Abstract
Phytoplankton are one of the key players in the ocean and contribute approximately 50% to global primary production. They serve as the basis for marine food webs, drive chemical composition of the global atmosphere and thereby climate. Seasonal environmental changes and nutrient availability naturally influence phytoplankton species composition. Since the industrial era, anthropogenic climatic influences have increased noticeably – also within the ocean. Our changing climate, however, affects the composition of phytoplankton species composition on a long-term basis and requires the organisms to adapt to this changing environment, influencing micronutrient bioavailability and other biogeochemical parameters. At the same time, phytoplankton themselves can influence the climate with their responses to environmental changes. Due to its key role, phytoplankton has been of interest in marine sciences for quite some time and there are several methodical approaches implemented in oceanographic sciences. There are ongoing attempts to improve predictions and to close gaps in the understanding of this sensitive ecological system and its responses.
You have full access to this open access chapter, Download conference paper PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Keywords
Introduction
Phytoplankton are some of the smallest marine organisms. Still, they are one of the most important players in the marine environment. They are the basis of many marine food webs and, at the same time, sequester as much carbon dioxide as all terrestrial plants together. As such, they are important players when it comes to ocean climate change.
In this chapter, the nature of phytoplankton will be investigated. Their different taxa will be explored and their ecological roles in food webs, carbon cycles, and nutrient uptake will be examined. A short introduction on the range of methodology available for phytoplankton studies is presented. Furthermore, the concept of ocean-related climate change is introduced. Examples of seasonal plankton variability are given, followed by an introduction to time series, an important tool to obtain long-term data. Finally, some predictions of phytoplankton community shifts related to climate change will be presented.
This review aims to give an introduction of phytoplankton, climate models and the interaction of phytoplankton with the environment. We want to point out small scale changes caused by seasonality as well as examples of whole ecosystem changes.
What Is Phytoplankton?
Plankton play a key role in the ocean as they provide the foundation of marine food webs. In general, the term plankton (“planktos” = wandering or drifting) indicates that these organisms dwell in water as they are not able to move against the currents (Hensen 1887). Nekton, on the contrary, can move freely and include mostly organisms bigger than around 2 cm. The broad range of planktonic organisms divides into several trophic levels and size classes as proposed by Sieburth et al. (1978). They belong to all different types of taxonomic groups such as viruses, archaea, bacteria, fungi, algae, protozoa, and animals. Viruses and bacteria (virio- and bacterioplankton) as well as archaea belong to femto- and picoplankton, which range from 0.02 to 0.2 μm and 0.2 to 2.0 μm in size, respectively. Mycoplankton (fungi) can mostly be found within nanoplankton (2.0–20 μm). Phytoplankton spans from picoplankton up to microplankton (2–200 μm), whereas zooplankton, in rare cases, can reach up to 200 cm (megaplankton).
The high diversity of phytoplankton extends from prokaryotes (cyanobacteria) to several groups of eukaryotes. Classification of phytoplankton groups constantly changes due to the increasing amount of molecular phylogenetic studies and is under constant flux of opinion (e.g., Parfrey et al. 2006). Cyanobacteria have been traditionally classified using morphological features. However, due to the different scientific communities, the bacterial classification is not easily comparable with the phycological taxonomy. In the last decades, several new concepts have been introduced (see e.g., Hoffmann et al. 2005; Komárek 2010; Komárek et al. 2014). With new approaches that are based on molecular techniques and the arising problems to integrate this new information into the classification, there have been several approaches for reaching a consensus in both communities (e.g., Komárek 2006; Palinska and Surosz 2014). So far, all major cyanobacterial groups, even cyanobacteria that have been categorized as freshwater species, can be found in the marine environment (Burja et al. 2001; Paerl 2012).
Adl et al. (2005) revised the classification of protozoa from Levine et al. (1980) and expanded it to other protists in the name of the International Society of Protistologists. They compared modern morphological approaches, biochemical pathways and molecular phylogenetics data to create a new classification. Only 7 years later Adl et al. (2012) revised this classification. This new revision proposes a division into six super-groups: Archaeplastida, Amoebozoa, Opisthokonta, Excavata, and SAR (Stramenopila, Alveolata, and Rhizaria). Throughout the last years, the concept of different super-groups has been applied for the eukaryotic phytoplankton. Changes and uncertainties are still present in the super-groups that are named here. Additionally, several groups of organisms exist, which do not belong to any of the super-groups, for example some groups of flagellates.
Phytoplankton Taxonomy and Morphology
Depending on area, season, and size class, different groups can act as dominating organisms in the food web and, therefore, regulate the seasonality of the predators as well. The most frequent dominating eukaryotic phytoplankton belong to diatoms (Stramenopila), dinoflagellates (Alveolata) or haptophytes (also called prymnesiophytes, no super-group) (Fig. 1). Other groups include Chlorophyta (Archaeplastida), Cryptophyta, Centrohelida and Telonemia, with the last three not belonging to any of the super-groups (e.g., Paerl 1988; Arrigo et al. 1999; Adl et al. 2012).
Exemplary schematic drawings of three important phytoplankton groups. (a) Triangular diatom Trigonium sp., (b) dinoflagellate Pyrodinium bahamense and (c) coccolithophorid Emiliania huxleyi (prymnesiophytes). (Adapted from the open source Plankton*Net Data Provider at the Alfred Wegener Insitute for Polar and Marine Research (a) and (c), and from Landsberg et al. (2006) (b))
Diatoms (Bacillariophyta) possess a so-called frustule of silica that consists of two overlapping valves (hypotheca and epitheca) and a girdle (cingulum). Reproduction is mostly asexual. The old cell divides and each daughter cell builds up a new smaller theca inside the parent wall. If the theca gets too small for further reproduction the cell dies. Prior to death, the cell releases auxospores, which grow into new cells. Another characteristic feature is the symmetry of diatoms. They are either centric or pennate symmetric. They occur as single cells or more often in colonies (Gross 1937). Diatoms are mainly autotrophs, with several heterotrophic strategies to survive during darkness (e.g., Tuchman et al. 2006; McMinn and Martin 2013).
Dinoflagellates consist of thecate and athecate groups. Thecate dinoflagellates possess a cover of cellulose plates in contrast to athecate dinoflagellates, which are more variable in shape. Both groups possess two characteristic parts: episome and hyposome. The cells also feature two grooves. A cingulum divides the cells into two parts and houses one transverse flagellum and the sulcus houses a second longitudinal flagellum. Dinoflagellates can be auto-, mixo-, and heterotrophs (e.g., Carvalho et al. 2008; McMinn and Martin 2013). Several species can cause so-called “red-tides” and harmful algae blooms (Loeblich 1976; Taylor et al. 2008).
Haptophytes belong to flagellates and consist of different groups and genera. They include, for example, coccolithophorids and the potentially toxic algae genus Prymnesium, which includes some cytotoxin, ichthyotoxin, neurotoxin, and haemolytic toxin producing species (Seoane et al. 2017). Motile haptophytes possess two flagella and a haptonema. The haptonema is a characteristic cell organelle and resembles a third flagellum. In contrast to the other two flagella, it is not used for swimming but to capture particles and to attach to surfaces (Hibberd 1976; Kawachi et al. 1991; Jordan and Chamberlain 1997; Andersen 2004).
Primary Production and Essential Elements
Due to its broad distribution and abundance in the ocean, phytoplankton is the fundamental primary producer and serves as a food source at the base of oceanic food webs. It is part of the microbial loop due to its interaction with bacteria and its decomposition by viral lysis and bacteria.
In general, phytoplankton is dependent on the availability of nutrients, light, and other prevalent conditions such as regional and seasonal changes both physically (temperature, salinity, currents, mixing of water layers, precipitation) as well as biologically (e.g., parasites, grazing of potential predators) (Falkowski and Oliver 2007; Racault et al. 2012, further reading: Mackas et al. 1985; Fenchel 1988; Reid et al. 1990).
Phytoplankton uses photosynthesis as energy source and, doing so, contributes with 48% noticeably to global carbon fixation by taking up and incorporating carbon from carbon dioxide. Another important environmental function of phytoplankton is the production of oxygen during photosynthesis (Field et al. 1998). Since photosynthesis requires light, active phytoplankton can only be found in the euphotic zone of the ocean (Fig. 2). Depth of the euphotic zone may differ enormously depending on the presence of biological and non-biological substances absorbing and scattering light within the water column. However, phytoplankton itself often narrows the euphotic zone (Lorenzen 1972).
Cycling of marine phytoplankton. Phytoplankton live in the photic zone of the ocean, where photosynthesis is possible. During photosynthesis, they assimilate carbon dioxide and release oxygen. If solar radiation is too high, phytoplankton may fall victim to photodegradation. For growth, phytoplankton cells depend on nutrients, which enter the ocean by rivers, continental weathering, and glacial ice meltwater on the poles. Phytoplankton release dissolved organic carbon (DOC) into the ocean. Since phytoplankton are the basis of marine food webs, they serve as prey for zooplankton, fish larvae and other heterotrophic organisms. They can also be degraded by bacteria or by viral lysis. Although some phytoplankton cells, such as dinoflagellates, are able to migrate vertically, they are still incapable of actively moving against currents, so they slowly sink and ultimately fertilize the seafloor with dead cells and detritus
Phytoplankton as primary producers are part of the biological carbon pump, since they take up carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere and bind the carbon in their cells, which are then taken up by higher trophic levels or become part of sinking particles and remineralisation. Time scales for the carbon to re-enter the cycle and to be reused can vary from days, over weeks and years up to several millennia, especially for carbon reaching the sediment surface (Emerson and Hedges 1988; Shen and Benner 2018). Sinking particles that originate from fragmentation, aggregation or egestion after consumption by higher trophic levels such as zooplankton can either be consumed again or be decomposed by microbial processes. At the same time, active vertical migration by the organisms distributes the carbon further within different water layers and therefore has a significant impact on the oceanic carbon cycle and productivity (Azam 1998; Buesseler et al. 2007). As consequence, phytoplankton are subject to high fluctuations and show seasonality as well as a spatial heterogeneity.
To produce biomass, phytoplankton need certain nutrients, the most important being carbon (C), nitrogen (N) and phosphorous (P). For marine primary production, Redfield (1958) calculated the ratio in which these essential nutrients are required as C:N:P = 106:16:1.
Important sources of nitrogen are nitrate and ammonium. Ammonium can be taken up effectively by phytoplankton and provides up to 35% of nitrogen assimilated depending on species and location (Eppley et al. 1971, 1979). Nitrate uptake as nitrogen source requires a higher amount of energy. Thus, ammonium uptake is generally preferred (Thompson et al. 1989). Furthermore, nitrate uptake is relatively slow. Phytoplankton show a great metabolic diversity. For example some phytoplankton species are incapable of nitrate uptake, whereas other species even prefer the uptake of nitrate to ammonium. Ammonium can, in high concentrations, even suppress growth (Glibert et al. 2016; Van Oostende et al. 2017). Nitrogen can be taken up faster by amino acids and fastest via ammonium (Dortch 1982), though only some phytoplankton species are able to take up amino acids (Wheeler et al. 1974).
In competitive environments, however, organic nitrogen such as urea can serve as valuable source to phytoplankton (Bradley et al. 2010). The availability of nitrogen in different forms can also have an influence on the respective species composition (Glibert et al. 2016; Van Oostende et al. 2017).
Phosphorus is also essential for phytoplankton and is usually taken up via phosphate, which frequently acts as limiting nutrient (Perry 1976). Both nitrogen and phosphorus can act as limiting nutrients for primary production (Smith 2006). Some phytoplankton species are capable of reducing their phosphorus demand by producing substitute lipids instead of phospholipids (Van Mooy et al. 2009). Marine diatoms, which can make up large fractions of phytoplankton communities, are furthermore dependent on silicate to form their characteristic external shell (Harvey 1939; Paasche 1973a, b; Treguer et al. 1995; Turner et al. 1998).
Apart from these crucial elements, a range of trace metals is required for phytoplankton growth. Morel and Price (2003) made a first attempt to calculate a stoichiometry for essential trace metals including iron, manganese, zinc, copper, cobalt, and cadmium. Particularly iron is a crucial trace metal that is strongly affecting the productivity of phytoplankton in vast areas of the ocean (Martin and Gordon 1988; Morel et al. 1991). To facilitate trace metal uptake, phytoplankton can make use of ligands, which are organic molecules that are able to complex metals and help to keep them in solution. Especially ligands complexing iron, so called siderophores, are beneficial for phytoplankton (Hassler et al. 2011; Boiteau et al. 2016).
Due to the strong effect iron has on the productivity of phytoplankton, its role was assessed in large scale experiments. After the first successful iron fertilization experiments, which tested the importance of iron in situ on a large scale (e.g., Martin et al. 1994; Coale et al. 1996), the possibility to reduce inorganic carbon with iron fertilization was defined, yielding in sequestering of carbon dioxide during blooms (Bakker et al. 2001, 2005; Boyd et al. 2007). While Buesseler et al. (2004) showed that the “Southern Ocean Iron Experiment” caused a small increase in carbon flux in the region, the “Kerguelen Ocean and Plateau compared Study” could prove an even higher carbon sequestration efficiency (Blain et al. 2007).
Other, more complex molecules are even more important for phytoplankton growth. Some species require exogenous vitamins to grow. Especially vitamin-B depletion can negatively influence phytoplankton productivity (Gobler et al. 2007).
Oceanic dissolved organic carbon (DOC) is one of the largest marine carbon reservoirs. Kirchman et al. (1991) calculated turnover rates of DOC using its bacterial uptake. DOC and dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) cycle differently from each other. During phytoplankton blooms, more DOC than DON is produced, presumably by phytoplankton (Kirchman et al. 1991). The amount of DOC bacteria can assimilate depends on the phytoplankton species releasing it (Malinsky-Rushansky and Legrand 1996). Phytoplankton release of DOC alone cannot meet bacterial needs and thus allochthonous DOC sources as well as sloppy feeding, viral lysis, hydrolysis by exoenzymes, and zooplankton excretion play a role in releasing additional DOC into the ocean (Fig. 2) (Mopper and Lindroth 1982; Baines and Pace 1991; Jiao and Azam 2011). DOC produced by phytoplankton contains both high and low molecular weight substances. Bacteria assimilate these low molecular weight substances, such as amino acids, peptides, and carbohydrates rather quickly. High molecular weight substances are only slowly or not at all assimilated and can contribute to refractory DOC (Sundh 1992). During phytoplankton blooms, polysaccharide particle formation can transform DOC to particulate organic matter. Such polysaccharides can provide binding sites for trace metals and could participate in controlling their residence time in the ocean (Engel et al. 2004). Therefore, a variety of potentially relevant bioactive molecules exists within the complex DOC pool produced by phytoplankton that influences the ecological interplay of phytoplankton with its environment.
Methods for Studying Phytoplankton Species Composition
Several comprehensive reviews providing good overviews over a variety of methods are available for plankton research. Techniques to assess phytoplankton diversity were collected by Johnson and Martiny (2015). Applications of flow cytometry have been reviewed by Dubelaar and Jonker (2000). A revision of case studies for molecular methods to estimate diversity is available from Medlin and Kooistra (2010). Reviews for nutrient quantification, pigment analysis and remote sensing are also available (Cloern 1996; Jeffrey et al. 1999; Roy et al. 2011; Blondeau-Patissier et al. 2014).
Methods that yield useful approaches to help understanding phytoplankton species composition and its interconnection to environmental conditions are summarized in Fig. 3.
Schematic overview of the methods used for phytoplankton studies. Three different possibilities to process the sample are using raw samples, fixation or preservation, and filtration. For microscopy and flow cytometry raw samples either are measured immediately or have to be fixed for later measurements. Since molecular methods, pigment analysis and detection of molecular tracers usually require concentrated cells, filter residues serve for phytoplankton measurements. Molecular characterization and quantification of trace molecules is performed using chromatography, mass spectrometry (MS), and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy
Climate Influences on Phytoplankton
Since the beginning of the industrial era, anthropogenic influences on the climate have steadily increased. Covering more than two thirds of the Earth’s surface, the area for exchange between the atmosphere and sea surface is large. Apart from that, the ocean is subject to several effects triggered by climate change.
Climate Change in the Ocean
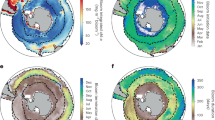
The two most prominent changes to the ocean triggered by climate change are ocean warming and acidification. Both aspects affect the ocean globally. Increasing anthropogenic carbon dioxide emissions have increased partial pressure of carbon dioxide, both, in the atmosphere and the ocean. The ocean acts as sink for anthropogenic carbon dioxide and is, by increasingly taking up carbon dioxide, gradually acidified. It is estimated that surface water pH decreased by 0.1 since the beginning of the industrial era. With increasing acidification, ocean surface water becomes gradually corrosive to calcium carbonate minerals, of which many seashells are composed (Fig. 4) (Ciais et al. 2013; Rhein et al. 2013).
Overview about climatic changes and their effects on the ocean after Ciais et al. (2013) and Rhein et al. (2013). Regional effects are displayed in italics. Excess solar radiation enters the atmosphere. Ice reflects this radiation, but it is taken up by the surface ocean, leading to its warming. Ocean warming results in land ice melt and thermal expansion, which both result in a sea level rise. Heating of vast areas of the surface ocean also slowly heats up the intermediate water layer which, among others, can ultimately lead to regional changes of deep water. Regional freshening occurs on sites with melting land ice. Regional salinification on the contrary happens in areas of vast evaporation. Surface ocean warming also decreases the solubility of gases, leading to a reduced oxygen concentration and thus changes in the sea-oxygen flux. Excess anthropogenic carbon dioxide enhances its uptake by the ocean and leads to a gradual acidification of the ocean. A decreasing pH results in bicarbonate undersaturation, which causes dissolving of shells and other minerals. Regional input of reactive nitrogen can lead to fertilization and eutrophication. Another regional effect is the occurrence of high waves. Heating, reduced oxygen concentrations and eutrophication lead to higher stratification of water masses
The ocean has a high heat capacity and absorbs solar radiation more readily than ice. It is virtually certain that the upper ocean has warmed. This warming dominates the global energy change inventory and accounts for more than 90% of the total energy change inventory, while melting ice, warming of continents, and the warming of the atmosphere play only a minor role. Warming of the upper ocean is an important factor that has led to an average sea level rise of 0.19 m between 1901 and 2010 and it is likely that the sea level rise will accelerate (Fig. 4) (Rhein et al. 2013).
Furthermore, there are plenty of regional changes connected to climate change such as patterns of salinity trends. The IPCC report defines a region as a territory characterized by specific geographical and climatological features, whose climate is affected by scale features (e.g., topography, land use characteristics, and lakes) and remote influences from other regions (IPCC 2013). Local changes in salinity are expected (Fig. 4). In general, a higher contrast between fresh and salty regions is expected with salty regions becoming saltier and vice versa. Sea level rise in combination with wind stress is expected to result in high waves in some regions. Intermediate and deep water changes are yet difficult to assess, since long-term data are lacking. Generally, changes in salinity, density, and temperature appear to occur regionally. Anthropogenic influences on coastal runoff and atmospheric deposition of nutrients are another important regional factor. Changing nutrients, such as the input of nitrogen fertilizers, can influence the biological carbon pump and ultimately lead to an increasing eutrophication of waters (Fig. 4) (Ciais et al. 2013; Rhein et al. 2013).
Seasonality and Future Changes in Phytoplankton Communities
Phytoplankton communities undergo seasonal changes. Depending on regional properties like climatic or biogeographic conditions, the changes can differ greatly. While regions near the equator undergo relatively small changes in temperature during the year, the poles are influenced by large changes caused by severe differences in sunshine intensity and daylight duration. As the environmental factors are already highly influenced by these changes, phytoplankton communities need to adapt to these different conditions as well. Specifically useful study sites are the poles, since seasonal climate variability is very distinct. Other sites that are under continuous and alternating changes are shelf and coastal systems, which are for example influenced by freshwater inflow from the mainland as well as tides and wave actions. The following examples of different regional seasonal changes over the globe and the corresponding phytoplankton community successions shall give a small overview about the vast influence of climate conditions on phytoplankton communities.
In the Arctic summer, glacial ice melt water adds iron and other nutrients into the Labrador Sea (Fig. 2). Apart from the coastal summer blooms resulting from that input, glacial meltwater nutrients travel distances of up to 300 km on the ocean’s surface (Arrigo et al. 2017). In the western Arctic, even at closely located sites, different stages of seasonal development could be observed for local phytoplankton communities. The considerable variability in quantitative abundances and biomass values of local phytoplankton species is highly dependent on the irregularity of seasonal processes in the physical environment, ice melting, heating, and the dynamics of stratification (Sukhanova et al. 2009). Furthermore, massive and widespread phytoplankton blooms could occur under the Arctic sea ice, given regional nitrogen concentrations higher than 10 μmol L−1 in 50% of the ice covered continental shelf. Those under-ice blooms are also an important factor to be taken into account when estimating changes in the arctic environment (Arrigo et al. 2012).
In the Antarctic, species abundance and composition are largely influenced by seasons in the distinct regions subjected to differences in environmental factors and processes (Deppeler and Davidson 2017). Tréguer and Jacques (1992) divided the Southern Ocean into four different zones, without considering the Permanent Ice Zone, with regard to their different nutrient regimes, physical parameters, and extents of primary production. While diatom-dominated blooms and severe nutrient decreases can be observed in the Coastal and Continental Shelf Zone, the Seasonal Ice Zone is characterized by a very variable hydrological system depending on the ice cover retreat and growth. The Permanently Open Ocean Zone is a nutrient rich region, while the northern part is characterized by a silicate limitation and the Polar Front Zone can harbor high amounts of phytoplankton. There are, however, vast regions, which are suffering under iron limitations. In general, nanoplankton dominates within sea ice and open water unless diatom blooms occur, which happens in May, November and December at the bottom of the ice as well as in January and February in open water (e.g., Perrin et al. 1987; Swart et al. 2015).
In the Cooperation Sea, which is located in the Seasonal Ice Zone as defined by Tréguer and Jacques (1992), nutrient concentrations increase throughout the year until December, where nitrate and silicate drop notably followed by a phosphate decrease. Here, the largest species diversity occurs during summer, while plenty of dead diatoms are observable in winter (Perrin et al. 1987).
On the Weddell Sea ice edge, huge differences between spring and autumn can be observed. During spring, long chains of vegetative cells form and diatoms as well as haptophytes build up gelatinous colonies in the open water, while only short chains and few single cells occur under the ice. The same conditions hold true for autumn, where short chains and single cells dominate. Furthermore, diatom spores with storage products and enlarged cells are produced then, as results of their sexual reproduction cycle. Thus, the ice edge serves as boundary of different life stages (Fryxell 1989).
One of the most productive regions in the Southern Ocean is the Western Antarctic Peninsula, where phytoplankton blooms occur around November to December, after the sea ice retreats in October. In 2012, the bloom was dominated by diatoms and Phaeocystis sp., with diatoms being the most dominant group at the peak of the bloom. Mixing events can cause a crash in the phytoplankton population, which happened in mid-December in this region. Afterwards, the population consisted of large groups of cryptophytes and Phaeocystis sp. In March, a second, smaller bloom, dominated by diatoms and Phaeocystis sp., could be observed (Goldman et al. 2015).
Within the Eastern English Channel, diatoms, Chrysophyceae, Raphidophyceae and Prymnesiophyceae contribute most to carbon biomass. 40 species of diatoms, and two species for Chrysophyceae and Raphidophyceae can be found, respectively. A yearly occurring Phaeocystis sp. spring bloom represents the group Prymnesiophyceae. During summer, mostly large diatoms (>100 μm) dominated the community, whereas during the rest of the year mostly small cells could be found. Furthermore, Cryptophyceae (seven genera) could be found in early spring and autumn, Dinophyceae (26 genera or species) were found with the highest abundance in summer as well as Chlorophyceae and Prasinophyceae (Breton et al. 2000).
Not et al. (2004) found that in the eukaryotic picoplankton the Prasinophyceae Micromonas pusilla was the dominating species in the Western English Channel. In contrast to bigger size classes, picoplankton shows a high abundance throughout the year. The microphytoplankton bloom was dominated by a few diatom species like Guinardia delicatula, Chaetoceros socialis, Pseudo-nitzschia spp. and Thalassiosira spp. during late spring and had maximum abundances during late summer (Ward et al. 2011).
Long-term data from Helgoland in the German Bight suggested interactions of different environmental conditions with phytoplankton seasonality. Increase in sunshine hours correlates with increasing Secchi depths (measure of water transparency) and water temperature. Less turbulence in the water body leads to increasing Secchi depths. Higher temperatures improve growth rates of phytoplankton, but cause lower abundances in early spring. Increased river discharge causes a decrease in salinity in spring, which negatively correlates with Secchi depth. Increasing Secchi depth and thus a bigger euphotic zone benefits the growth of phytoplankton. Concentrations of nutrients such as nitrate, phosphate, and silicate decline rapidly during spring, when the phytoplankton bloom starts and stay at low levels until autumn, when another phytoplankton bloom occurs. Depletion of nutrients causes inhibition of phytoplankton growth. In autumn and winter, new nutrients are released, causing concentrations to increase again. High zooplankton abundances cause belated phytoplankton blooms during spring. Higher grazing pressure during winter decreases phytoplankton abundances, which then need a longer recovery time (Wiltshire et al. 2015). The phytoplankton community is dominated by diatoms in spring and early summer according to daily counts (Wiltshire et al. 2008). Dinoflagellate abundance rose from spring and reached maximum values during summer, where Noctiluca scintillans, Gyrodinium spp., and Protoperidinium spp. dominated. Mixotrophic dinoflagellates occurred in lower abundances than heterotrophs, which correlate with phytoplankton availability. However, during summer 2007, a bloom could be observed, in which several dinoflagellates such as Lepidodinium chlorophorum, Scrippsiella/Pentapharsodinium spp., and Akashiwo sanguinea occurred (Löder et al. 2012). Cryptophytes could be found throughout the year with decline during diatom dominated times (Metfies et al. 2010).
As a sub-tropical region, the estuaries of the Gulf of Mexico are representing a warmer temperate region with long periods of warm temperatures as well as tropical storms (Georgiou et al. 2005; D’sa et al. 2011; Turner et al. 2017). In a study in the Pensacola Bay (Florida, USA) from 1999 to 2001, Murrell and Lores (2004) investigated the role of cyanobacteria on the seasonal dynamics. The three most abundant taxa were belonging to diatoms (Thalassiosira sp., Pennales, and Cyclotella sp.), and diatoms represented over 50% of total abundance of phytoplankton counts. During December and January, dinoflagellates had high abundances (Prorocentrum minimum, Gymnodinium sp.), whereas high abundances of chlorophytes and cryptophytes were found during the spring and summer months. Cyanobacteria showed a strong correlation with high water temperatures and had highest abundances in summer. Further characterization indicated that the cyanobacteria belonged to the Synechococcus genus. In total, cyanobacteria made up of a large percentage of total chlorophyll (on average 43%) and dominated the chlorophyll biomass during their summer peak (Murrell and Lores 2004).
Another study showing similar results was conducted by Dorado et al. (2015) in Galveston Bay (Texas, USA) from February 2008 to December 2009. North of Galveston Bay high phytoplankton biomass could be observed, with diatoms being the dominating phytoplankton group, followed by dinoflagellates, cryptophytes, and green algae. In comparison, the phytoplankton biomass was lower in the southern part of the bay and dominated by cyanobacteria. Cyanobacteria and green algae correlated inter alia to temperature and chlorophyll a. Results of a multivariate analysis also showed that dinoflagellates and cyanobacteria are more abundant in areas where vertical mixing is limited (mid- and lower region of the bay). Seasonal patterns showed that diatoms, dinoflagellates, and cryptophyte abundances were highest during winter and spring, whereas cyanobacteria were most abundant in summer. It was found that high freshwater discharge correlated with diatom growth, indicating that a decrease of freshwater is accompanied with lower nutrient concentrations. These conditions coupled with the temperature changes are then more favorable for cyanobacteria growth.
Time Series Monitoring of Phytoplankton Diversity
Due to the importance of phytoplankton for the environment and their large seasonal variability, long-term studies dealing with phytoplankton diversity are a very important feature to monitor changes and to yield predictions for the future (Zingone et al. 2015).
Examples for European time series are Plymouth Station L4 (Harris 2010) in the western English Channel, Helgoland Roads in the south-eastern North Sea (Wiltshire et al. 2010) or the HELCOM surveys in the Baltic Sea (Wasmund et al. 2011). One example for an automated system is the Continuous Plankton Recorder survey, which collects information about plankton communities in the North Atlantic basin (Reid et al. 2003; McQuatters-Gollop et al. 2015).
In general, time series use different time scales and sampling intervals, depending on the methods chosen, the amount and variety of parameters and sampling area. Therefore, sampling can range from daily sampling (e.g., Helgoland Roads) over monthly sampling to sampling during certain periods like phytoplankton spring blooms. A distinction can be made between manual sampling and automatic systems like ferry boxes, floats, gliders, and moorings for measurements in the open ocean or other places that are difficult to access. The latter are being implemented more and more, especially during the last decades (Wiltshire et al. 2010; Church et al. 2013).
The responses monitored depend on the focus of the respective phytoplankton studies. Short-term responses caused by nutrient changes can be tested in lab experiments as well as in situ during short time cruises. The observation of responses to habitat changes, regime shifts, climate change and other permanent adaptions require studies that cover one or more stations over a longer time period, which for climate change related studies is at least 30 years (e.g., Walther et al. 2002). Therefore, plankton time series are an important component in the study of long-term changes in marine biodiversity and the obtained data serve as a first indicator for changes in the ecosystem. They can help understanding changes in species distributions and, if explicit enough, provide working hypotheses, which can be tested in the laboratory. Applied benefits in using time series are a better understanding and prediction of the occurrence of possible toxic as well as invasive organisms. For these reasons, time series serve as important tool in marine ecological research (Boero et al. 2015).
A good example for using time series for predictions is the Continuous Plankton Recorder (CPR) survey of 50 years of monitoring dinoflagellate and diatom compositions in the northeast Atlantic Ocean and the North Sea, which could help to predict the following compositional changes. In this area, the ratio is shifting towards a larger diatom proportion. Increasing winds and resulting turbulences yielding better conditions for diatoms compared to dinoflagellates reinforce this assumption (Hinder et al. 2012). These composition shifts of the past and trends in combination with modelling approaches can therefore be used as a forecasting system.
However, the complexity of phytoplankton communities and a high analogy in their morphology make it difficult to identify in particular small sized nano- and picoplankton and to distinguish potentially toxic from non-toxic species. Most conventional time series still use traditional microscopy techniques. Due to their size, small protists are usually underreported or cannot be resolved to species level in these time series. During the last years scientists tried to implement new methods into these long-term studies to include yet underreported organisms. Whereas pigment analyses using HPLC or chlorophyll analyses are already part of many long-term studies (e.g., Karl et al. 2001; Harding Jr. et al. 2015), molecular methods such as DNA microarrays and next-generation sequencing have only been implemented in short-termed studies so far (e.g., Gescher et al. 2008; Medinger et al. 2010; Charvet et al. 2012).
Predictions of Phytoplankton Community Changes in Response to Climate Change
Phytoplankton can serve as indicator for climate or environmental change-induced shifts in the plankton community. Early studies showed that climate change does have an observable influence on the ocean (Madden and Ramanathan 1980; Manabe and Wetherald 1980; Cess and Goldenberg 1981; Hansen et al. 1981; Ramanathan 1981; Etkins and Epstein 1982). Enhanced carbon dioxide levels result in a climatic change all over the globe, influencing precipitation and temperature. Higher global temperatures ultimately lead to higher ocean temperatures and thus a reduction of sea ice in both coverage and thickness (Manabe and Stouffer 1980; Rhein et al. 2013). This results in a local desalination of the ocean, to which phytoplankton cells have to respond. Higher carbon dioxide saturation in the atmosphere will furthermore lead to a shift in equilibrium between air and water and result in elevated carbon dioxide concentrations in the ocean. As a result, the marine environment will become more acidic, potentially influencing sensitive molecular interactions (Kuma et al. 1996).
Physical and biological changes concerning the oceanic carbon sink have been predicted by Sarmiento et al. (1998). They predicted a possible reduction of carbon downward flux in the Southern Ocean due to increasing rainfall and stratification. Their simulations hinted at already occurring physical and biological changes due to climate change and atmosphere-ocean interactions. More recent studies and models show that already small changes in the Southern Ocean can induce feedbacks in the climate system due to extensive changes in the net atmosphere-ocean balance of carbon dioxide (Gruber et al. 2009). The authors also noted the possibly important role of other oceanic regions that could be large contributors to feedbacks in the climate system.
Primary production in the ocean has declined in the last decades and corresponds with increasing sea surface temperature and decreasing iron input. Since especially in high latitudes the ocean acts as important carbon sink, a climate change related further decline in primary production suggests major implications for the carbon cycle (Gregg et al. 2003). The same trend was predicted for many regions using a global model due to increasing stratification and nutrient limiting conditions in the ocean, with exception of the poles (Henson et al. 2018). Reduced sea ice and longer bloom periods in the Arctic have already lead to an increase in net primary production (Arrigo and van Dijken 2015). In contrast, net primary production decreases were also predicted with simulations from nine Earth system models within the framework of the fifth phase of the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project (CMIP5) (Fu et al. 2016).
Useful tools are one-dimensional biogeochemical models such as MEDUSA (Model of Ecosystem Dynamics, nutrient Utilisation, Sequestration and Acidification) that can globally simulate multi-decadal plankton ecosystem scenarios (Yool et al. 2011). In a global approach, the model was used to investigate spring bloom timing related to climate change in a high resolution. The change in bloom initiation timing was substantial, which could lead to food shortages for predators. Additionally, increasing ocean stratification and nutrient limiting conditions will likely result in less total primary production (Henson et al. 2018). Detailed future predictions using this one-dimensional biogeochemical model exist for the Ross Sea in the Antarctic. Primary production for the twenty-first century was estimated and presumably increases 5% in the early and 14% in the late twenty-first century. Melting ice, increased radiance, and decreasing mixed layer depths influence primary production during the first half, diatom mass likely stays constant while Phaeocystis antarctica multiplies, which then switches for the second half. Shallower mixed layer depths will change phytoplankton composition and carbon export (Kaufman et al. 2017).
On the Patagonian coast, average primary production will likely increase and phytoplankton communities sequester significant carbon amounts important for secondary production. However, these predictions cannot be made for open ocean areas without restrictions (Villafañe et al. 2015). Furthermore, changes will vastly differ regionally, showing increasing primary production in some areas and decreasing primary production in others. Another critical value influencing phytoplankton variability and competition is the increase of stratified conditions within the water column (Yoshiyama et al. 2009).
Many studies have been conducted to gather more information about phytoplankton community changes and their effects on the food web (e.g., Edwards and Richardson 2004; Schlüter et al. 2012; Harding Jr. et al. 2015). Fu et al. (2016) used a model to simulate climate change impacts on net primary production and export production. Using an intense warming scenario, the net primary production was critically dependent on the phytoplankton community structure. This model gives a good insight in the importance of community-based studies in order to monitor changes in this sensitive system. Changes in phytoplankton communities have, for example, already been observed under changing environmental conditions in the Arctic regions. Shifts in certain protist abundances indicate an enhanced presence of potentially toxic Alexandrium dinoflagellate species (Elferink et al. 2017).
Changes in the phytoplankton composition also cause the whole food web to change since predators might have to adapt to new food sources. Alternating environmental factors can facilitate the invasion of new species, which can migrate naturally inside the water masses or might be introduced via ballast water. These atypical range expansions cause structural changes in the food web, especially if the invasive species can adapt well or even better than indigenous species and may even become dominating (Walther et al. 2002; Olenina et al. 2010).
Other effects include the shifts of bloom events, mainly due to temporal and long-term climatic changes, or the timing of phyto- and zooplankton growth. These changes in timing could result in drastic consequences of ecosystem functionality. Existing studies on trophic mismatching in the plankton community are mostly focused on interactions between spring blooms (e.g., Edwards and Richardson 2004; Wiltshire et al. 2008). Therefore, not much is known about the ecological impacts and the functioning of the marine ecosystem (Thackeray 2012).
The floral composition of Chesapeake Bay at the US coast of the Atlantic Ocean revealed a shift in phytoplankton community. With nitrogen being the limiting nutrient but diatoms requiring relatively large amounts, the local community will likely shift to a smaller diatom proportion. Anthropogenic nutrient input might trigger changes as well as climate-related shifts in phytoplankton composition (Harding Jr. et al. 2015). Seasonal variability studies can provide useful insights into future climate changes, as they can give an impression about the mechanisms leading to changes. Studies at the coast of Patagonia in Argentina exposed seasonally different phytoplankton communities to possible future conditions, like enhanced temperatures and solar radiance, nutrient enrichment, and ocean acidification. Increasing ocean temperature has little effect on pre-bloom communities. However, ultraviolet radiance during blooms leads to photochemical inhibition of phytoplankton. Increasing temperatures might lead to a decreasing mixed layer depth, which would expose the community to higher radiations (Villafañe et al. 2013). Shallower mixed layers combined with stronger solar radiance as future condition might also result in cellular stress. Chlorophyll a can decline in phytoplankton cells as response to light stress. The cells can contract and move their chloroplasts, which leads to a temporary photoinhibition of photosynthesis (Kiefer 1973). Diatoms are more prone to ozone-related negative solar UV-B radiation, which can affect aquatic systems, thus generally likely dominating future communities (Häder et al. 2007).
Ocean acidification might lead to a shift in nutrient requirements and C:N:P stoichiometry, thus influencing biogeochemical cycles (Bellerby et al. 2008). In addition, decreasing pH influences micronutrient bioavailability such as leading to decreased concentrations of iron bioavailability and increase phytoplankton iron stress (Shi et al. 2010).
Besides phytoplankton being influenced by nutrients and other environmental factors, they themselves influence the climate and environment they are living in. One example is the role of phytoplankton in the formation of former ice ages. Iron-rich dust was transported to the Southern Ocean, where water masses were rich of nutrients such as nitrate and phosphate but lacked iron. This natural iron fertilization of phytoplankton in the Subantarctic could partly explain atmospheric carbon dioxide changes over the last 1.1 million years. Measurements of foraminifera-bound nitrogen isotopes from sediment cores taken in the Subantarctic Atlantic indicated dust flux, productivity and the degree of nitrate consumption as characterizing factors for peak glacial times and millennial cold events. Triggering blooms and changes in the Southern Ocean’s food web and biological pump can be seen as the cause of the full emergence of ice age conditions. However, the main drivers for the initial carbon dioxide decrease were most likely physical processes, such as surface water stratification, wind changes and changes in sea ice extent (Martínez-Garcia et al. 2009, 2014; Jaccard et al. 2013).
Another example for phytoplankton impacts on the climate is dimethylsulfide (DMS). DMS is the degradation product of dimethylsulfoniopropionate (DMSP), which is produced by phytoplankton as an osmoprotectant and degraded by marine bacteria (Yoch 2002). The main DMSP producing phytoplankton belong to the groups of dinoflagellates and prymnesiophytes, but also include some diatoms and Chrysophyceae species (Keller et al. 1989). Important phytoplankton include Phaeocystis sp., Emiliania huxleyi, Prorocentrum sp. and Gymnodinium sp. (Yoch 2002). Since atmospheric DMS is an important sulfur source for the global environment and its oxidation causes reflection of solar radiation, it can have a cooling effect on the Earth’s temperature (for further reading, see Yoch 2002; Stefels et al. 2007; Lana et al. 2012).
Effects like these make phytoplankton blooms interesting candidates to actively help reversing the effects of climate change, for example by trying to trigger carbon sequestering blooms (Bakker et al. 2005). However, large scale blooms may have unforeseen ecological effects, such as becoming toxic (Silver et al. 2010).
Harmful Algal Blooms
Harmful algal blooms (HABs) refer to blooms of diatoms, dinoflagellates, raphidophytes, haptophytes, cyanobacteria, and certain macroalgae perceived as harmful due a negative impact on the environment or public health. Some have the capability to express toxins under certain circumstances. Other blooms are harmful not due to toxins but because the build-up of high biomass leads to disruption of food webs and development of anoxic zones (Kudela et al. 2017).
Apart from ecological effects, HABs can affect human health upon exposure to poisoned seawater, food or marine aerosols and can have severe socio-economic impacts (Pierce et al. 2003; Fleming et al. 2007). Most frequent HAB related illness worldwide is Ciguatera Fish Poisoning (CFP), which occurs manly in the tropics and subtropics. A variety of dinoflagellate species can produce toxins, such as the Gambierdiscus toxicus species complex, which can produce the toxins maitotoxin and ciguatoxin (Murata et al. 1992).
Other illnesses are Paralytic Shellfish Poisoning (PSP) and Diarrhetic Shellfish Poisoning (DSP), which can occur worldwide (Berdalet et al. 2016). Prorocentrum lima can produce a variety of toxins, i.a. DSP causative okadaic acid (Murakami et al. 1982). HABs can have extensive ecological effects, such as mass mortality of whales suffering from PSP by feeding on mackerels poisoned with saxitoxins from dinoflagellates or enhanced fish kills (Geraci et al. 1989; Glibert et al. 2001; Nash et al. 2017).
Furthermore, some diatoms can also express toxins. Several species of the genus Pseudo-nitzschia are, for example, capable of producing domoic acid (Rao et al. 1988).
HABs can have widespread occurrences. They can occur at coastlines all over the world and have been reported throughout history from Canada, Japan, Scotland, Australia, and many other places (e.g., White 1977; Murakami et al. 1982; Bruno et al. 1989; Nash et al. 2017). Although toxic blooms are a natural phenomenon, they can also be a reaction to environmental shifts and the production of toxins can be connected to environmental conditions (Etheridge and Roesler 2005). Experiments with toxin producing Alexandrium sp. showed that increasing radiance and temperature significantly enhanced toxin production (Lim et al. 2006). Nutrient changes in particular can have distinct effects in triggering toxin production. Iron fertilization can lead to formation of a toxic Pseudo-nitzschia spp. bloom and natural iron fertilization might have the same effect (Silver et al. 2010). Also low ammonium concentrations and low salinities that can be found in estuaries can lead to enhanced toxin production in Alexandrium sp. (Hamasaki et al. 2001).
Because of the damages HABs may cause, their detection and prediction is an on-going scientific challenge, which is approached with different techniques, such as molecular methods, chromatographic pigment analysis, optical spectroscopy, and remote sensing (Millie et al. 1997; John et al. 2005; Trainer et al. 2009). Automated monitoring showed promising predictions (Campbell et al. 2010). Besides establishing a monitoring network, Wells et al. (2015) suggested parameters for routine measurements, including physical parameters, nutrient concentrations, phytoplankton identification, and toxin concentrations.
Linking the effects of climate change with changes in global HAB occurrence and developing monitoring strategies has been the subject of many studies up to date (e.g., Edwards et al. 2006; Moore et al. 2008; Hallegraeff 2010; Hinder et al. 2012; Kudela et al. 2017).
Conclusions
Phytoplankton are a very diverse and important player in the ocean due to their many roles in different marine cycles. Phytoplankton are highly dependent on a diversity of nutrients and influenced by physical and chemical properties in the ocean. Anthropogenic influences on the climate will change these conditions. Some of these effects are global, some remain regional. As diverse as these effects can be, changes to phytoplankton communities will occur as well. One of these examples are harmful algae blooms, which are a hot topic regarding ecological impacts. Another example are possible shifts of ecological niches, which influence the whole marine food web. When predicting such changes, a solid data base is crucial. A wide range of methods targeting different parameters are just as crucial as obtaining data over a long time period.
Seasonal variations in community shifts and changes of the cell morphology show, that phytoplankton adapt to changing environmental conditions regularly. Some of these seasonally observed changes can be extrapolated to future scenarios.
Climate change related conditions in the ocean will change phytoplankton composition and adaption, as they will have to deal with differing nutrient and trace metal bioavailability, physical conditions or temperatures. However, blooms triggered by such conditions can have an opposite effect by influencing the climate themselves.
Apart from species composition, cell physiology is another important aspect that can be changed by climate. Chemicals produced by phytoplankton, such as toxins, can have vast ecological impacts and are one of the most pressing topics when predicting phytoplankton changes.
In conclusion, phytoplankton are an important connecting element within the sensitive marine system. Therefore, accurate predictions are difficult to make, but the existing methods and models are a good way to improve the local understanding. In addition, new models and different approaches looking at factor interactions shall give new and better insights.
References
Adl SM, Simpson AGB, Farmer MA et al (2005) The new higher level classification of eukaryotes with emphasis on the taxonomy of protists. J Eukaryot Microbiol 52:399–451. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1550-7408.2005.00053.x
Adl SM, Simpson AG, Lane CE et al (2012) The revised classification of eukaryotes. J Eukaryot Microbiol 59:429–493. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1550-7408.2012.00644.x
Andersen RA (2004) Biology and systematics of Heterokont and haptophyte algae. Am J Bot 91:1508–1522. https://doi.org/10.3732/ajb.91.10.1508
Arrigo KR, van Dijken GL (2015) Continued increases in Arctic Ocean primary production. Prog Oceanogr 136:60–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pocean.2015.05.002
Arrigo KR, Robinson DH, Worthen DL et al (1999) Phytoplankton community structure and the drawdown of nutrients and CO2 in the Southern Ocean. Science 283:365–367. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.283.5400.365
Arrigo KR, Perovich DK, Pickart RS et al (2012) Massive phytoplankton blooms under Arctic Sea ice. Science 336:1408. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1215065
Arrigo KR, van Dijken GL, Castelao RM et al (2017) Melting glaciers stimulate large summer phytoplankton blooms in Southwest Greenland waters. Geophys Res Lett 44:6278–6285. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017GL073583
Azam F (1998) Microbial control of oceanic carbon flux: the plot thickens. Science 280:694–696. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.280.5364.694
Baines SB, Pace ML (1991) The production of dissolved organic matter by phytoplankton and its importance to bacteria: patterns across marine and freshwater systems. Limnol Oceanogr 36:1078–1090. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.1991.36.6.1078
Bakker DCE, Watson AJ, Law CS (2001) Southern Ocean iron enrichment promotes inorganic carbon drawdown. Deep Res Pt II 48:2483–2507. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0967-0645(01)00005-4
Bakker DCE, Bozec Y, Nightingale PD et al (2005) Iron and mixing affect biological carbon uptake in SOIREE and EisenEx, two Southern Ocean iron fertilisation experiments. Deep Res Pt I 52:1001–1019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsr.2004.11.015
Bellerby RGJ, Schulz KG, Riebesell U et al (2008) Marine ecosystem community carbon and nutrient uptake stoichiometry under varying ocean acidification during the PeECE III experiment. Biogeosciences 5:1517–1527. https://doi.org/10.5194/bg-5-1517-2008
Berdalet E, Fleming LE, Gowen R et al (2016) Marine harmful algal blooms, human health and wellbeing: challenges and opportunities in the 21st century. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 96:61–91. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0025315415001733
Blain S, Quéguiner B, Armand L et al (2007) Effect of natural iron fertilization on carbon sequestration in the Southern Ocean. Nature 446:1070–1074. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05700
Blondeau-Patissier D, Gower JFR, Dekker AG et al (2014) A review of ocean color remote sensing methods and statistical techniques for the detection, mapping and analysis of phytoplankton blooms in coastal and open oceans. Prog Oceanogr 123:123–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pocean.2013.12.008
Boero F, Kraberg AC, Krause G et al (2015) Time is an affliction: why ecology cannot be as predictive as physics and why it needs time series. J Sea Res 101:12–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seares.2014.07.008
Boiteau RM, Mende DR, Hawco NJ et al (2016) Siderophore-based microbial adaptations to iron scarcity across the eastern Pacific Ocean. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 113:14237–14242. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1608594113
Boyd PW, Jickells T, Law CS et al (2007) Mesoscale iron enrichment experiments 1993–2005: synthesis and future directions. Science 315:612–617. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1131669
Bradley PB, Sanderson MP, Frischer ME et al (2010) Inorganic and organic nitrogen uptake by phytoplankton and heterotrophic bacteria in the stratified Mid-Atlantic Bight. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 88:429–441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2010.02.001
Breton E, Brunet C, Sautour B et al (2000) Annual variations of phytoplankton biomass in the eastern English Channel: comparison by pigment signatures and microscopic counts. J Plankton Res 22:1423–1440. https://doi.org/10.1093/plankt/22.8.1423
Bruno DW, Dear G, Seaton DD (1989) Mortality associated with phytoplankton blooms among farmed Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L., in Scotland. Aquaculture 78:217–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/0044-8486(89)90099-9
Buesseler KO, Andrews JE, Pike SM et al (2004) The effects of iron fertilization. Science 304:414–417. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1086895
Buesseler KO, Antia AN, Chen M et al (2007) An assessment of the use of sediment traps for estimating upper ocean particle fluxes. J Mar Res 65:345–416. https://doi.org/10.1357/002224007781567621
Burja AM, Banaigs B, Abou-Mansour E et al (2001) Marine cyanobacteria – a profilic source of natural products. Tetrahedron 57:9347–9377
Campbell L, Olson RJ, Sosik HM et al (2010) First harmful dinophysis (Dinophyceae, Dinophysiales) bloom in the U.S. is revealed by automated imaging flow cytometry. J Phycol 75:66–75. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1529-8817.2009.00791.x
Carvalho WF, Minnhagen S, Granéli E (2008) Dinophysis norvegica (Dinophyceae), more a predator than a producer? Harmful Algae 7:174–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2007.07.002
Cess RD, Goldenberg SD (1981) The effect of ocean heat capacity upon global warming due to increasing atmospheric carbon dioxide. J Geophys Res 86:498–502. https://doi.org/10.1029/JC086iC01p00498
Charvet S, Vincent WF, Lovejoy C (2012) Chrysophytes and other protists in high Arctic lakes: molecular gene surveys, pigment signatures and microscopy. Polar Biol 35:733–748. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-011-1118-7
Church MJ, Lomas MW, Muller-Karger F (2013) Sea change: charting the course for biogeochemical ocean time-series research in a new millennium. Deep Res Pt II 93:2–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsr2.2013.01.035
Ciais P, Sabine C, Bala G et al (2013) Carbon and other biogeochemical cycles. In: Stocker TF, Qin D, Plattner G-K et al (eds) Climate change 2013: the physical science basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge/New York
Cloern JE (1996) Phytoplankton bloom dynamics in coastal ecosystems: a review with some general lessons from sustained investigation of San Francisco Bay, California. Rev Geophys 34:127–168. https://doi.org/10.1029/96RG00986
Coale KH, Johnson KS, Fitzwater SE et al (1996) A massive phytoplankton bloom induced by an ecosystem-scale iron fertilization experiment in the equatorial Pacific Ocean. Nature 383:495–501
D’sa EJ, Korobkin M, Ko DS (2011) Effects of Hurricane Ike on the Louisiana-Texas coast from satellite and model data. Remote Sens Lett 2:11–19. https://doi.org/10.1080/01411161.2010.489057
Deppeler SL, Davidson AT (2017) Southern Ocean phytoplankton in a changing climate. Front Mar Sci 4:40. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2017.00040
Dorado S, Booe T, Steichen J et al (2015) Towards an understanding of the interactions between freshwater inflows and phytoplankton communities in a subtropical estuary in the Gulf of Mexico. PLoS One 10:e0130931. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0130931
Dortch Q (1982) Effect of growth conditions on accumulation of internal nitrate, ammonium, amino acids, and protein in three marine diatoms. J Exp Mar Bio Ecol 61:243–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-0981(82)90072-7
Dubelaar GBJ, Jonker RR (2000) Flow cytometry as a tool for the study of phytoplankton. Sci Mar 64:135–156. https://doi.org/10.3989/scimar.2000.64n2135
Edwards M, Richardson AJ (2004) Impact of climate change on marine pelagic phenology and trophic mismatch. Nature 430:881–884. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02808
Edwards M, Johns DG, Leterme SC et al (2006) Regional climate change and harmful algal blooms in the Northeast Atlantic. Limnol Oceanogr 51:820–829
Elferink S, Neuhaus S, Wohlrab S et al (2017) Molecular diversity patterns among various phytoplankton size-fractions in West Greenland in late summer. Deep Res Pt I 121:54–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsr.2016.11.002
Emerson S, Hedges JI (1988) Processes controlling the organic carbon content of open ocean sediments. Paleoceanography 3:621–634. https://doi.org/10.1029/PA003i005p00621
Engel A, Thoms S, Riebesell U et al (2004) Polysaccharide aggregation as a potential sink of marine dissolved organic carbon. Nature 428:929–932. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02453
Eppley RW, Carlucci AF, Holm-Hansen O et al (1971) Phytoplankton growth and composition in shipboard cultures supplied with nitrate, ammonium, or urea as the nitrogen source. Limnol Oceanogr 16:741–751. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.1971.16.5.0741
Eppley RW, Renger EH, Hurrison WG et al (1979) Ammonium distribution in southern California coastal waters and its role in the growth of phytoplankton. Limnol Oceanogr 24:495–509. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.1979.24.3.0495
Etheridge SM, Roesler CS (2005) Effects of temperature, irradiance, and salinity on photosynthesis, growth rates, total toxicity, and toxin composition for Alexandrium fundyense isolates from the Gulf of Maine and Bay of Fundy. Deep Res Pt II 52:2491–2500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsr2.2005.06.026
Etkins R, Epstein ES (1982) The rise of global mean sea level as an indication of climate change. Science 215:287–289
Falkowski PG, Oliver MJ (2007) Mix and match: how climate selects phytoplankton. Nat Rev Microbiol 5:813–819. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro1751
Fenchel T (1988) Marine plankton food chains. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 19:19–38. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.es.19.110188.000315
Field CB, Behrenfeld MJ, Randerson JT et al (1998) Primary production of the biosphere: integrating terrestrial and oceanic components. Science 281:237–240. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.281.5374.237
Fleming LE, Kirkpatrick B, Pierce R et al (2007) Aerosolized red-tide toxins (Brevetoxins) and asthma. Chest 131:187–194. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.06-1830
Fryxell GA (1989) Marine phytoplankton at the Weddell Sea ice edge: seasonal changes at the specific level. Polar Biol 10:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00238285
Fu W, Randerson JT, Moore JK (2016) Climate change impacts on net primary production (PP) and export production (EP) regulated by increasing stratification and phytoplankton community structure in the CMIP5 models. Biogeosciences 13:5151–5170. https://doi.org/10.5194/bg-13-5151-2016
Georgiou IY, FitzGerald DM, Stone GW (2005) The impact of physical processes along the Louisiana coast. J Coast Res SI 44:72–89. https://doi.org/10.2307/25737050
Geraci JR, Anderson DM, Timperi RJ et al (1989) Humpback Whales (Megaptera novaeangliae) fatally poisoned by dinoflagellate toxin. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 46:1895–1898. https://doi.org/10.1139/f89-238
Gescher C, Metfies K, Frickenhaus S et al (2008) Feasibility of assessing the community composition of prasinophytes at the Helgoland roads sampling site with a DNA microarray. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:5305–5316. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01271-08
Glibert PM, Magnien R, Lomas MW et al (2001) Harmful algal blooms in the Chesapeake and coastal bays of Maryland, USA: comparison of 1997, 1998, and 1999 events. Estuaries 24:875–883. https://doi.org/10.2307/1353178
Glibert PM, Wilkerson FP, Dugdale RC et al (2016) Pluses and minuses of ammonium and nitrate uptake and assimilation by phytoplankton and implications for productivity and community composition, with emphasis on nitrogen-enriched conditions. Limnol Oceanogr 61:165–197. https://doi.org/10.1002/lno.10203
Gobler CJ, Norman C, Panzeca C et al (2007) Effect of B-vitamins (B1, B12) and inorganic nutrients on algal bloom dynamics in a coastal ecosystem. Aquat Microb Ecol 49:181–194. https://doi.org/10.3354/ame01132
Goldman JAL, Kranz SA, Young JN et al (2015) Gross and net production during the spring bloom along the western Antarctic peninsula. New Phytol 205:182–191. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.13125
Gregg WW, Conkright ME, Ginoux P et al (2003) Ocean primary production and climate: global decadal changes. Geophys Res Lett 30:10–13. https://doi.org/10.1029/2003GL016889
Gross F (1937) The life history of some marine planktonic diatoms. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B 228:1–47. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.1937.0008
Gruber N, Gloor M, Mikaloff Fletcher SE et al (2009) Oceanic sources, sinks, and transport of atmospheric CO2. Global Biogeochem Cycles 23:GB1005. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008GB003349
Häder D-P, Kumar HD, Smith RC et al (2007) Effects of solar UV radiation on aquatic ecosystems and interactions with climate change. Photochem Photobiol Sci 6:267–285. https://doi.org/10.1039/B700020K
Hallegraeff GM (2010) Ocean climate change, phytoplankton community responses, and harmful algal blooms: a formidable predictive challenge. J Phycol 46:220–235. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1529-8817.2010.00815.x
Hamasaki K, Horie M, Tokimitsu S et al (2001) Variability in toxicity of the dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense isolated from Hiroshima Bay, western Japan, as a reflecion of changing environmental conditions. J Plankton Res 23:271–278. https://doi.org/10.1093/plankt/23.3.271
Hansen J, Johnson D, Lacis A et al (1981) Climate impact of increasing atmospheric carbon dioxide. Science 213:957–966. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.213.4511.957
Harding LW Jr, Adolf JE, Mallonee ME et al (2015) Climate effects on phytoplankton floral composition in Chesapeake Bay. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 162:53–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2014.12.030
Harris R (2010) The L4 time-series: the first 20 years. J Plankton Res 32:577–583. https://doi.org/10.1093/plankt/fbq021
Harvey HW (1939) Substances controlling the growth of a diatom. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 23:499–520. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0025315400014041
Hassler CSC, Schoemann V, Nichols CM et al (2011) Saccharides enhance iron bioavailability to Southern Ocean phytoplankton. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:1076–1081. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1010963108
Hensen V (1887) Über die Bestimmung des Planktons oder des im Meere treibenden Materials an Pflanzen und Thieren. Ber Komm Wiss Unters dt Meere 5:1–108
Henson SA, Cole HS, Hopkins J et al (2018) Detection of climate change-driven trends in phytoplankton phenology. Glob Chang Biol 24:e101–e111. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.13886
Hibberd DJ (1976) The ultrastructure and taxonomy of the Chrysophyceae and Prymnesiophyceae (Haptophyceae): a survey with some new observations on the ultrastructure of the Chrysophyceae. Bot J Linn Soc 72:55–80. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8339.1976.tb01352.x
Hinder SL, Hays GC, Edwards M et al (2012) Changes in marine dinoflagellate and diatom abundance under climate change. Nat Clim Chang 2:271–275. https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate1388
Hoffmann L, Komárek J, Kaštovský J (2005) System of cyanoprokaryotes (cyanobacteria) – state in 2004. Arch Hydrobiol Suppl Algol Stud 117:95–115. https://doi.org/10.1127/1864-1318/2005/0117-0095
IPCC (2013) Annex III: glossary [Planton, S. (ed.)]. In: Stocker TF, Qin D, Plattner G-K et al (eds) Climate change 2013: the physical science basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge/New York
Jaccard SL, Hayes CT, Hodell DA et al (2013) Two modes of change in Southern Ocean productivity over the past millions years. Science 339:1419–1423
Jeffrey SW, Wright SW, Zapata M (1999) Recent advances in HPLC pigment analysis of phytoplankton. Mar Freshw Res 50:879–896. https://doi.org/10.1071/MF99109
Jiao N, Azam F (2011) Microbial carbon pump and its significance for carbon sequestration in the ocean. In: Jiao N, Azam F, Sanders S (eds) Microbial carbon pump in the ocean. Science/AAAS Business Office, Washington, DC, pp 43–45
John U, Medlin LK, Groben R (2005) Development of specific rRNA probes to distinguish between geographic clades of the Alexandrium tamarense species complex. J Plankton Res 27:199–204. https://doi.org/10.1093/plankt/fbh160
Johnson ZI, Martiny AC (2015) Techniques for quantifying phytoplankton biodiversity. Annu Rev Mar Sci 7:299–324. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-marine-010814-015902
Jordan RWR, Chamberlain AHL (1997) Biodiversity among haptophyte algae. Biodivers Conserv 6:131–152. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018383817777
Karl DM, Bidigare RR, Letelier RM (2001) Long-term changes in plankton community structure and productivity in the North Pacific subtropical gyre: the domain shift hypothesis. Deep Res Pt II 48:1449–1470. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0967-0645(00)00149-1
Kaufman DE, Friedrichs MAM, Smith WO et al (2017) Climate change impacts on southern Ross Sea phytoplankton composition, productivity, and export. J Geophys Res Ocean 122:2339–2359. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016JC012514
Kawachi M, Inouye I, Maeda O et al (1991) The haptonema as a food-capturing device: observations on Chrysochromulina hirta (Prymnesiophyceae). Phycologia 30:563–573. https://doi.org/10.2216/i0031-8884-30-6-563.1
Keller MD, Bellows WK, Gulliard RL (1989) Dimethyl sulfide production in marine phytoplankton. Am Chem Soc 81:168–182
Kiefer DA (1973) Chlorophyll α fluorescence in marine centric diatoms: responses of chloroplasts to light and nutrient stress. Mar Biol 23:39–46. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00394110
Kirchman DL, Suzuki Y, Garside C et al (1991) High turnover rates of dissolved organic carbon during a spring phytoplankton bloom. Nature 352:612–614. https://doi.org/10.1038/352612a0
Komárek J (2006) Cyanobacterial taxonomy: current problems and prospects for the integration of traditional and molecular approaches. Algae 21:349–375. https://doi.org/10.4490/ALGAE.2006.21.4.349
Komárek J (2010) Recent changes (2008) in cyanobacteria taxonomy based on a combination of molecular background with phenotype and ecological consequences (genus and species concept). Hydrobiologia 639:245–259. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-009-0031-3
Komárek J, Kaštovský J, Mareš J et al (2014) Taxonomic classification of cyanoprokaryotes (cyanobacterial genera) 2014, using a polyphasic approach. Preslia:295–335
Kudela RM, Berdalet E, Enevoldsen H et al (2017) GEOHAB – the global ecology and oceanography of harmful algal blooms program: motivation, goals, and legacy. Oceanography 30:12–21. https://doi.org/10.5670/oceanog.2017.106
Kuma K, Nishioka J, Matsunaga K (1996) Controls on iron(III) hydroxide solubility in seawater: the influence of pH and natural organic chelators. Limnol Oceanogr 41:396–407. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.1996.41.3.0396
Lana A, Simó R, Vallina SM et al (2012) Potential for a biogenic influence on cloud microphysics over the ocean: a correlation study with satellite-derived data. Atmos Chem Phys 12:7977–7993. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-12-7977-2012
Landsberg JH, Hall S, Johannessen JN et al (2006) Saxitoxin puffer fish poisoning in the United States, with the first report of Pyrodinium bahamense as the putative toxin source. Environ Health Perspect 114:1502–1507. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.8998
Levine NDD, Corliss JOO, Coc FEG et al (1980) A newly revised classification of the protozoa. J Protozool 27:37–58. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1550-7408.1980.tb04228.x
Lim PT, Leaw CP, Usup G et al (2006) Effects of light and temperature on growth, nitrate uptake, and toxin production of two tropical dinoflagellates: Alexandrium tamiyavanichii and Alexandrium minutum (Dinophyceae). J Phycol 42:786–799. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1529-8817.2006.00249.x
Löder MGJ, Kraberg AC, Aberle N et al (2012) Dinoflagellates and ciliates at Helgoland roads, North Sea. Helgol Mar Res 66:11–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10152-010-0242-z
Loeblich AR (1976) Dinoflagellate evolution: speculation and evidence. J Protozool 23:13–28. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1550-7408.1976.tb05241.x
Lorenzen CJ (1972) Extinction of light in the ocean by phytoplankton. ICES J Mar Sci 34:262–267. https://doi.org/10.1093/icesjms/34.2.262
Mackas DL, Denman KL, Abbott MR (1985) Plankton patchiness: biology in the physical vernacular. Bull Mar Sci 37:652–674
Madden RA, Ramanathan V (1980) Detecting climate change due to increasing carbon dioxide. Science 209:763–768. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.209.4458.763
Malinsky-Rushansky NZ, Legrand C (1996) Excretion of dissolved organic carbon by phytoplankton of different sizes and subsequent bacterial uptake. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 132:249–255. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps132249
Manabe S, Stouffer RJ (1980) Sensitivity of a global climate model to an increase of CO2 concentration in the atmosphere. J Geophys Res 85:5529–5554. https://doi.org/10.1029/JC085iC10p05529
Manabe S, Wetherald RT (1980) On the distribution of climate change resulting from an increase in CO2 content of the atmosphere. J Atmos Sci 37:99–118. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0469(1980)037<0099:OTDOCC>2.0.CO;2
Martin JH, Gordon RM (1988) Northeast Pacific iron distributions in relation to phytoplankton productivity. Deep Sea Res Pt A 35:177–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/0198-0149(88)90035-0
Martin JH, Coale KH, Johnson KS et al (1994) Testing the iron hypothesis in ecosystems of the equatorial Pacific Ocean. Nature 371:123–129. https://doi.org/10.1038/371123a0
Martínez-García A, Rosell-Melé A, Geibert W et al (2009) Links between iron supply, marine productivity, sea surface temperature, and CO2 over the last 11 Ma. Paleoceanography 24:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008PA001657
Martínez-García A, Sigman DM, Ren H et al (2014) Iron fertilization of the subantarctic ocean during the last ice age. Science 343:1347–1350. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1246848
McMinn A, Martin A (2013) Dark survival in a warming world. Proc R Soc B 280:20122909. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2012.2909
McQuatters-Gollop A, Edwards M, Helaouët P et al (2015) The continuous plankton recorder survey: how can long-term phytoplankton datasets contribute to the assessment of good environmental status? Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 162:88–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2015.05.010
Medinger R, Nolte V, Pandey RV et al (2010) Diversity in a hidden world: potential and limitation of next-generation sequencing for surveys of molecular diversity of eukaryotic microorganisms. Mol Ecol 19:32–40. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2009.04478.x
Medlin LK, Kooistra WHCF (2010) Methods to estimate the diversity in the marine photosynthetic protist community with illustrations from case studies: a review. Diversity 2:973–1014. https://doi.org/10.3390/d2070973
Metfies K, Gescher C, Frickenhaus S et al (2010) Contribution of the class cryptophyceae to phytoplankton structure in the German bight. J Phycol 46:1152–1160. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1529-8817.2010.00902.x
Millie DF, Schofield OM, Kirkpatrick GJ et al (1997) Detection of harmful algal blooms using photopigments and absorption signatures: a case study of the Florida red tide dinoflagellate, Gymnodinium breve. Limnol Oceanogr 42:1240–1251. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.1997.42.5_part_2.1240
Moore SK, Trainer VL, Mantua NJ et al (2008) Impacts of climate variability and future climate change on harmful algal blooms and human health. Environ Health 7:S4. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-069X-7-S2-S4
Mopper K, Lindroth P (1982) Diel and depth variations in dissolved free amino acids and ammonium in the Baltic Sea determined by shipboard HPLC analysis. Limnol Oceanogr 27:336–347. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.1982.27.2.0336
Morel FMM, Price NM (2003) The biogeochemical cycles of trace metals. Science 300:944–947. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1083545
Morel FMM, Hudson RJM, Price NM (1991) Limitation of productivity by trace metals in the sea. Limnol Oceanogr 36:1742–1755. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.1991.36.8.1742
Murakami Y, Oshima Y, Yasumoto T (1982) Identification of okadaic acid as a toxic component of a marine dinoflagellate Prorocentrum lima. Bull Japanese Soc Sci Fish 48:69–72. https://doi.org/10.2331/suisan.48.69
Murata M, Iwashita T, Yokoyama A et al (1992) Partial structures of Maitotoxin, the most potent marine toxin from dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus toxicus. J Am Chem Soc 114:6594–6596. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja00042a070
Murrell MC, Lores EM (2004) Phytoplankton and zooplankton seasonal dynamics in a subtropical estuary: importance of cyanobacteria. J Plankton Res 26:371–382. https://doi.org/10.1093/plankt/fbh038
Nash SMB, Baddock MC, Takahashi E et al (2017) Domoic acid poisoning as a possible cause of seasonal cetacean mass stranding events in Tasmania, Australia. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 98:8–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-016-1906-4
Not F, Latasa M, Marie D et al (2004) A single species, Micromonas pusilla (Prasinophyceae), dominates the eukaryotic picoplankton in the Western English Channel. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:4064–4072. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.70.7.4064
Olenina I, Wasmund N, Hajdu S et al (2010) Assessing impacts of invasive phytoplankton: the Baltic Sea case. Mar Pollut Bull 60:1691–1700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2010.06.046
Paasche E (1973a) Silicon and the ecology of marine plankton diatoms. I. Thalassiosira pseudonana (Cyclotella nana) grown in a chemostat with silicate as limiting nutrient. Mar Biol 19:117–126. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00353582
Paasche E (1973b) Silicon and the ecology of marine plankton diatoms. II. Silicate-uptake kinetics in five diatom species. Mar Biol 19:262–269. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02097147
Paerl HW (1988) Nuisance phytoplankton blooms in coastal, estuarine, and inland waters. Limnol Oceanogr 33:823–843. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.1988.33.4_part_2.0823
Paerl HW (2012) Marine plankton. In: Whitton BA (ed) Ecology of cyanobacteria ii: their diversity in space and time. Springer Science+Business Media B.V, Dordrecht, pp 127–153
Palinska KA, Surosz W (2014) Taxonomy of cyanobacteria: a contribution to consensus approach. Hydrobiologia 740:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-014-1971-9
Parfrey LW, Barbero E, Lasser E et al (2006) Evaluating support for the current classification of eukaryotic diversity. PLoS Genet 2:2062–2073. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.0020220
Perrin RA, Lu P, Marchant HJ (1987) Seasonal variation in marine phytoplankton and ice algae at a shallow antarctic coastal site. Hydrobiologia 146:33–46. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00007575
Perry MJ (1976) Phosphate utilization by an oceanic diatom in phosphorus-limited chemo-stat culture and in the oligotrophic waters of the central North Pacific. Limnol Oceanogr 21:88–107. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.1976.21.1.0088
Pierce RH, Henry MS, Blum PC et al (2003) Brevetoxin concentrations in marine aerosol: human exposure levels during a Karenia brevis harmful algal bloom. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 70:161–165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-002-0170-y.Brevetoxin
Plankton*Net Data Provider at the Alfred Wegener Insitute for Polar and Marine Research Plankton*Net. hdl:10013/de.awi.planktonnet
Racault MF, Le Quéré C, Buitenhuis E et al (2012) Phytoplankton phenology in the global ocean. Ecol Indic 14:152–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2011.07.010
Ramanathan V (1981) The role of ocean-atmosphere interactions in the CO2 climate problem. J Atmos Sci 38:918–930
Rao DVS, Quilliam MA, Pocklington R (1988) Domoic acid – a neurotoxic amino acid produced by the marine diatom Nitzschia pungens in culture. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 45:2076–2079. https://doi.org/10.1139/f88-241
Redfield AC (1958) The biological control of chemical factors in the environment. Am Sci 46:205–221. https://doi.org/10.5194/bg-11-1599-2014
Reid PC, Lancelot C, Gieskes WWC et al (1990) Phytoplankton of the North Sea and its dynamics: a review. Neth J Sea Res 26:295–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/0077-7579(90)90094-W
Reid PC, Colebrook JM, Matthews JBL et al (2003) The continuous plankton recorder: concepts and history, from plankton Indicator to undulating recorders. Prog Oceanogr 58:117–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pocean.2003.08.002
Rhein M, Rintoul SR, Aoki S et al (2013) Observations: ocean. In: Stocker TF, Qin D, Plattner G-K et al (eds) Climate change 2013: the physical science basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge/New York
Roy S, Llewellyn CA, Egeland ES et al (2011) Phytoplankton pigments: characterization, chemotaxonomy and applications in oceanography. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Sarmiento JL, Hughes TMC, Stouffer RJ et al (1998) Simulated response of the ocean carbon cycle to anthropogenic climate warming. Nature 393:245–249. https://doi.org/10.1038/30455
Schlüter MH, Kraberg A, Wiltshire KH (2012) Long-term changes in the seasonality of selected diatoms related to grazers and environmental conditions. J Sea Res 67:91–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seares.2011.11.001
Seoane S, Riobó P, Franco J (2017) Haemolytic activity in different species of the genus Prymnesium (Haptophyta). J Mar Biol Assoc UK 97:491–496. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0025315416001077
Shen Y, Benner R (2018) Mixing it up in the ocean carbon cycle and the removal of refractory dissolved organic carbon. Sci Rep 8:2542. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-20857-5
Shi D, Xu Y, Hopkinson BM et al (2010) Effect of ocean acidification on iron availability to marine phytoplankton. Science 327:676–679. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1183517
Sieburth JM, Smetacek V, Lenz J (1978) Pelagic ecosystem structure: heterotrophic compartments of the plankton and their relationship to plankton size fractions. Limnol Oceanogr 23:1256–1263. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.1978.23.6.1256
Silver MW, Bargu S, Coale SL et al (2010) Toxic diatoms and domoic acid in natural and iron enriched waters of the oceanic Pacific. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:20762–20767. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1006968107
Smith VH (2006) Responses of estuarine and coastal marine phytoplankton to nitrogen and phosphorus enrichment. Limnol Oceanogr 51:377–384. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.2006.51.1_part_2.0377
Stefels J, Steinke M, Turner S et al (2007) Environmental constraints on the production and removal of the climatically active gas dimethylsulphide (DMS) and implications for ecosystem modelling. Biogeochemistry 83:245–275. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-6214-8_18
Sukhanova IN, Flint MV, Pautova LA et al (2009) Phytoplankton of the western Arctic in the spring and summer of 2002: structure and seasonal changes. Deep Res Pt II 56:1223–1236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsr2.2008.12.030
Sundh I (1992) Biochemical composition of dissolved organic carbon derived from phytoplankton and used by heterotrophic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:2938–2947
Swart S, Thomalla SJ, Monteiro PMS (2015) The seasonal cycle of mixed layer dynamics and phytoplankton biomass in the Sub-Antarctic Zone: a high-resolution glider experiment. J Mar Syst 147:103–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmarsys.2014.06.002
Taylor FJR, Hoppenrath M, Saldarriaga JF (2008) Dinoflagellate diversity and distribution. Biodivers Conserv 17:407–418. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10531-007-9258-3
Thackeray SJ (2012) Mismatch revisited: what is trophic mismatching from the perspective of the plankton? J Plankton Res 34:1001–1010. https://doi.org/10.1093/plankt/fbs066
Thompson PA, Levasseur ME, Harrison PJ (1989) Light-limited growth on ammonium vs. nitrate: what is the advantage for marine phytoplankton? Limnol Oceanogr 34:1014–1024. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.1989.34.6.1014
Trainer VL, Hickey BM, Lessard EJ et al (2009) Variability of Pseudo-nitzschia and domoic acid in the Juan de Fuca eddy region and its adjacent shelves. Limnol Oceanogr 54:289–308. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.2009.54.1.0289
Tréguer P, Jacques G (1992) Dynamics of nutrients and phytoplankton, and fluxes of carbon, nitrogen and silicon in the Antarctic Ocean. Polar Biol 12:149–162. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00238255
Tréguer P, Nelson DM, Vanbennekom AJ et al (1995) The silica balance in the world ocean – a reestimate. Science 268:375–379. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.268.5209.375
Tuchman NC, Schollett MA, Rier ST et al (2006) Differential heterotrophic utilization of organic compounds by diatoms and bacteria under light and dark conditions. Hydrobiologia 561:167–177. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-005-1612-4
Turner RE, Qureshi N, Rabalais NN et al (1998) Fluctuating silicate:nitrate ratios and coastal plankton food webs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:13048–13051. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.95.22.13048
Turner RE, Rabalais NN, Justić D (2017) Trends in summer bottom-water temperatures on the northern Gulf of Mexico continental shelf from 1985 to 2015. PLoS One 12:e0184350. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0184350
Van Mooy BAS, Fredricks HF, Pedler BE et al (2009) Phytoplankton in the ocean use non-phosphorus lipids in response to phosphorus scarcity. Nature 458:69–72. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07659
Van Oostende N, Fawcett SE, Marconi D et al (2017) Variation of summer phytoplankton community composition and its relationship to nitrate and regenerated nitrogen assimilation across the North Atlantic Ocean. Deep Res Pt I 121:79–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsr.2016.12.012
Villafañe VE, Banaszak AT, Guendulain-García SD et al (2013) Influence of seasonal variables associated with climate change on photochemical diurnal cycles of marine phytoplankton from Patagonia (Argentina). Limnol Oceanogr 58:203–214. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.2013.58.1.0203
Villafañe VE, Valiñas MS, Cabrerizo MJ et al (2015) Physio-ecological responses of Patagonian coastal marine phytoplankton in a scenario of global change: role of acidification, nutrients and solar UVR. Mar Chem 177:411–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marchem.2015.02.012
Walther GR, Post E, Convey P et al (2002) Ecological responses to recent climate change. Nature 416:389–395. https://doi.org/10.1038/416389a
Ward BB, Rees AP, Somerfield PJ et al (2011) Linking phytoplankton community composition to seasonal changes in f-ratio. ISME J 5:1759–1770. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2011.50
Wasmund N, Tuimala J, Suikkanen S et al (2011) Long-term trends in phytoplankton composition in the western and Central Baltic Sea. J Mar Syst 87:145–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmarsys.2011.03.010
Wells ML, Trainer VL, Smayda TJ et al (2015) Harmful algal blooms and climate change: learning from the past and present to forecast the future. Harmful Algae 49:68–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2015.07.009
Wheeler PA, North BB, Stephens GC (1974) Amino acid uptake by marine phytoplankton. Limnol Oceanogr 19:249–259. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.1974.19.2.0249
White AW (1977) Dinoflagellate toxins as probable cause of an Atlantic herring (Clupea harengus harengus) kill, and pteropods as apparent vector. J Fish Res Board Can 34:2421–2424. https://doi.org/10.1139/f77-328
Wiltshire KH, Malzahn AM, Wirtz K et al (2008) Resilience of North Sea phytoplankton spring bloom dynamics: an analysis of long-term data at Helgoland Roads. Limnol Oceanogr 53:1294–1302. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.2008.53.4.1294
Wiltshire KH, Kraberg A, Bartsch I et al (2010) Helgoland roads, north sea: 45 years of change. Estuar Coasts 33:295–310. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-009-9228-y
Wiltshire KH, Boersma M, Carstens K et al (2015) Control of phytoplankton in a shelf sea: determination of the main drivers based on the Helgoland Roads Time Series. J Sea Res 105:42–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seares.2015.06.022
Yoch DC (2002) Dimethylsulfoniopropionate: its sources, role in the marine food web, and biological degradation to dimethylsulfide. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:5804–5815. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.68.12.5804
Yool A, Popova EE, Anderson TR (2011) MEDUSA-1.0: a new intermediate complexity plankton ecosystem model for the global domain. Geosci Model Dev 4:381–417. https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-4-381-2011
Yoshiyama K, Mellard JP, Litchman E et al (2009) Phytoplankton competition for nutrients and light in a stratified water column. Am Nat 174:190–203. https://doi.org/10.1086/600113
Zingone A, Harrison PJ, Kraberg A et al (2015) Increasing the quality, comparability and accessibility of phytoplankton species composition time-series data. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 162:151–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2015.05.024
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Appendix
Appendix
This article is related to the YOUMARES 8 conference session no. 10: “Phytoplankton in a Changing Environment – Adaptation Mechanisms and Ecological Surveys”. The original Call for Abstracts and the abstracts of the presentations within this session can be found in the appendix “Conference Sessions and Abstracts”, chapter “4 Phytoplankton in a Changing Environment – Adaptation Mechanisms and Ecological Surveys”, of this book.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This chapter is licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license and indicate if changes were made.
The images or other third party material in this book are included in the book's Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the book's Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder.
Copyright information
© 2018 The Author(s)
About this paper
Cite this paper
Käse, L., Geuer, J.K. (2018). Phytoplankton Responses to Marine Climate Change – An Introduction. In: Jungblut, S., Liebich, V., Bode, M. (eds) YOUMARES 8 – Oceans Across Boundaries: Learning from each other. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-93284-2_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-93284-2_5
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-93283-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-93284-2
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)