Abstract
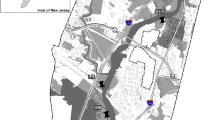
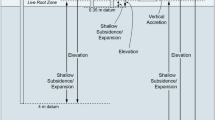
Wetland surface elevation and vertical accretion were measured from 1996 to 1999-–2000 using a sediment elevation table (SET) and feldspar marker horizons in nine paired wetlands receiving Mississippi River water from the Caernarvon, West Pointe a la Hache (WPH), and Violet river diversions. The Caernarvon study sites had wetland surface elevation change rates ranging from 0.16±0.31 to 0.42±0.21 cm y−1. Vertical accretion ranged from 0.75±0.04 to 1.57±0.05 cm y−1, and shallow subsidence ranged from 0.59 to 1.21 cm y−1. Wetland surface elevation at the WPH study sites initially increased 2.3 to 3.3 cm during the first seven months of the study and then steadily decreased over the following year. The overall rate of elevation change ranged from 0.27±0.09 to 0.70±0.11 cm y−1. Vertical accretion and shallow subsidence ranged from 1.24±0.08 to 1.84±0.07 cm y−1 and 0.54 to 1.27 cm y−1, respectively. The Violet sites lost elevation and had the highest subsidence rates in this study, most likely due to a combination of hydrologic alteration and low diversion discharge. Wetland elevation decreased throughout the study, with rates ranging from −1.10±0.24 to −2.34±0.41 cm y−1. Vertical accretion and shallow subsidence rates at the Violet-Near and Far sites were 0.44±0.10 and 0.44±0.11 cm y−1 and 2.78 to 1.54 cm y−1, respectively. The Violet-Mid site wetland was burned in Winter 1999, leading to more than 4.0 cm decrease in material measured over the marker horizon and contributing to the lowest accretion rate measured in this study of 0.34±0.05 cm y−1. Analysis of regional relative sea-level rise (RSLR) indicates that all Caernarvon sites and the WPH-Near and Mid sites are keeping pace with RSLR. This study indicates that the use of river diversions can be an effective coastal restoration tool, with efficiency related to the proximity to riverine source and degree of hydrologic alteration, quantity of river water released, and land uses of the receiving wetland basin. Landscape modifications such as spoil banks associated with oil and gas access canals negate the benefits of river water introduction by limiting wetland-water interaction and should be removed in conjunction with river diversion implementation for effective wetland restoration.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Barras, J., S. Beville, D. Britsch, S. Hartley, S. Hawes, J. Johnston, P. Kemp, Q. Kinler, A. Martucci, J. Porthouse, D. Reed, K. Roy, S. Sapkota, and J. Suhayda. 2003. Historical and projected coastal Louisiana land changes: 1978–2050. USGS Open File Report 03-334 (Revised January 2004).
Baumann, R. H., J. W. Day, and C. A. Miller. 1984. Mississippi deltaic wetland survival: sedimentation versus coastal submergence. Science 224: 1093–1095.
Boesch, D. F. 1996. Science and management in four U.S. coastal ecosystems dominated by land-ocean interactions. Journal of Coastal Conservation 2: 103–114.
Boesch, D. F., M. N. Josselyn, A. J. Mehta, J. T. Morris, W. K. Nuttle, C. A. Simenstad, and D. J. P. Swift. 1994. Scientific assessment of coastal wetland loss, restoration and management. Journal of Coastal Research Special Issue No. 20.
Boumans, R. M. J. and J. W. Day. 1993. High precision measurements of sediment elevation in shallow coastal areas using a sedimentation-erosion table. Estuaries 16: 375–380.
Boumans, R. M. and J. W. Day. 1994. Effects of two Louisiana marsh management plans on water and materials flux and short-term sedimentation. Wetlands 14: 247–261.
Bryant, J. C. and R. H. Chabreck. 1998. Effects of impoundment on vertical accretion of coastal marsh. Estuaries 21: 416–422.
Cahoon, D. R., J. W. Day, and D. J. Reed. 1999. The Influence of Surface and Shallow Subsurface soil Processes on Wetland Elevation: a Synthesis. Current Topics in Wetland Biogeochemistry 3: 72–88.
Cahoon, D. R., P. E. Marin, B. K. Black, and J. C. Lynch. 2000. A method for measuring vertical accretion, elevation, and compaction of soft, shallow-water sediments. Journal of sedimentary research 70: 1250–1253.
Cahoon, D. R. and D. J. Reed. 1994. Relationships among marsh surface topography, hydroperiod, and soil accretion in a deteriorating louisiana salt marsh. Journal of Coastal Research 11: 357–369.
Cahoon, D. R., D. J. Reed, and J. W. Day. 1995. Estimating shallow subsidence in microtidal salt marshes of the southeastern United States: Kaye and Barghoorn revisited. Marine Geology 128: 1–9.
Cahoon, D. R. and R. E. Turner. 1989. Accretion and canal impacts in a rapidly subsiding wetland II. Feldspar marker horizon technique. Estuaries 12: 260–268.
Chatry, M. and D. Chew. 1985. Freshwater diversion in coastal Louisiana: recommendations for development of management criteria. p. 71–84, In 4th Coastal Marsh and Estuary Mgt. Symposium.
Chatry, M., R. J. Dugas, and K. A. Easley. 1983. Optimum salinity regime for oyster production on Louisiana’s state seed grounds. Contributions in Marine Science 26: 81–94.
Childers, D. L., F. H. Sklar, B. Drake, and T. Jordan. 1993. Seasonal measurements of sediment elevation in three mid-atlantic estuaries. Journal of Coastal Research 9: 986–1003.
Colten, C. (ed.) 2000. Transforming New Orleans and its Environs. University of Pittsburgh Press, Pittsburgh, PA, USA.
Crandall, M. E. and J. L. Lindsey. 1981. Establishment of controlled freshwater diversion of the Mississippi River into Louisiana coastal zone. p. 139–146, In R. D. Cross and D. L. Williams (eds.) Procedings of the National Symposium on Freshwater Inflow to Estuaries, Slidell, LA, USA.
Davis, D. W. 2000. Historical perspective on crevasses, levees, and the Mississippi River. p. 84–106, In C. E. Colten (ed.) Transforming New Orleans and its Environs. University of Pittsburgh Press, Pittsburgh, PA, USA.
Day, J. W., L. D. Britsch, S. Hawes, G. Shaffer, D. J. Reed, and D. Cahoon. 2000. Pattern and process of land loss in the Mississippi Delta: a spatial and temporal analysis of wetland habitat change. Estuaries 23: 425–438.
Day, J. W., J. Martin, L. Cardoch, and P. Templete. 1997. System functioning as a basis for sustainable management of deltaic ecosystems. Coastal Management 25: 115–153.
Day, J. W., N. P. Psuty, and B. C. Perez. 2001. The role of pulsing events in the functioning of coastal barriers and wetlands: implications for human impact, management and the response to sea level rise. p. 633–659, In M. P. Weinstein and D. A. Kreeger (eds.) Concepts and Controversies in Tidal Marsh Ecology. Kuwer Acedemic Publishers, Boston, MA, USA.
Day, J. W., J. Rybczyk, F. Scarton, A. Rismondo, D. Are, and G. Cecconi. 1999. Soil accretionary dynamics, sea-level rise and the survival of wetlands in Venice Lagoon: a field and modeling approach. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 49: 607–628.
Day, J. W. and P. H. Templet. 1989. Consequences of sea level rise: implications from the Mississippi delta. Coastal Management 17: 241–257.
Deegan, L. A., H. M. Kennedy, and C. Neill. 1984. Natural factors and human modifications contributing to marsh loss in Louisiana’s Mississippi River deltaic plain. Environmental Management 8: 519–528.
DeLaune, R. D., R. H. Baumann, and J. G. Gosselink. 1983. Relationships among vertical accretion, coastal submergence, and erosion in a Louisiana Gulf Coast marsh. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology 53: 0147–0157.
DeLaune, R. D., R. J. Buresh, and W. H. Patrick. 1979. Relationship of soil properties to standing crop biomass of Spartina alternafloria in a Louisiana marsh. Estuarine and Coastal Marine Science 8: 477–487.
DeLaune, R. D., A. Jugsujinda, G. W. Peterson, and W. H. Patrick. 2003. Impact of Mississippi River freshwater reintroduction on enhancing marsh accretionary processes in a Louisiana estuary. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 58: 653–662.
Delaune, R. D. and S. R. Pezeshki. 2003. The role of soil organic carbon in maintaining surface elevation in rapidly subsiding U.S. Gulf of Mexico coastal marshes. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution 3: 167–179.
Gagliano, S. M. 1999. Faulting, subsidence and land loss in coastal Louisiana: in Coast 2050: Toward a Sustainable Coastal Louisiana, Appendix B, Section 3, p. 21–72, In Louisiana Coastal Wetlands Conservation and Restoration Task Force and Wetlands Conservation Restoration Authority. Louisiana Department of Natural Resources, Baton Rouge, LA, USA. (http://www.coast2050.gov/2050reports.htm).
Hackney, C. T. and A. A. de la Cruz. 1983. Effects of winter fire on the productivity and species composition of two brackish marsh communities in Mississippi. International Journal of Ecology and Environmental Science 9: 185–208.
Hatton, R. S., R. D. Delaune, and J. W. H. Patrick. 1983. Sedimentation, accretion, and subsidence in marshes of Baritaria Basin, Louisiana. Limnology and Oceanography 28: 494–502.
Haywood, E. L. and W. M. Boshart. 1998. West pointe a la hache freshwater diversion: three-year comprehensive report. Louisiana Department of Natural Resources/Coastal Restoration Division, Baton Rouge, LA, USA. Monitoring Series No. BA-04-MSTY-0498-1
Ibanez, C., A. Canicio, J. W. Day, and A. Curco. 1997. Morphologic evolution, relative sea level rise and sustainable management of water and sediment in the Ebre Delta. Journal of Coastal Conservation 3: 191–202.
Kesel, R. H. 1988. The decline in the suspended load of the Lower Mississippi River and its influence on adjacent wetlands. Environmental and Geological Water Science 11: 271–281.
Kesel, R. H. 1989. The role of the lower Mississippi River in wetland loss in southeastern Louisiana, USA. Environmental and Geological Water Science 13: 183–193.
Lane, R. R., J. W. Day, and B. Thibodeaux. 1999. Water quality analysis of a freshwater diversion at Caernarvon, Louisiana. Estuaries 22: 327–336.
Lane, R. 2003. The effect of water quality of riverine input into coastal wetlands. Ph.D. Dissertation. Deptartment of Oceanography and Coastal Sciences, Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge, LA, USA.
LDNR. 1998. Coast 2050: Toward a Sustainable Coastal Louisiana Louisiana Coastal Wetlands Conservation and Restoration Task Force and the Wetlands Conservation and Restoration Authority. Louisiana Department of Natural Resources, Baton Rouge, LA, USA.
Lynch, J. J. 1941. The place of burning in wildlife management of the Gulf coast wildlife refuges. Journal of Wildlife Management 5: 454–457.
Mancil, E. M. 1972. An historical geography of industrial cypress lumbering. Ph.D. Dissertation. Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge, Louisiana.
Mendelssohn, I. A. and K. L. Mckee. 2000. Salt marshes and mangroves. p. 501–536, In M. G. Barbour and W. D. Billings (eds.) North American Vegetation. Cambridge University Press, New York, NY, USA.
Mendelssohn, I. A., K. L. McKee, and J. W. H. Patrick. 1981. Oxygen deficiency in Spartina alterniflora roots: metabolic adaption to anoxia. Science 214: 439–441.
Mendelssohn, I. A. and J. T. Morris. 2000. Eco-physiological controls on the productivity of Spartina alterniflora loisel. p. 59–80, In M. P. Weinstein and D. A. Kreeger (eds.) Concepts and Controversies in Tidal Marsh Ecology. Kuwer Acedemic Publishers, Boston, MA, USA.
Mossa, J. 1996. Sediment dynamics in the lowermost Mississippi River. Engineering Geology 45: 457–479.
Nyman, J. A. and R. H. Chabreck. 1995. Fire in coastal marshes: history and recent concerns. p. 135–141, In R. T. Engstrom, S. I. Cerulean, and R. T. Engstrom (eds.) Proceedings 19th Tall Timbers Fire Ecology Conference-Fire in wetlands: a management perspective. Tall Timbers Research, Inc. Tallahassee, FL, USA.
Penland, S., R. Boyd, and J. R. Suter. 1988. Transgressive depositional systems of the Mississippi Delta plain: a model for barrier shoreline and shelf sand development. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology 58: 932–949.
Penland, S. and K. E. Ramsey. 1990. Relative sea-level rise in Louisiana and the Gulf of Mexico: 1908–1988. Journal of Coastal Research 6: 323–342.
Pont, D., J. Day, P. Hensel, E. Franquet, F. Torre, P. Rioual, C. Ibanez, and E. Coulet. 2002. Response scenarios for the deltaic plain of the Rhône in the face of an acceleration in the rate of sea level rise, with a special attention for Salicornia-type environments. Estuaries 25: 337–358.
Reed, D. J. 1992. Effect of weirs on sediment deposition in Louisiana coastal marshes. Environmental Management 16: 55–65.
Reed, D. J., N. D. Luca, and A. L. Foote. 1997. Effect of hydrolic management on marsh surface sediment deposition in coastal Louisiana. Estuaries 20: 301–311.
Roberts, H. H. 1997. Dynamic changes of the holocene Mississippi river delta plain: the delta cycle. Journal of Coastal Research 13: 605–627.
Salinas, L. M., R. D. DeLaune, and W. H. Patrick. 1986. Changes occurring along a rapidly submerging coastal area: Louisiana. Journal of Coastal Research 2: 269–284.
Sall, J. and A. Lehman. 1996. JMP Start Statistics, a Guide to Statistical and Data Analysis using JMP and JMP IN Software. Duxbury Press, New York, NY, USA.
Scruton, P. C. 1960. Delta building and the deltaic sequence. Recent Sediments, NW Gulf Coast of Mexico AAPG Symposium., p. 82–102.
Swenson, E. M. and R. E. Turner. 1987. Spoil banks: effects on a coastal marsh water-level regime. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 24: 599–609.
Templet, P. H. and K. J. Meyer-Arendt. 1988. Louisiana wetland loss: a regional water management approach to the problem. Environmental Management 12: 181–192.
Viosca, P. 1931. Spontaneous combustion in the Marshes of Southern Louisiana. Ecology 12: 439–442.
Welder, F. A. 1959. Processes of deltaic sedimentation in the lower Mississippi River. Louisiana State University, Coastal Studies Institute Technical Report, Baton Rouge, LA, USA.
Wheelock, K. 2003. Pulsed river flooding effects on sediment deposition in Breton Sound estuary, Louisiana. M.S. Thesis. Deptartment of Oceanography and Coastal Sciences, Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge, LA, USA.
Whipple, S. A. and D. White. 1977. The effects of fire on two Louisiana marshes. Association of Southeastern Biologists Bulletin. 24: 95.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lane, R.R., Day, J.W. & Day, J.N. Wetland surface elevation, vertical accretion, and subsidence at three Louisiana Estuaries receiving diverted Mississippi River water. Wetlands 26, 1130–1142 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1672/0277-5212(2006)26[1130:WSEVAA]2.0.CO;2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1672/0277-5212(2006)26[1130:WSEVAA]2.0.CO;2