Abstract
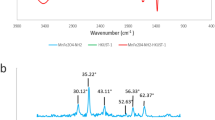
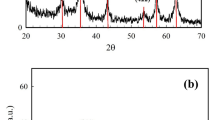
Dye wastewater seriously affects human living environment and human health. This experiment develops green and efficient recyclable Fe3O4@MIL-100(Fe) under room temperature conditions. The microscopic morphology, chemical structure and magnetic properties of Fe3O4@MIL-100 (Fe) were characterized by SEM, FT-IR, XRD and VSM, and the adsorption capacity and adsorption mechanism of the adsorbent on methylene blue (MB) were investigated. The results showed that MIL-100(Fe) was successfully grown on Fe3O4, and the composite had excellent crystalline shape and morphology and good magnetic response. The specific surface area of Fe3O4@MIL-100(Fe) is 1203.18 m2 g−1 by N2 adsorption isothermal curve, and MIL-100(Fe) still has high specific surface area after compounding with magnetic particles. The adsorption process follows the quasi-level kinetic equation and the Langmuir isothermal model, according to which the adsorption capacity of Fe3O4@MIL-100 (Fe) on MB can be up to 487.8 mg g−1 for a single molecular layer. The thermodynamic experiments show that the adsorption of MB by the adsorbent is a spontaneous heat absorption process. In addition, the adsorption amount of Fe3O4@MIL-100 (Fe) on MB was still maintained at 88.4% after 6 cycles with good reusability, and its crystalline shape did not change significantly, indicating that Fe3O4@MIL-100 (Fe) can be used as an efficient and regenerable adsorbent for the treatment of printing and dyeing wastewater.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be provided on reasonable request from the corresponding author.
References
Alsbaiee, A., Smith, B. J., Xiao, L., Ling, Y., Helbling, D. E., & Dichtel, W. R. (2016). Rapid removal of organic micropollutants from water by a porous β-cyclodextrin polymer. Nature, 529, 190–194. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature16185
Aslam, S., Zeng, J., Subhan, F., Li, M., Lyu, F., Li, Y., et al. (2017). In situ one-step synthesis of Fe3O4@MIL-100(Fe) core-shells for adsorption of methylene blue from water. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 505, 186–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.05.090
Ba-Abbad, M. M., Benamour, A., Ewis, D., Mohammad, A. W., & Mahmoudi, E. (2022). Synthesis of Fe3O4 nanoparticles with different shapes through a co-precipitation method and their application. JOM Journal of the Minerals Metals and Materials Society (1989), 2022(74), 3531–3539. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-022-05380-3
Baig, M. T., & Kayan, A. (2023). Eco-friendly novel adsorbents composed of hybrid compounds for efficient adsorption of methylene blue and Congo red dyes: Kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Separation Science and Technology, 58, 862–883. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2023.2166845
Bhattacharjee, A., Gumma, S., & Purkait, M. K. (2017). Fe3O4 promoted metal organic framework MIL-100(Fe) for the controlled release of doxorubicin hydrochloride. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 259, 203–210.
Bilal, M., & Asgher, M. (2015). Sandal reactive dyes decolorization and cytotoxicity reduction using manganese peroxidase immobilized onto polyvinyl alcohol-alginate beads. Chemistry Central Journal, 9, 47. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13065-015-0125-0
Buvaneswari, N., & Kannan, C. (2011). Plant toxic and non-toxic nature of organic dyes through adsorption mechanism on cellulose surface. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 189, 294–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.02.036
Cundari, L., Sari, K. F., & Anggraini, L. (2018). Batch study, kinetic and equilibrium isotherms studies of dye adsorption of jumputan wastewater onto betel nuts adsorbent. Journal of Physics. Conference Series, 1095, 12018. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1095/1/012018
Czikkely, M., Oláh, J., Lakner, Z., Fogarassy, C., & Popp, J. (2018). Waste water treatment with adsorptions by mushroom compost. International Journal of Engineering Business Management, 10, 1655964006. https://doi.org/10.1177/1847979018809863
Dai, W., Zhang, J., Xiao, Y., Luo, W., & Yang, Z. (2021). Dual function of modified palm leaf sheath fibers in adsorbing reactive yellow 3 and Cr(VI) from dyeing wastewater. Journal of Polymers and the Environment, 29, 3854–3866. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-021-02157-8
Darwish, A. S., Attia, S. K., & Osman, D. I. (2022). Accelerated activation of H2O2 and persulfate by Sm-doped ZnO@highly-defective layered yttria nanocomposite under visible-light irradiation for dyeing wastewater treatment: Comprehensive dominance of oxygen vacancies in photocatalytic advanced oxidation processes. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 925, 1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.166742
Eltaweil, A. S., Abd El-Monaem, E. M., El-Subruiti, G. M., Abd El-Latif, M. M., & Omer, A. M. (2020). Fabrication of UiO-66/MIL-101(Fe) binary MOF/carboxylated-GO composite for adsorptive removal of methylene blue dye from aqueous solutions. RSC Advances, 10, 19008–19019. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0RA02424D
Fonseca, J., Gong, T., Jiao, L., & Jiang, H. (2021). Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) beyond crystallinity: Amorphous MOFs, MOF liquids and MOF glasses. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, Materials for Energy and Sustainability 9, 1562–611. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1ta01043c
Garole, V. J., Choudhary, B. C., Tetgure, S. R., Garole, D. J., & Borse, A. U. (2018). Detoxification of toxic dyes using biosynthesized iron nanoparticles by photo-Fenton processes. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology (Tehran), 15, 1649–1656. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-017-1510-0
Hamedi, A., & Taheri, M. (2022). Synthesis of Fe3O4@MIL-100(Fe) nanocatalyst and comparative evaluation of photocatalytic behavior of Fe3O4 and core-shell structure of catalyst on methylene blue degradation. Molecular Crystals and Liquid Crystals, 736, 103–112. https://doi.org/10.1080/15421406.2021.1992086
Hamedi, A., Trotta, F., Borhani Zarandi, M., Zanetti, M., Caldera, F., Anceschi, A., et al. (2019). In situ synthesis of MIL-100(Fe) at the surface of Fe3O4@AC as highly efficient dye adsorbing nanocomposite. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20, 5612. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20225612
Hamedi, A., Anceschi, A., Trotta, F., Hasanzadeh, M., & Caldera, F. (2021). Rapid temperature-assisted synthesis of nanoporous γ-cyclodextrin-based metal–organic framework for selective CO2 adsorption. Journal of Inclusion Phenomena and Macrocyclic Chemistry, 99, 245–253. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-020-01039-1
Hamedi, A., Anceschi, A., Patrucco, A., & Hasanzadeh, M. (2022). A gamma-cyclodextrin-based metal-organic framework (gamma-CD-MOF): A review of recent advances for drug delivery application. Journal of Drug Targeting, 30, 381–393. https://doi.org/10.1080/1061186X.2021.2012683
Hamedia, A., Zarandia, M. B., & Nateghib, M. R. (2019). Highly efficient removal of dye pollutants by MIL-101(Fe) metal-organic framework loaded magnetic particles mediated by Poly L-Dopa. JECE, 7, 102882.
Horcajada, P., Surblé, S., Serre, C., Hong, D., Seo, Y., & Chang, J., et al. (2007). Synthesis and catalytic properties of MIL-100(Fe), an iron (iii) carboxylate with large pores. Chemical Communications, 27, 2820–2822. https://doi.org/10.1039/B704325B
Ke, X., Song, X., Qin, N., Cai, Y., & Ke, F. (2019). Rational synthesis of magnetic Fe3O4@MOF nanoparticles for sustained drug delivery. Journal of Porous Materials, 26, 813–818. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-018-0682-4
Lan, D., Zhu, H., & Zhang, J. (2022). Adsorptive removal of organic dyes via porous materials for wastewater treatment in recent decades: A review on species, mechanisms and perspectives. Chemosphere. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.133464
Liu, S., Zhao, Y., Wang, T., Liang, N., & Hou, X. (2019). Core–shell Fe3O4@MIL-100(Fe) magnetic nanoparticle for effective removal of meloxicam and naproxen in aqueous solution. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 64, 2997–3007. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jced.9b00061
Liu, H., Chen, J., Yuan, W., Jiang, C., Li, H., Li, J., et al. (2021a). Structure engineering of Fe-based MOF aerogel by Halloysite Nanotubes for efficient methylene blue adsorption. Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology, 99, 55–62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-021-05540-y
Liu, Q., Yao, C., Liu, J., Wang, S., Shao, B., & Yao, K. (2021b). An efficient method to enrich, detect and remove bisphenol A based on Fe3O4@MIL-100(Fe). Microchemical Journal, 165, 106–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MICROC.2021.106168
Luo, P., Zhao, Y., Zhang, B., Liu, J., Yang, Y., & Liu, J. (2010). Study on the adsorption of Neutral Red from aqueous solution onto halloysite nanotubes. Water Research, 44, 1489–1497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2009.10.042
Nimbalkar, M. N., & Bhat, B. R. (2021). Simultaneous adsorption of methylene blue and heavy metals from water using Zr-MOF having free carboxylic group. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 9, 106216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.106216
Panda, J., Sahoo, J. K., & Panda, P. K. (2019). Adsorptive behavior of zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 towards anionic dye in aqueous media: Combined experimental and molecular docking study. Journal of Molecular Liquids. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.01.033
Sajjadi, S., Khataee, A., Darvishi, R., Soltani, C., Bagheri, N., Karimi, A., et al. (2018). Implementation of magnetic Fe3O4@ZIF-8 nanocomposite to activate sodium percarbonate for highly effective degradation of organic compound in aqueous solution. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry., 68, 406–415.
Sturini, M., Puscalau, C., Guerra, G., Maraschi, F., Bruni, G., Monteforte, F., et al. (2021). Combined layer-by-layer/hydrothermal synthesis of Fe3O4@MIL-100(Fe) for ofloxacin adsorption from environmental waters. Nanomaterials (Basel), 11, 3275. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11123275
Tahazadeh, S., Karimi, H., Mohammadi, T., Emrooz, H. B. M., & Tofighy, M. A. (2021). Fabrication of biodegradable cellulose acetate/MOF-derived porous carbon nanocomposite adsorbent for methylene blue removal from aqueous solutions. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 299, 122180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2021.122180
Tan, Y., Lv, X., Wang, W., Cui, C., Bao, Y., & Jiao, S. (2023). Surface-functionalization of hydrogen titanate nanowires for efficiently selective adsorption of methylene blue. Applied Surface Science, 615, 156265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.156265
Vishtal, A., & Kraslawski, A. (2011). Challenges in industrial applications of technicallignins. Bioresources, 6, 3547–3568.
Wang, R., Ching, C., Dichtel, W. R., & Helbling, D. E. (2020). Evaluating the removal of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances from contaminated groundwater with different adsorbents using a suspect screening approach. Environmental Science & Technology Letters, 7, 954–960. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.estlett.0c00736
Wua, Z., Deng, W., Zhou, W., & Luo, J. (2019). Novel magnetic polysaccharide/graphene oxide @Fe3O4 gel beads for adsorbing heavy metal ions. Carbohydrate Polymers. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.04.020
Yaqub, A., Syed, S. M., Ajab, H., & Zia Ul Haq, M. (2023). Activated carbon derived from Dodonaea Viscosa into beads of calcium-alginate for the sorption of methylene blue (MB): Kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamics. Journal of Environmental Management, 327, 116925. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.116925
Zhang, L., Meng, G., Fan, G., Chen, K., Wu, Y., & Liu, J. (2021). High flux photocatalytic self-cleaning nanosheet C3N4 membrane supported by cellulose nanofibers for dye wastewater purification. Nano Research, 14, 2568–2573. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-020-3256-0
Zhou, Q., Qiu, L., & Zhu, M. (2022). Eucommia ulmoides Oliver derived magnetic activated carbon for eliminating methylene blue from dyeing wastewater and its economic efficiency assessment. Industrial Crops & Products. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2022.115537
吴恩辉, 军李, 静侯, 众徐, 平黄. 石墨/钒氧化物的制备、表征及其对亚甲基蓝的吸附性能. 稀有金属材料与工程 2023.
杨赟, 赵莹鑫, 王玉龙, 杨水金. 镍掺杂MIL-53 (Fe) 对亚甲基蓝吸附性能研究. 工业水处理 2023.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the following: Thanks to Professor Wu Ying for her help in all aspects. Acknowledgement of support for the project on efficient degradation of ammonia and nitrogen contaminants in urban drinking water (1120018).
Funding
This study was supported by a research project on the efficient degradation of ammonia and nitrogen contaminants in urban drinking water (1120018). The South Xinjiang Innovation and Development Program of Key Industries of Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps (Grant No. 2020DB002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QF conceived, drafted and approved this research article. Conceptualization: YW. Data compilation: QF. Funding acquisition: YW. Methodology: QF. Role/writing—original draft: QF. Writing—review and editing: QF and YW. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval
All authors have read, understood and have complied as applicable with the statement on “Ethical responsibilities of Authors” as found in the Instructions for Authors and are aware that with minor exceptions, no changes can be made to authorship once the paper is submitted.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, Q., Wu, Y. Adsorption behavior and mechanism of action of magnetic MIL-100(Fe) on MB. Environ Monit Assess 195, 745 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11282-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11282-x