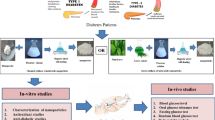
Abstract
Gastric ulcer is a chronic disease that affects about 10% of the world’s population. This disease is caused by factors such as stress, smoking, alcohol consumption, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), Helicobacter pylori infection, and genetic factors. Herbal medicines such as plant extracts are new sources of drugs with promising results in treating gastric ulcers. Nanotechnology and nanomedicine have been able to reach this objective to some extent. Green synthesis is an alternative method adapted for chemical and physical methods. In the last few years, fungi, bacteria, viruses, algae, and plants have been used to produce metallic nanoparticles. Since nanoparticles synthesized by the green method can be effective in anticancer, antidiabetic, antiulcer, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant treatments, the aim of this review was to study the effect of metal nanoparticles and metal oxides produced by the green method on the treatment of gastric ulcers. For this purpose, an electronic search of published research and review articles in PubMed, Scopus, Science Direct, Cochrane databases, and Google Scholar was conducted using a combination of keywords of “gastric ulcers and nanoparticles”, “gastric ulcers and Green synthesis” and “stomach ulcers and nanoparticles”. After a full review of published articles and their references, 120 articles were identified for further detailed review. The articles selected were between 2000 and March 2023, and 2 articles published in 1972 and 1997 were utilized. The results of this study have shown that polymeric, metal, and metal oxide nanoparticles synthesized from plants can be effective in treating gastric ulcers, especially ulcers caused by H. pylori, ethanol, and NSAIDs.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data sets generated during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abd El-Rady NM, Dahpy MA, Ahmed A et al (2021) Interplay of biochemical, genetic, and immunohistochemical factors in the etio-pathogenesis of gastric ulcer in rats: a comparative study of the effect of pomegranate loaded nanoparticles versus pomegranate peel extract. Front Physiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2021.649462
Abou Baker DH, Abbas HS (2023) Antimicrobial activity of biosynthesized Cuo/Se nanocomposite against Helicobacter pylori. Arab J Chem 16:105095. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2023.105095
Adebayo-Tayo BC, Akinsete TO, Odeniyi AO (2016) Phytochemical composition and comparative evaluation of antimicrobial activities of the juice extract of Citrus Aurantifolia and its silver nanoparticles. Niger J Pharm 12:59–64
Agarwal H, Shanmugam V (2020) A review on anti-inflammatory activity of green synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticle: mechanism-based approach. Bioorg Chem 94:103423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2019.103423
Agarwal H, Nakara A, Shanmugam VK (2019) Anti-inflammatory mechanism of various metal and metal oxide nanoparticles synthesized using plant extracts: a review. Biomed Pharmacother 109:2561–2572. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.11.116
Ahmad T, Wani IA, Lone IH et al (2013) Antifungal activity of gold nanoparticles prepared by solvothermal method. Mater Res Bull 48:12–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2012.09.069
Ahmad S, Munir S, Zeb N et al (2019) Green nanotechnology: a review on green synthesis of silver nanoparticles—an ecofriendly approach. Int J Nanomed 14:5087–5107. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S200254
Ahmad K, Asif HM, Afzal T et al (2023) Green synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles through the Piper cubeba ethanolic extract and their enzyme inhibitory activities. Front Chem. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2023.1065986
Ahmadi A, Ebrahimzadeh MA, Ahmad-Ashrafi S et al (2011) Hepatoprotective, antinociceptive and antioxidant activities of cimetidine, ranitidine and famotidine as histamine H2 receptor antagonists. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 25:72–79. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1472-8206.2009.00810.x
Akanbi OM (2013) In vivo study of antiplasmodial activity of terminalia avicennioides and its effect on lipid profile and oxidative stress in mice infected with plasmodium berghei. Br Microbiol Res J. https://doi.org/10.9734/BMRJ/2013/3680
Akbarnejad Samani Z, Shamili M, Samari F (2020) The toxicity potential of Ag nanoparticles synthesized from Cordia myxa L. Adv Hortic Sci 34:93–104
Akturk A, Güler FK, Taygun ME et al (2020) Synthesis and antifungal activity of soluble starch and sodium alginate capped copper nanoparticles. Mater Res Express 6(12):1250g3. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab677e
Al-Zubaidy AA, Khalil AM (2022) Gastroprotective effect of capparis spinosa on indomethacin-induced gastric ulcer in rats. Arch Razi Inst 77:1437–1445
Aman RM, Zaghloul RA, El-Dahhan MS (2021) Formulation, optimization and characterization of allantoin-loaded chitosan nanoparticles to alleviate ethanol-induced gastric ulcer: in-vitro and in-vivo studies. Sci Rep 11:2216. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-81183-x
Amin M, Hameed S, Ali A et al (2014) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles: structural features and in vivo and in vitro therapeutic effects against Helicobacter pylori induced gastritis. Bioinorg Chem Appl 2014:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/135824
Amin M, Anwar F, Janjua MRSA et al (2012) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles through reduction with Solanum xanthocarpum L. berry extract: characterization, antimicrobial and urease inhibitory activities against Helicobacter pylori. Int J Mol Sci 13(8):9923–9941. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13089923
Anbuvannan M, Ramesh M, Viruthagiri G et al (2015) Anisochilus carnosus leaf extract mediated synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles for antibacterial and photocatalytic activities. Mater Sci Semicond Process 39:621–628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2015.06.005
Angajala G, Pavan P, Subashini R (2014) One-step biofabrication of copper nanoparticles from Aegle marmelos correa aqueous leaf extract and evaluation of its anti-inflammatory and mosquito larvicidal efficacy. RSC Adv 4:51459–51470. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA10003D
Asomie J, Aina A, Owolo O et al (2021) Biogenic synthesis and characterization of Silver nanoparticles from seed extract of Spondia mombins and screening of its antibacterial activity. Int J Nano Dimens 12:175–185
Babu PJ, Sharma P, Saranya S et al (2013) Synthesis of gold nanoparticles using ethonolic leaf extract of Bacopa monnieri and UV irradiation. Mater Lett 93:431–434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2012.11.034
Banavar S, Deshpande A, Sur S et al (2021) Ceria nanoparticle theranostics: harnessing antioxidant properties in biomedicine and beyond. J Phys Materials 4:042003. https://doi.org/10.1088/2515-7639/ac0594
Baruah D, Goswami M, Yadav RNS et al (2018) Biogenic synthesis of gold nanoparticles and their application in photocatalytic degradation of toxic dyes. J Photochem Photobiol B 186:51–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2018.07.002
Beiranvand M, Bahramikia S (2020) Ameliorating and protective effects mesalazine on ethanol-induced gastric ulcers in experimental rats. Eur J Pharmacol 888:173573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173573
Beiranvand M, Bahramikia S, Dezfoulian O (2021) Evaluation of antioxidant and anti-ulcerogenic effects of Eremurus persicus (Jaub & Spach) boiss leaf hydroalcoholic extract on ethanol-induced gastric ulcer in rats. Inflammopharmacology 29:1503–1518. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-021-00868-x
Bhattacharya S (2007) Healing property of the Piper betel phenol, allylpyrocatechol against indomethacin-induced stomach ulceration and mechanism of action. World J Gastroenterol 13:3705. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i27.3705
Bi W-P (2014) Efficacy and safety of herbal medicines in treating gastric ulcer: a review. World J Gastroenterol 20:17020. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i45.17020
Bindhu MR, Umadevi M (2014) Antibacterial activities of green synthesized gold nanoparticles. Mater Lett 120:122–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2014.01.108
Brett S (2004) Science review: the use of proton pump inhibitors for gastric acid suppression in critical illness. Crit Care 9:45. https://doi.org/10.1186/cc2980
Carrillo-López LM, Zavaleta-Mancera HA, Vilchis-Nestor A et al (2014) Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Chenopodium ambrosioides. J Nanomater 2014:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/951746
Chang C-H, Huang W-Y, Lai C-H et al (2011) Development of novel nanoparticles shelled with heparin for berberine delivery to treat Helicobacter pylori. Acta Biomater 7:593–603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2010.08.028
Chaturvedi A, Kumar MM, Bhawani G et al (2007) Effect of ethanolic extract of Eugenia jambolana seeds on gastric ulceration and secretion in rats. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 51(2):131
Chauhan R, Ibrahim M, Narayanan S et al (2015) Cytotoxic effect on human osteosarcoma cell line mg-63 and antimicrobial activity on clinical pathogens by plant-mediated silver nanoparticles. World J Pharm Res 4:1012–1027
Cheng HC, Sheu BSh (2011) Intravenous proton pump inhibitors for peptic ulcer bleeding: clinical benefits and limits. World J Gastrointest Endosc 3:49. https://doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v3.i3.49
De Souza MPC, De Camargo BAF, Spósito L et al (2021) Highlighting the use of micro and nanoparticles based-drug delivery systems for the treatment of Helicobacter pylori infections. Crit Rev Microbiol 47:435–460. https://doi.org/10.1080/1040841X.2021.1895721
Dhar SA, Chowdhury RA, Das S et al (2021) Plant-mediated green synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Phyllanthus emblica fruit extract. Mater Today Proc 42:1867–1871. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.12.222
Dixit AK, Khan NS (2017) Green synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using centella asiatica (l.) urban. World J Pharm Res 6:1095–1105
Durgawale PP, Phatak RS, Hendre AS (2015) Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using latex of syandenium grantii hook f and its assessment of antibacterial activities. Dig J Nanomater Biostructures 10(3):847
Elemike EE, Onwudiwe DC, Ekennia AC (2020) Eco-friendly synthesis of silver nanoparticles using umbrella plant, and evaluation of their photocatalytic and antibacterial activities. Inorg Nano-Met Chem 50:389–399. https://doi.org/10.1080/24701556.2020.1716005
Elmehbad NY, Mohamed NA, Abd El-ghany NA et al (2022) Green synthesis of nano-silver/sodium alginate/carboxymethyl xanthan gum hydrogel and evaluation of its anti-inflammatory and anti-helicobacter pylori activity. Cellul Chem Technol 56:983–995. https://doi.org/10.35812/CelluloseChemTechnol.2022.56.88
Elumalai A, Naresh V, Eswaraiah MC et al (2012) Evaluation of antiulcer activity of Couroupita guianensis Aubl leaves. Asian J Pharm Technol 2:64–66
Fuloria S, Mehta J, Chandel A et al (2022) A comprehensive review on the therapeutic potential of Curcuma longa Linn. In relation to its major active constituent curcumin. Front Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.820806
Gangaram S, Naidoo Y, Dewir YH et al (2021) Phytochemicals and biological activities of Barleria (Acanthaceae). Plants 11:82. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11010082
Gohar AA, Zaki AA (2014) Assessment of some herbal drugs for prophylaxis of peptic ulcer. Iran J Pharm Res 13:1081–1086
Gonçalves IC, Henriques PC, Seabra CL et al (2014) The potential utility of chitosan micro/nanoparticles in the treatment of gastric infection. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 12:981–992. https://doi.org/10.1586/14787210.2014.930663
Gopinath V, Priyadarshini S, Loke MF et al (2017) Biogenic synthesis, characterization of antibacterial silver nanoparticles and its cell cytotoxicity. Arab J Chem 10:1107–1117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2015.11.011
Gopinath V, Priyadarshini S, MubarakAli D et al (2019) Anti-Helicobacter pylori, cytotoxicity and catalytic activity of biosynthesized gold nanoparticles: Multifaceted application. Arab J Chem 12:33–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2016.02.005
Grande R, Sisto F, Puca V et al (2020) Antimicrobial and antibiofilm activities of new synthesized silver ultra-nanoclusters (SUNCs) against Helicobacter pylori. Front Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.01705
Gu X, Xu Z, Gu L et al (2021) Preparation and antibacterial properties of gold nanoparticles: a review. Environ Chem Lett 19:167–187. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-020-01071-0
Habeeb Rahuman HB, Dhandapani R, Narayanan S et al (2022) Medicinal plants mediated the green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their biomedical applications. IET Nanobiotechnol 16:115–144. https://doi.org/10.1049/nbt2.12078
Hamelian M, Zangeneh MM, Shahmohammadi A et al (2020) Pistacia atlantica leaf extract mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their antioxidant, cytotoxicity, and antibacterial effects under in vitro condition. Appl Organomet Chem. https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.5278
Hou T, Sankar Sana S, Li H et al (2022) Development of plant protein derived tri angular shaped nano zinc oxide particles with inherent antibacterial and neurotoxicity properties. Pharmaceutics 14:2155. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14102155
Hu J, Luo J, Zhang M et al (2021) Protective effects of radix sophorae flavescentis carbonisata-based carbon dots against ethanol-induced acute gastric ulcer in rats: anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities. Int J Nanomed 16:2461–2475. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S289515
Ibrahim IAA, Hussein AI, Muter MS et al (2022) Effect of nano silver on gastroprotective activity against ethanol-induced stomach ulcer in rats. Biomed Pharmacother 154:113550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113550
Jagaran K, Singh M (2020) Nanomedicine for COVID-19: potential of copper nanoparticles. Biointerface Res Appl Chem 11:10716–10728. https://doi.org/10.33263/BRIAC113.1071610728
Jonnalagadda A, Maharaja KK, Kumar NP (2012) Combined effect of Syzygium cumini seed kernel extract with oral hypoglycemics in diabetes induced increase in susceptability to ulcerogenic stimuli. J Diabetes Metab. https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-6156.1000236
Karuppannan SK, Ramalingam R, Mohamed Khalith SB et al (2021) Characterization, antibacterial and photocatalytic evaluation of green synthesized copper oxide nanoparticles. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 31:101904. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2020.101904
Kaur D, Rana AC, Sharma N et al (2012) Herbal drugs with anti ulcer activity. J Appl Pharm Sci 2:160–165
Kazemzadeh H, Hamidian E, Hosseini FS et al (2022) Isoindolin-1-ones fused to barbiturates: from design and molecular docking to synthesis and urease inhibitory evaluation. ACS Omega 7:19401–19411. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.2c01028
Keskin M (2022) Humulus lupulus L. (Hop) based silver nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization and enzyme inhibition eefects. Acta Sci Pol Hortorum Cultus 21:11–20. https://doi.org/10.24326/asphc.2022.4.2
Khan I, Bawazeer S, Rauf A et al (2022) Synthesis, biological investigation and catalytic application using the alcoholic extract of black cumin (Bunium Persicum) seeds-based silver nanoparticles. J Nanostructure Chem 12:59–77. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40097-021-00402-z
Khazaei F, Yadegari M, Ghanbari E et al (2022) Therapeutic applications and characteristics of Falcaria vulgaris in traditional medicine and experimental studies. Avicenna J Phytomed 12:116–130. https://doi.org/10.22038/AJP.2021.18488
Khuda F, Ul Haq Z, Ilahi I et al (2021) Synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Sambucus wightiana extract and investigation of its antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and analgesic activities. Arab J Chem 14:103343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2021.103343
Khushi A, Mona Hassan S, Sharif Mughal SH (2022) Antimicrobial and structural investigation of green synthesized ZnO nanostructures from Bougainvillea glabra leaves extract. Biochem Mol Biol 7:61–69
Kinnear C, Moore TL, Rodriguez-Lorenzo L et al (2017) Form follows function: nanoparticle shape and its implications for nanomedicine. Chem Rev 117:11476–11521. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00194
Kumar A, Mazinder Boruah B, Liang X-J (2011) Gold nanoparticles: promising nanomaterials for the diagnosis of cancer and HIV/AIDS. J Nanomater 2011:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/202187
Kuna L, Jakab J, Smolic R et al (2019) Peptic ulcer disease: abrief review of conventional therapy and herbal treatment options. J Clin Med 8:179. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8020179
Lara HH, Ayala-Nuñez NV, Ixtepan-Turrent L, Rodriguez-Padilla C (2010) Mode of antiviral action of silver nanoparticles against HIV-1. J Nanobiotechnol 8:1. https://doi.org/10.1186/1477-3155-8-1
Lashari A, Mona Hassan S, Sharif Mughal SH (2022) Biosynthesis, characterization and biological applications of BaO nanoparticles using Linum usitatissimum. Am J Appl Sci Res 8:58–68
Li P, Chen X, Shen Y et al (2019) Mucus penetration enhanced lipid polymer nanoparticles improve the eradication rate of Helicobacter pylori biofilm. J Control Release 300:52–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2019.02.039
Lopes D, Nunes C, Martins MCL et al (2014) Eradication of Helicobacter pylori: past, present and future. J Control Release 189:169–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2014.06.020
Maji A, Beg M, Das S et al (2020) Study on the antibacterial activity and interaction with human serum albumin of Tagetes erecta inspired biogenic silver nanoparticles. Process Biochem 97:191–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2020.07.017
Malapermal V, Botha I, Krishna SBN, Mbatha JN (2017) Enhancing antidiabetic and antimicrobial performance of Ocimum basilicum, and Ocimum sanctum (L.) using silver nanoparticles. Saudi J Biol Sci 24:1294–1305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2015.06.026
Mehrabi F, Moshafi MH, Bahraminejad S, Ranjbar M (2022) Eco-friendly synthesis, characterization, and antimicrobial study of chitosan/Bi (OH)3 nanocomposites. Avicenna J Clin Microb Infec 9:171–178. https://doi.org/10.34172/ajcmi.2022.3413
Menaga S, Kripa KG, Sangeetha R (2017) Evaluation of in vitro inhibition of proton-pump by nanosilver particles synthesized using seeds of anethum graveolens. Asian J Pharm Clin Res 10:363. https://doi.org/10.22159/ajpcr.2017.v10i6.16896
Miri A, Darroudi M, Entezari R, Sarani M (2018) Biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles using Prosopis farcta extract and its in vitro toxicity on colon cancer cells. Res Chem Intermed 44:3169–3177. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-018-3299-y
Miri A, Mahdinejad N, Ebrahimy O et al (2019) Zinc oxide nanoparticles: biosynthesis, characterization, antifungal and cytotoxic activity. Mater Sci Eng C 104:109981. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2019.109981
Mohamed S, Mohamed L (2022) Eco-friendly, non-toxic, and highly antimicrobialbiosynthesized of silver nanoparticles (pagnps) from pomegranate (punica granatum) peel (waste) extract (ppe) with many applications in nano industries and pathogen elimination from water. Egypt J Chem. https://doi.org/10.21608/ejchem.2022.156513.6782
Mohamed Lotfy BM, Mousa MR, Samir Fawzy M et al (2021) Therapeutic potency of Gallium verum extract on ethanol-induced gastric ulcer in rats. Biointerface Res Appl Chem 12:6010–6020
Mohammed NA (2019) In vitro study of antimicrobial activity of silver nanoparticles usage (curcuma longa l.) rhizomes against Helicobacter pylori. Plant Arch 19:1102–1106
Moon S, Lee J, Kim K-T et al (2013) Antimicrobial effect of 7-O-butylnaringenin, a novel flavonoid, and various natural flavonoids against Helicobacter pylori strains. Int J Environ Res Public Health 10:5459–5469. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph10115459
Motegi M, Nagamachi Y, Matsuzaki S (1997) Effects of H2-receptor antagonist on the cellular function of gastric mucosa in the rat. Kita Kanto Igaku 47:291–300. https://doi.org/10.2974/kmj.47.291
Muhammad W, Khan M, Ullah N (2019) The significance of phyto-fabricated nanoparticles in curing gastric ulcer. Nanoscale Reports 2(1):1–2. https://doi.org/10.26524/nr1911
Naseer M, Ramadan R, Xing J, Samak NA (2021) Facile green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles for the eradication of multidrug resistant Klebsiella pneumonia and Helicobacter pylori biofilms. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 159:105201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2021.105201
Naseri M, Delfani H, Mirzaeei S et al (2022) Protective effect of nanoparticles of oleoresin of Pistacia atlantica var. mutica against acetic acid-induced ulcerative colitis in rats. Tradit Integr Med. https://doi.org/10.18502/tim.v7i2.9915
Pakrashi A, Pandit S, Bandyopadhyay SK, Pakrashi SC (2003) Antioxidant effect of phyllanthus emblica fruits on healing of indomethacin induced gastric ulcer in rats. Indian J Clin Biochem 18:15–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02867660
Paramasivam G, Kannan R, Paulraj SM, Pandiarajan J (2017) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Morinda tinctoria Roxb and scrutiny of its multi facet on biomedical applications. Pharm Biol Eval 4:222. https://doi.org/10.26510/2394-0859.pbe.2017.35
Pisal V, Wakchaure P, Patil N, Bhagwat S (2019) Green synthesized CeO 2 quantum dots: a study of its antimicrobial potential. Mater Res Express 6:115409. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab4fa5
Radif H (2020) Evaluation of potent silver nanoparticles production from Agaricus bisporus against Helicobacter pylori. Pak J Agric Sci 57:1197–1201
Rajeshkumar S, Rinitha G (2018) Nanostructural characterization of antimicrobial and antioxidant copper nanoparticles synthesized using novel Persea americana seeds. OpenNano 3:18–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.onano.2018.03.001
Ramalakshmi C, Kalirajan A, Ranjitsingh AJA et al (2014) Bioprospecting of medicinal plant Couroupita guianensis for its potential anti -ulcer activity. Int j Appl Biol Pharm 5(3):226–232
Ramasubbu K, Padmanabhan S, Al-Ghanim KA et al (2023) Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using Sesbania grandiflora leaf extract and their evaluation of anti-diabetic, cytotoxic, anti-microbial, and anti-inflammatory properties in an in-vitro approach. Ferment 9:332. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9040332
Rezaei ZB, Rastegarzadeh S, Kiasat A (2019) A sensitive and selective colorimetric probe for cimetidine determination based on surface plasmon resonance of chitosan-encapsulated gold nanoparticles. Plasmonics 14:1169–1177. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-019-00905-0
Rhodes J (1972) Etiology of gastric ulcer. Gastroenterol 63:171–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-5085(19)33363-3
Rónavári A, Igaz N, Adamecz DI et al (2021) Green silver and gold nanoparticles: biological synthesis approaches and potentials for biomedical applications. Mol 26(4):844. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26040844
Rozhin A, Batasheva S, Kruychkova M et al (2021) Biogenic silver nanoparticles: synthesis and application as antibacterial and antifungal agents. Micromachines 12:1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12121480
Sabarathinam J, Madhulaxmi R (2021) Development of anti inflammatory and antimicrobial silver nanoparticles coated suture materials. Int J Dent Oral Sci. https://doi.org/10.19070/2377-8075-21000395
Safari S, Bahrami Kia S, Dezfoulian O (2023) Silver nanoparticles synthesized from Quercus brantii ameliorated ethanol-induced gastric ulcers in rats by decreasing oxidative stress and improving antioxidant systems. Inflammopharmacology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-023-01284-z
Safarov T, Kiran B, Bagirova M et al (2019) An overview of nanotechnology-based treatment approaches against Helicobacter Pylori. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 17:829–840. https://doi.org/10.1080/14787210.2019.1677464
Sakhare DT (2022) Green approach to synthesis, characterization of silver nanoparticles by using tridax procumbens leaf extract and their antibacterial activity. IJFANS 11:126–133
Salem NA, Wahba MA, Eisa WH et al (2018) Silver oxide nanoparticles alleviate indomethacin-induced gastric injury: a novel antiulcer agent. Inflammopharmacology 26:1025–1035. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-017-0424-2
Serov DA, Khabatova VV, Vodeneev V et al (2023) A review of the antibacterial, fungicidal and antiviral properties of selenium nanoparticles. Mater 16:5363. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16155363
Shabbir N, Mona Hassan S, Sharif Mughal S et al (2022) Eletteria cardamomum and greenly synthesized Mgo NPs: a detailed review of their properties and applications. Eng Sci 7:15. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.es.20220701.12
Shareef SH, Hadi INM, Badeea MA et al (2022) Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Zingiber Officinale rhizomes aqueous extract and its gastroprotective activity against ethanol-produced stomach ulcer in rodents. Cihan Univ-Erbil Sci 6:68–75. https://doi.org/10.24086/cuesj.v6n2y2022.pp68-75
Shrivastava N, Srivastava A, Banerjee A et al (2006) Anti Ulcer activity of Adhatoda vasica nees. J Herb Pharmacother 6(2):43–49. https://doi.org/10.1080/J157v06n02_04
Singh KR, Nayak V, Singh J et al (2021) Potentialities of bioinspired metal and metal oxide nanoparticles in biomedical sciences. RSC Adv 11:24722–24746. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1RA04273D
Sreelakshmy V, Deepa MK, Mridula P (2016) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Glycyrrhiza glabra root extract for the treatment of gastric ulcer. J Dev Drugs. https://doi.org/10.4172/2329-6631.1000152
Stedman CAM, Barclay ML (2000) Review article: comparison of the pharmacokinetics, acid suppression and efficacy of proton pump inhibitors. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 14:963–978. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2036.2000.00788.x
Strasser M, Noriega P, Löbenberg R et al (2014) Antiulcerogenic potential activity of free and nanoencapsulated Passiflora serratodigitata L. extracts. Biomed Res Int 2014:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/434067
Sukweenadhi J, Setiawan KI, Avanti C, et al (2022) Scale-up of green synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using ethanol extract of Plantago major L. leaf and its antibacterial potential: a recent study. In: Challenges and Advances in Chemical Science Vol 8. Book Publisher International (a part of SCIENCEDOMAIN International), pp 29–43
Suleiman MM, Yusuf S, Amaechi EL (2006) Effect of crude methanol extract of Terminalia avicennioides in normal gastric/histamine-induced hcl secretions in rats. J Herbs Spices Med Plants. https://doi.org/10.1300/J044v12n04_03
Sumner SE, Markley RL, Kirimanjeswara GS (2019) Role of selenoproteins in bacterial pathogenesis. Biol Trace Elem Res 192:69–82. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-019-01877-2
Supraja N, Prasad TNVKV, Krishna TG, David E (2016) Synthesis, characterization, and evaluation of the antimicrobial efficacy of Boswellia ovalifoliolata stem bark-extract-mediated zinc oxide nanoparticles. Appl Nanosci 6:581–590. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-015-0472-0
Suvidya R, Pravin L, Shubhangi B, Satyawati J (2013) Rapid green synthesis and biological activity of silver nanoparticles using Adhatoda vasica leaf extract. Adv Sci Eng Med 5:319–324. https://doi.org/10.1166/asem.2013.1258
Thirumagal N, Jeyakumari AP (2020) Photocatalytic and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) using palm (Borassus flabellifer L.) water (Pathaneer). Indian J Sci Technol 13(18):1856–1866
Torabi S, Mansoorkhani MJK, Majedi A, Motevalli S (2020) REVIEW: synthesis, medical and photocatalyst applications of nano-Ag2O. J Coord Chem 73:1861–1880. https://doi.org/10.1080/00958972.2020.1806252
Velayutham L, Parvathiraja C, Anitha DC et al (2023) Antibacterial and photocatalytic dye degradation activities of green synthesized nise nanoparticles from Hibiscus rosa-sinensis leaf extract. Water 15:1380. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15071380
Yadav SK, Singh MJ, Singh A (2021) Review of conventional and herbal treatment for peptic ulcer disease. Nat Vol Essent Oil 8:6310–6324
Yugandhar P, Vasavi T, Uma Maheswari Devi P et al (2017) Bioinspired green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles from Syzygium alternifolium (Wt.) Walp: characterization and evaluation of its synergistic antimicrobial and anticancer activity. Appl Nanosci 7:417–427. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-017-0584-9
Zangeneh MM, Ghaneialvar H, Akbaribazm M et al (2019) Novel synthesis of Falcaria vulgaris leaf extract conjugated copper nanoparticles with potent cytotoxicity, antioxidant, antifungal, antibacterial, and cutaneous wound healing activities under in vitro and in vivo condition. J Photochem Photobiol B 197:111556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2019.111556
Żarowska B, Koźlecki T, Piegza M et al (2019) New look on antifungal activity of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs). Pol J Microbiol 68:515–525. https://doi.org/10.33073/pjm-2019-051
Acknowledgements
We, the undersigned, declare that all authors have seen and approved the final version of the manuscript submitted. We warrant that the article is the authors’ review article, has not been published before, and is not under consideration for publication elsewhere.
Funding
The authors received no financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SB: supervised and participated in directing the study and editing of the manuscript. RI: searched and collected the documents and wrote the manuscript, and collected all the images. All authors provided approval for publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bahramikia, S., Izadi, R. Plant-based green synthesis of nanoparticles as an effective and safe treatment for gastric ulcer. Inflammopharmacol 31, 2843–2855 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-023-01367-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-023-01367-x