Abstract
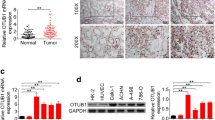
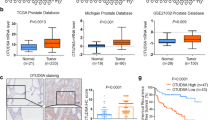
Dysregulation of deubiquitination contributes to various diseases, including cancer, and aberrant expression of deubiquitinating enzymes is involved in carcinoma progression. As a member of the ovarian tumor (OTU) deubiquitinases, OTUD4 is considered a tumor suppressor in many kinds of malignancies. The biological characteristics and mechanisms of OTUD4 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) remain unclear. The downregulation of OTUD4 in ccRCC was confirmed based on the TCGA database and a validation cohort of 30-paired ccRCC and para-carcinoma samples. Moreover, OTUD4 expression was detected by immunohistochemistry in 50 cases of ccRCC tissues, and patients with lower levels of OTUD4 showed larger tumor size (p = 0.015). TCGA data revealed that patients with high expression of OTUD4 had a longer overall survival rate. In vitro and in vivo studies revealed that downregulation of OTUD4 was essential for tumor cell growth and metastasis in ccRCC, and OTUD4 overexpression inhibited these malignant phenotypes. We further found that OTUD4 sensitized ccRCC cells to Erastin-induced ferroptosis, and ferrostain-1 inhibited OTUD4-induced ferroptotic cell death. Mechanistic studies indicated that OTUD4 functioned as an anti-proliferative and anti-metastasic factor through the regulation of RNA-binding protein 47 (RBM47)-mediated activating transcription factor 3 (ATF3). OTUD4 directly interacted with RBM47 and promoted its stability via deubiquitination events. RBM47 was critical in ccRCC progression by regulating ATF3 mRNA stability, thereby promoting ATF3-mediated ferroptosis. RBM47 interference abolished the suppressive role of OTUD4 overexpression in ccRCC. Our findings provide mechanistic insight into OTUD4 of ccRCC progression and indicate a novel critical pathway OTUD4/RBM47/ATF3 may serve as a potential therapeutic pathway for ccRCC.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD (2016) Jemal A (2016) Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 66(1):7–30
Rini BI, Campbell SC, Escudier B (2009) Renal cell carcinoma. Lancet 373(9669):1119–1132
Hsieh JJ, Purdue MP, Signoretti S et al (2017) Renal cell carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers 3:17009
Xu J, Latif S, Wei S (2012) Metastatic renal cell carcinoma presenting as gastric polyps: A case report and review of the literature. Int J Surg Case Rep 3(12):601–604
Martinez-Salamanca JI, Huang WC, Millan I et al (2011) Prognostic impact of the 2009 UICC/AJCC TNM staging system for renal cell carcinoma with venous extension. Eur Urol 59(1):120–127
Nijman SM, Luna-Vargas MP, Velds A et al (2005) A genomic and functional inventory of deubiquitinating enzymes. Cell 123(5):773–786
Mevissen TET, Komander D (2017) Mechanisms of Deubiquitinase Specificity and Regulation. Annu Rev Biochem 86:159–192
Di M, Miao J, Pan Q et al (2022) OTUD4-mediated GSDME deubiquitination enhances radiosensitivity in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by inducing pyroptosis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 41(1):328
Wu Z, Qiu M, Guo Y et al (2019) OTU deubiquitinase 4 is silenced and radiosensitizes non-small cell lung cancer cells via inhibiting DNA repair. Cancer Cell Int 19:99
Zhao X, Su X, Cao L et al (2020) OTUD4: A Potential Prognosis Biomarker for Multiple Human Cancers. Cancer Management Res 12:1503–1512
Tang Z, Li C, Kang B et al (2017) GEPIA: a web server for cancer and normal gene expression profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res 45(W1):W98–W102
Qin H, Ni H, Liu Y et al (2020) RNA-binding proteins in tumor progression. J Hematol Oncol 13(1):90
Shen DJ, Jiang YH, Li JQ, Xu LW, Tao KY (2020) The RNA-binding protein RBM47 inhibits non-small cell lung carcinoma metastasis through modulation of AXIN1 mRNA stability and Wnt/beta-catentin signaling. Surg Oncol 34:31–39
Rokavec M, Kaller M, Horst D, Hermeking H (2017) Pan-cancer EMT-signature identifies RBM47 down-regulation during colorectal cancer progression. Sci Rep 7(1):4687
Vanharanta S, Marney CB, Shu W et al (2014) Loss of the multifunctional RNA-binding protein RBM47 as a source of selectable metastatic traits in breast cancer. eLife 3:e02734
Radine C, Peters D, Reese A et al (2020) The RNA-binding protein RBM47 is a novel regulator of cell fate decisions by transcriptionally controlling the p53–p21-axis. Cell Death Differ 27(4):1274–1285
Li JH, Liu S, Zhou H, Qu LH, Yang JH (2014) starBase v2.0: decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein-RNA interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data. Nucleic Acids Res 42:D92-7
Gao S, Gao L, Wang S et al (2021) ATF3 Suppresses Growth and Metastasis of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma by Deactivating EGFR/AKT/GSK3beta/beta-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Frontiers Cell Develop Biol 9:618987
Tong X, Tang R, Xiao M et al (2022) Targeting cell death pathways for cancer therapy: recent developments in necroptosis, pyroptosis, ferroptosis, and cuproptosis research. J Hematol Oncol 15(1):174
Cao X, Yan Z, Chen Z et al (2023) The Emerging Role of Deubiquitinases in Radiosensitivity. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 118(5):1347–1370
Liu T, Jiang L, Tavana O, Gu W (2019) The Deubiquitylase OTUB1 Mediates Ferroptosis via Stabilization of SLC7A11. Cancer Res 79(8):1913–1924
Mou Y, Wang J, Wu J et al (2019) Ferroptosis, a new form of cell death: opportunities and challenges in cancer. J Hematol Oncol 12(1):34
Zhao L, Zhou X, Xie F et al (2022) Ferroptosis in cancer and cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Commun (Lond) 42(2):88–116
Tang R, Xu J, Zhang B et al (2020) Ferroptosis, necroptosis, and pyroptosis in anticancer immunity. J Hematol Oncol 13(1):110
Zhang C, Liu X, Jin S, Chen Y, Guo R (2022) Ferroptosis in cancer therapy: a novel approach to reversing drug resistance. Mol Cancer 21(1):47
Wang J, Yin X, He W et al (2021) SUV39H1 deficiency suppresses clear cell renal cell carcinoma growth by inducing ferroptosis. Acta Pharm Sin B 11(2):406–419
Wang L, Liu Y, Du T et al (2020) ATF3 promotes erastin-induced ferroptosis by suppressing system Xc. Cell Death Differ 27(2):662–675
Fu D, Wang C, Yu L, Yu R (2021) Induction of ferroptosis by ATF3 elevation alleviates cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer by restraining Nrf2/Keap1/xCT signaling. Cell Mol Biol Lett 26(1):26
Mevissen TET, Hospenthal MK, Geurink PP et al (2013) OTU deubiquitinases reveal mechanisms of linkage specificity and enable ubiquitin chain restriction analysis. Cell 154(1):169–184
Li Z, Xin S, Yu S, Liang J, Zhang X (2022) Prognostic Signatures and Therapeutic Value Based on the Notch Pathway in Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2022:1669664
Fendler A, Bauer D, Busch J et al (2020) Inhibiting WNT and NOTCH in renal cancer stem cells and the implications for human patients. Nat Commun 11(1):929
Xue YJ, Chen SN, Chen WG et al (2019) Cripto-1 expression in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma is associated with poor disease outcome. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 38(1):378
Lu Y, Qin H, Jiang B et al (2021) KLF2 inhibits cancer cell migration and invasion by regulating ferroptosis through GPX4 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Lett 522:1–13
Zhang Q, Deng T, Zhang H et al (2022) Adipocyte-Derived Exosomal MTTP Suppresses Ferroptosis and Promotes Chemoresistance in Colorectal Cancer. Adv Sci (Weinh) 9(28):e2203357
Miotto G, Rossetto M, Di Paolo ML et al (2020) Insight into the mechanism of ferroptosis inhibition by ferrostatin-1. Redox Biol 28:101328
Liu H, Fan J, Zhang W et al (2020) OTUD4 alleviates hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury by suppressing the K63-linked ubiquitination of TRAF6. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 523(4):924–930
Liuyu T, Yu K, Ye L et al (2019) Induction of OTUD4 by viral infection promotes antiviral responses through deubiquitinating and stabilizing MAVS. Cell Res 29(1):67–79
Zhao Y, Mudge MC, Soll JM et al (2018) OTUD4 Is a Phospho-Activated K63 Deubiquitinase that Regulates MyD88-Dependent Signaling. Mol Cell 69(3):505-516.e5
Chen L, Lu H, Peng D et al (2023) Activation of NOTCH signaling via DLL1 is mediated by APE1-redox-dependent NF-κB activation in oesophageal adenocarcinoma. Gut 72(3):421–432
Komander D, Clague MJ, Urbé S (2009) Breaking the chains: structure and function of the deubiquitinases. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10(8):550–563
Fraile JM, Quesada V, Rodríguez D, Freije JMP, López-Otín C (2012) Deubiquitinases in cancer: new functions and therapeutic options. Oncogene 31(19):2373–2388
Louis M, Hofmann K, Broemer M (2015) Evolutionary Loss of Activity in De-Ubiquitylating Enzymes of the OTU Family. PLoS ONE 10(11):e0143227
Zhao X, Su X, Cao L et al (2020) OTUD4: A Potential Prognosis Biomarker for Multiple Human Cancers. Cancer Manag Res 12:1503–1512
Peired AJ, Campi R, Angelotti ML et al (2021) Sex and Gender Differences in Kidney Cancer: Clinical and Experimental Evidence. Cancers (Basel) 13(18):4588
Fukushima H, Saito K, Yasuda Y et al (2020) Female Gender Predicts Favorable Prognosis in Patients With Non-metastatic Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Undergoing Curative Surgery: Results From the International Marker Consortium for Renal Cancer (INMARC). Clin Genitourin Cancer 18(2):111-116.e1
Liu N, Chen Y, Yang L et al (2022) Both SUMOylation and ubiquitination of TFE3 fusion protein regulated by androgen receptor are the potential target in the therapy of Xp11.2 translocation renal cell carcinoma. Clin Transl Med 12(4):e797
Otto T, Sicinski P (2017) Cell cycle proteins as promising targets in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 17(2):93–115
Shivalingappa PKM, Sharma V, Shiras A, Bapat SA (2021) RNA binding motif 47 (RBM47): emerging roles in vertebrate development, RNA editing and cancer. Mol Cell Biochem 476(12):4493–4505
Qin Y, Sun W, Wang Z et al (2022) RBM47/SNHG5/FOXO3 axis activates autophagy and inhibits cell proliferation in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Cell Death Dis 13(3):270
Xiang Y, Zhou S, Hao J et al (2020) Development and validation of a prognostic model for kidney renal clear cell carcinoma based on RNA binding protein expression. Aging (Albany NY) 12(24):25356–25372
Wei Y, Zhang F, Zhang Y et al (2019) Post-transcriptional regulator Rbm47 elevates IL-10 production and promotes the immunosuppression of B cells. Cell Mol Immunol 16(6):580–589
Xu X-C, He S, Zhou Y-Q et al (2021) RNA-binding motif protein RBM47 promotes tumorigenesis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma through multiple pathways. J Genet Genomics 48(7):595–605
Sakurai T, Isogaya K, Sakai S et al (2016) RNA-binding motif protein 47 inhibits Nrf2 activity to suppress tumor growth in lung adenocarcinoma. Oncogene 35(38):5000–5009
Guo T, You K, Chen X et al (2022) RBM47 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma progression by targeting UPF1 as a DNA/RNA regulator. Cell Death Discov 8(1):320
Wang Y, Quan F, Cao Q et al (2021) Quercetin alleviates acute kidney injury by inhibiting ferroptosis. J Adv Res 28:231–243
Yang WS, Stockwell BR (2016) Ferroptosis: Death by Lipid Peroxidation. Trends Cell Biol 26(3):165–176
Dell’Atti L, Bianchi N, Aguiari G (2022) New therapeutic interventions for kidney carcinoma: looking to the future. Cancers (Basel) 14(15):3616
Lei G, Zhuang L, Gan B (2022) Targeting ferroptosis as a vulnerability in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 22(7):381–396
Mai TT, Hamaï A, Hienzsch A et al (2017) Salinomycin kills cancer stem cells by sequestering iron in lysosomes. Nat Chem 9(10):1025–1033
Yang WS, SriRamaratnam R, Welsch ME et al (2014) Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by GPX4. Cell 156(1–2):317–331
Miess H, Dankworth B, Gouw AM et al (2018) The glutathione redox system is essential to prevent ferroptosis caused by impaired lipid metabolism in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Oncogene 37(40):5435–5450
Jiang X, Stockwell BR, Conrad M (2021) Ferroptosis: mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 22(4):266–282
Bogdan AR, Miyazawa M, Hashimoto K, Tsuji Y (2016) Regulators of Iron Homeostasis: New Players in Metabolism, Cell Death, and Disease. Trends Biochem Sci 41(3):274–286
Yan H, Talty R, Jain A et al (2023) Discovery of decreased ferroptosis in male colorectal cancer patients with KRAS mutations. Redox Biol 62:102699
Liu T, Xu P, Ke S et al (2022) Histone methyltransferase SETDB1 inhibits TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in pulmonary fibrosis by regulating SNAI1 expression and the ferroptosis signaling pathway. Arch Biochem Biophys 715:109087
Cui X, Shang X, Xie J et al (2023) Cooperation between IRTKS and deubiquitinase OTUD4 enhances the SETDB1-mediated H3K9 trimethylation that promotes tumor metastasis via suppressing E-cadherin expression. Cancer Lett 575:216404
Xiao W, Gao Z, Duan Y, Yuan W, Ke Y (2017) Notch signaling plays a crucial role in cancer stem-like cells maintaining stemness and mediating chemotaxis in renal cell carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 36(1):41
Zhou B, Lin W, Long Y et al (2022) Notch signaling pathway: architecture, disease, and therapeutics. Signal Transduct Target Ther 7(1):95
Zhu Q, Wang H, Jiang B et al (2018) Loss of ATF3 exacerbates liver damage through the activation of mTOR/p70S6K/ HIF-1α signaling pathway in liver inflammatory injury. Cell Death Dis 9(9):910
Gerri C, Marass M, Rossi A, Stainier DYR (2018) Hif-1α and Hif-2α regulate hemogenic endothelium and hematopoietic stem cell formation in zebrafish. Blood 131(9):963–973
Ciria M, García NA, Ontoria-Oviedo I et al (2017) Mesenchymal Stem Cell Migration and Proliferation Are Mediated by Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α Upstream of Notch and SUMO Pathways. Stem cells and development 26(13):973–985
Acknowledgements
Not applicable
Funding
This work was supported by the China Scholarship Council (No. 202007045011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Lin Ye and Siyan Wang designed the experiments. Ziyao Li, Ye Tian, and Huafeng Zong analyzed the data and prepared the manuscript. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Xuelei Wang, Dongyang Li, Adili Keranmu, Shiyong Xin, Bowen Ye, Rong Bai, Weihua Chen, and Guosheng Yang. Guosheng Yang and Lin Ye provided technical support. All authors read and approved the final paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University. This study was performed in accordance with the ethical standards in the Declaration of Helsinki.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Tian, Y., Zong, H. et al. Deubiquitinating enzyme OTUD4 stabilizes RBM47 to induce ATF3 transcription: a novel mechanism underlying the restrained malignant properties of ccRCC cells. Apoptosis (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-024-01953-6
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-024-01953-6