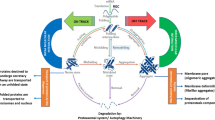
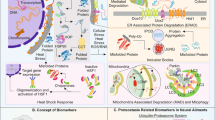
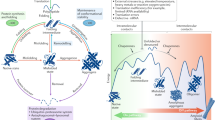
Abstract
Proteostasis refers to the dynamic regulation of protein homeostasis which is mediated by a network of molecular machines responsible for both protein synthesis and degradation. With age and various diseases, proteostasis can be disrupted, leading to the formation of intracellular protein aggregates (Labbadia and Morimoto 2015). Under normal conditions, aggregated proteins are broken down through the ubiquitin-proteasomal system or through activation of the autophagy pathway. In pathological conditions however, these protein degradation pathways can be dysregulated. Protein misfolding is a hallmark of many neurodegenerative disorders and is associated with numerous disease processes in autophagy (Watanabe et al. 2020; Limanaqi et al. 2020).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akomolafe A, Beiser A, Meigs JB, Au R, Green RC, Farrer LA, Wolf PA, Seshadri S (2006) Diabetes mellitus and risk of developing Alzheimer disease: results from the Framingham study. Arch Neurol 63:1551–1555
Alavi Naini SM, Soussi-Yanicostas N (2015) Tau hyperphosphorylation and oxidative stress, a critical vicious circle in neurodegenerative tauopathies? Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2015:151979. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/151979
Alegre-Abarrategui J, Christian H, Lufino MMP, Mutihac R, Venda LL, Ansorge O, Wade-Martins R (2009) LRRK2 regulates autophagic activity and localizes to specific membrane microdomains in a novel human genomic reporter cellular model. Hum Mol Genet 18:4022–4034
Alvarez-Erviti L, Rodriguez-Oroz MC, Cooper JM, Caballero C, Ferrer I, Obeso JA, Schapira AHV (2010) Chaperone-mediated autophagy markers in Parkinson disease brains. Arch Neurol 67:1464–1472
Armstrong RA (2019) Risk factors for Alzheimer’s disease. Folia Neuropathol 57:87–105
Arvanitakis Z, Wilson RS, Bienias JL, Evans DA, Bennett DA (2004) Diabetes mellitus and risk of alzheimer disease and decline in cognitive function. Arch Neurol 61(5):661–666
Arvanitakis Z, Schneider JA, Wilson RS, Bienias JL, Kelly JF, Evans DA, Bennett DA (2008) Statins, incident Alzheimer disease, change in cognitive function, and neuropathology. Neurology 70:1795–1802
Bang Y, Kim KS, Seol W, Choi HJ (2016) LRRK2 interferes with aggresome formation for autophagic clearance. Mol Cell Neurosci 75:71–80
Bateman GA, Levi CR, Schofield P, Wang Y, Lovett EC (2006) Quantitative measurement of cerebral haemodynamics in early vascular dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. J Clin Neurosci 13:563–568
Beal MF (2002) Oxidatively modified proteins in aging and disease. Free Radic Biol Med 32:797–803
Begg DP (2015) Insulin transport into the brain and cerebrospinal fluid. In: Vitamins and hormones. Academic, New York, pp 229–248
Belinson H, Lev D, Masliah E, Michaelson DM (2008) Activation of the amyloid cascade in apolipoprotein E4 transgenic mice induces lysosomal activation and neurodegeneration resulting in marked cognitive deficits. J Neurosci 28:4690–4701
Belvisi D, Pellicciari R, Fabbrini G, Tinazzi M, Berardelli A, Defazio G (2020) Modifiable risk and protective factors in disease development, progression and clinical subtypes of Parkinson’s disease: what do prospective studies suggest? Neurobiol Dis 134:104671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2019.104671
Bender A, Krishnan KJ, Morris CM et al (2006) High levels of mitochondrial DNA deletions in substantia nigra neurons in aging and Parkinson disease. Nat Genet 38:515–517
Beyer K, Lao JI, Latorre P, Ariza A (2005) Age at onset: an essential variable for the definition of genetic risk factors for sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1057:260–278
Boland B, Kumar A, Lee S, Platt FM, Wegiel J, Yu WH, Nixon RA (2008) Autophagy induction and autophagosome clearance in neurons: relationship to autophagic pathology in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci 28:6926–6937
Bondolfi L, Ermini F, Long JM, Ingram DK, Jucker M (2004) Impact of age and caloric restriction on neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of C57BL/6 mice. Neurobiol Aging 25:333–340
Bonello F, Hassoun SM, Mouton-Liger F et al (2019) LRRK2 impairs PINK1/Parkin-dependent mitophagy via its kinase activity: pathologic insights into Parkinson’s disease. Hum Mol Genet 28:1645–1660
Boulos C, Yaghi N, El HR, Heraoui GNHA, Fakhoury-Sayegh N (2019) Nutritional risk factors, microbiota and parkinson’s disease: what is the current evidence? Nutrients 11(8):1896. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081896
Bové J, Martínez-Vicente M, Vila M (2011) Fighting neurodegeneration with rapamycin: mechanistic insights. Nat Rev Neurosci 12:437–452
Bravo-San Pedro JM, Niso-Santano M, Gómez-Sánchez R et al (2013) The LRRK2 G2019S mutant exacerbates basal autophagy through activation of the MEK/ERK pathway. Cell Mol Life Sci 70:121–136
Burillo J, Marqués P, Jiménez B, González-Blanco C, Benito M, Guillén C (2021) Insulin resistance and diabetes mellitus in Alzheimer’s disease. Cell 10:1–42
Busche MA, Hyman BT (2020) Synergy between amyloid-β and tau in Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Neurosci 23:1183–1193
Butterfield DA, Kanski J (2001) Brain protein oxidation in age-related neurodegenerative disorders that are associated with aggregated proteins. Mech Ageing Dev 122:945–962
Butterfield DA, Swomley AM, Sultana R (2013) Amyloid β-peptide (1-42)-induced oxidative stress in Alzheimer disease: importance in disease pathogenesis and progression. Antioxidants Redox Signal 19:823–835
Caccamo A, De Pinto V, Messina A, Branca C, Oddo S (2014) Genetic reduction of mammalian target of rapamycin ameliorates Alzheimer’s disease-like cognitive and pathological deficits by restoring hippocampal gene expression signature. J Neurosci 34:7988–7998
Candeias E, Duarte AI, Sebastião I et al (2017) Middle-aged diabetic females and males present distinct susceptibility to Alzheimer disease-like pathology. Mol Neurobiol 54:6471–6489
Cerri S, Blandini F (2019) Role of autophagy in Parkinson’s disease. Curr Med Chem 26:3702–3718
Cha MY, Kim DK, Mook-Jung I (2015) The role of mitochondrial DNA mutation on neurodegenerative diseases. Exp Mol Med 47:e150
Chandra S, Jana M, Pahan K (2018) Aspirin induces lysosomal biogenesis and attenuates amyloid plaque pathology in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease via PPARα. J Neurosci 38:6682–6699
Chaudhuri TK, Paul S (2006) Protein-misfolding diseases and chaperone-based therapeutic approaches. FEBS J 273:1331–1349
Chen Z, Zhong C (2014) Oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Bull 30:271–281
Cho MH, Cho K, Kang HJ, Jeon EY, Kim HS, Kwon HJ, Kim HM, Kim DH, Yoon SY (2014) Autophagy in microglia degrades extracellular β-amyloid fibrils and regulates the NLRP3 inflammasome. Autophagy 10:1761–1775
Chong CM, Ke M, Tan Y, Huang Z, Zhang K, Ai N, Ge W, Qin D, Lu JH, Su H (2018) Presenilin 1 deficiency suppresses autophagy in human neural stem cells through reducing γ-secretase-independent ERK/CREB signaling. Cell Death Dis 9(9):879. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-0945-7
Choubey V, Safiulina D, Vaarmann A, Cagalinec M, Wareski P, Kuum M, Zharkovsky A, Kaasik A (2011) Mutant A53T α-Synuclein induces neuronal death by increasing mitochondrial autophagy. J Biol Chem 286:10814–10824
Congdon EE, Wu JW, Myeku N, Figueroa YH, Herman M, Marinec PS, Gestwicki JE, Dickey CA, Yu WH, Duff KE (2012) Methylthioninium chloride (methylene blue) induces autophagy and attenuates tauopathy in vitro and in vivo. Autophagy 8:609–622
Cordero JG, García-Escudero R, Avila J, Gargini R, García-Escudero V (2018) Benefit of oleuropein aglycone for Alzheimer’s disease by promoting autophagy. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2018:5010741. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/5010741
Corti O, Lesage S, Brice A (2011) What genetics tells us about the causes and mechanisms of Parkinson’s disease. Physiol Rev 91:1161–1218
Costa LG, Garrick JM, Roquè PJ, Pellacani C (2016) Mechanisms of neuroprotection by quercetin: counteracting oxidative stress and more. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2016:2986796. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/2986796
Cuervo AM, Stafanis L, Fredenburg R, Lansbury PT, Sulzer D (2004) Impaired degradation of mutant α-synuclein by chaperone-mediated autophagy. Science 805:1292–1295
De Mello NP, Orellana AM, Mazucanti CH, De Morais LG, Scavone C, Kawamoto EM (2019) Insulin and autophagy in neurodegeneration. Front Neurosci 13:1–17
Dehay B, Bové J, Rodríguez-Muela N, Perier C, Recasens A, Boya P, Vila M (2010) Pathogenic lysosomal depletion in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurosci 30:12535–12544
Deng H, Mi M-T (2016) Resveratrol attenuates Aβ 25–35 caused neurotoxicity by inducing autophagy through the TyrRS-PARP1-SIRT1 signaling pathway. Neurochem Res 41:2367–2379
Di Giovanni G (2009) A diet for dopaminergic neurons? In: Birth, life death dopaminergic neurons substantia nigra. Springer, Vienna, pp 317–331
Di Meco A, Curtis ME, Lauretti E, Praticò D (2020) Autophagy dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease: mechanistic insights and new therapeutic opportunities. Biol Psychiatry 87:797–807
Dickson DW, Braak H, Duda JE et al (2009) Neuropathological assessment of Parkinson’s disease: refining the diagnostic criteria. Lancet Neurol 8:1150–1157
Diedrich M, Kitada T, Nebrich G, Koppelstaetter A, Shen J, Zabel C, Klose J, Mao L (2011) Brain region specific mitophagy capacity could contribute to selective neuronal vulnerability in Parkinson’s disease. Proteome Sci 9:59
Dionísio PA, Amaral JD, Rodrigues CMP (2021) Oxidative stress and regulated cell death in Parkinson’s disease. Ageing Res Rev 67:101263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2021.101263
Dorval V, Fraser PE (2006) Small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) modification of natively unfolded proteins tau and α-synuclein. J Biol Chem 281:9919–9924
Du J, Liang Y, Xu F, Sun B, Wang Z (2013) Trehalose rescues Alzheimer’s disease phenotypes in APP/PS1 transgenic mice. J Pharm Pharmacol 65:1753–1756
Ellis CE, Schwartzberg PL, Grider TL, Fink DW, Nussbaum RL (2001) α-Synuclein is phosphorylated by members of the Src family of protein-tyrosine kinases. J Biol Chem 276:3879–3884
Eshraghi M, Adlimoghaddam A, Mahmoodzadeh A, Sharifzad F, Yasavoli-sharahi H, Lorzadeh S, Albensi BC, Ghavami S (2021) Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis: role of autophagy and mitophagy focusing in microglia. Int J Mol Sci 22:1–36
Esposito E, Rotilio D, Di Matteo V, Di Giulio C, Cacchio M, Algeri S (2002) A review of specific dietary antioxidants and the effects on biochemical mechanisms related to neurodegenerative processes. Neurobiol Aging 23:719–735
Fernández-Sanz P, Ruiz-Gabarre D, García-Escudero V (2019) Modulating effect of diet on Alzheimer’s disease. Diseases 7:12
Ferretta A, Gaballo A, Tanzarella P et al (2014) Effect of resveratrol on mitochondrial function: implications in parkin-associated familiar Parkinson’s disease. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol basis Dis 1842:902–915
Galasko DR, Peskind E, Clark CM et al (2012) Antioxidants for Alzheimer disease a randomized clinical trial with cerebrospinal fluid biomarker measures. Trial Regist Clin Identifier NCT00117403. Arch Neurol 69:836–841
Gautier CA, Kitada T, Shen J (2008) Loss of PINK1 causes mitochondrial functional defects and increased sensitivity to oxidative stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:11364–11369
Geisler S, Holmström KM, Skujat D, Fiesel FC, Rothfuss OC, Kahle PJ, Springer W (2010) PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy is dependent on VDAC1 and p62/SQSTM1. Nat Cell Biol 12:119–131
Ghadernezhad N, Khalaj L, Pazoki-Toroudi H, Mirmasoumi M, Ashabi G (2016) Metformin pretreatment enhanced learning and memory in cerebral forebrain ischaemia: the role of the AMPK/BDNF/P70SK signalling pathway. Pharm Biol 54:2211–2219
Giasson BI, Duda JE, Murray IVJ, Chen Q, Souza JM, Hurtig HI, Ischiropoulos H, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VMY (2000) Oxidative damage linked to neurodegeneration by selective α-synuclein nitration in synucleinopathy lesions. Science 290:985–989
Grote CW, Wright DE (2016) A role for insulin in diabetic neuropathy. Front Neurosci 10:581
Guo YJ, Dong SY, Cui XX, Feng Y, Liu T, Yin M, Kuo SH, Tan EK, Zhao WJ, Wu YC (2016) Resveratrol alleviates MPTP-induced motor impairments and pathological changes by autophagic degradation of α-synuclein via SIRT1-deacetylated LC3. Mol Nutr Food Res 60:2161–2175
Hara T, Nakamura K, Matsui M et al (2006) Suppression of basal autophagy in neural cells causes neurodegenerative disease in mice. Nature 441:885–889
Hayashi T, Ishimori C, Takahashi-Niki K, Taira T, Kim Y-c, Maita H, Maita C, Ariga H, Iguchi-Ariga SMM (2009) DJ-1 binds to mitochondrial complex I and maintains its activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 390:667–672
Heckmann BL, Teubner BJW, Tummers B, Guy CS, Zakharenko SS, Green DR (2019) LC3-associated endocytosis facilitates β-amyloid clearance and mitigates neurodegeneration in murine Alzheimer’s disease. Cell 178:536–551
Hochrainer K, Jackman K, Anrather J, Iadecola C (2012) Reperfusion rather than ischemia drives the formation of ubiquitin aggregates after middle cerebral artery occlusion. Stroke 43:2229–2235
Horton AC, Ehlers MD (2003) Neuronal polarity and trafficking. Neuron 40:277–295
Houtman J, Freitag K, Gimber N, Schmoranzer J, Heppner FL, Jendrach M (2019) Beclin1-driven autophagy modulates the inflammatory response of microglia via NLRP 3. EMBO J 38(4):e99430. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.201899430
Hsieh CH, Shaltouki A, Gonzalez AE, Bettencourt da Cruz A, Burbulla LF, St Lawrence E, Schüle B, Krainc D, Palmer TD, Wang X (2016) Functional impairment in miro degradation and mitophagy is a shared feature in familial and sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Cell Stem Cell 19:709–724
Hsu LJ, Sagara Y, Arroyo A, Rockenstein E, Sisk A, Mallory M, Wong J, Takenouchi T, Hashimoto M, Masliah E (2000) alpha-synuclein promotes mitochondrial deficit and oxidative stress. Am J Pathol 157:401–410
Hu BR, Martone ME, Jones YZ, Liu CL (2000) Protein aggregation after transient cerebral ischemia. J Neurosci 20:3191–3199
Huang Y, Mahley RW (2014) Apolipoprotein E: structure and function in lipid metabolism, neurobiology, and Alzheimer’s diseases. Neurobiol Dis 72:3–12
Ishihara L, Brayne C (2005) A systematic review of nutritional risk factors of Parkinson’s disease. Nutr Res Rev 18:259–282
Ji ZS, Müllendorff K, Cheng IH, Miranda RD, Huang Y, Mahley RW (2006) Reactivity of apolipoprotein E4 and amyloid β peptide: lysosomal stability and neurodegeneration. J Biol Chem 281:2683–2692
Junn E, Jang WH, Zhao X, Jeong BS, Mouradian MM (2009) Mitochondrial localization of DJ-1 leads to enhanced neuroprotection. J Neurosci Res 87:123–129
Kahl A, Blanco I, Jackman K, Baskar J, Milaganur Mohan H, Rodney-Sandy R, Zhang S, Iadecola C, Hochrainer K (2018) Cerebral ischemia induces the aggregation of proteins linked to neurodegenerative diseases. Sci Rep 8(1):2701. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-21063-z
Kalia LV, Lang AE (2015) Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 386:896–912
Kang L, Moriarty GM, Woods LA, Ashcroft AE, Radford SE, Baum J (2012) N-terminal acetylation of α-synuclein induces increased transient helical propensity and decreased aggregation rates in the intrinsically disordered monomer. Protein Sci 21:911–917
Karuppagounder SS, Xu H, Shi Q, Chen LH, Pedrini S, Pechman D, Baker H, Beal MF, Gandy SE, Gibson GE (2009) Thiamine deficiency induces oxidative stress and exacerbates the plaque pathology in Alzheimer’s mouse model. Neurobiol Aging 30:1587–1600
Katila N, Bhurtel S, Shadfar S, Srivastav S, Neupane S, Ojha U, Jeong GS, Choi DY (2017) Metformin lowers α-synuclein phosphorylation and upregulates neurotrophic factor in the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Neuropharmacology 125:396–407
Kim J, Basak JM, Holtzman DM (2009) The role of apolipoprotein E in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron 63:287–303
Kim YM, Jang WH, Quezado MM, Oh Y, Chung KC, Junn E, Mouradian MM (2011) Proteasome inhibition induces α-synuclein SUMOylation and aggregate formation. J Neurol Sci 307:157–161
Kim J, Yoon H, Basak J, Kim J (2014) Apolipoprotein E in synaptic plasticity and Alzheimer’s disease: potential cellular and molecular mechanisms. Mol Cells 37:833–840
Kloske CM, Wilcock DM (2020) The important Interface between apolipoprotein E and Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Front Immunol 11:754. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.00754
Komatsu M, Waguri S, Chiba T et al (2006) Loss of autophagy in the central nervous system causes neurodegeneration in mice. Nature 441:880–884
Kondapalli C, Kazlauskaite A, Zhang N et al (2012) PINK1 is activated by mitochondrial membrane potential depolarization and stimulates Parkin E3 ligase activity by phosphorylating serine 65. Open Biol 2:120080
Korecka JA, Thomas R, Christensen DP, Hinrich AJ, Ferrari EJ, Levy SA, Hastings ML, Hallett PJ, Isacson O (2019) Mitochondrial clearance and maturation of autophagosomes are compromised in LRRK2 G2019S familial Parkinson’s disease patient fibroblasts. Hum Mol Genet 28:3232–3243
Krumova P, Meulmeester E, Garrido M et al (2011) Sumoylation inhibits α-synuclein aggregation and toxicity. J Cell Biol 194:49–60
Labbadia J, Morimoto RI (2015) The biology of proteostasis in aging and disease. Annu Rev Biochem 84:435–464
Lahiri DK, Sambamurti K, Bennett DA (2004) Apolipoprotein gene and its interaction with the environmentally driven risk factors: molecular, genetic and epidemiological studies of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 25:651–660
Lansbury PT, Brice A (2002) Genetics of Parkinson’s disease and biochemical studies of implicated gene products: commentary. Curr Opin Cell Biol 14:653–660
Lapchak PA, Araujo DM (2001) Preclinical development of neurosteroids as neuroprotective agents for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Int Rev Neurobiol 46:379–397
Lee JY, Nagano Y, Taylor JP, Lim KL, Yao TP (2010) Disease-causing mutations in Parkin impair mitochondrial ubiquitination, aggregation, and HDAC6-dependent mitophagy. J Cell Biol 189:671–679
Lewitt PA (2015) Levodopa therapy for Parkinson’s disease: pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Mov Disord 30:64–72
Li Q, Liu Y, Sun M (2017) Autophagy and Alzheimer’s disease. Cell Mol Neurobiol 37:377–388
Li HH, Lin CL, Huang CN (2018) Neuroprotective effects of statins against amyloid β-induced neurotoxicity. Neural Regen Res 13:198–206
Liao F, Yoon H, Kim J (2017) Apolipoprotein E metabolism and functions in brain and its role in Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Opin Lipidol 28:60–67
Limanaqi F, Biagioni F, Gambardella S, Familiari P, Frati A, Fornai F (2020) Promiscuous roles of autophagy and proteasome in neurodegenerative proteinopathies. Int J Mol Sci 21(8):3028. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21083028
Liu J, Li L (2019) Targeting autophagy for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease: challenges and opportunities. Front Mol Neurosci 12:1–9
Liu K, Shi N, Sun Y, Zhang T, Sun X (2013) Therapeutic effects of rapamycin on MPTP-induced parkinsonism in mice. Neurochem Res 38:201–207
Liu Z, Li T, Li P, Wei N, Zhao Z, Liang H, Ji X, Chen W, Xue M, Wei J (2015) The ambiguous relationship of oxidative stress, tau hyperphosphorylation, and autophagy dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2015:352723. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/352723
Liu R, Yang J, Liu L, Lu Z, Shi Z, Ji W, Shen J, Zhang X (2020) An “amyloid-β cleaner” for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease by normalizing microglial dysfunction. Adv Sci 7(2):1901555. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.201901555
Long JM, Holtzman DM (2019) Alzheimer disease: an update on pathobiology and treatment strategies. Cell 179:312–339
Lovell MA, Ehmann WD, Butler SM, Markesbery WR (1995) Elevated thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances and antioxidant enzyme activity in the brain in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 45:1594–1601
Lu M, Su C, Qiao C, Bian Y, Ding J, Hu G (2016) Metformin prevents dopaminergic neuron death in MPTP/P-induced mouse model of Parkinson’s disease via autophagy and mitochondrial ROS clearance. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 19:1–11
Lucin KM, O’Brien CE, Bieri G et al (2013) Microglial beclin 1 regulates retromer trafficking and phagocytosis and is impaired in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron 79:873–886
MacKnight C, Rockwood K, Awalt E, McDowell I (2002) Diabetes mellitus and the risk of dementia, Alzheimer’s disease and vascular cognitive impairment in the Canadian study of health and aging. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 14:77–83
Manzoni C, Mamais A, Dihanich S et al (2013) Pathogenic Parkinson’s disease mutations across the functional domains of LRRK2 alter the autophagic/lysosomal response to starvation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 441:862–866
Marcus DL, Thomas C, Rodriguez C, Simberkoff K, Tsai JS, Strafaci JA, Freedman ML (1998) Increased peroxidation and reduced antioxidant enzyme activity in Alzheimer’s disease. Exp Neurol 150:40–44
Margolis RU, Altszuler N (1967) Insulin in the cerebrospinal fluid. Nature 215:1375–1376
Marotta NP, Cherwien CA, Abeywardana T, Pratt MR (2012) O-GlcNAc modification prevents peptide-dependent acceleration of α-synuclein aggregation. Chembiochem 13:2665–2670
Martin B, Pearson M, Kebejian L et al (2007) Sex-dependent metabolic, neuroendocrine, and cognitive responses to dietary energy restriction and excess. Endocrinology 148:4318–4333
Martinat C, Shendelman S, Jonason A, Leete T, Beal MF, Yang L, Floss T, Abeliovich A (2004) Sensitivity to oxidative stress in DJ-1-deficient dopamine neurons: an ES-derived cell model of primary parkinsonism. PLoS Biol 2:e327
Martinez-Vicente M (2017) Neuronal mitophagy in neurodegenerative diseases. Front Mol Neurosci 10:64. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2017.00064
Masters CL, Bateman R, Blennow K, Rowe CC, Sperling RA, Cummings JL (2015) Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Rev Dis Prim 1:1–18
Mazucanti CH, Liu QR, Lang D, Huang N, O’Connell JF, Camandola S, Egan JM (2019) Release of insulin produced by the choroids plexus is regulated by serotonergic signaling. JCI Insight 4(23):e131682. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.131682
McNeill A, Magalhaes J, Shen C et al (2014) Ambroxol improves lysosomal biochemistry in glucocerebrosidase mutation-linked Parkinson disease cells. Brain 137:1481–1495
Meng F, Yao D, Shi Y et al (2011) Oxidation of the cysteine-rich regions of parkin perturbs its E3 ligase activity and contributes to protein aggregation. Mol Neurodegener 6:34
Mezey E, Dehejia AM, Harta G, Suchy SF, Nussbaum RL, Brownstein MJ, Polymeropoulos MH (1998) Alpha synuclein is present in Lewy bodies in sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Mol Psychiatry 3:493–499
Mizushima N (2005) Aβ generation in autophagic vacuoles. J Cell Biol 171:15–17
Mizushima N, Komatsu M (2011) Autophagy: renovation of cells and tissues. Cell 147:728–741
Münch G, Lüth HJ, Wong A, Arendt T, Hirsch E, Ravid R, Riederer P (2000) Crosslinking of α-synuclein by advanced glycation endproducts—an early pathophysiological step in Lewy body formation? J Chem Neuroanat 20:253–257
Narendra D, Tanaka A, Suen DF, Youle RJ (2008) Parkin is recruited selectively to impaired mitochondria and promotes their autophagy. J Cell Biol 183:795–803
Nguyen HN, Byers B, Cord B et al (2011) LRRK2 mutant iPSC-derived da neurons demonstrate increased susceptibility to oxidative stress. Cell Stem Cell 8:267–280
Nixon RA, Wegiel J, Kumar A, Yu WH, Peterhoff C, Cataldo A, Cuervo AM (2005) Extensive involvement of autophagy in Alzheimer disease: an immuno-electron microscopy study. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 64:113–122
Norris EH, Giasson BI, Ischiropoulos H, Lee VMY (2003) Effects of oxidative and nitrative challenges on α-synuclein fibrillogenesis involve distinct mechanisms of protein modifications. J Biol Chem 278:27230–27240
Ntsapi C, du Toit A, Loos B (2019) Dietary impact on neuronal autophagy control and brain health. In: Feed your mind—how does nutrition modulate brain function throughout life? IntechOpen, London. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.85228
Numajiri N, Takasawa K, Nishiya T et al (2011) On-off system for PI3-kinase-Akt signaling through S-nitrosylation of phosphatase with sequence homology to tensin (PTEN). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:10349–10354
Okochi M, Walter J, Koyama A, Nakajo S, Baba M, Iwatsubo T, Meijer L, Kahle PJ, Haass C (2000) Constitutive phosphorylation of the Parkinson’s disease associated α-synuclein. J Biol Chem 275:390–397
Pani G (2015) Neuroprotective effects of dietary restriction: evidence and mechanisms. Semin Cell Dev Biol 40:106–114
Patel NV, Gordon MN, Connor KE, Good RA, Engelman RW, Mason J, Morgan DG, Morgan TE, Finch CE (2005) Caloric restriction attenuates Aβ-deposition in Alzheimer transgenic models. Neurobiol Aging 26:995–1000
Patil SP, Jain PD, Ghumatkar PJ, Tambe R, Sathaye S (2014) Neuroprotective effect of metformin in MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease in mice. Neuroscience 277:747–754
Perez-Pardo P, Dodiya HB, Engen PA et al (2019) Role of TLR4 in the gut-brain axis in Parkinson’s disease: a translational study from men to mice. Gut 68(5):829–843. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2018-316844
Peric A, Annaert W (2015) Early etiology of Alzheimer’s disease: tipping the balance toward autophagy or endosomal dysfunction? Acta Neuropathol 129:363–381
Pericak-Vance MA, Haines JL (1995) Genetic susceptibility to Alzheimer disease. Trends Genet 11:504–508
Pietrocola F, Lachkar S, Enot DP et al (2015) Spermidine induces autophagy by inhibiting the acetyltransferase EP300. Cell Death Differ 22:509–516
Pietrocola F, Castoldi F, Markaki M et al (2018) Aspirin recapitulates features of caloric restriction. Cell Rep 22:2395–2407
Plowey ED, Cherra SJ, Liu YJ, Chu CT (2008) Role of autophagy in G2019S-LRRK2-associated neurite shortening in differentiated SH-SY5Y cells. J Neurochem 105:1048–1056
Pocernich CB, Butterfield DA (2012) Elevation of glutathione as a therapeutic strategy in Alzheimer disease. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 1822:625–630
Polymeropoulos MH, Lavedan C, Leroy E et al (1997) Mutation in the α-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson’s disease. Science 276:2045–2047
Potter H, Wisniewski T (2012) Apolipoprotein E: essential catalyst of the Alzheimer amyloid cascade. Int J Alzheimers Dis 2012:489428. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/489428
Puig KL, Kulas JA, Franklin W, Rakoczy SG, Taglialatela G, Brown-Borg HM, Combs CK (2016) The Ames dwarf mutation attenuates Alzheimer’s disease phenotype of APP/PS1 mice. Neurobiol Aging 40:22–40
Puschmann A, Fiesel FC, Caulfield TR et al (2017) Heterozygous PINK1 p.G411S increases risk of Parkinson’s disease via a dominant-negative mechanism. Brain 140:98–117
Quinn PMJ, Moreira PI, Ambrósio AF, Alves CH (2020) PINK1/PARKIN signalling in neurodegeneration and neuroinflammation. Acta Neuropathol Commun 8:189
Recio MC, Andujar I, Rios JL (2012) Anti-inflammatory agents from plants: progress and potential. Curr Med Chem 19:2088–2103
Reddy PH, Manczak M, Yin X et al (2018) Protective effects of Indian spice curcumin against amyloid-ß in Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 61:843–866
Richter F, Fleming SM, Watson M et al (2014) A GCase chaperone improves motor function in a mouse model of synucleinopathy. Neurotherapeutics 11:840–856
Rocchi A, Yamamoto S, Ting T et al (2017) A Becn1 mutation mediates hyperactive autophagic sequestration of amyloid oligomers and improved cognition in Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS Genet 13(8):e1006962. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1006962
Rochet JC, Conway KA, Lansbury PT (2000) Inhibition of fibrillization and accumulation of prefibrillar oligomers in mixtures of human and mouse α-synuclein. Biochemistry 39:10619–10626
Rosenberg RN, Lambracht-Washington D, Yu G, Xia W (2016) Genomics of Alzheimer disease: a review. JAMA Neurol 73:867–874
Sabogal-Guáqueta AM, Muñoz-Manco JI, Ramírez-Pineda JR, Lamprea-Rodriguez M, Osorio E, Cardona-Gómez GP (2015) The flavonoid quercetin ameliorates Alzheimer’s disease pathology and protects cognitive and emotional function in aged triple transgenic Alzheimer’s disease model mice. Neuropharmacology 93:134–145
Sánchez-Danés A, Richaud-Patin Y, Carballo-Carbajal I et al (2012) Disease-specific phenotypes in dopamine neurons from human iPS-based models of genetic and sporadic Parkinson’s disease. EMBO Mol Med 4:380–395
Sandusky-Beltran LA, Kovalenko A, Ma C et al (2019) Spermidine/spermine-N 1-acetyltransferase ablation impacts tauopathy-induced polyamine stress response. Alzheimers Res Ther 11(1):58. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13195-019-0507-y
Schafer MJ, Alldred MJ, Lee SH, Calhoun ME, Petkova E, Mathews PM, Ginsberg SD (2015) Reduction of β-amyloid and γ-secretase by calorie restriction in female Tg2576 mice. Neurobiol Aging 36:1293–1302
Scheltens P, De Strooper B, Kivipelto M, Holstege H, Chételat G, Teunissen CE, Cummings J, van der Flier WM (2021) Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 397:1577–1590
Schwartz MW, Bergman RN, Kahn SE, Taborsky GJ, Fisher LD, Sipols AJ, Woods SC, Steil GM, Porte D (1991) Evidence for entry of plasma insulin into cerebrospinal fluid through an intermediate compartment in dogs. Quantitative aspects and implications for transport. J Clin Invest 88:1272–1281
Shakeri A, Cicero AFG, Panahi Y, Mohajeri M, Sahebkar A (2019) Curcumin: a naturally occurring autophagy modulator. J Cell Physiol 234:5643–5654
Shibuya Y, Chang CCY, Huang LH, Bryleva EY, Chang TY (2014) Inhibiting ACAT1/SOAT1 in microglia stimulates autophagy-mediated lysosomal proteolysis and increases Aβ1-42 clearance. J Neurosci 34:14484–14501
Shinohara M, Sato N, Shimamura M, Kurinami H, Hamasaki T, Chatterjee A, Rakugi H, Morishita R (2014) Possible modification of Alzheimer’s disease by statins in midlife: interactions with genetic and non-genetic risk factors. Front Aging Neurosci 6:71. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2014.00071
Simonovitch S, Schmukler E, Bespalko A, Iram T, Frenkel D, Holtzman DM, Masliah E, Michaelson DM, Pinkas-Kramarski R (2016) Impaired autophagy in APOE4 astrocytes. J Alzheimers Dis 51:915–927
Singleton AB, Farrer M, Johnson J et al (2003) α-Synuclein locus triplication causes Parkinson’s disease. Science 302:841
Son JH, Shim JH, Kim KH, Ha JY, Han JY (2012) Neuronal autophagy and neurodegenerative diseases. Exp Mol Med 44:89–98
Song JX, Lu JH, Liu LF, Chen LL, Durairajan SSK, Yue Z, Zhang HQ, Li M (2014) HMGB1 is involved in autophagy inhibition caused by SNCA/a-synuclein overexpression: a process modulated by the natural autophagy inducer corynoxine B. Autophagy 10:144–154
Spilman P, Podlutskaya N, Hart MJ, Debnath J, Gorostiza O, Bredesen D, Richardson A, Strong R, Galvan V (2010) Inhibition of mTOR by rapamycin abolishes cognitive deficits and reduces amyloid-β levels in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS One 5(4):e9979. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0009979
Steen E, Terry BM, Rivera EJ, Cannon JL, Neely TR, Tavares R, Xu XJ, Wands JR, De La Monte SM (2005) Impaired insulin and insulin-like growth factor expression and signaling mechanisms in Alzheimer’s disease—is this type 3 diabetes? J Alzheimers Dis 7:63–80
Stefanis L (2012) α-Synuclein in Parkinson’s disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2:a009399
Strittmatter WJ, Roses AD (1996) Apolipoprotein E and Alzheimer’s disease. Annu Rev Neurosci 19:53–77
Sun X-Y, Dong Q-X, Zhu J, Sun X, Zhang L-F, Qiu M, Yu X-L, Liu R-T (2019) Resveratrol rescues tau-induced cognitive deficits and neuropathology in a mouse model of tauopathy. Curr Alzheimer Res 16:710–722
Takamura A, Komatsu M, Hara T, Sakamoto A, Kishi C, Waguri S, Eishi Y, Hino O, Tanaka K, Mizushima N (2011) Autophagy-deficient mice develop multiple liver tumors. Genes Dev 25:795–800
Takano K, Koarashi K, Kawabe K, Itakura M, Nakajima H, Moriyama M, Nakamura Y (2018) Insulin expression in cultured astrocytes and the decrease by amyloid β. Neurochem Int 119:171–177
Thomas KJ, McCoy MK, Blackinton J, Beilina A, van der Brug M, Sandebring A, Miller D, Maric D, Cedazo-Minguez A, Cookson MR (2011) DJ-1 acts in parallel to the PINK1/parkin pathway to control mitochondrial function and autophagy. Hum Mol Genet 20:40–50
Tong Y, Giaime E, Yamaguchi H, Ichimura T, Liu Y, Si H, Cai H, Bonventre JV, Shen J (2012) Loss of leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 causes age-dependent bi-phasic alterations of the autophagy pathway. Mol Neurodegener 7:2
Van Acker ZP, Bretou M, Annaert W (2019) Endo-lysosomal dysregulations and late-onset Alzheimer’s disease: impact of genetic risk factors. Mol Neurodegener 14(1):20. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13024-019-0323-7
Vargas KJ, Makani S, Davis T, Westphal CH, Castillo PE, Chandra SS (2014) Synucleins regulate the kinetics of synaptic vesicle endocytosis. J Neurosci 34:9364–9376
Vincow ES, Merrihew G, Thomas RE, Shulman NJ, Beyer RP, MacCoss MJ, Pallanck LJ (2013) The PINK1-Parkin pathway promotes both mitophagy and selective respiratory chain turnover in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:6400–6405
Vingtdeux V, Giliberto L, Zhao H et al (2010) AMP-activated protein kinase signaling activation by resveratrol modulates amyloid-β peptide metabolism. J Biol Chem 285:9100–9113
Vogiatzi T, Xilouri M, Vekrellis K, Stefanis L (2008) Wild type α-synuclein is degraded by chaperone-mediated autophagy and macroautophagy in neuronal cells. J Biol Chem 283:23542–23556
Wang D, Chan CC, Cherry S, Hiesinger PR (2013) Membrane trafficking in neuronal maintenance and degeneration. Cell Mol Life Sci 70:2919–2934
Wang C, Zhang X, Teng Z, Zhang T, Li Y (2014) Downregulation of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in curcumin-induced autophagy in APP/PS1 double transgenic mice. Eur J Pharmacol 740:312–320
Watanabe Y, Taguchi K, Tanaka M (2020) Ubiquitin, autophagy and neurodegenerative diseases. Cells 9(9):2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9092022
Wauters F, Cornelissen T, Imberechts D, Martin S, Koentjoro B, Sue C, Vangheluwe P, Vandenberghe W (2020) LRRK2 mutations impair depolarization-induced mitophagy through inhibition of mitochondrial accumulation of RAB10. Autophagy 16:203–222
William Langston J, Ballard P, Tetrud JW, Irwin I (1983) Chronic parkinsonism in humans due to a product of meperidine-analog synthesis. Science 219:979–980
Williams TI, Lynn BC, Markesbery WR, Lovell MA (2006) Increased levels of 4-hydroxynonenal and acrolein, neurotoxic markers of lipid peroxidation, in the brain in mild cognitive impairment and early Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 27:1094–1099
Winslow AR, Chen CW, Corrochano S et al (2010) α-Synuclein impairs macroautophagy: implications for Parkinson’s disease. J Cell Biol 190:1023–1037
Wirth M, Benson G, Schwarz C et al (2018) The effect of spermidine on memory performance in older adults at risk for dementia: a randomized controlled trial. Cortex 109:181–188
Xie Z, Klionsky DJ (2007) Autophagosome formation: core machinery and adaptations. Nat Cell Biol 9:1102–1109
Xilouri M, Vogiatzi T, Vekrellis K, Park D, Stefanis L (2009) Abberant α-synuclein confers toxicity to neurons in part through inhibition of chaperone-mediated autophagy. PLoS One 4:e5515
Xu CY, Kang WY, Chen YM, Jiang TF, Zhang J, Zhang LN, Ding JQ, Liu J, Di CS (2017) DJ-1 inhibits α-synuclein aggregation by regulating chaperone-mediated autophagy. Front Aging Neurosci 9:308. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2017.00308
Yamamoto S, Kuramoto K, Wang N, Situ X, Priyadarshini M, Zhang W, Cordoba-Chacon J, Layden BT, He C (2018) Autophagy differentially regulates insulin production and insulin sensitivity. Cell Rep 23:3286–3299
Yang Y, Zhang L (2020) The effects of caloric restriction and its mimetics in Alzheimer’s disease through autophagy pathways. Food Funct 11:1211–1224
Yue Z, Yang XW (2013) Dangerous duet: LRRK2 and α-synuclein jam at CMA. Nat Neurosci 16:375–377
Zhang L, Wang L, Wang R, Gao Y, Che H, Pan Y, Fu P (2017) Evaluating the effectiveness of GTM-1, rapamycin, and carbamazepine on autophagy and Alzheimer disease. Med Sci Monit 23:801–808
Zhao Y, Zhao B (2013) Oxidative stress and the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2013:316523. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/316523
Zhu Y, Wang C, Yu M, Cui J, Liu L, Xu Z (2013) ULK1 and JNK are involved in mitophagy incurred by LRRK2 G2019S expression. Protein Cell 4:711–721
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Russell, A.E. et al. (2022). Crosstalk Between Autophagy and Nutrigenomics in Neurodegenerative Diseases. In: Salama, M. (eds) Nutrigenomics and the Brain. Nutritional Neurosciences. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-9205-5_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-9205-5_13
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-16-9204-8
Online ISBN: 978-981-16-9205-5
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)