Abstract
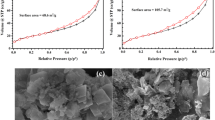
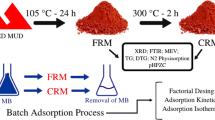
Adsorption of Escherichia coli (E. coli) cells on red mud (RM) is important in the interactions between RM and bacteria. The objective of this work is to study adsorption of E. coli onto RM and to determine its influence in relation to the surface properties of RM. The effects of different calcination temperatures on the surface properties of red mud were investigated by thermogravimetric analysis, x-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, Brunauer, Emmett, Teller (surface measurement)/N2 adsorption method, and zeta potential analysis. A higher adsorption capacity was observed from RM calcinated at 700 °C (RM700) due to larger pores formed on the surface of RM. The correlation between the adsorption efficacy and surface properties of RM is discussed and the extended Derjaguin-Landau-Verwey-Overbeek theory suggests that when the adsorption reaches equilibrium, the increased adsorption of E. coli onto RM is due to the smaller energy barrier between E. coli and RM700 as compared with that between E. coli and raw RM (RM0).









Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.C. Sahu, R. Patel, and B.C. Ray: Utilization of activated CO2-neutralized red mud for removal of arsenate from aqueous solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 179, 1007 (2010).
W.W. Huang, S.B. Wang, Z.H. Zhu, L. Lia, X.D. Yao, V. Rudolph, and F. Haghseresht: Phosphate removal from wastewater using red mud. J. Hazard. Mater. 158, 35 (2008).
S.J. Palmer, R.L. Frost, and T. Nguyen: Hydrotalcites and their role in coordination of anions in Bayer liquors: Anion binding in layered double hydroxides. Coord. Chem. Rev. 253, 250 (2009).
S.B. Wang, H.M. Ang, and M.O. Tade: Novel applications of red mud as coagulant, adsorbent and catalyst for environmentally benign processes. Chemosphere 72, 1621 (2008).
A.R. Hind, S.K. Bhargava, and S.C. Grocott: The surface chemistry of Bayer process solids: A review. Colloids Surf., A 146, 359 (1999).
Y. Zhang, Y. Qu, and S. Wu: Engineering geological properties and comprehensive utilization of the solid waste (red mud) in aluminium industry. Environ. Geol. 41, 249 (2001).
C. Brunori, C. Cremisini, P. Massanisso, V. Pinto, and L. Torricelli: Reuse of a treated red mud bauxite waste: Studies on environmental compatibility. J. Hazard. Mater. 117, 55 (2005).
R.K. Paramguru, P.C. Rath, and V.N. Misra: Trends in red mud utilization - a review. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 26, 1 (2004).
Y.J. Liu, R. Naidu, and H. Ming: Red mud as an amendment for pollutants in solid and liquid phases. Geoderma 163, 1 (2011).
S.M. Barns and S.A. Nierzwicki-Bauer: Microbial diversity in modern subsurface, ocean, surface environments, in Geomicrobiology: Interactions Between Microbes and Minerals, Vol. 35, edited by J.F. Banfield and K. H. Nealson (Rev. Mineral. Geochem., Springer-Verlag Ibérica, 1997), p. 35.
J.W. Foppena, Y. Liemb, and J. Schijvenc: Effect of humic acid on the attachment of Escherichia coli in columns of goethite-coated sand. Water Res. 42, 211 (2008).
S.M. Dorner, W.B. Anderson, T. Gaulin, H.L. Candon, R.M. Slawson, P. Payment, and P.M. Huck: Pathogen and indicator variability in a heavily impacted watershed. J. Water Health 5, 241 (2007).
G.B. McBride and M.N. Mittinity: Explaining differential timing of peaks of a pathogen versus a faecal indicator during flood events. In MODSIM 2007: International Congress on Modelling and Simulation: Land, Water and Environmental Management: Integrated Systems for Sustainability, L. Oxley and D. Kulasiri, eds. (Modelling & Simulation Soc Australia & New Zealand Inc., Christchurch, New Zealand, 2007); p. 2417.
T. Guo, S.J. Cao, R. Su, Z.Q. Li, P. Hu, and Z. Xu: Adsorptive property of Cu2+-loaded montmorillonite clays for Escherichia coli K88 in vitro. J. Environ. Sci. 23, 1808 (2011).
R.W. Muirhead, R.P. Collins, and P.J. Bremer: Erosion and subsequent transport state of Escherichia coli from cowpats. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 71, 2875 (2005).
D.M. Oliver, C.D. Clegg, A.L. Heathwaite, and P.M. Haygarth: Preferential attachment of Escherichia coli to different particle size fractions of an agricultural grassland soil. Water Air Soil Pollut. 185, 369 (2007).
W. Zhang, B. Rittmann, and Y.S. Chen: Size effects on adsorption of hematite nanoparticles on E. coli cells. Environ. Sci. Technol. 45, 2172 (2011).
W.P. Johnson and B.E. Logan: Enhanced transport of bacteria in porous media by sediment-phase and aqueous-phase natural organic matter. Water Res. 30, 923 (1996).
X.P. Zheng, P.J. Arps, and R.W. Smith: Adhesion of two bacteria onto dolomite and apatite: Their effect on dolomite depression in anionic flotation. Int. J. Miner. Process. 62, 159 (2001).
G.E. Ho, R.A. Gibbs, and K. Mathew: Bacteria and virus removal from secondary effluent in sand and red mud columns. Water Sci. Technol. 23, 261 (1991).
Z.C. Zhen, Y.H. Zhang, J.H. Ji, Y.X. Yin, W.S. Tong, and P.K. Chu: Novel functional materials with active adsorption and antimicrobial properties. Mater. Lett. 89, 19 (2012).
P. Castaldi, M. Silvetti, L. Santona, S. Enzo, and P. Melis: XRD, FTIR, and thermal analysis of bauxite ore-processing waste (red mud) exchanged with heavy metals. Clays Clay Miner. 56, 461 (2008).
P. Castaldi, L. Santona, C. Cozza, V. Giuliano, C. Abruzzese, V. Nastro, and P. Melis: Thermal and spectroscopic studies of zeolites exchanged with metal cations. J. Mol. Struct. 734, 99 (2005).
J.M.R. Mercury, A.A. Cabral, A.E.M. Paiva, R.S. Angelica, R.F. Neves, and T. Scheller: Thermal behavior and evolution of the mineral phases of Brazilian red mud. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 104, 635 (2011).
M. Laskou, G. Margomenou-Leonidopoulou, and V. Balek: Thermal characterization of bauxite samples. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 84, 141 (2006).
A. Alp and M.S. Goral: The influence of soda additive on the thermal properties of red mud. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 73, 201 (2003).
A. Atasoy: An investigation on the characterization and thermal analysis of the Aughinish red mud. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 81, 357 (2005).
V.M. Sglavo, S. Maurina, A. Conci, A. Salviati, G. Carturan, and G. Cocco: Bauxite ‘red mud’ in the ceramic industry. Part 2: Production of clay-based ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 20, 245 (2000).
C.F. Linares, S. Sanchez, C.U. de Navarro, K. Rodriguez, and M.R. Goldwasser: Study of cancrinite-type zeolites as possible antacid agents. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 77, 215 (2005).
Y.L. Ma, B. Yang, and L. Xie: Adsorptive property of Cu2+-ZnO/cetylpyridinium–montmorillonite complexes for pathogenic bacterium in vitro. Colloids Surf., B 79, 390 (2010).
S. Karaca, A. Gurses, M. Ejder, and M. Acikyildiz: Adsorptive removal of phosphate from aqueous solutions using raw and calcinated dolomite. J. Hazard. Mater. 128, 273 (2006).
Y.T. He, J.M. Wan, and T. Tokunaga: Kinetic stability of hematite nanoparticles: The effect of particle sizes. J. Nanopart. Res. 10, 321 (2008).
D.R.E. Snoswell, J.M. Duan, D. Fornasiero, and J. Ralston: Colloid stability of synthetic titania and the influence of surface roughness. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 286, 526 (2005).
M. Hermansson: The DLVO theory in microbial adhesion. Colloids. Surf., B 14, 105 (1999).
Z. Adamczyk, and P. Weronski: Application of the DLVO theory for particle deposition problems. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 83, 137 (1999).
M. Bostrom, D.R.M. Williams, and B.W. Ninham: Specific ion effects: Why DLVO theory fails for biology and colloid systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 1681031–1681034 (2001).
Y. Cengeloglu, A. Tor, M. Ersoz, and G. Arslan: Removal of nitrate from aqueous solution by using red mud. Sep. Purif. Technol. 51, 374 (2006).
Acknowledgments
This study was jointly supported by National High Technology Research and Development Program (863 Program 2012AA06A109) of China, the open foundation of National Laboratory of Mineral Materials of China University of Geosciences (Grant Nos. 519002310062 and 08A005), as well as Hong Kong Research Grants Council (RGC) General Research Funds (GRF) Nos. CityU 112510 and 112212.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tong, W., Zhang, Y., Zhen, Z. et al. Effects of surface properties of red mud on interactions with Escherichia coli. Journal of Materials Research 28, 2332–2338 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2013.53
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2013.53