Abstract
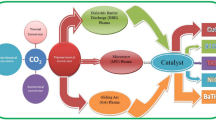
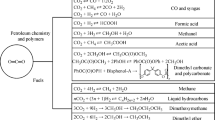
The world is facing huge environmental problems due to the increasing emission of carbon dioxide (CO2) from industries and various resources. Therefore, immediate attention is required for the utilization of CO2. Fortunately, CO2 can be converted to value-added products and fuels by various processes. Out of these processes, plasma has the highest potential, ascribed to the high bond stability of CO2. Out of the existing plasmas, non-thermal plasma is a promising area to convert CO2 to various chemical products and fuels, at temperatures as low as room temperature and pressures around/lower than atmospheric pressure. Therefore, there is an immediate need to pay attention to the recent progress of various non-thermal plasmas. The review brings both researchers’ and industries’ attention to the critical non-thermal plasmas like microwave, dielectric barrier discharge, and gliding arc discharge, with particular attention to microwave plasma. These plasmas have a high potential for producing value-added products having high market values. There is an immediate need from researchers and industries to carry out further studies in this emerging area for sustainable development with due attention to the environment.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sabat KC, Murphy AB (2017) Hydrogen plasma processing of iron ore. Metall Mater Trans B Process Metall Mater Process Sci 48:1561–1594
Sabat KC, Rajput P, Paramguru RK, Bhoi B, Mishra BK (2014) Reduction of oxide minerals by hydrogen plasma: an overview. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 34:1–23
Sabat KC, Paramguru RK, Mishra BK (2018) Formation of copper-nickel alloy from their oxide mixtures through reduction by low-temperature hydrogen plasma. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 38:621–635
Sabat KC (2019) Formation of CuCo alloy from their oxide mixtures through reduction by low-temperature hydrogen plasma. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 39:1071–1086
Sabat KC, Paramguru RK, Mishra BK (2017) Reduction of oxide mixtures of (Fe2O3 + CuO) and (Fe2O3 + Co3O4) by low-temperature hydrogen plasma. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 37:979–995
Fridman A (2008) Plasma Chem 9780521847
Fridman AA, Kennedy LA (2004) Plasma physics and engineering
Rajput P, Sabat KC, Paramguru RK, Bhoi B, Mishra BK (2014) Direct reduction of iron in low temperature hydrogen plasma. Ironmak Steelmak 41:721–731
Chen G, Godfroid T, Britun N, Georgieva V, Delplancke-Ogletree MP, Snyders R (2017) Plasma-catalytic conversion of CO2 and CO2/H2O in a surface-wave sustained microwave discharge. Appl Catal B Environ 214:114–125
Chen G, Britun N, Godfroid T, Georgieva V, Snyders R, Delplancke-Ogletree M-P (2017) An overview of CO2 conversion in a microwave discharge: the role of plasma-catalysis. J Phys D Appl Phys 50:84001
Huang Q, Zhang D, Wang D, Liu K, Kleyn AW (2017) Carbon dioxide dissociation in non-thermal radiofrequency and microwave plasma. J Phys D Appl Phys 50:294001
Mitsingas CM, Rajasegar R, Hammack S, Do H, Lee T (2016) High energy efficiency plasma conversion of CO2 at atmospheric pressure using a direct-coupled microwave plasma system. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci 44:651–656
Berthelot A, Bogaerts A (2017) Modeling of CO2 splitting in a microwave plasma: how to improve the conversion and energy efficiency. J Phys Chem C 121:8236–8251
Silva T, Britun N, Godfroid T, Snyders R (2014) Optical characterization of a microwave pulsed discharge used for dissociation of CO2. Plasma Sources Sci Technol 23
Bongers W, Bouwmeester H, Wolf B, Peeters F, Welzel S, van den Bekerom D, den Harder N, Goede A, Graswinckel M, Groen PW, Kopecki J, Leins M, van Rooij G, Schulz A, Walker M, van de Sanden R (2017) Plasma-driven dissociation of CO2 for fuel synthesis. Plasma Process Polym 14
den Harder N, van den Bekerom DCM, Al RS, Graswinckel MF, Palomares JM, Peeters FJJ, Ponduri S, Minea T, Bongers WA, van de Sanden MCM (2017) Homogeneous CO2 conversion by microwave plasma: wave propagation and diagnostics. Plasma Process Polym 14:1600120
van den Bekerom DCM, Linares JMP, Verreycken T, Van Veldhuizen EM, Nijdam S, Berden G, Bongers WA, Van De Sanden MCM, van Rooij GJ (2019) The importance of thermal dissociation in CO2 microwave discharges investigated by power pulsing and rotational Raman scattering. Plasma Sources Sci Technol 28:55015
Zhang J-Q, Yang Y-J, Zhang J-S, Liu Q (2002) Study on the conversion of CH4 and CO2 using a pulsed microwave plasma under atmospheric pressure. ACTA Chim Sin Ed 60:1973–1980
Ihara T, Kiboku M, Iriyama Y (1994) Plasma reduction of CO2 with H2O for the formation of organic compounds. Bull Chem Soc Jpn 67:312–314
Ihara T, Ouro T, Ochiai T, Kiboku M, Iriyama Y (1996) Formation of methanol by microwave-plasma reduction of CO2 with H2O. Bull Chem Soc Jpn 69:241–244
Chen G, Silva T, Georgieva V, Godfroid T, Britun N, Snyders R, Delplancke-Ogletree MP (2015) Simultaneous dissociation of CO2 and H2O to syngas in a surface-wave microwave discharge. Int J Hydrogen Energy 40:3789–3796
Hayashi N, Yamakawa T, Baba S (2006) Effect of additive gases on synthesis of organic compounds from carbon dioxide using non-thermal plasma produced by atmospheric surface discharges. Vacuum 80:1299–1304
de la Fuente JF, Moreno SH, Stankiewicz AI, Stefanidis GD (2016) A new methodology for the reduction of vibrational kinetics in non-equilibrium microwave plasma: application to CO2 dissociation. React Chem Eng 1:540–554
Sun SR, Wang HX, Mei DH, Tu X, Bogaerts A (2017) CO2 conversion in a gliding arc plasma: performance improvement based on chemical reaction modeling. J CO2 Util 17:220–34
Devid E, Zhang D, Wang D, Ronda-Lloret M, Huang Q, Rothenberg G, Shiju NR, Kleyn AW (2020) Dry reforming of methane under mild conditions using radio frequency Plasma. Energy Technol 8
Snoeckx R, Ozkan A, Reniers F, Bogaerts A (2017) The quest for value-added products from carbon dioxide and water in a dielectric barrier discharge: a chemical kinetics study. Chemsuschem 10:409–424
Snoeckx R, Bogaerts A (2017) Plasma technology-a novel solution for CO2 conversion? Chem Soc Rev 46:5805–5863
De Bie C, Van Dijk J, Bogaerts A (2016) CO2 hydrogenation in a dielectric barrier discharge plasma revealed. J Phys Chem C 120:25210–25224
Chen G, Britun N, Godfroid T, Georgieva V, Snyders R, Delplancke-Ogletree MP (2017) An overview of CO2 conversion in a microwave discharge: the role of plasma-catalysis. J Phys D Appl Phys 50:084001
Li L, Zhang H, Li X, Kong X, Xu R, Tay K, Tu X (2019) Plasma-assisted CO2 conversion in a gliding arc discharge: Improving performance by optimizing the reactor design. J CO2 Util 29:296–303
Li L, Zhang H, Li X, Huang J, Kong X, Xu R, Tu X (2020) Magnetically enhanced gliding arc discharge for CO2 activation. J CO2 Util 35:28–37
Tu X, Whitehead JC (2014) Plasma dry reforming of methane in an atmospheric pressure AC gliding arc discharge: Co-generation of syngas and carbon nanomaterials. Int J Hydrogen Energy 39:9658–9669
Mei D, Zhu X, He Y-L, Yan JD, Tu X (2014) Plasma-assisted conversion of CO2 in a dielectric barrier discharge reactor: understanding the effect of packing materials. Plasma Sources Sci Technol 24:15011
Indarto A, Choi JW, Lee H, Song HK (2006) Effect of additive gases on methane conversion using gliding arc discharge. Energy 31:2986–2995
Nunnally T, Gutsol K, Rabinovich A, Fridman A, Gutsol A, Kemoun A (2011) Dissociation of CO2 in a low current gliding arc plasmatron. J Phys D Appl Phys 44(27):274009
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Sabat, K.C., Singh, A., Das, S. (2022). Plasma Processing of Carbon Dioxide. In: Verma, P., Samuel, O.D., Verma, T.N., Dwivedi, G. (eds) Advancement in Materials, Manufacturing and Energy Engineering, Vol. I. Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-5371-1_41
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-5371-1_41
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-16-5370-4
Online ISBN: 978-981-16-5371-1
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)