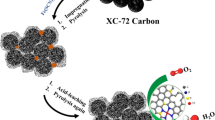
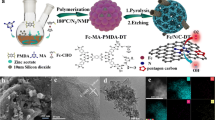
Abstract
We developed a strategy based on coordination polymer to synthesize singleatom site Fe/N and S-codoped hierarchical porous carbon (Fe1/N,S-PC). The as-obtained Fe1/N,S-PC exhibited superior oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) performance with a half-wave potential (E1/2, 0.904 V vs. RHE) that was better than that of commercial Pt/C (E1/2, 0.86 V vs. RHE), single-atom site Fe/N-doped hierarchical porous carbon (Fe1/N-PC) without S-doped (E1/2, 0.85 V vs. RHE), and many other nonprecious metal catalysts in alkaline medium. Moreover, the Fe1/N,S-PC revealed high methanol tolerance and firm stability. The excellent electrocatalytic activity of Fe1/N,S-PC is attributed to the synergistic effects from the atomically dispersed porphyrin-like Fe-N4 active sites, the heteroatom codoping (N and S), and the hierarchical porous structure in the carbon materials. The calculation based on density functional theory further indicates that the catalytic performance of Fe1/N,S-PC is better than that of Fe1/N-PC owing to the sulfur doping that yielded different rate-determining steps.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhou, M.; Wang, H.-L.; Guo, S. J. Towards high-efficiency nanoelectrocatalysts for oxygen reduction through engineering advanced carbon nanomaterials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 1273–1307.
Becknell, N.; Son, Y.; Kim, D.; Li, D. G.; Yu, Y.; Niu, Z. Q.; Lei, T.; Sneed, B. T.; More, K. L.; Markovic, N. M. et al. Control of architecture in rhombic dodecahedral Pt–Ni nanoframe electrocatalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 11678–11681.
Shen, M. X.; Wei, C. T.; Ai, K. L.; Lu, L. H. Transition metal–nitrogen–carbon nanostructured catalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction: From mechanistic insights to structural optimization. Nano Res. 2017, 10, 1449–1470.
Shang, C. Q.; Yang, M. Y.; Wang, Z. Y.; Li, M. C.; Liu, M.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, Y. G.; Zhou, L J..; Cheng, H.; Gu, Y. Y. et al. Encapsulated MnO in N-doping carbon nanofibers as efficient ORR electrocatalysts. Sci. China Mater. 2017, 60, 937–946.
Wu, S. S.; Zhu, Y. G.; Huo, Y. F.; Luo, Y. C.; Zhang, L. H.; Wan, Y.; Nan, B.; Cao, L. J.; Wang, Z. Y.; Li, M. C. et al. Bimetallic organic frameworks derived CuNi/carbon nanocomposites as efficient electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reaction. Sci. China Mater. 2017, 60, 654–663.
Wang, Q.; Zhou, Z. Y.; Lai, Y. J.; You, Y.; Liu, J. G.; Wu, X. L.; Terefe, E.; Chen, C.; Song, L.; Rauf, M. et al. Phenylenediamine-based FeNx/C catalyst with high activity for oxygen reduction in acid medium and its active-site probing. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 10882–10885.
Wang, J.; Li, L. Q.; Chen, X. L.; Lu, Y.; L. Yang, W. S.; Duan X. A Co-N/C hollow-sphere electrocatalyst derived from a metanilic CoAl layered double hydroxide for the oxygen reduction reaction, and its active sites in various pH media. Nano Res. 2017, 10, 2508–2518.
Jing, H. Y.; Song, X. D.; Ren, S. Z.; Shi, Y. T.; An, Y. L.; Yang, Y.; Feng, M. Q.; Ma, S. B.; Hao, C. ZIF-67 derived nanostructures of Co/CoO and Co@N-doped graphitic carbon as counter electrode for highly efficient dye-sensitized solar cells. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 213, 252–259.
Chen, M.; Zhao, G.; Shao, L.-L.; Yuan, Z.-Y.; Jing, Q.-S.; Huang, K.-J.; Huang, Z.-Y.; Zhao, X.-H.; Zou, G.-D. Controlled synthesis of nickel encapsulated into nitrogendoped carbon nanotubes with covalent bonded interfaces: The structural and electronic modulation strategy for an efficient electrocatalyst in dye-sensitized solar cells. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 9680–9694.
Ma, X.; Zhao, X.; Huang, J. S.; Sun, L. T.; Li, Q.; Yang, X. R. Fine Co nanoparticles encapsulated in a N-doped porous carbon matrix with superficial N-doped porous carbon nanofibers for efficient oxygen reduction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 21747–21755.
Zhu, Q.-L.; Xia, W.; Zheng, L.-R.; Zou, R. Q.; Liu, Z.; Xu, Q. Atomically dispersed Fe/N-doped hierarchical carbon architectures derived from a metal-organic framework composite for extremely efficient electrocatalysis. ACS Energy Lett. 2017, 2, 504–511.
Feng, S. Q.; Liu, C.; Chai, Z. G.; Li, Q.; Xu, D. S. Cobalt-based hydroxide nanoparticles@N-doping carbonic frameworks core–shell structures as highly efficient bifunctional electrocatalysts for oxygen evolution and oxygen reduction reactions. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 1482–1489.
Zheng, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Zhu, Y. H.; Cai, Q. R.; Vasileff, A.; Li, L. H.; Han, Y.; Chen, Y.; Qiao, S. Z. Molecule-level g-C3N4 coordinated transition metals as a new class of electrocatalysts for oxygen electrode reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 3336–3339.
Yan, D. F.; Guo, L.; Xie, C.; Wang, Y. Y.; Li, Y. X.; Li, H.; Wang, S. Y. N, P-dual doped carbon with trace Co and rich edge sites as highly efficient electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction reaction. Sci. China Mater. 2018, 61, 679–685.
Zang, Y. P.; Zhang, H. M.; Zhang, X.; Liu, R. R.; Liu, S. W.; Wang, G. Z.; Zhang, Y. X.; Zhao, H. J. Fe/Fe2O3 nanoparticles anchored on Fe-N-doped carbon nanosheets as bifunctional oxygen electrocatalysts for rechargeable zinc-air batteries. Nano Res. 2016, 9, 2123–2137.
Sun, M.; Zhang, G.; Liu, H. J.; Liu, Y.; Li, J. H. α- and γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticle/nitrogen doped carbon nanotube catalysts for high-performance oxygen reduction reaction. Sci. China Mater. 2015, 58, 683–692.
Xiao, J. W.; Xu, Y. Y.; Xia, Y. T.; Xi, J. B.; Wang, S. Ultra-small Fe2N nanocrystals embedded into mesoporous nitrogen doped graphitic carbon spheres as a highly active, stable, and methanol tolerant electrocatalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction. Nano Energy 2016, 24, 121–129.
Shen, H. J.; Gracia-Espino, E.; Ma, J. Y.; Zang, K. T.; Luo, J.; Wang, L.; Gao, S. S.; Mamat, X.; Hu, G. Z.; Wagberg, T. et al. Synergistic effects between atomically dispersed Fe-N-C and C-S-C for the oxygen reduction reaction in acidic media. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 13800–13804.
Zhang, G. X.; Jin, X. Y.; Li, H. Y.; Wang, L.; Hu, C. J.; Sun, X. M. N-doped crumpled graphene: Bottom-up synthesis and its superior oxygen reduction performance. Sci. China Mater. 2016, 59, 337–347.
Liu, Z. Y.; Zhang, G. X.; Lu, Z. Y.; Jin, X. Y.; Chang, Z.; Sun, X. M. One-step scalable preparation of N-doped nanoporous carbon as a high-performance electrocatalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction. Nano Res. 2013, 6, 293–301.
Wang, G.; Sun, Y. H.; Li, D. B.; Liang, H.-W.; Dong, R. H.; Feng, X. L.; Müllen, K. Controlled synthesis of N-doped carbon nanospheres with tailored mesopores through selfassembly of colloidal silica. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 15191–15196.
Liang, H. W.; Zhuang, X. D.; Brüller, S.; Feng X. L.; Müllen, K. Hierarchically porous carbons with optimized nitrogen doping as highly active electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4973.
Liang, H. W.; Wei, W.; Wu, Z. S.; Feng X. L.; Müllen, K. Mesoporous metal-nitrogen-doped carbon electrocatalysts for highly efficient oxygen reduction reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 16002–16005.
Masa, J.; Xia, W.; Muhler, M.; Schuhmann, W. On the role of metals in nitrogen-doped carbon electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 10102–10120.
Liu, D. B.; Wu, C. Q.; Chen, S. M.; Ding, S. Q.; Xie, Y. F.; Wang, C. D.; Wang, T.; Haleem, Y. A.; Rehman, Z.; Sang, Y. et al. In situ trapped high-density single metal atoms within graphene: Iron-containing hybrids as representatives for efficient oxygen reduction. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 2217–2228.
Chen, Y. J.; Ji, S. F.; Wang, Y. G.; Dong, J. C.; Chen, W. X.; Li, Z.; Shen, R. A.; Zheng, L. R.; Zhuang, Z. B.; Wang, D. S. et al. Isolated single iron atoms anchored on N-doped porous carbon as an efficient electrocatalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 6937–6941.
Yin, P. Q.; Yao, T.; Wu, Y.; Zheng, L. R.; Lin, Y.; Liu, W.; Ju, H. X.; Zhu, J. F.; Hong, X.; Deng, Z. X. et al. Single cobalt atoms with precise N-coordination as superior oxygen reduction reaction catalysts. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 10800–10805.
Song, P.; Luo, M.; Liu, X. Z.; Xing, W.; Xu, W. L.; Jiang Z.; Gu, L. Zn single atom catalyst for highly efficient oxygen reduction reaction. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1700802. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.201700802.
Han, Y. H.; Wang, Y. G.; Chen, W. X.; Xu, R. R.; Zheng, L. R.; Zhang, J.; Luo, J.; Shen, R. A.; Zhu, Y. Q.; Cheong, W. C. et al. Hollow N-doped carbon spheres with isolated cobalt single atomic sites: Superior electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 17269–17272.
Wang, J.; Huang, Z. Q.; Liu, W.; Chang, C. R.; Tang, H. L.; Li, Z. J.; Chen, W. X.; Jia, C. J.; Yao, T.; Wei, S. Q. et al. Design of N-coordinated dual-metal sites: A stable and active Pt-free catalyst for acidic oxygen reduction reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 17281–17284.
Chen, P. Z.; Zhou, T. P.; Xing, L. L.; Xu, K.; Tong, Y.; Xie, H.; Zhang, L. D.; Yan, W. S.; Chu, W. S.; Wu, C. Z. et al. Atomically dispersed iron-nitrogen species as electrocatalysts for bifunctional oxygen evolution and reduction reactions. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 610–614.
Zhu, C. Z.; Fu, S. F.; Shi, Q. R.; Du, D.; Lin, Y. H. Singleatom electrocatalysts. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 13944–13960.
Wang, Y. L.; Zhu, C. Z.; Feng, S.; Shi, Q. R.; Fu, S. F.; Du, D.; Zhang, Q.; Lin, Y. H. Interconnected Fe, S, N-codoped hollow and porous carbon nanorods as efficient electrocatalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 40298–40306.
Stephens, P. J.; Devlin, F. J.; Chabalowski, C. F.; Frisch, M. J. Ab initio calculation of vibrational absorption and circular dichroism spectra using density functional force fields. J. Phys. Chem. 1994, 98, 11623–11627.
Nicklass, A.; Dolg, M.; Stoll, H.; Preuss, H. Ab initio energy-adjusted pseudopotentials for the noble gases Ne through Xe: Calculation of atomic dipole and quadrupole polarizabilities. J. Chem. Phys. 1995, 102, 8942–8952.
Hay, P. J.; Wadt, W. R. Ab initio effective core potentials for molecular calculations. Potentials for K to Au including the outermost core orbitals. J. Chem. Phys. 1985, 82, 299–310.
Bondino, F.; Magnano, E.; Malvestuto, M.; Parmigiani, F.; McGuire, M. A.; Sefat, A. S.; Sales, B. C.; Jin, R.; Mandrus, D.; Plummer, E. W. et al. Evidence for strong itinerant spin fluctuations in the normal state of CeFeAsO0.89F0.11 ironoxypnictide superconductors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 101, 267001.
Zheng, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Zhu, Y. H.; Li, L. H.; Han, Y.; Chen, Y.; Du, A. J.; Jaroniec, M.; Qiao, S. Z. Hydrogen evolution by a metal-free electrocatalyst. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3783.
Jiao, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Jaroniec, M.; Qiao, S. Z. Design of electrocatalysts for oxygen- and hydrogen-involving energy conversion reactions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 2060–2086.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by China Ministry of Science and Technology under Contract of 2016YFA (0202801), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21521091, 21390393, U1463202, 21573119, 21590792, and 21501004). We thanks for the help from the Beijing Synchrotron Radiation Facility (BSRF) and National Synchrotron Radiation Laboratory (NSRL) in characterizations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
12274_2018_2149_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Porphyrin-like Fe-N4 sites with sulfur adjustment on hierarchical porous carbon for different rate-determining steps in oxygen reduction reaction
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, K., Chen, X., Liu, S. et al. Porphyrin-like Fe-N4 sites with sulfur adjustment on hierarchical porous carbon for different rate-determining steps in oxygen reduction reaction. Nano Res. 11, 6260–6269 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-018-2149-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-018-2149-y