; Zhang, R. F.; Yan, X. Y.; Fan, K. L. Superoxide dismutase nanozymes: An emerging star for anti-oxidation. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 6939–6957.
Puchoňová, M.; Švorec, J.; Švorc, L.; Pavlik, J.; Mazúr, M.; Dlháň, L’.; Růzičková, Z.; Moncol’, J.; Valigura, D. Synthesis, spectral, magnetic properties, electrochemical evaluation and SOD mimetic activity of four mixed-ligand Cu(II) complexes. Inorg. Chim. Acta. 2017, 455, 298–306.
Guan, Y. J.; Gao, N.; Ren, J. S.; Qu, X. G. Rationally designed CeNP@MnMoS4 core-shell nanoparticles for modulating multiple facets of Alzheimer’s disease. Chem. -Eur. J. 2016, 22, 14523–14526.
Proctor, R. N. The history of the discovery of the cigarette-lung cancer link: Evidentiary traditions, corporate denial, global toll. Tob. Control. 2012, 21, 87–91.
Bluhm, A. L.; Weinstein, J.; Sousa, J. A. Free radicals in tobacco smoke. Nature 1971, 229, 500.
Onizawa, S.; Aoshiba, K.; Kajita, M.; Miyamoto, Y.; Nagai, A. Platinum nanoparticle antioxidants inhibit pulmonary inflammation in mice exposed to cigarette smoke. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 22, 340–349.
Aghapour, M.; Raee, P.; Moghaddam, S. J.; Hiemstra, P. S.; Heijink, I. H. Airway epithelial barrier dysfunction in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Role of cigarette smoke exposure. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2018, 58, 157–169.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 22074095), Beijing Municipal Natural Science Foundation (No. 2222005) and High-level Teachers in Beijing Municipal Universities in the Period of 13th Five-Year Plan (No. CIT&TCD20190330).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
12274_2022_4557_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Superoxide-like Cu/GO single-atom catalysts nanozyme with high specificity and activity for removing superoxide free radicals
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, M., Wang, J., Ren, G. et al. Superoxide-like Cu/GO single-atom catalysts nanozyme with high specificity and activity for removing superoxide free radicals. Nano Res. 15, 8804–8809 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-4557-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-4557-2