Abstract
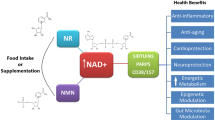
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN), a naturally occurring biologically active nucleotide, mainly functions via mediating the biosynthesis of NAD+. In recent years, its excellent pharmacological activities including anti-aging, treating neurodegenerative diseases, and protecting the heart have attracted increasing attention from scholars and entrepreneurs for production of a wide range of formulations, including functional food ingredients, health care products, active pharmaceuticals, and pharmaceutical intermediates. Presently, the synthesis methods of NMN mainly include two categories: chemical synthesis and biosynthesis. With the development of biocatalyst engineering and synthetic biology strategies, bio-preparation has proven to be efficient, economical, and sustainable methods. This review summarizes the chemical synthesis and biosynthetic pathways of NMN and provides an in-depth investigation on the mining and modification of enzyme resources during NMN biosynthesis, as well as the screening of hosts and optimization of chassis cells via metabolic engineering, which provide effective strategies for efficient production of NMN. In addition, an overview of the significant physiological functions and activities of NMN is elaborated. Finally, future research on technical approaches to further enhance NMN synthesis and strengthen clinical studies of NMN are prospected, which would lay the foundation for further promoting the application of NMN in nutrition, healthy food, and medicine in the future.
Key points
• NMN supplementation effectively increases the level of NAD+.
• The chemical and biological synthesis of NMN are comprehensively reviewed.
• The impact of NMN on the treatment of various diseases is summarized.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alano CC, Ying W, Swanson RA (2004) Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1-mediated cell death in astrocytes requires NAD+ depletion and mitochondrial permeability transition. J Biol Chem 279(18):18895–18902. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M313329200
Amjad S, Nisar S, Bhat AA, Shah AR, Frenneaux MP, Fakhro K, Haris M, Reddy R, Patay Z, Baur J, Bagga P (2021) Role of NAD(+) in regulating cellular and metabolic signaling pathways. Mol Metab 49:101195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmet.2021.101195
Assiri MA, Ali HR, Marentette JO, Yun Y, Liu J, Hirschey MD, Saba LM, Harris PS, Fritz KS (2019) Investigating RNA expression profiles altered by nicotinamide mononucleotide therapy in a chronic model of alcoholic liver disease. Hum Genomics 13(1):65. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40246-019-0251-1
Belenky P, Bogan KL, Brenner C (2007) NAD+ metabolism in health and disease. Trends Biochem Sci 32(1):12–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2006.11.006
Bieganowski P, Brenner C (2004) Discoveries of nicotinamide riboside as a nutrient and conserved NRK genes establish a Preiss-Handler independent route to NAD+ in fungi and humans. Cell 117(4):495–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(04)00416-7
Black WB, Aspacio D, Bever D, King E, Zhang L, Li H (2020) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for optimized biosynthesis of nicotinamide mononucleotide, a noncanonical redox cofactor. Microb Cell Fact 19(1):150. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-020-01415-z
Bové J, Prou D, Perier C, Przedborski S (2005) Toxin-induced models of Parkinson’s disease. NeuroRx 2(3):484–494. https://doi.org/10.1602/neurorx.2.3.484
Brito S, Baek JM, Cha B, Heo H, Lee SH, Lei L, Jung SY, Lee SM, Lee SH, Kwak BM, Chae S, Lee MG, Bin BH (2022) Nicotinamide mononucleotide reduces melanin production in aged melanocytes by inhibiting cAMP/Wnt signaling. J Dermatol Sci 106(3):159–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdermsci.2022.05.002
Caton PW, Kieswich J, Yaqoob MM, Holness MJ, Sugden MC (2011) Nicotinamide mononucleotide protects against pro-inflammatory cytokine-mediated impairment of mouse islet function. Diabetologia 54(12):3083–3092. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-011-2288-0
Chandrasekaran K, Choi J, Arvas MI, Salimian M, Singh S, Xu S, Gullapalli RP, Kristian T, Russell JW (2020) Nicotinamide mononucleotide administration prevents experimental diabetes-induced cognitive impairment and loss of hippocampal neurons. Int J Mol Sci 21(11):3756. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21113756
Chen X, Amorim JA, Moustafa GA, Lee JJ, Yu Z, Ishihara K, Iesato Y, Barbisan P, Ueta T, Togka KA, Lu L, Sinclair DA, Vavvas DG (2020) Neuroprotective effects and mechanisms of action of nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) in a photoreceptor degenerative model of retinal detachment. Aging (Albany NY) 12(24):24504–24521. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.202453
Covarrubias AJ, Perrone R, Grozio A, Verdin E (2021) NAD(+) metabolism and its roles in cellular processes during ageing. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 22(2):119–141. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-020-00313-x
Cros C, Margier M, Cannelle H, Charmetant J, Hulo N, Laganier L, Grozio A, Canault M (2022) Nicotinamide mononucleotide administration triggers macrophages reprogramming and alleviates inflammation during sepsis induced by experimental peritonitis. Front Mol Biosci 9:895028. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2022.895028
de Picciotto NE, Gano LB, Johnson LC, Martens CR, Sindler AL, Mills KF, Imai S, Seals DR (2016) Nicotinamide mononucleotide supplementation reverses vascular dysfunction and oxidative stress with aging in mice. Aging Cell 15(3):522–530. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.12461
Fan H, Yang HC, You L, Wang YY, He WJ, Hao CM (2013) The histone deacetylase, SIRT1, contributes to the resistance of young mice to ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury. Kidney Int 83(3):404–413. https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.2012.394
Fu RZ, Zhang Q (2018a) Method for preparing nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN). US Patent 0162895 A1
Fu RZ, Zhang Q (2018b) Nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransfrrase (NAMPT) mutant and use thereof. US Patent 0230443 A1
Gong JS, Zhang Q, Gu BC, Dong TT, Li H, Li H, Lu ZM, Shi JS, Xu ZH (2018) Efficient biocatalytic synthesis of nicotinic acid by recombinant nitrilase via high density culture. Bioresour Technol 260:427–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.03.109
Guan Y, Wang SR, Huang XZ, Xie QH, Xu YY, Shang D, Hao CM (2017) Nicotinamide mononucleotide, an NAD(+) precursor, rescues age-associated susceptibility to AKI in a sirtuin 1-dependent manner. J Am Soc Nephrol 28(8):2337–2352. https://doi.org/10.1681/asn.2016040385
He Z, Yang X, Tian X, Li L, Liu M (2022) Yeast cell surface engineering of a nicotinamide riboside kinase for the production of β-nicotinamide mononucleotide via whole-cell catalysis. ACS Synth Biol 11(10):3451–3459. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.2c00350
He JJ, Liu XX, Li Y, Wang Z, Shi HL, Kan YC, Yao LG, Tang CD (2023) High level expression of nicotinamide nucleoside kinase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae and its purification and immobilization by one-step method. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 11:1134152. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2023.1134152
Hershberger KA, Martin AS, Hirschey MD (2017) Role of NAD(+) and mitochondrial sirtuins in cardiac and renal diseases. Nat Rev Nephrol 13(4):213–225. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneph.2017.5
Hong W, Mo F, Zhang Z, Huang M, Wei X (2020) Nicotinamide mononucleotide: a promising molecule for therapy of diverse diseases by targeting NAD+ metabolism. Front Cell Dev Biol 8:246. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2020.00246
Hosseini L, Vafaee MS, Badalzadeh R (2020) Melatonin and nicotinamide mononucleotide attenuate myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via modulation of mitochondrial function and hemodynamic parameters in aged rats. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther 25(3):240–250. https://doi.org/10.1177/1074248419882002
Hroudova J, Singh N, Fisar Z (2014) Mitochondrial dysfunctions in neurodegenerative diseases: relevance to Alzheimer’s disease. Biomed Res Int 2014:175062. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/175062
Hsu CP, Zhai P, Yamamoto T, Maejima Y, Matsushima S, Hariharan N, Shao D, Takagi H, Oka S, Sadoshima J (2010) Silent information regulator 1 protects the heart from ischemia/reperfusion. Circulation 122(21):2170–2182. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.958033
Huang Z, Li N, Yu S, Zhang W, Zhang T, Zhou J (2022) Systematic engineering of Escherichia coli for efficient production of nicotinamide mononucleotide from nicotinamide. ACS Synth Biol 11(9):2979–2988. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.2c00100
In Ro B, Won Kang J, Min Kim S, Cheol Shin H (2020) Therapeutic effects of growth factor cocktail (CellcurinTM) containing FGF5s (fibroblast growth factor 5 short) and NMN (nicotinamide mononucleotide) in patients with androgenetic alopecia: a split study. Global Dermatol 7:1–5. https://doi.org/10.15761/god.1000229
Jafari-Azad A, Hosseini L, Rajabi M, Hoilund-Carlsen PF, Vafaee MS, Feyzizadeh S, Badalzadeh R (2021) Nicotinamide mononucleotide and melatonin counteract myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by activating SIRT3/FOXO1 and reducing apoptosis in aged male rats. Mol Biol Rep. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06351-8
Jeck R, Heik P, Woenckhaus C (1974) Simple methods of preparing nicotinamide mononucleotide. FEBS Lett 42(2):161–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-5793(74)80776-3
Jia Y, Kang X, Tan L, Ren Y, Qu L, Tang J, Liu G, Wang S, Xiong Z, Yang L (2021) Nicotinamide mononucleotide attenuates renal interstitial fibrosis after AKI by suppressing tubular DNA damage and senescence. Front Physiol 12:649547. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2021.649547
Kane AE, Sinclair DA (2018) Sirtuins and NAD(+) in the development and treatment of metabolic and cardiovascular diseases. Circ Res 123(7):868–885. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.312498
Katayoshi T, Nakajo T, Tsuji-Naito K (2021) Restoring NAD(+) by NAMPT is essential for the SIRT1/p53-mediated survival of UVA- and UVB-irradiated epidermal keratinocytes. J Photochem Photobiol B 221:112238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2021.112238
Khan JA, Xiang S, Tong L (2007) Crystal structure of human nicotinamide riboside kinase. Structure 15(8):1005–1013. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2007.06.017
Kim H-W, Ryoo G-H, Jang H-Y, Rah S-Y, Lee DH, Kim D-K, Bae EJ, Park B-H (2022) NAD+-boosting molecules suppress mast cell degranulation and anaphylactic responses in mice. Theranostics 12(7):3316–3328. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.69684
Kiss T, Balasubramanian P, Valcarcel-Ares MN, Tarantini S, Yabluchanskiy A, Csipo T, Lipecz A, Reglodi D, Zhang XA, Bari F, Farkas E, Csiszar A, Ungvari Z (2019) Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) treatment attenuates oxidative stress and rescues angiogenic capacity in aged cerebromicrovascular endothelial cells: a potential mechanism for the prevention of vascular cognitive impairment. GeroScience 41(5):619–630. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-019-00074-2
Kiss T, Giles CB, Tarantini S, Yabluchanskiy A, Balasubramanian P, Gautam T, Csipo T, Nyul-Toth A, Lipecz A, Szabo C, Farkas E, Wren JD, Csiszar A, Ungvari Z (2019) Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) supplementation promotes anti-aging miRNA expression profile in the aorta of aged mice, predicting epigenetic rejuvenation and anti-atherogenic effects. Geroscience 41(4):419–439. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-019-00095-x
Kiss T, Nyul-Toth A, Balasubramanian P, Tarantini S, Ahire C, Yabluchanskiy A, Csipo T, Farkas E, Wren JD, Garman L, Csiszar A, Ungvari Z (2020) Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) supplementation promotes neurovascular rejuvenation in aged mice: transcriptional footprint of SIRT1 activation, mitochondrial protection, anti-inflammatory, and anti-apoptotic effects. Geroscience 42(2):527–546. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-020-00165-5
Klimova N, Fearnow A, Long A, Kristian T (2020) NAD(+) precursor modulates post-ischemic mitochondrial fragmentation and reactive oxygen species generation via SIRT3 dependent mechanisms. Exp Neurol 325:113144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2019.113144
Kong LH, Liu TY, Yao QS, Zhang XH, Xu WN, Qin JY (2023) Enhancing the biosynthesis of nicotinamide mononucleotide in Lactococcus lactis by heterologous expression of FtnadE. J Sci Food Agric 103(1):450–456. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.12253
Lee J, Churchil H, Choi WB, Lynch JE, Roberts FE, Volante RP, Reider PJ (1999) A chemical synthesis of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+). ChemComm 8:729–730. https://doi.org/10.1039/A809930H
Lee Y, Jeong H, Park KH, Kim KW (2020) Effects of NAD(+) in Caenorhabditis elegans models of neuronal damage. Biomolecules 10(7):993. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10070993
Lee D, Tomita Y, Miwa Y, Jeong H, Shinojima A, Ban N, Yamaguchi S, Nishioka K, Negishi K, Yoshino J, Kurihara T (2022) Nicotinamide mononucleotide protects against retinal dysfunction in a murine model of carotid artery occlusion. Int J Mol Sci 23(23):14711. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314711
Liao B, Zhao Y, Wang D, Zhang X, Hao X, Hu M (2021) Nicotinamide mononucleotide supplementation enhances aerobic capacity in amateur runners: a randomized, double-blind study. J Int Soc Sports Nutr 18(1):54. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12970-021-00442-4
Lin JB, Kubota S, Ban N, Yoshida M, Santeford A, Sene A, Nakamura R, Zapata N, Kubota M, Tsubota K, Yoshino J, Imai SI, Apte RS (2016) NAMPT-mediated NAD(+) biosynthesis is essential for vision in mice. Cell Rep 17(1):69–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2016.08.073
Lin Q, Zuo W, Liu Y, Wu K, Liu Q (2021) NAD(+) and cardiovascular diseases. Clin Chim Acta 515:104–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2021.01.012
Liu J, Zong Z, Zhang W, Chen Y, Wang X, Shen J, Yang C, Liu X, Deng H (2021) Nicotinamide mononucleotide alleviates LPS-induced inflammation and oxidative stress via decreasing COX-2 expression in macrophages. Front Mol Biosci 8:702107. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2021.702107
Liu Y, Yasawong M, Yu B (2021) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for biosynthesis of β-nicotinamide mononucleotide from nicotinamide. Microb Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-7915.13901
Long AN, Owens K, Schlappal AE, Kristian T, Fishman PS, Schuh RA (2015) Effect of nicotinamide mononucleotide on brain mitochondrial respiratory deficits in an Alzheimer’s disease-relevant murine model. BMC Neurol 15:19. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12883-015-0272-x
Lu L, Tang L, Wei W, Hong Y, Chen H, Ying W, Chen S (2014) Nicotinamide mononucleotide improves energy activity and survival rate in an in vitro model of Parkinson’s disease. Exp Ther Med 8(3):943–950. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2014.1842
Maharjan A, Singhvi M, Kim BS (2021) Biosynthesis of a therapeutically important nicotinamide mononucleotide through a phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthetase 1 and 2 engineered strain of Escherichia coli. ACS Synth Biol 10(11):3055–3065. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.1c00333
Majeed Y, Halabi N, Madani AY, Engelke R, Bhagwat AM, Abdesselem H, Agha MV, Vakayil M, Courjaret R, Goswami N, Hamidane HB, Elrayess MA, Rafii A, Graumann J, Schmidt F, Mazloum NA (2021) SIRT1 promotes lipid metabolism and mitochondrial biogenesis in adipocytes and coordinates adipogenesis by targeting key enzymatic pathways. Sci Rep 11(1):8177. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-87759-x
Marinescu GC, Popescu RG, Stoian G, Dinischiotu A (2018) beta-Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) production in Escherichia coli. Sci Rep 8(1):12278. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-30792-0
Meng YF, Pu Q, Dai SY, Ma Q, Li X, Zhu W (2021) Nicotinamide mononucleotide alleviates hyperosmolarity-induced IL-17a secretion and macrophage activation in corneal epithelial cells/macrophage co-culture system. J Inflamm Res 14:479–493. https://doi.org/10.2147/JIR.S292764
Miao Y, Cui Z, Gao Q, Rui R, Xiong B (2020) Nicotinamide mononucleotide supplementation reverses the declining quality of maternally aged oocytes. Cell Rep 32(5):107987. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2020.107987
Mikhailopulo IA, Pricota TI, Timoshchuk VA (1981) Akhrem AA (1981) Synthesis of glycosides of nicotinamide and nicotinamide mononucleotide. Synthesis 05:388–389. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-1981-29462
Mills KF, Yoshida S, Stein LR, Grozio A, Kubota S, Sasaki Y, Redpath P, Migaud ME, Apte RS, Uchida K, Yoshino J, Imai SI (2016) Long-term administration of nicotinamide mononucleotide mitigates age-associated physiological decline in mice. Cell Metab 24(6):795–806. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2016.09.013
Morris MJ, Beilharz JE, Maniam J, Reichelt AC, Westbrook RF (2015) Why is obesity such a problem in the 21st century? The intersection of palatable food, cues and reward pathways, stress, and cognition. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 58:36–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2014.12.002
Petriti B, Williams PA, Lascaratos G, Chau KY, Garway-Heath DF (2021) Neuroprotection in glaucoma: NAD(+)/NADH redox state as a potential biomarker and therapeutic target. Cells 10(6):1402. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10061402
Poddar SK, Sifat AE, Haque S, Nahid NA, Chowdhury S, Mehedi I (2019) Nicotinamide mononucleotide: exploration of diverse therapeutic applications of a potential molecule. Biomolecules 9(1):34. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9010034
Preiss J, Handler P (1957) Enzymatic synthesis of nicotinamide mononucleotide. J Biol Chem 225:759–770. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(18)64875-6
Qian X-L, Dai Y-S, Li C-X, Pan J, Xu J-H, Mu B (2022) Enzymatic synthesis of high-titer nicotinamide mononucleotide with a new nicotinamide riboside kinase and an efficient ATP regeneration system. Bioresour Bioprocess 9(1):26. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40643-022-00514-6
Rajabi M, Vafaee MS, Hosseini L, Badalzadeh R (2022) Pretreatment with nicotinamide mononucleotide increases the effect of ischaemic postconditioning on cardioprotection and mitochondrial function following ex vivo myocardial reperfusion injury in aged rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 49(4):474–482. https://doi.org/10.1111/1440-1681.13616
Ratajczak J, Joffraud M, Trammell SA, Ras R, Canela N, Boutant M, Kulkarni SS, Rodrigues M, Redpath P, Migaud ME, Auwerx J, Yanes O, Brenner C, Canto C (2016) NRK1 controls nicotinamide mononucleotide and nicotinamide riboside metabolism in mammalian cells. Nat Commun 7:13103. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms13103
Revollo JR, Korner A, Mills KF, Satoh A, Wang T, Garten A, Dasgupta B, Sasaki Y, Wolberger C, Townsend RR, Milbrandt J, Kiess W, Imai S (2007) Nampt/PBEF/Visfatin regulates insulin secretion in beta cells as a systemic NAD biosynthetic enzyme. Cell Metab 6(5):363–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2007.09.003
Ru M, Wang W, Zhai Z, Wang R, Li Y, Liang J, Kothari D, Niu K, Wu X (2022) Nicotinamide mononucleotide supplementation protects the intestinal function in aging mice and D-galactose induced senescent cells. Food Funct 13(14):7507–7519. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2fo00525e
Sanada S, Komuro I, Kitakaze M (2011) Pathophysiology of myocardial reperfusion injury: preconditioning, postconditioning, and translational aspects of protective measures. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 301(5):H1723–H1741. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00553.2011
Sauve A, Mohammed FSY (2020) Efficient synthesis of nicotinamide mononucleotide. US Patent 0216487 A1
Schondorf DC, Ivanyuk D, Baden P, Sanchez-Martinez A, De Cicco S, Yu C, Giunta I, Schwarz LK, Di Napoli G, Panagiotakopoulou V, Nestel S, Keatinge M, Pruszak J, Bandmann O, Heimrich B, Gasser T, Whitworth AJ, Deleidi M (2018) The NAD+ precursor nicotinamide riboside rescues mitochondrial defects and neuronal loss in iPSC and fly models of Parkinson’s disease. Cell Rep 23(10):2976–2988. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2018.05.009
Shang Y-T, Qin J, Gong J-S, Wang Z-K, Li H, Li H, Shi J-S, Xu Z-H (2021) High-throughput screening of a nicotinate dehydrogenase producing Pseudomonas putida mutant for efficient biosynthesis of 6-hydroxynicotinic acid. Mol Catal 509:111600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcat.2021.111600
Shen Q, Zhang SJ, Xue YZ, Peng F, Cheng DY, Xue YP, Zheng YG (2021) Biological synthesis of nicotinamide mononucleotide. Biotechnol Lett 43(12):2199–2208. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-021-03191-1
Shoji S, Yamaji T, Makino H, Ishii J, Kondo A (2020) Metabolic design for selective production of nicotinamide mononucleotide from glucose and nicotinamide. Metab Eng 65:167–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2020.11.008
Sinclair DA, Ear PH (2016) Bological production of nad precursors and analogs. US Patent 0287621 A1
Sonntag T, Ancel S, Karaz S, Cichosz P, Jacot G, Giner MP, Sanchez-Garcia JL, Pannerec A, Moco S, Sorrentino V, Canto C, Feige JN (2022) Nicotinamide riboside kinases regulate skeletal muscle fiber-type specification and are rate-limiting for metabolic adaptations during regeneration. Front Cell Dev Biol 10:1049653. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2022.1049653
Sugiyama K, Iijima K, Yoshino M, Dohra H, Tokimoto Y, Nishikawa K, Idogaki H, Yoshida N (2021) Nicotinamide mononucleotide production by fructophilic lactic acid bacteria. Sci Rep 11(1):7662. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-87361-1
Tanimori S, Ohta T, Kirihata M (2002) An efficient chemical synthesis of nicotinamide riboside (NAR) and analogues. Bioorg Med Chem 12(8):1135–1137. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-894X(02)00125-7
Tarantini S, Valcarcel-Ares MN, Toth P, Yabluchanskiy A, Tucsek Z, Kiss T, Hertelendy P, Kinter M, Ballabh P, Sule Z, Farkas E, Baur JA, Sinclair DA, Csiszar A, Ungvari Z (2019) Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) supplementation rescues cerebromicrovascular endothelial function and neurovascular coupling responses and improves cognitive function in aged mice. Redox Biol 24:101192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2019.101192
Tian Y, Zhu CL, Li P, Li HR, Liu Q, Deng XM, Wang JF (2023) Nicotinamide mononucleotide attenuates LPS-induced acute lung injury with anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidative and anti-apoptotic effects. J Surg Res 283:9–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2022.09.030
Walt DR, Findeis MA, Rios-Mercadillo VM, Auge J, Whitesides GM (2002) An efficient chemical and enzymic synthesis of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+). J A Chem Soc 106(1):234–239. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja00313a045
Wang X, Hu X, Yang Y, Takata T, Sakurai T (2016) Nicotinamide mononucleotide protects against beta-amyloid oligomer-induced cognitive impairment and neuronal death. Brain Res 1643:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2016.04.060
Wang ZK, Gong JS, Qin J, Li H, Lu ZM, Shi JS, Xu ZH (2021) Improving the intensity of integrated expression for microbial production. ACS Synth Biol 10(11):2796–2807. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.1c00334
Wu L, Sinclair DA, Meetze K (2018) Enzymatic systems and methods for synthesizing nicotinamide mononucleotide and nicotinic acid mononucleotide. US Patent 0163243 A1
Yamamoto T, Byun J, Zhai P, Ikeda Y, Oka S, Sadoshima J (2014) Nicotinamide mononucleotide, an intermediate of NAD+ synthesis, protects the heart from ischemia and reperfusion. PLoS One 9(6):e98972. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0098972
Yao Z, Yang W, Gao Z, Jia P (2017) Nicotinamide mononucleotide inhibits JNK activation to reverse Alzheimer disease. Neurosci Lett 647:133–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2017.03.027
Yi L, Maier AB, Tao R, Lin Z, Vaidya A, Pendse S, Thasma S, Andhalkar N, Avhad G, Kumbhar V (2023) The efficacy and safety of beta-nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) supplementation in healthy middle-aged adults: a randomized, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, dose-dependent clinical trial. Geroscience 45(1):29–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-022-00705-1
Yoshino J, Mills KF, Yoon MJ, Imai S (2011) Nicotinamide mononucleotide, a key NAD(+) intermediate, treats the pathophysiology of diet- and age-induced diabetes in mice. Cell Metab 14(4):528–536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2011.08.014
Yoshino M, Yoshino J, Kayser BD, Patti GJ, Franczyk MP, Mills KF, Sindelar M, Pietka T, Patterson BW, Imai S-I, Klein S (2021) Nicotinamide mononucleotide increases muscle insulin sensitivity in prediabetic women. Science 372(6547):1224–1229. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abe9985
Zhan T, Xiong H, Pang J, Zhang W, Ye Y, Liang Z, Huang X, He F, Jian B, He W, Gao Y, Min X, Zheng Y, Yang H (2021) Modulation of NAD(+) biosynthesis activates SIRT1 and resists cisplatin-induced ototoxicity. Toxicol Lett 349:115–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2021.05.013
Zhang YS, Gong JS, Yao ZY, Jiang JY, Su C, Li H, Kang CL, Liu L, Xu ZH, Shi JS (2022) Insights into the source, mechanism and biotechnological applications of hyaluronidases. Biotechnol Adv 60:108018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2022.108018
Zhang Y, Zhu W, Wang M, Xi P, Wang H, Tian D (2023) Nicotinamide mononucleotide alters body composition and ameliorates metabolic disorders induced by a high-fat diet. IUBMB Life. https://doi.org/10.1002/iub.2707
Zhou C, Feng J, Wang J, Hao N, Wang X, Chen K (2022) Design of an in vitro multienzyme cascade system for the biosynthesis of nicotinamide mononucleotide. Catal Sci Technol 12(4):1080–1091. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1cy01798e
Zong Z, Liu J, Wang N, Yang C, Wang Q, Zhang W, Chen Y, Liu X, Deng H (2021) Nicotinamide mononucleotide inhibits hepatic stellate cell activation to prevent liver fibrosis via promoting PGE2 degradation. Free Radic Biol Med 162:571–581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.11.014
Zou XD, Guo SQ, Hu ZW, Li WL (2016) NAMPT protects against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced neurotoxicity in PC12 cells through modulating SIRT1 activity. Mol Med Rep 13(5):4058–4064. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2016.5034
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Key R & D Program of China (No. 2021YFC2100900), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 32171261, 21978116), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. JUSRP22047).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JG and JS conceived of and designed the study. MG, CS, and ZX analyzed data. YL wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Gong, JS., Marshall, G. et al. Technology and functional insights into the nicotinamide mononucleotide for human health. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 107, 4759–4775 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12612-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12612-2