Abstract
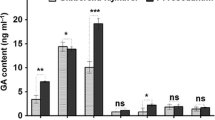
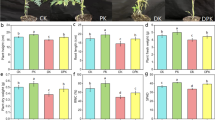
Hemin can improve the stress resistance of plants through the heme oxygenase system. Additionally, substances contained in plants, such as secondary metabolites, can improve stress resistance. However, few studies have explored the effects of hemin on secondary metabolite content. Therefore, the effects of hemin on saponin synthesis and the mechanism of plant injury relief by hemin in Conyza blinii were investigated in this study. Hemin treatment promoted plant growth and increased the antioxidant enzyme activity and saponin content of C. blinii under osmotic stress and cold stress. Further study showed that hemin could provide sufficient precursors for saponin synthesis by improving the photosynthetic capacity of C. blinii and increasing the gene expression of key enzymes in the saponin synthesis pathway, thus increasing the saponin content. Moreover, the promotion effect of hemin on saponin synthesis is dependent on heme oxygenase-1 and can be reversed by the inhibitor Zn-protoporphyrin-IX (ZnPPIX). This study revealed that hemin can increase the saponin content of C. blinii and alleviate the damage caused by abiotic stress, and it also broadened the understanding of the relationship between hemin and secondary metabolites in plant abiotic stress relief.
概要
目的
研究氯化血红素对金龙胆草皂苷含量的影响,以及与植物非生物胁迫的相关性。
创新点
通过施加外源氯化血红素研究金龙胆草中皂苷的变化与冷胁迫或渗透胁迫的相关性。
方法
在渗透胁迫和低温胁迫下,施加外源氯化血红素及其抑制剂,检测并分析金龙胆草多项生理指标、皂苷含量差异和关键基因表达量差异。
结论
氯化血红素能通过依赖血红素加氧酶-1的调控方式,提高金龙胆草皂苷的含量,从而减轻非生物胁迫对金龙胆草的伤害。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bacon CW, Palencia ER, Hinton DM, 2015. Abiotic and biotic plant stress-tolerant and beneficial secondary metabolites produced by endophytic Bacillus species. In: Arora NK (Ed.), Plant Microbes Symbiosis: Applied Facets. Springer, New Delhi, p.163–177. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-81-322-2068-8_8
Baudouin E, Frendo P, le Gleuher M, et al., 2004. A Medicago sativa haem oxygenase gene is preferentially expressed in root nodules. J Exp Bot, 55(394):43–47. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erh020
Becker EM, Cardoso DR, Skibsted LH, 2011. Quenching of excited states of red-pigment zinc protoporphyrin IX by hemin and natural reductors in dry-cured hams. Eur Food Res Technol, 232(2):343–349. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-010-1392-6
Chen H, Cheng ZJ, Ma XD, et al., 2013. A knockdown mutation of YELLOW-GREEN LEAF2 blocks chlorophyll biosynthesis in rice. Plant Cell Rep, 32(12):1855–1867. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-013-1498-y
Chen Q, Gong CY, Ju X, et al., 2018. Hemin through the heme oxygenase 1/ferrous iron, carbon monoxide system involved in zinc tolerance in Oryza sativa L. J Plant Growth Regul, 37(3):947–957. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-018-9793-z
Dennery PA, Visner G, Weng YH, et al., 2003. Resistance to hyperoxia with heme oxygenase-1 disruption: role of iron. Free Radic Biol Med, 34(1):124–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0891-5849(02)01295-9
Ekhtari S, Razeghi J, Hasanpur K, et al., 2019. Different regulations of cell-type transcription by UV-B in multicellular green alga Volvox carteri. Plant Signal Behav, 14(11):1657339. https://doi.org/10.1080/15592324.2019.1657339
Fu GQ, Zhang LF, Cui WT, et al., 2011. Induction of heme oxygenase-1 with β-CD-hemin complex mitigates cadmium-induced oxidative damage in the roots of Medicago sativa. Plant Soil, 345(1–2):271–285. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-011-0779-x
Geng DS, Zhao LP, Shi RM, et al., 2013. A study on antitussive, expectorant and anti-inflammatory effects of total saponins from Uyghur Herb Nigella glandulifera Freyn. J Xinjiang Med Univ, 36(7):908–911 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1009-5551.2013.07.005
Ghasemzadeh A, Jaafar HZE, 2011. Effect of CO2 enrichment on synthesis of some primary and secondary metabolites in ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe). Int J Mol Sci, 12(2):1101–1114. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12021101
Gheisari HR, Møller JKS, Adamsen CE, et al., 2010. Sodium chloride or heme protein induced lipid oxidation in raw, minced chicken meat and beef. Czech J Food Sci, 28(5):364–375. https://doi.org/10.17221/182/2009-CJFS
Gitelson AA, Gritz Y, Merzlyak MN, 2003. Relationships between leaf chlorophyll content and spectral reflectance and algorithms for non-destructive chlorophyll assessment in higher plant leaves. J Plant Physiol, 160(3):271–282. https://doi.org/10.1078/0176-1617-00887
Ishikawa K, Sugawara D, Wang XP, et al., 2001. Heme oxygenase-1 inhibits atherosclerotic lesion formation in LDL-receptor knockout mice. Circ Res, 88(5):506–512. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.RES.88.5.506
Jiang Y, Sun FF, Zhan YG, et al., 2019. Effect of carbon monoxide on growth and triterpenoid production in Betula platyphylla suspension cells. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs, 50(15):3681–3686 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2019.15.025
Jin QJ, Zhu KK, Xie YJ, et al., 2013. Heme oxygenase-1 is involved in ascorbic acid-induced alleviation of cadmium toxicity in root tissues of Medicago sativa. Plant Soil, 366(1–2):605–616. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-012-1451-9
Jin QJ, Cui WT, Dai C, et al., 2016. Involvement of hydrogen peroxide and heme oxygenase-1 in hydrogen gas-induced osmotic stress tolerance in alfalfa. Plant Growth Regul, 80(2):215–223. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-016-0159-x
Jung HY, Kim DW, Yim HS, et al., 2016. Heme oxygenase-1 protects neurons from ischemic damage by upregulating expression of Cu,Zn-superoxide dismutase, catalase, and brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the rabbit spinal cord. Neurochem Res, 41(4):869–879. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-015-1764-1
Li H, Jiang M, Che LL, et al., 2012. BjHO-1 is involved in the detoxification of heavy metal in India mustard (Brassica juncea). BioMetals, 25(6):1269–1279. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-012-9588-9
Liu HY, Hu CX, Sun NN, et al., 2017. A triterpenoidal saponin fraction of Conyza blinii H.Lév. is a dual-targeting autophagy inhibitor for HeLa cells. RSC Adv, 7(39):24291–24297. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA02626A
Liu P, Zhou LJ, Su YF, et al., 2011. Effects of total saponins from Conyza blinii on the apoptosis of Hela cells and SPC-A1 cells. China Pharmacy, 22(35):3288–3291 (in Chinese).
Liu YY, Chen Q, Li N, et al., 2016. Heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) promote anthocyanin accumulation in the hypocotyl of radish sprouts. Acta Horticult Sin, 43(3):507–514 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2015-0693
Luo WW, Wang Y, Yang HW, et al., 2018. Heme oxygenase-1 ameliorates oxidative stress-induced endothelial senescence via regulating endothelial nitric oxide synthase activation and coupling. Aging, 10(7):1722–1744. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.101506
Ma L, Liu JG, 2014. The protective activity of Conyza blinii saponin against acute gastric ulcer induced by ethanol. J Ethnopharmacol, 158:358–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/jjep.2014.10.052
Ma L, Liu HY, Meng LP, et al., 2017a. Evaluation of the anti-cancer activity of the triterpenoidal saponin fraction isolated from the traditional Chinese medicine Conyza blinii H. Lév. RSC Adv, 7(6):3408–3412. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA26361E
Ma L, Liu HY, Qin P, et al., 2017b. Saponin fraction isolated from Conyza blinii H. Lév. demonstrates strong anti-cancer activity that is due to its NF-κB inhibition. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 483(1):779–785. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.12.066
Maines MD, Panahian N, 2001. The heme oxygenase system and cellular defense mechanisms. Do HO-1 and HO-2 have different functions? In: Roach RC, Wagner PD, Hackett PH (Eds.), Hypoxia: From Genes to the Bedside. Springer, Boston, p.249–272. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4757-3401-0_17
Matthus E, Wilkins KA, Swarbreck SM, et al., 2019. Phosphate starvation alters abiotic-stress-induced cytosolic free calcium increases in roots. Plant Physiol, 179(4):1754–1767. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.18.01469
Mei YQ, Song SQ, 2010. Response to temperature stress of reactive oxygen species scavenging enzymes in the cross-tolerance of barley seed germination. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 11(12):965–972. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1000147
Müllebner A, Moldzio R, Redl H, et al., 2015. Heme degradation by heme oxygenase protects mitochondria but induces ER stress via formed bilirubin. Biomolecules, 5(2):679–701. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom5020679
Noriega G, Cruz DS, Batlle A, et al., 2012. Heme oxygenase is involved in the protection exerted by jasmonic acid against cadmium stress in soybean roots. J Plant Growth Regul, 31(1):79–89. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-011-9221-0
Noriega GO, Balestrasse KB, Batlle A, et al., 2004. Heme oxygenase exerts a protective role against oxidative stress in soybean leaves. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 323(3):1003–1008. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.08.199
Nzowa LK, Barboni L, Teponno RB, et al., 2010. Rheediinosides A and B, two antiproliferative and antioxidant triterpene saponins from Entada rheedii. Phytochemistry, 71(2–3):254–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2009.10.004
Orrenius S, Kass GEN, Nicotera P, 1992. Oxygen free radicals and cell death. Neurochem Int, 21(Suppl):S13. https://doi.org/10.1016/0197-0186(92)91761-K
Otterbein LE, Soares MP, Yamashita K, et al., 2003. Heme oxygenase-1: unleashing the protective properties of heme. Trends Immunol, 24(8):449–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1471-4906(03)00181-9
Ozdener Y, Aydin BK, 2010. The effect of zinc on the growth and physiological and biochemical parameters in seedlings of Eruca sativa (L.) (Rocket). Acta Physiol Plant, 32(3):469–476. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-009-0423-z
Podkalicka P, Mucha O, Józkowicz A, et al., 2018. Heme oxygenase inhibition in cancers: possible tools and targets. Contemp Oncol, 2(1A):23–32. https://doi.org/10.5114/wo.2018.73879
Shah K, Nahakpam S, 2012. Heat exposure alters the expression of SOD, POD, APX and CAT isozymes and mitigates low cadmium toxicity in seedlings of sensitive and tolerant rice cultivars. Plant Physiol Biochem, 57:106–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2012.05.007
Shamloul R, Wang R, 2006. Increased intracavernosal pressure response in hypertensive rats after chronic hemin treatment. J Sex Med, 3(4):619–627. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1743-6109.2006.00211.x
Su YF, Koike K, Guo DA, et al., 2001. New apiose-containing triterpenoid saponins from Conyza blinii. Tetrahedron, 57(31):6721–6726. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-4020(01)00632-9
Sun R, Liu S, Gao JL, et al., 2014. Cloning and expression analysis of 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate synthase gene from the medicinal plant Conyza blinii H.Lév. Turk J Biol, 38(5):664–670. https://doi.org/10.3906/biy-1401-91
Sun WJ, Zhan JY, Zheng TR, et al., 2018. The jasmonate-responsive transcription factor CbWRKY24 regulates terpenoid biosynthetic genes to promote saponin biosynthesis in Conyza blinii H. Lév. J Genet, 97(5):1379–1388. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-018-1026-5
Troxler RF, 1972. Synthesis of bile pigments in plants. Formation of carbon monoxide and phycocyanobilin in wild-type and mutant strains of the alga, Cyanidium caldarium. Biochemistry, 11(23):4235–4242. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi00773a007
Velini ED, Trindade MLB, Alves E, et al., 2005. Eucalyptus ESTs corresponding to the protoporphyrinogen IX oxidase enzyme related to the synthesis of heme, chlorophyll, and to the action of herbicides. Genet Mol Biol, 28(3 Suppl):548–554. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1415-47572005000400009
Wagener FADTG, Volk HD, Willis D, et al., 2003. Different faces of the heme-heme oxygenase system in inflammation. Pharmacol Rev, 55(3):551–571. https://doi.org/10.1124/pr.55.3.5.
Wang J, Doré S, 2007. Heme oxygenase-1 exacerbates early brain injury after intracerebral haemorrhage. Brain, 130(6):1643–1652. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awm095
Wang SQ, Wang XM, Sun FF, et al., 2019. Carbon monoxide: effect on growth and triterpene accumulation of phellinus linteus mycelium. Chin Agric Sci Bull, 35(21):90–95 (in Chinese).
Xiong CW, Li XW, Xu DJ, et al., 2017. Determination of total saponins in quinoa by spectrophotometry. J Anhui Agric Sci, 45(26):96–98,121 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2017.26.029
Xuan W, Zhu FY, Xu S, et al., 2008. The heme oxygenase/carbon monoxide system is involved in the auxin-induced cucumber adventitious rooting process. Plant Physiol, 148(2):881–893. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.108.125567
Yang CR, He ZT, Li XC, et al., 1989. Blinin, a neoclerodane diterpene from Conyza blinii. Phytochemistry, 28(11):3131–3134. https://doi.org/10.1016/0031-9422(89)80292-4
Yannarelli GG, Noriega GO, Batlle A, et al., 2006. Heme oxygenase up-regulation in ultraviolet-B irradiated soybean plants involves reactive oxygen species. Planta, 224(5):1154–1162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-006-0297-x
Zhan JY, Yang Q, Lin ZY, et al., 2021. Enhanced antioxidant capacity and upregulated transporter genes contribute to the UV-B-induced increase in blinin in Conyza blinii. Environ Sci Pollut Res, 28(11):13275–13287. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11502-8
Zheng TR, Wang MJ, Zhan JY, et al., 2020. Ferrous iron-induced increases in capitate glandular trichome density and upregulation of CbHO-1 contributes to increases in blinin content in Conyza blinii. Planta, 252(5):81. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-020-03492-1
Zhu ZB, Huang YF, Wu X, et al., 2019. Increased antioxidative capacity and decreased cadmium uptake contribute to hemin-induced alleviation of cadmium toxicity in Chinese cabbage seedlings. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf, 177: 47–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.03.113
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Sichuan Science and Technology Program (No. 2020YFH0136), China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Junyi ZHAN and Tianrun ZHENG designed research; Junyi ZHAN, Tianrun ZHENG, Wenjun SUN, Ming YANG, and
Corresponding author
Additional information
Compliance with ethics guidelines
Tianrun ZHENG, Junyi ZHAN, Ming YANG, Maojia WANG, Wenjun SUN, Zhi SHAN, and Hui CHEN declare that they have no conflict of interest.
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, T., Zhan, J., Yang, M. et al. Hemin-induced increase in saponin content contributes to the alleviation of osmotic and cold stress damage to Conyza blinii in a heme oxygenase 1-dependent manner. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 22, 682–694 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2000697
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2000697