Abstract
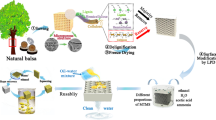
Tremendous efforts have been exerted to develop effective and ecofriendly materials for separation of oil/water mixtures and emulsions. However, porous materials with superwettability for oil/water separation are usually fabricated from nonrenewable precursors, which contradicts with the concept of green development. Inspired by the cellular porosity and hierarchical organization of wood, biodegradable cut and sawed wood slices with different pore sizes were separately machined by a razor blade and a fine-toothed saw. The cut and sawed slices separately possessed rough single- and double-layer structures. After silylation with MTCS, both machined slices repelled water entirely but allowed the complete permeation of oils. The fragment-free cut slice with relatively large pore size was able to separate immiscible oil/water mixtures, while the fragment-covered sawed slice with relatively small pore size could separate water-in-oil emulsions. Compared with other wood slice by sawing, the section structure and superoleophilic property made the slices have a high oil flux for a series of mixtures and emulsions, which reached 72 kL m−2 h−1 and 464 L m−2 h−1, respectively. The flux was high even after 10 cycles, exhibiting favorable recyclable stability.
Graphic abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Noamani, S, Niroomand, S, Rastgar, M, Sadrzadeh, M, “Carbon-based polymer nanocomposite membranes for oily wastewater treatment.” npj Clean Water, 2 1–14 (2019)
Jamaly, S, Giwa, A, Hasan, SW, “Recent improvements in oily wastewater treatment: Progress, challenges, and future opportunities.” J. Environ. Sci., 37 15–30 (2015)
Yu, ZP, Zhan, B, Dong, LM, Jiang, W, Song, Y, Hu, SA, “Self-healing structured graphene surface with reversible wettability for oil-water separation.” ACS Appl. Nano Mater., 2 1505–1515 (2019)
Cui, M, Mu, P, Shen, Y, Zhu, G, Luo, L, Li, J, “Three-dimensional attapulgite with sandwich-like architecture used for multifunctional water remediation.” Sep. Purif. Technol., 235 116210 (2020)
Zhang, H, Shen, Y, Li, M, Zhu, G, Feng, H, Li, J, “Egg shell powders-coated membrane for surfactant-stabilized crude oil-in-water emulsions efficient separation.” ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng., 7 10880–10887 (2019)
Das, S, Kumar, S, Samal, SK, Mohanty, S, Nayak, SK, “A review on superhydrophobic polymer nanocoatings: Recent development and applications.” Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 57 2727–2745 (2018)
Bai, X, Shen, Y, Tian, H, Yang, Y, Feng, H, Li, J, “Facile fabrication of superhydrophobic wood slice for effective water-in-oil emulsion separation.” Sep. Purif. Technol., 210 402–408 (2019)
Wang, B, Lei, B, Tang, Y, Xiang, D, Li, H, Ma, Q, Zhao, C, Li, Y, “Facile fabrication of robust superhydrophobic cotton fabrics modified by polysiloxane nanowires for oil/water separation.” J. Coat. Technol. Res., 15 611–621 (2018)
Feng, L, Zhang, Z, Mai, Z, Ma, Y, Liu, B, Jiang, L, Zhu, DA, “A super-hydrophobic and super-oleophilic coating mesh film for the separation of oil and water.” Angew. Chem., 116 2046–2048 (2004)
Cheng, B, Li, Z, Li, Q, Ju, J, Kang, W, Naebe, M, “Development of smart poly(vinylidene fluoride)-graft-poly(acrylic acid) tree-like nanofiber membrane for pH-responsive oil/water separation.” J. Membr. Sci., 534 1–8 (2017)
Li, F, Wang, Z, Pan, Y, Zhao, X, “A facile and effective method to fabricate superhydrophobic/superoeophilic surface for the separation of both water/oil mixtures and water-in-oil emulsions.” Polymers, 9 563 (2017)
Cai, Y, Chen, D, Li, N, Xu, QH, Li, J, He, J, Lu, J, “A facile method to fabricate a double-layer stainless steel mesh for effective separation of water-in-oil emulsions with high flux.” J. Mater. Chem. A, 4 18815–18821 (2016)
Liu, M, Hou, Y, Li, J, Guo, Z, “Stable superwetting meshes for on-demand separation of immiscible oil/water mixtures and emulsions.” Langmuir, 33 3702–3710 (2017)
Zhang, W, Liu, N, Cao, Y, Lin, X, Liu, Y, Feng, L, “Superwetting porous materials for wastewater treatment: From immiscible oil/water mixture to emulsion separation.” Adv. Mater. Interfaces, 4 1600029 (2017)
Ma, Q, Cheng, H, Fane, AG, Wang, R, Zhang, H, “Recent development of advanced materials with special wettability for selective oil/water separation.” Small, 12 2186–2202 (2016)
Wang, B, Liang, W, Guo, Z, Liu, W, “Biomimetic super-lyophobic and super-lyophilic materials applied for oil/water separation: A new strategy beyond nature.” Chem. Soc. Rev., 44 336–361 (2015)
Yong, J, Huo, J, Chen, F, Yang, Q, Hou, X, "Oil/water separation based on natural materials with super-wettability: Recent advances." Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 20 25140–25163 (2018)
Zhu, H, Guo, Z, “Understanding the separations of oil/water mixtures from immiscible to emulsions on super-wettable surfaces.” J. Bionic Eng., 13 1–29 (2016)
Vidiella del Blanco, M, Fischer, EJ, Cabane, E, “Underwater superoleophobic wood cross sections for efficient oil/water separation.” Adv. Mater. Interfaces, 4 1700584 (2017)
Yong, J, Chen, F, Huo, J, Fang, Y, Yang, Q, “Green, biodegradable, underwater superoleophobic wood sheet for efficient oil/water separation.” ACS Omega, 3 1395–1402 (2018)
Wang, K, Liu, X, Tan, Y, Zhang, W, Zhang, S, Li, J, “Two-dimensional membrane and three-dimensional bulk aerogel materials via top-down wood nanotechnology for multibehavioral and reusable oil/water separation.” J. Chem. Eng. J., 371 769–780 (2019)
Bai, X, Shen, Y, Tian, H, Yang, Y, Feng, H, Li, J, “Facile fabrication of superhydrophobic wood slice for effective water-in-oil emulsion separation.” J. Sep. Purif. Technol., 210 402–408 (2019)
Stehr, M, Gardner, DJ, Wålinder, ME, “Dynamic wettability of different machined wood surfaces.” J. Adhes., 76 185–200 (2001)
Sogutlu, C, Togay, A, “The effect of the process parameters in the planing processes on the surface roughness of cherry and pear woods.” Afr. J. Biotechnol., 10 4392–4399 (2011)
de Moura, LF, Hernández, RE, “Effects of abrasive mineral, grit size and feed speed on the quality of sanded surfaces of sugar maple wood.” Wood Sci. Technol., 40 517–530 (2006)
Boatright, SWJ, Garrett, GG, “The effect of microstructure and stress state on the fracture behaviour of wood.” J. Mater. Sci., 18 2181–2199 (1983)
Da Silva, A, Kyriakides, S, “Compressive response and failure of balsa wood.” Int. J. Solids Struct., 44 8685–8717 (2007)
Borrega, M, Ahvenainen, P, Serimaa, R, Gibson, L, “Composition and structure of balsa (Ochroma pyramidale) wood.” Wood Sci. Technol., 49 403–420 (2015)
Wallström, L, Lindberg, KAH, “Measurement of cell wall penetration in wood of water-based chemicals using SEM/EDS and STEM/EDS technique.” Wood Sci. Technol., 33 111–122 (1999)
McGovern, ME, Kallury, KM, “Role of solvent on the silanization of glass with octadecyltrichlorosilane.” Langmuir, 10 3607–3614 (1994)
Lu, Y, Feng, M, Zhan, H, “Preparation of SiO2-wood composites by an ultrasonic-assisted sol–gel technique.” Cellulose, 21 4393–4403 (2014)
Khoo, HS, Tseng, FG, “Engineering the 3D architecture and hydrophobicity of methyltrichlorosilane nanostructures.” Nanotechnology, 19 345603 (2008)
Wang, H, Huang, X, Li, B, Gao, J, “Facile preparation of super-hydrophobic nanofibrous membrane for oil/water separation in a harsh environment.” J. Mater. Sci., 53 10111–10121 (2018)
Gindl, M, Sinn, G, Reiterer, A, Tschegg, S, “Wood surface energy and time dependence of wettability: A comparison of different wood surfaces using an acid-base approach.” Holzforschung, 55 433–440 (2001)
Liptáková, E, Kúdela, J, Bastl, Z, Spirovová, I, “Influence of mechanical surface treatment of wood on the wetting process.” Holzforschung, 49 369–375 (1995)
Jiang, F, Li, T, Li, Y, Zhang, Y, Gong, A, Dai, J, Hu, L, “Wood-based nanotechnologies toward sustainability.” Adv. Mater., 30 1703453 (2018)
Boutilier, MS, Lee, J, Chambers, V, Venkatesh, V, “Water filtration using plant xylem.” PLoS One, 9 e89934 (2014)
Che, W, Xiao, Z, Wang, Z, Li, J, “Wood-based mesoporous filter decorated with silver nanoparticles for water purification.” ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng., 7 5134–5141 (2019)
Guan, H, Cheng, Z, Wang, X, “Highly compressible wood sponges with a spring-like lamellar structure as effective and reusable oil absorbents.” ACS Nano, 12 10365–10373 (2018)
Huang, W, Zhang, L, Lai, X, Li, H, Zeng, X, “Highly hydrophobic F-rGO@wood sponge for efficient clean-up of viscous crude oil.” Chem. Eng. J., 386 123994 (2020)
Hakkou, M, Pétrissans, M, Zoulalian, A, Gérardin, P, “Investigation of wood wettability changes during heat treatment on the basis of chemical analysis.” Polym. Degrad. Stabil., 89 1–5 (2005)
Dashairya, L, Barik, DD, Saha, P, “Methyltrichlorosilane functionalized silica nanoparticles-treated superhydrophobic cotton for oil–water separation.” J. Coat. Technol. Res., 16 1021–1032 (2019)
Pintor, AM, Vieira, BR, Santos, SC, Boaventura, RA, Botelho, CM, “Arsenate and arsenite adsorption onto iron-coated cork granulates.” Sci. Total Environ., 642 1075–1089 (2018)
Zheng, Z, Wang, H, Zhang, N, Zhao, X, “Preparation of self-cleaning polyester fabrics by chemical vapor deposition of methyltrichlorosilane/dimethyldichlorosilane.” Fibres Text. East. Eur., 25 121–124 (2017)
Wang, X, Yu, J, Sun, G, “Electrospun nanofibrous materials: A versatile medium for effective oil/water separation.” Mater. Today, 19 403–414 (2016)
Lee, YS, Lim, YT, Choi, WS, “One-step synthesis of environmentally friendly superhydrophilic and superhydrophobic sponges for oil/water separation.” Materials, 12 1182 (2019)
Acknowledgments
This research was financially support by Natural Science Foundation of Henan Province (162300410208), Foundation of Henan Educational Committee (16A150058), and High-level Talent Foundation of Pingdingshan University (PXY-BSQD-2015003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file2 (MP4 12497 kb)
Supplementary file3 (MP4 32520 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Y., Qu, K., Luo, X. et al. Different machined wood slices for separation of both oil/water mixtures and emulsions. J Coat Technol Res 18, 1431–1443 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11998-021-00511-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11998-021-00511-y