Abstract
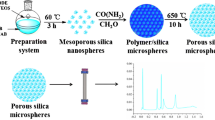
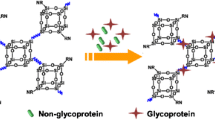
Ionic liquids are becoming widely applied in the extraction/separation of biological molecules. In this study, the solidification of ionic liquid 1-hydroxyethyl-3-vinylimidazole chloride ([HVIM]Cl) was achieved via one-pot free radical copolymerisation with divinylbenzene (DVB) as a cross-linking reagent, giving a mesoporous hydrophilic polymeric ionic liquid (PIL). Mesoporous PIL possesses a large surface area of 328.32 m2·g−1 and a high pore volume of 0.45 cm3·g−1. Owing to hydrophilic interactions and π–π stacking interactions, the PIL adsorbs ovalbumin (Ova) selectively with a theoretical maximum adsorption capacity of 2468.0 mg·g−1, and this Ova adsorption fit the Langmuir model well. The captured Ova was efficiently recovered using sodium dodecyl sulphate (0.4%, m·v−1) with an elution efficiency of 94.7%. Circular dichroism spectra indicated that the adsorption-elution process caused no conformational changes in Ova, indicating that the prepared PIL is highly biocompatible. The practicability of this mesoporous PIL was well demonstrated by the selective adsorption of Ova from protein mixtures and the efficient isolation of Ova from chicken egg white.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AIBN:
-
2,2′-Azobis(2-methylpropionitrile)
- BR:
-
Britton-Robinson
- CD:
-
Circular dichroism
- DI:
-
Deionised
- DVB:
-
Divinylbenzene
- FT-IR:
-
Fourier transform infrared
- [HVIM]Cl:
-
1-Hydroxyethyl-3-vinylimidazole chloride
- IL:
-
Ionic liquid
- PIL:
-
Polymeric ionic liquid
- Lys:
-
Lysozyme
- Ova:
-
Ovalbumin
- SDS:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulphate
- SDS-PAGE:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulphate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- SEM:
-
Scanning electron microscopy
- TEM:
-
Transmission electron microscopy
- TGA:
-
Thermogravimetric analysis
- Tris:
-
Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane
References
Dang M, Deng Q, Fang G, Zhang D, Liu J, Wang S (2017) Preparation of novel anionic polymeric ionic liquid materials and their potential application to protein adsorption. J Mater Chem B 5:6339–6347. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7TB01234A
Han L, Shu Y, Wang X, Chen X, Wang J (2013) Encapsulation of silica nano-spheres with polymerized ionic liquid for selective isolation of acidic proteins. Anal Bioanal Chem 405:8799–8806. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-013-7295-1
Fan J, Tian Z, Tong S, Zhang X, Xie Y, Xu R, Qin Y, Li L, Zhu J, Ouyang X (2013) A novel molecularly imprinted polymer of the specific ionic liquid monomer for selective separation of synephrine from methanol–water media. Food Chem 141:3578–3585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.06.040
Fan J, Yu J, Yang X, Zhang X, Yuan T, Peng H (2018) Preparation, characterization, and application of multiple stimuli-responsive rattle-type magnetic hollow molecular imprinted poly (ionic liquids) nanospheres (Fe3O4@void@PILMIP) for specific recognition of protein. Chem Eng J 337:722–732. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.12.159
Fan J, Zhang F, Yang X, Zhang X, Cao Y, Peng H (2018) Preparation of a novel supermacroporous molecularly imprinted cryogel membrane with a specific ionic liquid for protein recognition and permselectivity. J Appl Polym Sci 135:46740. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.46740
Zhan T, Song Y, Li X, Hou W (2016) Electrochemical sensor for bisphenol a based on ionic liquid functionalized Zn-Al layered double hydroxide modified electrode. Mater Sci Eng C 64:354–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2016.03.093
Mao H, Liang J, Ji C, Zhang H, Pei Q, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Hisaeda Y, Song X (2016) Poly(zwitterionic liquids) functionalized polypyrrole/graphene oxide nanosheets for electrochemically detecting dopamine at low concentration. Mater Sci Eng C 65:143–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2016.04.023
Jin L, Shi Z, Zhang X, Liu X, Li H, Wang J, Liang F, Zhao W, Zhao C (2019) Intelligent antibacterial surface based on ionic liquid molecular brushes for bacterial killing and release. J Mater Chem B 7:5520–5527. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9TB01199D
Florio W, Becherini S, D’Andrea F, Lupetti A, Chiappe C, Guazzelli L (2019) Comparative evaluation of antimicrobial activity of different types of ionic liquids. Mater Sci Eng C 104:109907. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2019.109907
Guo Z, Jiang Q, Shi Y, Li J, Yang X, Hou W, Zhou Y, Wang J (2017) Tethering dual hydroxyls into mesoporous poly(ionic liquid)s for chemical fixation of CO2 at ambient conditions: a combined experimental and theoretical study. ACS Catal 7:6770–6780. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.7b02399
Guo Z, Cai X, Xie J, Wang X, Zhou Y, Wang J (2016) Hydroxyl-exchanged nanoporous ionic copolymer toward low temperature cycloaddition of atmospheric carbon dioxide into carbonates. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:12812–12821. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b02461
Kim BK, Lee E, Kang Y, Lee JJ (2018) Application of ionic liquids for metal dissolution and extraction. J Ind Eng Chem 61:388–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2017.12.038
Belchior DCV, Quental MV, Pereira MM, Mendonça CMN, Duarte IF, Freire MG (2020) Performance of tetraalkylammonium-based ionic liquids as constituents of aqueous biphasic systems in the extraction of ovalbumin and lysozyme. Sep Purif Technol 233:116019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.116019
Bowers AN, Rodríguez MJT, Farooq MQ, Anderson JL (2019) Extraction of DNA with magnetic ionic liquids using in situ dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction. Anal Bioanal Chem 411:7375–7385. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-019-02163-9
Deng N, Li M, Zhao L, Lu C, de Rooy SL, Warner IM (2011) Highly efficient extraction of phenolic compounds by use of magnetic room temperature ionic liquids for environmental remediation. J Hazard Mater 192:1350–1357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.06.053
Skoronskia E, Fernandes M, Malaret FJ, Hallett JP (2020) Use of phosphonium ionic liquids for highly efficient extraction of phenolic compounds from water. Sep Purif Technol 248:117069. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.117069
Gomez-Herrero E, Tobajas M, Polo A, Rodriguez JJ, Mohedano AF (2019) Removal of imidazolium-based ionic liquid by coupling Fenton and biological oxidation. J Hazard Mater 365:289–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.10.097
Neves CMSS, Lemus J, Freire MG, Palomar J, Coutinho JAP (2014) Enhancing the adsorption of ionic liquids onto activated carbon by the addition of inorganic salts. Chem Eng J 252:305–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.05.009
Cheng M, Jiang J, Wang J, Fan J (2019) Highly salt resistant polymer supported ionic liquid adsorbent for ultrahigh capacity removal of p-nitrophenol from water. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7:8195–8205. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b06198
Zhu G, Cheng G, Lu T, Cao Z, Wang L, Li Q, Fan J (2019) An ionic liquid functionalized polymer for simultaneous removal of four phenolic pollutants in real environmental samples. J Hazard Mater 373:347–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.03.101
Ni R, Wang Y, Wei X, Chen J, Xu P, Xu W, Meng J, Zhou Y (2019) Ionic liquid modified molybdenum disulfide and reduced graphene oxide magnetic nanocomposite for the magnetic separation of dye from aqueous solution. Anal Chim Acta 1054:47–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2018.12.037
Herrmann S, Kostrzewa M, Wierschem A, Streb C (2014) Polyoxometalate ionic liquids as self-repairing acid-resistant corrosion protection. Angew Chem Int Ed 53:13596–13599. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201408171
Zhao B, Wu D, Chu H, Wang C, Wei Y (2019) Magnetic mesoporous nanoparticles modified with poly(ionic liquids) with multi-functional groups for enrichment and determination of pyrethroid residues in apples. J Sep Sci 42:1896–1904. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201900038
Wei Y, Li Y, Tian A, Fan Y, Wang X (2013) Ionic liquid modified magnetic microspheres for isolation of heme protein with high binding capacity. J Mater Chem B 1:2066–2071. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3TB00576C
Li S, Guo Z, Zeng G, Zhang Y, Xue W, Liu Z (2018) Polyethylenimine-modified fluorescent carbon dots as vaccine delivery system for intranasal immunization. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 4:142–150. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.7b00370
Lv M, Li S, Zhao H, Wang K, Chen Q, Guo Z, Liu Z, Xue W (2017) Redox-responsive hyperbranched poly(amido amine) and polymer dots as a vaccine delivery system for cancer immunotherapy. J Mater Chem B 5:9532–9545. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7TB02334K
Mahony D, Cavallaro AS, Stahr F, Mahony TJ, Qiao S, Mitter N (2013) Mesoporous silica nanoparticles act as a self-adjuvant for ovalbumin model antigen in mice. Small 9:3138–3146. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201300012
Zhou Y, Zhang W, Ma L, Zhou Y, Wang J (2019) Amino acid anion paired mesoporous poly(ionic liquids) as metal-/halogen-free heterogeneous catalysts for carbon dioxide fixation. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7:9387–9398. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b00591
Thommes M, Kaneko K, Neimark AV, Olivier JP, Rodriguez-Reinoso F, Rouquerol J, Sing KSW (2015) Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl Chem 87:1051–1069. https://doi.org/10.1515/pac-2014-1117
Cychosz K, Guillet-Nicolas R, Garcıa-Martınez J, Thommes M (2017) Recent advances in the textural characterization of hierarchically structured nanoporous materials. Chem Soc Rev 46:389–414. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CS00391E
Hosseini-Eshbala F, Sedrpoushan A, Breit B, Mohanazadeh F, Veisi H (2020) Ionic-liquid-modified CMK-3 as a support for the immobilization of molybdate ions (MoO42-): heterogeneous nanocatalyst for selective oxidation of sulfides and benzylic alcohols. Mater Sci Eng C 110:110577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2019.110577
Wang N, Xu Z, Xu W, Xu J, Chen Y, Zhang M (2018) Comparison of coagulation and magnetic chitosan nanoparticle adsorption on the removals of organic compound and coexisting humic acid: a case study with salicylic acid. Chem Eng J 347:514–524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.04.131
Hu Z, Meng J, Wang X, Li W, Chen X (2020) Tailoring the surface properties of co-based metal-organic frameworks for highly efficient and selective enrichment of immunoglobulin G. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12:55453–55459. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c16821
Wang X, Wan H, Han M, Gao L, Guan G (2012) Removal of thiophene and its derivatives from model gasoline using polymer-supported metal chlorides ionic liquid moieties. Ind Eng Chem Res 51:3418–3424. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie201931a
Gao H, Kan T, Zhao S, Qian Y, Cheng X, Wu W, Wang X, Zheng L (2013) Removal of anionic azo dyes from aqueous solution by functional ionic liquid cross-linked polymer. J Hazard Mater 261:83–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.07.001
Sha X, Sheng X, Zhou Y, Wang B, Zhu Z, Liao Q, Liu Y (2020) Synthesis of P123-templated and DVB-cross-linked mesomacroporous poly (ionic liquids) with high-performance alkylation. Appl Organometal Chem 34:e5460. https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.5460
Lin Y, Wang F, Zhang Z, Yang J, Wei Y (2014) Polymer-supported ionic liquids: synthesis, characterization and application in fuel desulfurization. Fuel 116:273–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2013.08.014
Cheng M, Zhang X, Shi Y, Shi D, Zhu G, Fan J (2019) Highly efficient removal of ceftiofur sodium using a superior hydroxyl group functionalized ionic liquid-modified polymer. Sci Total Environ 662:324–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.01.223
Sun L, Luo J, Gao M, Tang S (2020) Bi-functionalized ionic liquid porous copolymers for CO2 adsorption and conversion under ambient pressure. React Funct Polym 154:104636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2020.104636
Xu W, Cao J, Zhang Y, Shu Y, Wang J (2020) Boronic acid modified polyoxometalate-alginate hybrid for the isolation of glycoproteins at neutral environment. Talanta 210:120620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.120620
Wan X, Xiang X, Tang S, Yu D, Huang H, Hu Y (2017) Immobilization of candida antarctic lipase B on MWNTs modified by ionic liquids with different functional groups. Colloids Surf B 160:416–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2017.09.037
Suo H, Gao Z, Xu L, Xu C, Yu D, Xiang X, Huang H, Hu Y (2019) Synthesis of functional ionic liquid modified magnetic chitosan nanoparticles for porcine pancreatic lipase immobilization. Mater Sci Eng C 96:356–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2018.11.041
Zhang Y, Zhuang Y, Shen H, Chen X, Wang J (2017) A super hydrophilic silsesquioxane-based composite for highly selective adsorption of glycoproteins. Microchim Acta 184:1037–1044. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2100-z
Qiao M, Liu X, Song J, Yang T, Chen M, Wang J (2018) Improving the adsorption capacity for ovalbumin by functional modification of aminated mesoporous silica nanoparticles with tryptophan. J Mater Chem B 6:7703–7709. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TB02221F
Zhu H, Yao H, Xia K, Liu J, Yin X, Zhang W, Pan J (2018) Magnetic nanoparticles combining teamed boronate affinity and surface imprinting for efficient selective recognition of glycoproteins under physiological pH. Chem Eng J 346:317–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.03.170
Li S, Qin Y, Zhong G, Cai C, Chen X, Chen C (2018) Highly efficient separation of glycoprotein by dual-functional magnetic metal-organic framework with hydrophilicity and boronic acid affinity. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10:27612–27620. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b07671
Wang X, Zhang Y, Shu Y, Chen X, Wang J (2015) Ionic liquid poly(3-n-dodecyl-1-vinylimidazolium) bromide as an adsorbent for the sorption of hemoglobin. RSC Adv 5:31496–31501. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra00036j
Guo Z, Hai X, Wang Y, Shu Y, Chen X, Wang J (2018) Core−corona magnetic nanospheres functionalized with zwitterionic polymer ionic liquid for highly selective isolation of glycoprotein. Biomacromol 19:53–61. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.7b01231
Liu J, Liang Y, Shen J, Bai Q (2018) Polymeric ionic liquid-assembled graphene-immobilized silica composite for selective isolation of human serum albumin from human whole blood. Anal Bioanal Chem 410:573–584. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-017-0758-z
Guo P, Wang X, Wang M, Yang T, Chen M, Wang J (2019) Boron-titanate monolayer nanosheets for highly selective adsorption of immunoglobulin G. Nanoscale 11:9362–9368. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9NR01111K
Michaux C, Pomroy N, Privé G (2008) Refolding SDS-denatured proteins by the addition of amphipathic cosolvents. J Mol Biol 375:1477–1488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2007.11.026
Shu Y, Chen X, Wang J (2010) Ionic liquid–polyvinyl chloride ionomer for highly selective isolation of basic proteins. Talanta 81:637–642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2009.12.059
Zhang D, Hu L, Chen Q, Chen X, Wang J (2016) Selective adsorption of hemoglobin with polyoxometalate-derived hybrid by solidification of super-lacunary phosphotungstate polyoxoanions. Talanta 159:23–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2016.06.005
Wang X, Hu Z, Guo P, Chen M, Wang J (2020) Purification of hemoglobin by adsorption on nitrogen-doped flower-like carbon superstructures. Microchim Acta 187:162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-4151-9
Acknowledgements
The authors appreciate the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21727811) and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (N2005027).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Lisa White.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, S., Zhang, C., Hu, Z. et al. Biocompatible mesoporous polymeric ionic liquid with high adsorption capacity for selective isolation of ovalbumin. J Mater Sci 56, 19283–19295 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-021-06529-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-021-06529-2