Abstract
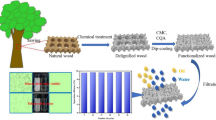
The preparation of environmentally friendly oil/water separation materials remains a great challenge. Freeze-drying of wood after lignin removal yields wood aerogels, which can be used as substrates to prepare fluorine-free environmentally friendly superhydrophobic materials, However, they are more suitable for absorption rather than filtration applications due to their poor strength. A study using cross-sections of pristine wood chips as substrates retains the original strength of wood, but the use of the cross-sectional of wood pieces limits their thickness, strength, and size. In this paper, a degradable fluorine-free superhydrophobic film (max. water contact angle of approximately 164.2°) with self-cleaning and abrasion resistance characteristics was prepared by a one-step method using pristine and activated walnut longitudinal section films as the substrate, with tetraethyl orthosilicate as a precursor and dodecyltriethoxysilane as a modifier. The tensile strength results show that superhydrophobic films with pristine or activated wood substrates maintained the strength of pristine wood and were 2.2 times stronger than the wood aerogel substrate. In addition, after cross-laminating the two samples, the films had the ability to separate oil and water by continuous filtration with high efficiency (98.5%) and flux (approximately 1.3 × 103 L·m−·h−1). The method has potential for the large-scale fabrication of degradable superhydrophobic filtration separation membranes.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wen L, Tian Y, Jiang L. Bioinspired super-wettability from fundamental research to practical applications. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2015, 54(11): 3387–3399
Wang S, Liu K, Yao X, Jiang L. Bioinspired surfaces with superwettability: new insight on theory, design, and applications. Chemical Reviews, 2015, 115(16): 8230–8293
Liu M, Wang S, Jiang L. Nature-inspired superwettability systems. Nature Reviews Materials, 2017, 2(7): 1–17
Yin X, Wang Z, Shen Y, Mu P, Zhu G, Li J. Facile fabrication of superhydrophobic copper hydroxide coated mesh for effective separation of water-in-oil emulsions. Separation and Purification Technology, 2020, 230: 115856
Xu W, Song J, Sun J, Lu Y, Yu Z. Rapid fabrication of large-area, corrosion-resistant superhydrophobic Mg alloy surfaces. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2011, 3(11): 4404–4414
Varanasi K K, Deng T, Smith J D, Hsu M, Bhate N. Frost formation and ice adhesion on superhydrophobic surfaces. Applied Physics Letters, 2010, 97(23): 234102
Zhang C, Liang F, Zhang W, Liu H, Ge M, Zhang Y, Dai J, Wang H, Xing G, Lai Y, Tang Y. Constructing mechanochemical durable and self-healing superhydrophobic surfaces. ACS Omega, 2020, 5(2): 986–994
Zhang J, Seeger S. Polyester materials with superwetting silicone nanofilaments for oil/water separation and selective oil absorption. Advanced Functional Materials, 2011, 21(24): 4699–4704
Ge M, Cao C, Huang J, Zhang X, Tang Y, Zhou X, Zhang K, Chen Z, Lai Y. Rational design of materials interface at nanoscale towards intelligent oil-water separation. Nanoscale Horizons, 2018, 3(3): 235–260
Feng L, Zhang Z, Mai Z, Ma Y, Liu B, Jiang L, Zhu D. A super-hydrophobic and super-oleophilic coating mesh film for the separation of oil and water. Angewandte Chemie, 2004, 116(15): 2046–2048
Li L, Xu Z, Sun W, Chen J, Dai C, Yan B, Zeng H. Bio-inspired membrane with adaptable wettability for smart oil/water separation. Journal of Membrane Science, 2020, 598: 117661
Lu K J, Zhao D, Chen Y, Chang J, Chung T S. Rheologically controlled design of nature-inspired superhydrophobic and self-cleaning membranes for clean water production. npj Clean Water, 2020, 3(1): 1–10
Zhang W, Shi Z, Zhang F, Liu X, Jin J, Jiang L. Superhydrophobic and superoleophilic PVDF membranes for effective separation of water-in-oil emulsions with high flux. Advanced Materials, 2013, 25(14): 2071–2076
Wang D, Sun Q, Hokkanen M J, Zhang C, Lin F Y, Liu Q, Zhu S P, Zhou T, Chang Q, He B, Zhou Q, Chen L, Wang Z, Ras R H A, Deng X. Design of robust superhydrophobic surfaces. Nature, 2020, 582(7810): 55–59
Peng Y, Zhu W, Shen S, Feng L, Deng Y. Strain-induced surface micro/nanosphere structure: a new technique to design mechanically robust superhydrophobic surfaces with rose petallike morphology. Advanced Materials Interfaces, 2017, 4(20): 1700497
Tian X, Verho T, Ras R H A. Moving superhydrophobic surfaces toward real-world applications. Science, 2016, 352(6282): 142–143
Hussain S M, Braydich-Stolle L K, Schrand A M, Murdock R C, Yu K O, Mattie D M, Schlager J J, Terrones M. Toxicity evaluation for safe use of nanomaterials: recent achievements and technical challenges. Advanced Materials, 2009, 21(16): 1549–1559
Berglund L A, Burgert I. Bioinspired wood nanotechnology for functional materials. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(19): 1704285
Jiang F, Li T, Li Y, Zhang Y, Gong A, Dai J, Hitz E, Luo W, Hu L. Wood-based nanotechnologies toward sustainability. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(1): 1703453
Chen F, Gong A S, Zhu M, Chen G, Lacey S D, Jiang F, Li Y, Wang Y, Dai J, Yao Y, Song J, Liu B, Fu K, Das S, Hu L. Mesoporous, three-dimensional wood membrane decorated with nanoparticles for highly efficient water treatment. ACS Nano, 2017, 11(4): 4275–4282
Vidiella del Blanco M, Fischer E J, Cabane E. Underwater superoleophobic wood cross sections for efficient oil/water separation. Advanced Materials Interfaces, 2017, 4(21): 1700584
Wang K, Liu X, Tan Y, Zhang W, Zhang S, Li J. Two-dimensional membrane and three-dimensional bulk aerogel materials via top-down wood nanotechnology for multibehavioral and reusable oil/water separation. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 371: 769–780
Fu Q, Ansari F, Zhou Q, Berglund L A. Wood nanotechnology for strong, mesoporous, and hydrophobic biocomposites for selective separation of oil/water mixtures. ACS Nano, 2018, 12(3): 2222–2230
Mulyadi A, Zhang Z, Deng Y. Fluorine-free oil absorbents made from cellulose nanofibril aerogels. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(4): 2732–2740
Bai X, Shen Y, Tian H, Yang Y, Feng H, Li J. Facile fabrication of superhydrophobic wood slice for effective water-in-oil emulsion separation. Separation and Purification Technology, 2019, 210: 402–408
Wang X, Liu S, Chang H, Liu J. Sol-gel deposition of TiO2 nanocoatings on wood surfaces with enhanced hydrophobicity and photostability. Wood and Fiber Science, 2014, 46(1): 109–117
Liu M, Qing Y, Wu Y, Liang J, Luo S. Facile fabrication of superhydrophobic surfaces on wood substrates via a one-step hydrothermal process. Applied Surface Science, 2015, 330: 332–338
Chang H, Tu K, Wang X, Liu J. Fabrication of mechanically durable superhydrophobic wood surfaces using polydimethylsiloxane and silica nanoparticles. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(39): 30647–30653
Wu Y, Jia S, Qing Y, Luo S, Liu M. A versatile and efficient method to fabricate durable superhydrophobic surfaces on wood, lignocellulosic fiber, glass, and metal substrates. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2016, 4(37): 14111–14121
Hsieh C T, Chang B S, Lin J Y. Improvement of water and oil repellency on wood substrates by using fluorinated silica nanocoating. Applied Surface Science, 2011, 257(18): 7997–8002
Xie L, Tang Z, Jiang L, Breedveld V, Hess D W. Creation of superhydrophobic wood surfaces by plasma etching and thin-film deposition. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2015, 281: 125–132
Unger B, Bücker M, Reinsch S, Hübert T. Chemical aspects of wood modification by sol-gel-derived silica. Wood Science and Technology, 2013, 47(1): 83–104
Wang X, Chai Y, Liu J. Formation of highly hydrophobic wood surfaces using silica nanoparticles modified with long-chain alkylsilane. Holzforschung, 2013, 67(6): 667–672
Ma P, Chen B, Di M. Activation processes of wood fiber under freezing by NaOH/urea aqueous solution. Biomass Chemical Engineering, 2018, 52: 16–22
Yong J, Chen F, Huo J, Fang Y, Yang Q, Bian H, Li W, Wei Y, Dai Y, Hou X. Green, Biodegradable, underwater superoleophobic wood sheet for efficient oil/water separation. ACS Omega, 2018, 3(2): 1395–1402
Chen Y, Lin X, Liu N, Cao Y, Lu F, Xu L, Feng L. Magnetically recoverable efficient demulsifier for water-in-oil emulsions. ChemPhysChem, 2015, 16(3): 595–600
Mi R, Li T, Dalgo D, Chen C, Kuang Y, He S, Zhao X, Xie W, Gan W, Zhu J, Srebric J, Yang R, Hu L. A clear, strong, and thermally insulated transparent wood for energy efficient windows. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 30(1): 1907511
Tu K, Wang X, Kong L, Chang H, Liu J. Fabrication of robust, damage-tolerant superhydrophobic coatings on naturally micro-grooved wood surfaces. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(1): 701–707
Liu F, Wang S, Zhang M, Ma M, Wang C, Li J. Improvement of mechanical robustness of the superhydrophobic wood surface by coating PVA/SiO2 composite polymer. Applied Surface Science, 2013, 280: 686–692
Feng L, Li S, Li Y, Li H, Zhang L, Zhai J, Song Y, Liu B, Jiang L, Zhu D. Super-hydrophobic surfaces: from natural to artificial. Advanced Materials, 2002, 14(24): 1857–1860
Faix O, Böttcher J H. The influence of particle size and concentration in transmission and diffuse reflectance spectroscopy of wood. European Journal of Wood & Wood Products, 1992, 50(6): 221–226
Popescu C M, Popescu M C, Vasile C. Structural analysis of photodegraded lime wood by means of FT-IR and 2D IR correlation spectroscopy. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2011, 48(4): 667–675
Labbé N, Rials T G, Kelley S S, Cheng Z M, Kim J Y, Li Y. FT-IR imaging and pyrolysis-molecular beam mass spectrometry: new tools to investigate wood tissues. Wood Science and Technology, 2005, 39(1): 61–76
Gao S, Dong X, Huang J, Li S, Li Y, Chen Z, Lai Y. Rational construction of highly transparent superhydrophobic coatings based on a non-particle, fluorine-free and water-rich system for versatile oil–water separation. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 333: 621–629
Hong J K, Kim H R, Park H H. The effect of sol viscosity on the sol-gel derived low density SiO2 xerogel film for intermetal dielectric application. Thin Solid Films, 1998, 332(1): 449–454
Liu C, Wang S, Shi J, Wang C. Fabrication of superhydrophobic wood surfaces via a solution-immersion process. Applied Surface Science, 2011, 258(2): 761–765
Arkles B, Larson G L. Silicon Compounds: Silanes & Silicones. 3rd edition. Morrisville, PA: Gelest, Inc., 2013
Zhu T, Cheng Y, Huang J, Xiong J, Ge M, Mao J, Liu Z, Dong X, Chen Z, Lai Y. A transparent superhydrophobic coating with mechanochemical robustness for anti-icing, photocatalysis and self-cleaning. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 399: 125746
Li J, Lu Y, Wu Z, Bao Y, Xiao R, Yu H, Chen Y. Durable, self-cleaning and superhydrophobic bamboo timber surfaces based on TiO2 films combined with fluoroalkylsilane. Ceramics International, 2016, 42(8): 9621–9629
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51776070) and the State Grid Science and Technology Program (Grant No. SGGNSW00YWJS2100024).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xing, T., Dong, C., Wang, X. et al. Biodegradable, superhydrophobic walnut wood membrane for the separation of oil/water mixtures. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 16, 1377–1386 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-022-2157-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-022-2157-z