Abstract
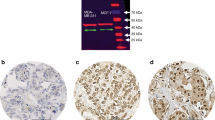
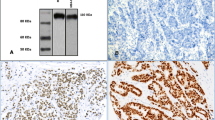
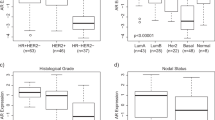
The glucocorticoid receptor (GR) is a member of the nuclear receptor superfamily of transcription factors, which exerts anti-proliferative and anti-apoptotic activities. The GR is expressed in a large proportion of breast cancer (BC) although levels generally decrease during cancer progression. This study aimed to determine the clinical and biological significance of GR expression using a large series of early-stage BC with long-term follow-up and BC cell lines. Immunohistochemistry was used to assess the expression of GR in 999 cases of primary invasive BC prepared as tissue microarrays. Reverse phase protein microarray was used to assess the expression of GR in MCF7 and MDA-MB-231 cell lines. Nuclear expression of GR was observed in 61.6 % of breast tumours and was associated with features of good prognosis including smaller tumour size and lower grade with less pleomorphism and low mitotic count. GR expression was positively correlated with expression of oestrogen (ER) and progesterone receptors. In ER-positive tumours, GR was associated with other features of favourable outcome including FOXA1, GATA3 and BEX1 expression, while low GR expression was associated with high Ki67, p53 and CD71 expression. GR expression is associated with features of good outcome but does not provide prognostic information independent of size, stage and grade. Understanding the receptor and its effects on BC behaviour is essential for avoiding any unwanted effects from the use of glucocorticoids in routine oncology practice.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kricker A, Price M, Butow P, Goumas C, Armes JE, Armstrong BK (2009) Effects of life event stress and social support on the odds of a > or = 2 cm breast cancer. Cancer Causes Control 20(4):437–447
Michael YL, Carlson NE, Chlebowski RT, Aickin M, Weihs KL, Ockene JK, Bowen DJ, Ritenbaugh C (2009) Influence of stressors on breast cancer incidence in the Women’s Health Initiative. Health Psychol 28(2):137–146
Hermes GL, Delgado B, Tretiakova M, Cavigelli SA, Krausz T, Conzen SD, McClintock MK (2009) Social isolation dysregulates endocrine and behavioral stress while increasing malignant burden of spontaneous mammary tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(52):22393–22398
Baschant U, Tuckermann J (2010) The role of the glucocorticoid receptor in inflammation and immunity. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 120(2–3):69–75
Hollenberg SM, Weinberger C, Ong ES, Cerelli G, Oro A, Lebo R, Thompson EB, Rosenfeld MG, Evans RM (1985) Primary structure and expression of a functional human glucocorticoid receptor cDNA. Nature 318(6047):635–641
Francke U, Foellmer BE (1989) The glucocorticoid receptor gene is in 5q31-q32 [corrected]. Genomics 4(4):610–612
Govindan MV, Devic M, Green S, Gronemeyer H, Chambon P (1985) Cloning of the human glucocorticoid receptor cDNA. Nucl Acids Res 13(23):8293–8304
Keightley MC (1998) Steroid receptor isoforms: exception or rule? Mol Cell Endocrinol 137(1):1–5
Lu NZ, Wardell SE, Burnstein KL, Defranco D, Fuller PJ, Giguere V, Hochberg RB, McKay L, Renoir JM, Weigel NL et al (2006) International Union of Pharmacology. LXV. The pharmacology and classification of the nuclear receptor superfamily: glucocorticoid, mineralocorticoid, progesterone, and androgen receptors. Pharmacol Rev 58(4):782–797
Rhen T, Cidlowski JA (2005) Antiinflammatory action of glucocorticoids—new mechanisms for old drugs. N Engl J Med 353(16):1711–1723
Dickson RB, Lippman ME (1988) Control of human breast cancer by estrogen, growth factors, and oncogenes. Cancer Treat Res 40:119–165
Mikosz CA, Brickley DR, Sharkey MS, Moran TW, Conzen SD (2001) Glucocorticoid receptor-mediated protection from apoptosis is associated with induction of the serine/threonine survival kinase gene, sgk-1. J Biol Chem 276(20):16649–16654
De Bosscher K, Vanden Berghe W, Haegeman G (2003) The interplay between the glucocorticoid receptor and nuclear factor-kappaB or activator protein-1: molecular mechanisms for gene repression. Endocr Rev 24(4):488–522
Shaulian E, Karin M (2002) AP-1 as a regulator of cell life and death. Nat Cell Biol 4(5):E131–136
Osborne CK, Monaco ME, Kahn CR, Huff K, Bronzert D, Lippman ME (1979) Direct inhibition of growth and antagonism of insulin action by glucocorticoids in human breast cancer cells in culture. Cancer Res 39(7 Pt 1):2422–2428
Goya L, Maiyar AC, Ge Y, Firestone GL (1993) Glucocorticoids induce a G1/G0 cell cycle arrest of Con8 rat mammary tumor cells that is synchronously reversed by steroid withdrawal or addition of transforming growth factor-alpha. Mol Endocrinol 7(9):1121–1132
Fryer CJ, Kinyamu HK, Rogatsky I, Garabedian MJ, Archer TK (2000) Selective activation of the glucocorticoid receptor by steroid antagonists in human breast cancer and osteosarcoma cells. J Biol Chem 275(23):17771–17777
Karck U, Kommoss F (2000) Does tamoxifen change oestrogen and progesterone receptor expression in the endometrium and breast? Eur J Cancer 36(Suppl 4):S45–46
Curran JE, Vaughan T, Lea RA, Weinstein SR, Morrison NA, Griffiths LR (1999) Association of A vitamin D receptor polymorphism with sporadic breast cancer development. Int J Cancer 83(6):723–726
Allegra JC, Lippman ME, Thompson EB, Simon R, Barlock A, Green L, Huff KK, Do HM, Aitken SC (1979) Distribution, frequency, and quantitative analysis of estrogen, progesterone, androgen, and glucocorticoid receptors in human breast cancer. Cancer Res 39(5):1447–1454
Buxant F, Engohan-Aloghe C, Noël JC (2010) Estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and glucocorticoid receptor expression in normal breast tissue, breast in situ carcinoma, and invasive breast cancer. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 18(3):254–257
Reiche EM, Nunes SO, Morimoto HK (2004) Stress, depression, the immune system, and cancer. Lancet Oncol 5(10):617–625
Reiche EM, Morimoto HK, Nunes SM (2005) Stress and depression-induced immune dysfunction: implications for the development and progression of cancer. Int Rev Psychiatr 17(6):515–527
Lien HC, Lu YS, Cheng AL, Chang WC, Jeng YM, Kuo YH, Huang CS, Chang KJ, Yao YT (2006) Differential expression of glucocorticoid receptor in human breast tissues and related neoplasms. J Pathol 209(3):317–327
Vilasco M, Communal L, Mourra N, Courtin A, Forgez P, Gompel A (2011) Glucocorticoid receptor and breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 130(1):1–10
Green AR, Powe DG, Rakha EA, Soria D, Lemetre C, Nolan CC, Barros FF, Macmillan RD, Garibaldi JM, Ball GR et al (2013) Identification of key clinical phenotypes of breast cancer using a reduced panel of protein biomarkers. Br J Cancer 109(7):1886–1894
Abd El-Rehim DM, Ball G, Pinder SE, Rakha E, Paish C, Robertson JF, Macmillan D, Blamey RW, Ellis IO (2005) High-throughput protein expression analysis using tissue microarray technology of a large well-characterised series identifies biologically distinct classes of breast cancer confirming recent cDNA expression analyses. Int J Cancer 116(3):340–350
Rhodes DR, Ateeq B, Cao Q, Tomlins SA, Mehra R, Laxman B, Kalyana-Sundaram S, Lonigro RJ, Helgeson BE, Bhojani MS et al (2009) AGTR1 overexpression defines a subset of breast cancer and confers sensitivity to losartan, an AGTR1 antagonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(25):10284–10289
Habashy HO, Powe DG, Rakha EA, Ball G, Macmillan RD, Green AR, Ellis IO (2010) The prognostic significance of PELP1 expression in invasive breast cancer with emphasis on the ER-positive luminal-like subtype. Breast Cancer Res Treat 120(3):603–612
Habashy HO, Powe DG, Staka CM, Rakha EA, Ball G, Green AR, Aleskandarany M, Paish EC, Douglas Macmillan R, Nicholson RI et al (2010) Transferrin receptor (CD71) is a marker of poor prognosis in breast cancer and can predict response to tamoxifen. Breast Cancer Res Treat 119(2):283–293
Habashy HO, Rakha EA, Ellis IO, Powe DG (2013) The oestrogen receptor coactivator CARM1 has an oncogenic effect and is associated with poor prognosis in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 140(2):307–316
Winters ZE, Hunt NC, Bradburn MJ, Royds JA, Turley H, Harris AL, Norbury CJ (2001) Subcellular localisation of cyclin B, Cdc2 and p21(WAF1/CIP1) in breast cancer. association with prognosis. Eur J Cancer 37(18):2405–2412
Habashy HO, Powe DG, Rakha EA, Ball G, Paish C, Gee J, Nicholson RI, Ellis IO (2008) Forkhead-box A1 (FOXA1) expression in breast cancer and its prognostic significance. Eur J Cancer 44(11):1541–1551
Kouros-Mehr H, Slorach EM, Sternlicht MD, Werb Z (2006) GATA-3 maintains the differentiation of the luminal cell fate in the mammary gland. Cell 127(5):1041–1055
Cho Y, Gorina S, Jeffrey PD, Pavletich NP (1994) Crystal structure of a p53 tumor suppressor-DNA complex: understanding tumorigenic mutations. Science 265(5170):346–355
Finlin BS, Gau CL, Murphy GA, Shao H, Kimel T, Seitz RS, Chiu YF, Botstein D, Brown PO, Der CJ et al (2001) RERG is a novel ras-related, estrogen-regulated and growth-inhibitory gene in breast cancer. J Biol Chem 276(45):42259–42267
Scholzen T, Gerdes J (2000) The Ki-67 protein: from the known and the unknown. J Cell Physiol 182(3):311–322
McCarty KS Jr, Miller LS, Cox EB, Konrath J, McCarty KS Sr (1985) Estrogen receptor analyses. Correlation of biochemical and immunohistochemical methods using monoclonal antireceptor antibodies. Arch Pathol Lab Med 109(8):716–721
Camp RL, Dolled-Filhart M, Rimm DL (2004) X-tile: a new bio-informatics tool for biomarker assessment and outcome-based cut-point optimization. Clin Cancer Res 10(21):7252–7259
Negm OH, Mannsperger HA, McDermott EM, Drewe E, Powell RJ, Todd I, Fairclough LC, Tighe PJ (2014) A pro-inflammatory signalome is constitutively activated by C33Y mutant TNF receptor 1 in TNF receptor associated periodic syndrome (TRAPS). Eur J Immunol 44(7):2096–2110
Alshareeda AT, Negm OH, Green AR, Nolan C, Tighe P, Albarakati N, Sultana R, Madhusudan S, Ellis IO, Rakha EA (2014) SUMOylation proteins in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 144(3):519–530
Aleskandarany MA, Negm OH, Green AR, Ahmed MA, Nolan CC, Tighe PJ, Ellis IO, Rakha EA (2014) Epithelial mesenchymal transition in early invasive breast cancer: an immunohistochemical and reverse phase protein array study. Breast Cancer Res Treat 145(2):339–348
Alshareeda AT, Negm OH, Albarakati N, Green AR, Nolan C, Sultana R, Madhusudan S, Benhasouna A, Tighe P, Ellis IO et al (2013) Clinicopathological significance of KU70/KU80, a key DNA damage repair protein in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 139(2):301–310
Mannsperger HA, Gade S, Henjes F, Beissbarth T, Korf U (2010) RPPanalyzer: analysis of reverse-phase protein array data. Bioinformatics 26(17):2202–2203
Habashy HO, Powe DG, Glaab E, Ball G, Spiteri I, Krasnogor N, Garibaldi JM, Rakha EA, Green AR, Caldas C et al (2011) RERG (Ras-like, oestrogen-regulated, growth-inhibitor) expression in breast cancer: a marker of ER-positive luminal-like subtype. Breast Cancer Res Treat 128(2):315–326
Gujral TS, Karp RL, Finski A, Chan M, Schwartz PE, MacBeath G, Sorger P (2013) Profiling phospho-signaling networks in breast cancer using reverse-phase protein arrays. Oncogene 32(29):3470–3476
Oakley RH, Cidlowski JA (2011) Cellular processing of the glucocorticoid receptor gene and protein: new mechanisms for generating tissue-specific actions of glucocorticoids. J Biol Chem 286(5):3177–3184
Perou CM, Sorlie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, Pollack JR, Ross DT, Johnsen H, Akslen LA et al (2000) Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 406(6797):747–752
Sorlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, Aas T, Geisler S, Johnsen H, Hastie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS et al (2001) Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(19):10869–10874
Teulings FA, van Gilse HA (1977) Demonstration of glucocorticoid receptors in human mammary carcinomas. Horm Res 8(2):107–116
Belova L, Delgado B, Kocherginsky M, Melhem A, Olopade OI, Conzen SD (2009) Glucocorticoid receptor expression in breast cancer associates with older patient age. Breast Cancer Res Treat 116(3):441–447
Allegra JC, Lippman ME, Simon R, Thompson EB, Barlock A, Green L, Huff KK, Do HM, Aitken SC, Warren R (1979) Association between steroid hormone receptor status and disease-free interval in breast cancer. Cancer Treat Rep 63(8):1271–1277
Pan D, Kocherginsky M, Conzen SD (2011) Activation of the glucocorticoid receptor is associated with poor prognosis in estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer. Cancer Res 71(20):6360–6370
Herr I, Gassler N, Friess H, Buchler MW (2007) Regulation of differential pro- and anti-apoptotic signaling by glucocorticoids. Apoptosis 12(2):271–291
Lin A, Karin M (2003) NF-kappaB in cancer: a marked target. Semin Cancer Biol 13(2):107–114
Skor MN, Wonder EL, Kocherginsky M, Goyal A, Hall BA, Cai Y, Conzen SD (2013) Glucocorticoid receptor antagonism as a novel therapy for triple-negative breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 19(22):6163–6172
Acknowledgments
Rezvan Abduljabbar is funded by the Human Capacity Development Program, Ministry of Higher Education, Kurdistan Regional Government, IRAQ.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Ola H. Negm: First joint author.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abduljabbar, R., Negm, O.H., Lai, CF. et al. Clinical and biological significance of glucocorticoid receptor (GR) expression in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 150, 335–346 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-015-3335-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-015-3335-1