Abstract
Purpose
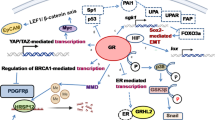
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is a highly heterogeneous and aggressive breast malignancy. Glucocorticoid (GC)–glucocorticoid receptor (GR) pathway plays a pivotal role in the cellular responses to various stresses including chemotherapy. Serum- and glucocorticoid-induced kinase-1 (SGK1) is known as an important downstream effector molecule in the GR signaling pathway, we attempted to explore its clinicopathological and functional significance in TNBC in which GR is expressed.
Methods
We first immunolocalized GR and SGK1 and correlated the results with clinicopathological variables and clinical outcome in 131 TNBC patients. We also evaluated the effects of SGK1 on the cell proliferation and migration in TNBC cell lines with administration of dexamethasone (DEX) to further clarify the significance of SGK1.
Results
The status of SGK1 in carcinoma cells was significantly associated with adverse clinical outcome in TNBC patients examined and was significantly associated with lymph node metastasis, pathological stage, and lymphatic invasion of the patients. In particular, SGK1 immunoreactivity was significantly associated with an increased risk of recurrence in GR-positive TNBC patients. Subsequent in vitro studies also demonstrated that DEX promoted TNBC cell migration and the silencing of gene expression did inhibit the cell proliferation and migration of TNBC cells under DEX treatment.
Conclusions
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to explore an association between SGK1 and clinicopathological variables and clinical outcome of TNBC patients. SGK1 status was significantly positively correlated with adverse clinical outcome of TNBC patients and promoted carcinoma cell proliferation and migration of carcinoma cells.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed in the present study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Yin L, Duan JJ, Bian XW, Yu SC (2020) Triple-negative breast cancer molecular subtyping and treatment progress. Breast Cancer Res 22(1):61. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13058-020-01296-5
Belova L, Delgado B, Kocherginsky M, Melhem A, Olopade OI, Conzen SD (2009) Glucocorticoid receptor expression in breast cancer associates with older patient age. Breast Cancer Res Treat 116(3):441–447. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-008-0136-9
Abduljabbar R, Negm OH, Lai CF, Jerjees DA, Al-Kaabi M, Hamed MR et al (2015) Clinical and biological significance of glucocorticoid receptor (GR) expression in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 150(2):335–346. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-015-3335-1
Baker GM, Murphy T, Block T, Nguyen D, Lynch FJ (2015) Development and validation of an immunohistochemistry assay to assess glucocorticoid receptor expression for clinical trials of mifepristone in breast cancer. Cancer Manag Res 7:361–368. https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S91546
Obradovic M, Hamelin B, Manevski N, Couto JP, Sethi A, Coissieux MM et al (2019) Glucocorticoids promote breast cancer metastasis. Nature 567(7749):540–544. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1019-4
Miesfeld R, Okret S, Wikstrom AC, Wrange O, Gustafsson JA, Yamamoto KR (1984) Characterization of a steroid hormone receptor gene and mRNA in wild-type and mutant cells. Nature 312(5996):779–781. https://doi.org/10.1038/312779a0
Frank F, Ortlund EA, Liu X (2021) Structural insights into glucocorticoid receptor function. Biochem Soc Trans 49(5):2333–2343. https://doi.org/10.1042/BST20210419
Pan D, Kocherginsky M, Conzen SD (2011) Activation of the glucocorticoid receptor is associated with poor prognosis in estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer. Cancer Res 71(20):6360–6370. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-0362
Sorrentino G, Ruggeri N, Zannini A, Ingallina E, Bertolio R, Marotta C et al (2017) Glucocorticoid receptor signalling activates YAP in breast cancer. Nat Commun 8:14073. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms14073
Yang F, Ma Q, Liu Z, Li W, Tan Y, Jin C et al (2017) Glucocorticoid receptor: MegaTrans switching mediates the repression of an ERalpha-regulated transcriptional program. Mol Cell 66(3):321–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2017.03.019
Lippman M, Bolan G, Huff K (1976) The effects of glucocorticoids and progesterone on hormone-responsive human breast cancer in long-term tissue culture. Cancer Res 36(12):4602–4609
Wu W, Chaudhuri S, Brickley DR, Pang D, Karrison T, Conzen SD (2004) Microarray analysis reveals glucocorticoid-regulated survival genes that are associated with inhibition of apoptosis in breast epithelial cells. Cancer Res 64(5):1757–1764. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-03-2546
Pearce LR, Komander D, Alessi DR (2010) The nuts and bolts of AGC protein kinases. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 11(1):9–22. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm2822
Zhu R, Yang G, Cao Z, Shen K, Zheng L, Xiao J et al (2020) The prospect of serum and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase 1 (SGK1) in cancer therapy: a rising star. Ther Adv Med Oncol 12:431411310. https://doi.org/10.1177/1758835920940946
Sahoo S, Brickley DR, Kocherginsky M, Conzen SD (2005) Coordinate expression of the PI3-kinase downstream effectors serum and glucocorticoid-induced kinase (SGK-1) and Akt-1 in human breast cancer. Eur J Cancer 41(17):2754–2759. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2005.07.018
Yao Y, Jiang Q, Jiang L, Wu J, Zhang Q, Wang J et al (2016) Lnc-SGK1 induced by Helicobacter pylori infection and highsalt diet promote Th2 and Th17 differentiation in human gastric cancer by SGK1/Jun B signaling. Oncotarget 7(15):20549–20560. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.7823
Tang Z, Shen Q, Xie H, Zhou Z, Shi G, Zhang C et al (2018) Serum and glucocorticoid-regulated kinase 1 (SGK1) is a predictor of poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer, and its dynamic pattern following treatment with SGK1 inhibitor and gamma-ray irradiation was elucidated. Oncol Rep 39(3):1505–1515. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2018.6181
Szmulewitz RZ, Chung E, Al-Ahmadie H, Daniel S, Kocherginsky M, Razmaria A et al (2012) Serum/glucocorticoid-regulated kinase 1 expression in primary human prostate cancers. Prostate 72(2):157–164. https://doi.org/10.1002/pros.21416
Kanai A, McNamara KM, Iwabuchi E, Miki Y, Onodera Y, Guestini F et al (2020) Significance of glucocorticoid signaling in triple-negative breast cancer patients: a newly revealed interaction with androgen signaling. Breast Cancer Res Treat 180(1):97–110. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-020-05523-7
McCarty KJ, Miller LS, Cox EB, Konrath J, McCarty KS (1985) Estrogen receptor analyses. Correlation of biochemical and immunohistochemical methods using monoclonal antireceptor antibodies. Arch Pathol Lab Med 109(8):716–721
Ueki S, Fujishima F, Kumagai T, Ishida H, Okamoto H, Takaya K et al (2020) GR, Sgk1, and NDRG1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: their correlation with therapeutic outcome of neoadjuvant chemotherapy. BMC Cancer 20(1):161. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-020-6652-7
Zhang Z, Xu Q, Song C, Mi B, Zhang H, Kang H et al (2020) Serum- and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase 1 is essential for osteoclastogenesis and promotes breast cancer bone metastasis. Mol Cancer Ther 19(2):650–660. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-18-0783
Lang F, Stournaras C (2013) Serum and glucocorticoid inducible kinase, metabolic syndrome, inflammation, and tumor growth. Hormones (Athens) 12(2):160–171. https://doi.org/10.14310/horm.2002.1401
Wu W, Zou M, Brickley DR, Pew T, Conzen SD (2006) Glucocorticoid receptor activation signals through forkhead transcription factor 3a in breast cancer cells. Mol Endocrinol 20(10):2304–2314. https://doi.org/10.1210/me.2006-0131
Isikbay M, Otto K, Kregel S, Kach J, Cai Y, Vander GD et al (2014) Glucocorticoid receptor activity contributes to resistance to androgen-targeted therapy in prostate cancer. Horm Cancer 5(2):72–89. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12672-014-0173-2
Godbole M, Togar T, Patel K, Dharavath B, Yadav N, Janjuha S et al (2018) Up-regulation of the kinase gene SGK1 by progesterone activates the AP-1-NDRG1 axis in both PR-positive and -negative breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem 293(50):19263–19276. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA118.002894
Lee L, Woolley C, Starkey T, Biswas S, Mirshahi T, Bardella C et al (2019) Serum- and glucocorticoid-induced kinase Sgk1 directly promotes the differentiation of colorectal cancer cells and restrains metastasis. Clin Cancer Res 25(2):629–640. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-1033
Schmidt EM, Gu S, Anagnostopoulou V, Alevizopoulos K, Foller M, Lang F, Stournaras C (2012) Serum- and glucocorticoid-dependent kinase-1-induced cell migration is dependent on vinculin and regulated by the membrane androgen receptor. FEBS J 279(7):1231–1242. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2012.08515.x
Zhang Y, Shi G, Zhang H, Xiong Q, Cheng F, Wang H et al (2021) Dexamethasone enhances the lung metastasis of breast cancer via a PI3K-SGK1-CTGF pathway. Oncogene 40(35):5367–5378. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-021-01944-w
Mitre-Aguilar IB, Moreno-Mitre D, Melendez-Zajgla J, Maldonado V, Jacobo-Herrera NJ, Ramirez-Gonzalez V et al (2022) The role of glucocorticoids in breast cancer therapy. Curr Oncol 30(1):298–314. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30010024
Lu YS, Lien HC, Yeh PY, Yeh KH, Kuo ML, Kuo SH et al (2005) Effects of glucocorticoids on the growth and chemosensitivity of carcinoma cells are heterogeneous and require high concentration of functional glucocorticoid receptors. World J Gastroenterol 11(40):6373–6380. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i40.6373
Wang H, Wang Y, Rayburn ER, Hill DL, Rinehart JJ, Zhang R (2007) Dexamethasone as a chemosensitizer for breast cancer chemotherapy: potentiation of the antitumor activity of adriamycin, modulation of cytokine expression, and pharmacokinetics. Int J Oncol 30(4):947–953. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.30.4.947
Wang H, Li M, Rinehart JJ, Zhang R (2004) Pretreatment with dexamethasone increases antitumor activity of carboplatin and gemcitabine in mice bearing human cancer xenografts: in vivo activity, pharmacokinetics, and clinical implications for cancer chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res 10(5):1633–1644. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-0829-3
Skor MN, Wonder EL, Kocherginsky M, Goyal A, Hall BA, Cai Y et al (2013) Glucocorticoid receptor antagonism as a novel therapy for triple-negative breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 19(22):6163–6172. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-3826
Maestro I, Boya P, Martinez A (2020) Serum- and glucocorticoid-induced kinase 1, a new therapeutic target for autophagy modulation in chronic diseases. Expert Opin Ther Targets 24(3):231–243. https://doi.org/10.1080/14728222.2020.1730328
Sherk AB, Frigo DE, Schnackenberg CG, Bray JD, Laping NJ, Trizna W et al (2008) Development of a small-molecule serum- and glucocorticoid-regulated kinase-1 antagonist and its evaluation as a prostate cancer therapeutic. Cancer Res 68(18):7475–7483. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-1047
Yang L, Li N, Xue Z, Liu LR, Li J, Huang X et al (2020) Synergistic therapeutic effect of combined PDGFR and SGK1 inhibition in metastasis-initiating cells of breast cancer. Cell Death Differ 27(7):2066–2080. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-019-0485-4
Liu G, Honisch S, Liu G, Schmidt S, Pantelakos S, Alkahtani S et al (2015) Inhibition of SGK1 enhances mAR-induced apoptosis in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Cancer Biol Ther 16(1):52–59. https://doi.org/10.4161/15384047.2014.986982
Tangir J, Bonafe N, Gilmore-Hebert M, Henegariu O, Chambers SK (2004) SGK1, a potential regulator of c-fms related breast cancer aggressiveness. Clin Exp Metastasis 21(6):477–483. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-004-4226-8
Acknowledgements
We thank the members of the Department of Pathology and the Department of Breast and Endocrine Surgical Oncology in Tohoku University Graduate School of Medicine for their support.
Funding
This study was not funded by any grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committees (Tohoku University Hospital: 2020-1-6, Sagara Hospital: 15-2, JCHO Kurume General Hospital: 148) and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Miki, Y., Iwabuchi, E. et al. Induction of SGK1 via glucocorticoid-influenced clinical outcome of triple-negative breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat 200, 323–335 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-023-06990-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-023-06990-4