Abstract
A review of solar cycle prediction methods and their performance is given, including forecasts for cycle 24. The review focuses on those aspects of the solar cycle prediction problem that have a bearing on dynamo theory. The scope of the review is further restricted to the issue of predicting the amplitude (and optionally the epoch) of an upcoming solar maximum no later than right after the start of the given cycle.
Prediction methods form three main groups. Precursor methods rely on the value of some measure of solar activity or magnetism at a specified time to predict the amplitude of the following solar maximum. Their implicit assumption is that each numbered solar cycle is a consistent unit in itself, while solar activity seems to consist of a series of much less tightly intercorrelated individual cycles. Extrapolation methods, in contrast, are based on the premise that the physical process giving rise to the sunspot number record is statistically homogeneous, i.e., the mathematical regularities underlying its variations are the same at any point of time and, therefore, it lends itself to analysis and forecasting by time series methods. Finally, instead of an analysis of observational data alone, model based predictions use physically (more or less) consistent dynamo models in their attempts to predict solar activity.
In their overall performance during the course of the last few solar cycles, precursor methods have clearly been superior to extrapolation methods. Nevertheless, most precursor methods overpredicted cycle 23, while some extrapolation methods may still be worth further study. Model based forecasts have not yet had a chance to prove their skills. One method that has yielded predictions consistently in the right range during the past few solar cycles is that of K. Schatten et al., whose approach is mainly based on the polar field precursor.
The incipient cycle 24 will probably mark the end of the Modern Maximum, with the Sun switching to a state of less strong activity. It will therefore be an important testbed for cycle prediction methods and, by inference, for our understanding of the solar dynamo.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
Solar cycle prediction is an extremely extensive topic, covering a very wide variety of proposed prediction methods and prediction attempts on many different timescales, ranging from short term (month-year) forecasts of the runoff of the ongoing solar cycle to predictions of long term changes in solar activity on centennial or even millennial scales. As early as 1963, Vitinsky published a whole monograph on the subject, later updated and extended (Vitinsky, 1963, 1973). More recent overviews of the field or aspects of it include Hathaway (2009), Kane (2001), and Pesnell (2008). In order to narrow down the scope of the present review, we constrain our field of interest in two important respects.
Firstly, instead of attempting to give a general review of all prediction methods suggested or citing all the papers with forecasts, here we will focus on those aspects of the solar cycle prediction problem that have a bearing on dynamo theory. We will thus discuss in more detail empirical methods that, independently of their success rate, have the potential of shedding some light on the physical mechanism underlying the solar cycle, as well as the prediction attempts based on solar dynamo models.
Secondly, we will here only be concerned with the issue of predicting the amplitude (and optionally the epoch) of an upcoming solar maximum no later than right after the start of the given cycle. This emphasis is also motivated by the present surge of interest in precisely this topic, prompted by the unusually long and deep recent solar minimum and by sharply conflicting forecasts for the maximum of the incipient solar cycle 24.
As we will see, significant doubts arise both from the theoretical and observational side as to what extent such a prediction is possible at all (especially before the time of the minimum has become known). Nevertheless, no matter how shaky their theoretical and empirical backgrounds may be, forecasts must be attempted. Making verifiable or falsifiable predictions is obviously the core of the scientific method in general; but there is also a more imperative urge in the case of solar cycle prediction. Being the prime determinant of space weather, solar activity clearly has enormous technical, scientific, and financial impact on activities ranging from space exploration to civil aviation and everyday communication. Political and economic decision makers expect the solar community to provide them with forecasts on which feasibility and profitability calculations can be based. Acknowledging this need, the Space Weather Prediction Center of the US National Weather Service does present annually or semiannually updated “official” predictions of the upcoming sunspot maximum, emitted by a Solar Cycle Prediction Panel of experts, starting shortly before the (expected) minimum (SWPC). The unusual lack of consensus during the early meetings of this panel during the recent minimum, as well as the concurrent more frequently updated but wildly varying predictions of a NASA MSFC team (MSFC) have put on display the deficiencies of currently applied prediction techniques; on the other hand, they also imply that cycle 24 may provide us with crucial new insight into the physical mechanisms underlying cyclic solar activity.
While a number of indicators of solar activity exist, by far the most commonly employed is still the smoothed relative sunspot number R; the “Holy Grail” of sunspot cycle prediction attempts is to get R right for the next maximum. We, therefore, start by briefly introducing the sunspot number and inspecting its known record. Then, in Sections 2, 3, and 4 we discuss the most widely employed methods of cycle predictions. Section 5 presents a summary evaluation of the past performance of different forecasting methods and collects some forecasts for cycle 24 derived by various approaches. Finally, Section 6 concludes the paper.
1.1 The sunspot number
Despite its somewhat arbitrary construction, the series of relative sunspot numbers constitutes the longest homogeneous global indicator of solar activity determined by direct solar observations and carefully controlled methods. For this reason, their use is still predominant in studies of solar activity variation. As defined originally by Wolf (1859), the relative sunspot number is
where g is the number of sunspot groups (including solitary spots), f is the total number of all spots visible on the solar disc, while k is a correction factor depending on a variety of circumstances, such as instrument parameters, observatory location, and details of the counting method. Wolf, who decided to count each spot only once and not to count the smallest spots, the visibility of which depended on seeing, used k = 1. The counting system employed was changed by Wolf’s successors to count even the smallest spots, attributing a higher weight (i.e., f > 1) to spots with a penumbra, depending on their size and umbral structure. As the new counting naturally resulted in higher values, the correction factor was set to k = 0:6 for subsequent determinations of RW to ensure continuity with Wolf’s work, even though there was no change in either the instrument or the observing site. This was followed by several further changes in the details of the counting method (Waldmeier, 1961; see Kopecký et al., 1980, Hoyt and Schatten, 1998, and Hathaway, 2010b for further discussions on the determination of RW).
In addition to introducing the relative sunspot number, Wolf (1861) also used earlier observational records available to him to reconstruct its monthly mean values since 1749. In this way, he reconstructed 11-year sunspot cycles back to that date, introducing their still universally used numbering. (In a later work he also determined annual mean values for each calendar year going back to 1700.)
In 1981, the observatory responsible for the official determination of the sunspot number changed from Zürich to the Royal Observatory of Belgium in Brussels. The website of the SIDC (originally Sunspot Index Data Center, recently renamed Solar Influences Data Analysis Center), http://sidc.oma.be, is now the most authoritative source of archive sunspot number data. But it has to be kept in mind that the sunspot number is also regularly determined by other institutions: these variants are informally known as the American sunspot number (collected by AAVSO and available from the National Geophysical Data Center, http://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/ngdc.html) and the Kislovodsk Sunspot Number (available from the web page of the Pulkovo Observatory, http://www.gao.spb.ru). Cycle amplitudes determined by these other centers may differ by up to 6 – 7% from the SIDC values, NOAA numbers being consistently lower, while Kislovodsk numbers show no such systematic trend.
These significant disagreements between determinations of RW by various observatories and observers are even more pronounced in the case of historical data, especially prior to the mid-19th century. In particular, the controversial suggestion that a whole solar cycle may have been missed in the official sunspot number series at the end of the 18th century is taken by some as glaring evidence for the unreliability of early observations. Note, however, that independently of whether the claim for a missing cycle is well founded or not, there is clear evidence that this controversy is mostly due to the very atypical behaviour of the Sun itself in the given period of time, rather than to the low quality and coverage of contemporary observations. These issues will be discussed further in Section 3.2.2.
Given that RW is subject to large fluctuations on a time scale of days to months, it has become customary to use annual mean values for the study of longer term activity changes. To get rid of the arbitrariness of calendar years, the standard practice is to use 13-month boxcar averages of the monthly averaged sunspot numbers, wherein the first and last months are given half the weight of other months:
Rm;i being the mean monthly value of RW for ith calendar month counted from the present month. It is this running mean R that we will simply call “the sunspot number” throughout this review and what forms the basis of most discussions of solar cycle variations and their predictions.
In what follows, R (n)max and R (n)min will refer to the maximum and minimum value of R in cycle n (the minimum being the one that starts the cycle). Similarly, t (n)max and t (n)min will denote the epochs when R takes these extrema.
1.1.1 Alternating series and nonlinear transforms
Instead of the “raw” sunspot number series R(t) many researchers prefer to base their studies on some transformed index R′. The motivation behind this is twofold.
(a) The strongly peaked and asymmetrical sunspot cycle profiles strongly deviate from a sinusoidal profile; also the statistical distribution of sunspot numbers is strongly at odds with a Gaussian distribution. This can constitute a problem as many common methods of data analysis rely on the assumption of an approximately normal distribution of errors or nearly sinusoidal profiles of spectral components. So transformations of R (and, optionally, t) that reduce these deviations can obviously be helpful during the analysis. In this vein, e.g., Max Waldmeier often based his studies of the solar cycle on the use of logarithmic sunspot numbers R′ = logR; many other researchers use R′ = Rα with 0.5 ≤ α < 1, the most common value being α = 0:5.
(b) As the sunspot number is a rather arbitrary construct, there may be an underlying more physical parameter related to it in some nonlinear fashion, such as the toroidal magnetic field strength B, or the magnetic energy, proportional to B2. It should be emphasized that, contrary to some claims, our current understanding of the solar dynamo does not make it possible to guess what the underlying parameter is, with any reasonable degree of certainty. In particular, the often used assumption that it is the magnetic energy, lacks any sound foundation. If anything, on the basis of our current best understanding of flux emergence we might expect that the amount of toroidal flux emerging from the tachocline should be ƒ |B — B0| dA where B0 is some minimal threshold field strength for Parker instability and the surface integral goes across a latitudinal cross section of the tachocline (cf. Ruzmaikin, 1997). As, however, the lifetime of any given sunspot group is finite and proportional to its size (Petrovay and van Driel-Gesztelyi, 1997; Henwood et al., 2010), instantaneous values of R or the total sunspot area should also depend on details of the probability distribution function of B in the tachocline. This just serves to illustrate the difficulty of identifying a single physical governing parameter behind R.
One transformation that may still be well motivated from the physical point of view is to attribute an alternating sign to even and odd Schwabe cycles: this results in the the alternating sunspot number series R±. The idea is based on Hale’s well known polarity rules, implying that the period of the solar cycle is actually 22 years rather than 11 years, the polarity of magnetic fields changing sign from one 11-year Schwabe cycle to the next. In this representation, first suggested by Bracewell (1953), usually odd cycles are attributed a negative sign. This leads to slight jumps at the minima of the Schwabe cycle, as a consequence of the fact that for a 1 – 2 year period around the minimum, spots belonging to both cycles are present, so the value of R never reaches zero; in certain applications, further twists are introduced into the transformation to avoid this phenomenon.
After first introducing the alternating series, in a later work Bracewell (1988) demonstrated that introducing an underlying “physical” variable RB such that
(i.e., α = 2/3 in the power law mentioned in item (a) above) significantly simplifies the cycle profile. Indeed, upon introducing a “rectified” phase variableFootnote 1 in each cycle to compensate for the asymmetry of the cycle profile, RB is a nearly sinusoidal function of ϕ. The empirically found 3/2 law is interpreted as the relation between the time-integrated area of a typical sunspot group vs. its peak area (or peak RW value), i.e., the steeper than linear growth of R with the underlying physical parameter RB would be due to the larger sunspot groups being observed longer, and therefore giving a disproportionately larger contribution to the annual mean sunspot numbers. If this interpretation is correct, as suggested by Bracewell’s analysis, then RB should be considered proportional to the total toroidal magnetic flux emerging into the photosphere in a given interval. (But the possibility must be kept in mind that the same toroidal flux bundle may emerge repeatedly or at different heliographic longitudes, giving rise to several active regions.)
1.2 Other indicators of solar activity
Reconstructions of R prior to the early 19th century are increasingly uncertain. In order to tackle problems related to sporadic and often unreliable observations, Hoyt and Schatten (1998) introduced the Group Sunspot Number (GSN) as an alternative indicator of solar activity. In contrast to RW, the GSN only relies on counts of sunspot groups as a more robust indicator, disregarding the number of spots in each group. Furthermore, while RW is determined for any given day from a single observer’s measurements (a hierarchy of secondary observers is defined for the case if data from the primary observer were unavailable), the GSN uses a weighted average of all observations available for a given day. The GSN series has been reproduced for the whole period 1611 – 1998 (Figure 1) and it is generally agreed that for the period 1611 – 1818 it is a more reliable reconstruction of solar activity than the relative sunspot number. Yet there have been relatively few attempts to date to use this data series for solar cycle prediction. One factor in this could be the lack of regular updates of the GSN series, i.e., the unavailability of precise GSN values for the past decade.
Instead of the sunspot number, the total area of all spots observed on the solar disk might seem to be a less arbitrary measure of solar activity. However, these data have been available since 1874 only, covering a much shorter period of time than the sunspot number data. In addition, the determination of sunspot areas, especially farther from disk center, is not as trivial as it may seem, resulting in significant random and systematic errors in the area determinations. Area measurements performed in two different observatories often show discrepancies reaching ∼ 30% for smaller spots (cf. the figure and discussion in Appendix A of Petrovay et al., 1999).
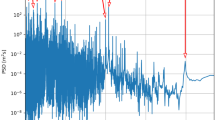
A number of other direct indicators of solar activity have become available from the 20th century. These include, e.g., various plage indices or the 10.7 cm solar radio flux — the latter is considered a particularly good and simple to measure indicator of global activity (see Figure 2). As, however, these data sets only cover a few solar cycles, their impact on solar cycle prediction has been minimal.
Monthly values of the 10.7 cm radio flux in solar flux units for the period 1947 – 2009. The solar flux unit is defined as 10–22 W/m2 Hz. The green curve shows Rm + 60, where Rm is the monthly mean relative sunspot number. (The vertical shift is for better comparison.) Data are from the NRC Canada (Ottawa/Penticton).
Of more importance are proxy indicators such as geomagnetic indices (the most widely used of which is the aa index), the occurrence frequency of aurorae or the abundances of cosmogenic radionuclides such as 14C and 10Be. For solar cycle prediction uses such data sets need to have a sufficiently high temporal resolution to reflect individual 11-year cycles. For the geomagnetic indices such data have been available since 1868, while an annual 10Be series covering 600 years has been published very recently by Berggren et al. (2009). Attempts have been made to reconstruct the epochs and even amplitudes of solar maxima during the past two millennia from oriental naked eye sunspot records and from auroral observations (Stephenson and Wolfendale, 1988; Nagovitsyn, 1997), but these reconstructions are currently subject to too many uncertainties to serve as a basis for predictions. Isotopic data with lower temporal resolution are now available for up to 50 000 years in the past; while such data do not show individual Schwabe cycles, they are still useful for the study of long term variations in cycle amplitude. Inferring solar activity parameters from such proxy data is generally not straightforward.
1.3 The solar cycle and its variation
The series of R values determined as described in Section 1.1 is plotted in Figure 3. It is evident that the sunspot cycle is rather irregular. The mean length of a cycle (defined as lasting from minimum to minimum) is 11.02 years (median 10.7 years), with a standard deviation of 1.2 years. The mean amplitude is 113 (median 115), with a standard deviation of 40. It is this wide variation that makes the prediction of the next cycle maximum such an interesting and vexing issue.
It should be noted that the period covered by the relative sunspot number record includes an extended interval of atypically strong activity, the so called Modern Maximum (see below), cycles 17 – 23. Excluding these cycles from the averaging, the mean, and median values of the cycle amplitude are very close to 100, with a standard deviation of 35. The mean and median cycle length then become 11.1 and 11.2 years, respectively, with a standard deviation of 1.3 years.
1.4 Secular activity variations
Inspecting Figure 3 one can discern an obvious long term variation. For the study of such long term variations, the series of cycle parameters is often smoothed on time scales significantly longer than a solar cycle: this procedure is known as secular smoothing. One popular method is the so-called Gleissberg filter or 12221 filter (Gleissberg, 1967). For instance, the Gleissberg filtered amplitude of cycle n is given by
The Gleissberg filtered sunspot number series is plotted in Figure 4. One long-term trend is an overall secular increase of solar activity, the last six or seven cycles being unusually strong. (Four of them are markedly stronger than average and none is weaker than average.) This period of elevated sunspot activity level from the mid-20th century is known as the “Modern Maximum”. On the other hand, cycles 5, 6, and 7 are unusually weak, forming the so-called “Dalton Minimum”. Finally, the rather long series of moderately weak cycles 12 – 16 is occasionally referred to as the “Gleissberg Minimum” — but note that most of these cycles are less than 1 σ below the long-term average.
While the Dalton and Gleissberg minima are but local minima in the ever changing Gleissberg filtered SSN series, the conspicuous lack of sunspots in the period 1640 – 1705, known as the Maunder Minimum (Figure 1) quite obviously represents a qualitatively different state of solar activity. Such extended periods of high and low activity are usually referred to as grand maxima and grand minima. Clearly, in comparison with the Maunder Minimum, the Dalton Minimum could only be called a “semi-grand minimum”, while for the Gleissberg Minimum even that adjective is undeserved.
A number of possibilities have been proposed to explain the phenomenon of grand minima and maxima, including chaotic behaviour of the nonlinear solar dynamo (Weiss et al., 1984), stochastic fluctuations in dynamo parameters (Moss et al., 2008; Usoskin et al., 2009b) or a bimodal dynamo with stochastically induced alternation between two stationary states (Petrovay, 2007).
The analysis of long-term proxy data, extending over several millennia further showed that there exist systematic long-term statistical trends and periods such as the so called secular and supersecular cycles (see Section 3.2).
1.4.1 Does the Sun have a long term memory?
Following customary usage, by “memory” we will refer to some physical (or, in the case of a model, mathematical) mechanism by which the state of a system at a given time will depend on its previous states. In any system there may be several different such mechanisms at work simultaneously - if this is so, again following common usage we will speak of different “types” of memory. A very mundane example are the RAM and the hard disk in a computer: devices that store information over very different time scales and the effect of which manifests itself differently in the functioning of the system.
There is no question that the solar dynamo (i.e., the mechanism that gives rise to the sunspot number series) does possess a memory that extends at least over the course of a single solar cycle. Obviously, during the rise phase solar activity “remembers” that it should keep growing, while in the decay phase it keeps decaying, even though exactly the same range of R values are observed in both phases. Furthermore, profiles of individual sunspot cycles may, in a first approximation, be considered a one-parameter ensemble (Hathaway et al., 1994). This obvious effect will be referred to here as intracycle memory.
As we will see, correlations between activity parameters in different cycles are generally much weaker than those within one cycle, which strongly suggests that the intracycle memory mechanism is different from longer term memory effects, if such are present at all. Referring back to our analogy, the intracycle memory may work like computer RAM, periodically erased at every reboot (i.e., at the start of a new cycle).
The interesting question is whether, in addition to the intracycle memory effect, any other type of memory is present in the solar dynamo or not. To what extent is the amplitude of a sunspot cycle determined by previous cycles? Are subsequent cycles essentially independent, randomly drawn from some stochastic distribution of cycle amplitudes around the long term average? Or, in the alternative case, for how many previous cycles do we need to consider solar activity for successful forecasts?
The existence of long lasting grand minima and maxima suggests that the sunspot number record must have a long-term memory extending over several consecutive cycles. Indeed, elementary combinatorical calculations show that the occurrence of phenomena like the Dalton minimum (3 of the 4 lowest maxima occurring in a row) or the Modern maximum (4 of the 5 highest maxima occurring within a series of 5 cycles) in a random series of 24 recorded solar maxima has a rather low probability (5% and 3 %, respectively). This conclusion is corroborated by the analysis of long-term proxy data, extending over several millennia, which showed that the occurrence of grand minima and grand maxima is more common than what would follow from Gaussian statistics (Usoskin et al., 2007).
It could be objected that for sustained grand minima or maxima a memory extending only from one cycle to the next would suffice. In contrast to long-term (multidecadal or longer) memory, this would constitute another kind of short-term (≲ 10 years) memory: a cycle-to-cycle or intercycle memory effect. In our computer analogy, think of system files or memory cache written on the hard disk, often with the explicit goal of recalling the system status (e.g., desktop arrangement) after the next reboot. While these files survive the reboot, they are subject to erasing and rewriting in every session, so they have a much more temporary character than the generic data files stored on the disk.
The intercycle memory explanation of persistent secular activity minima and maxima, however, would imply a good correlation between the amplitudes of subsequent cycles, which is not the case (cf. Section 2.1 below). With the known poor cycle-to-cycle correlation, strong deviations from the long-term mean would be expected to be damped on time scales short compared to, e.g., the length of the Maunder minimum. This suggests that the persistent states of low or high activity are due to truly long term memory effects extending over several cycles.
Further evidence for a long-term memory in solar activity comes from the persistence analysis of activity indicators. The parameter determined in such studies is the Hurst exponent 0 < H < 1. Essentially, H is the steepness of the growth of the total range \(\mathcal{R}\) of measured values plotted against the number n of data in a time series, on a logarithmic plot: \(\mathcal{R}\). For a Markovian random process with no memory H = 0:5. Processes with H > 0:5 are persistent (they tend to stay in a stronger-than-average or weaker-than-average state longer), while those with H < 0:5 are anti-persistent (their fluctuations will change sign more often).
Hurst exponents for solar activity indices have been derived using rescaled range analysis by many authors (Mandelbrot and Wallis, 1969; Ruzmaikin et al., 1994; Komm, 1995; Oliver and Ballester, 1996; Kilcik et al., 2009). All studies coherently yield a value H = 0:85 – 0:88 for time scales exceeding a year or so, and somewhat lower values (H ∼ 0:75) on shorter time scales. Some doubts regarding the significance of this result for a finite series have been raised by Oliver and Ballester (1998); however, Qian and Rasheed (2004) have shown using Monte Carlo experiments that for time series of a length comparable to the sunspot record, H values exceeding 0.7 are statistically significant.
A complementary method, essentially equivalent to rescaled range analysis is detrended fluctuation analysis. Its application to solar data (Ogurtsov, 2004) has yielded results in accordance with the H values quoted above.
The overwhelming evidence for the persistent character of solar activity and for the intermittent appearance of secular cyclicities, however, is not much help when it comes to cycle-to-cycle prediction. It is certainly reassuring to know that forecasting is not a completely idle enterprise (which would be the case for a purely Markovian process), and the long-term persistence and trends may make our predictions statistically somewhat different from just the long-term average. There are, however, large decadal scale fluctuations superposed on the long term trends, so the associated errors will still be so large as to make the forecast of little use for individual cycles.
1.4.2 Waldmeier effect and amplitude-frequency correlation
“Greater activity on the Sun goes with shorter periods, and less with longer periods. I believe this law to be one of the most important relations among the Solar actions yet discovered.”
(Wolf, 1861)
It is apparent from Figure 3 that the profile of sunspot cycles is asymmetrical, the rise being steeper than the decay. Solar activity maxima occur 3 to 4 years after the minimum, while it takes another 7 – 8 years to reach the next minimum. It can also be noticed that the degree of this asymmetry correlates with the amplitude of the cycle: to be more specific, the length of the rise phase anticorrelates with the maximal value of R (Figure 5), while the length of the decay phase shows weak or no such correlation.
Monthly smoothed sunspot number R at cycle maximum plotted against the rise time to maximum (left) and against cycle length (right). Cycles are labeled with their numbers. In the plots the red dashed lines are linear regressions to all the data, while the blue solid lines are fits to all data except outliers. Cycle 19 is considered an outlier on both plots, cycle 4 on the right hand plot only. The corresponding correlation coefficients are shown.
_
Historically, the relation was first formulated by Waldmeier (1935) as an inverse correlation between the rise time and the cycle amplitude; however, as shown by Tritakis (1982), the total rise time is a weak (inverse logarithmic) function of the rise rate, so this representation makes the correlation appear less robust. (Indeed, when formulated with the rise time it is not even present in some activity indicators, such as sunspot areas - cf. Dikpati et al., 2008b.) As pointed out by Cameron and Schüssler (2008), the weak link between rise time and slope is due to the fact that in steeper rising cycles the minimum will occur earlier, thus partially compensating for the shortening due to a higher rise rate. The effect is indeed more clearly seen when the rate of the rise is used instead of the rise time (Lantos, 2000; Cameron and Schüssler, 2008). The observed correlation between rise rate and maximum cycle amplitude is approximately linear, good (correlation coefficient r ∼ 0:85), and quite robust, being present in various activity indices.
Nevertheless, when coupled with the nearly nonexistent correlation between the decay time and the cycle amplitude, even the weaker link between the rise time and the maximum amplitude is sufficient to forge a weak inverse correlation between the total cycle length and the cycle amplitude (Figure 5). This inverse relationship was first noticed by Wolf (1861).
A stronger inverse correlation was found between the cycle amplitude and the length of the previous cycle by Hathaway et al. (1994). This correlation is also readily explained as a consequence of the Waldmeier effect, as demonstrated in a simple model by Cameron and Schüssler (2007). Note that in a more detailed study Solanki et al. (2002) find that the correlation coefficient of this relationship has steadily decreased during the course of the historical sunspot number record, while the correlation between cycle amplitude and the length of the third preceding cycle has steadily increased. The physical significance (if any) of this latter result is unclear.
In what follows, the relationships found by Wolf (1861), Hathaway et al. (1994), and Solanki et al. (2002), discussed above, will be referred to as “Rmax - tcycle;n correlations” with n = 0, -1 or -3, respectively.
Modern time series analysis methods offer several ways to define an instantaneous frequency f in a quasiperiodic series. One simple approach was discussed in the context of Bracewell’s transform, Equation (3), above. Mininni et al. (2000) discuss several more sophisticated methods to do this, concluding that Gábor’s analytic signal approach yields the best performance. This technique was first applied to the sunspot record by Paluš and Novotná (1999), who found a significant long term correlation between the smoothed instantaneous frequency and amplitude of the signal. On time scales shorter than the cycle length, however, the frequency-amplitude correlation has not been convincingly proven, and the fact that the correlation coefficient is close to the one reported in the right hand panel of Figure 5 indicates that all the fashionable gadgetry of nonlinear dynamics could achieve was to recover the effect already known to Wolf. It is clear from this that the “frequency-amplitude correlation” is but a secondary consequence of the Waldmeier effect.
On the left hand panel of Figure 5, within the band of correlation the points seem to be sitting neatly on two parallel strings. Any number of faint hearted researchers would dismiss this as a coincidence or as another manifestation of the “Martian canal effect”. But Kuklin (1986) boldly speculated that the phenomenon may be real. Fair enough, cycles 22 and 23 dutifully took their place on the lower string even after the publication of Kuklin’s work. This speculation was supported with further evidence by Nagovitsyn (1997) who offered a physical explanation in terms of the amplitude-frequency diagram of a forced nonlinear oscillator (cf. Section 4.5).
Indeed, an anticorrelation between cycle length and amplitude is characteristic of a class of stochastically forced nonlinear oscillators and it may also be reproduced by introducing a stochastic forcing in dynamo models (Stix, 1972; Ossendrijver et al., 1996; Charbonneau and Dikpati, 2000). In some such models the characteristic asymmetric profile of the cycle is also well reproduced (Mininni et al., 2000, 2002). The predicted amplitude-frequency relation has the form
Nonlinear dynamo models including some form of α-quenching also have the potential to reproduce the effects described by Wolf and Waldmeier without recourse to stochastic driving. In a dynamo with a Kleeorin-Ruzmaikin type feedback on α, Kitiashvili and Kosovichev (2009) are able to qualitatively reproduce the Waldmeier effect. Assuming that the sunspot number is related to the toroidal field strength according to the Bracewell transform, Equation (3), they find a strong link between rise time and amplitude, while the correlations with fall time and cycle length are much weaker, just as the observations suggest. They also find that the form of the growth time- amplitude relationship differs in the regular (multiperiodic) and chaotic regimes. In the regular regime the plotted relationship suggests
while in the chaotic case
Note that based on the actual sunspot number series Waldmeier originally proposed
while according to Dmitrieva et al. (2000) the relation takes the form
At first glance, these logarithmic empirical relationships seem to be more compatible with the relation (5) predicted by the stochastic models. These, on the other hand, do not actually reproduce the Waldmeier effect, just a general asymmetric profile and an amplitude-frequency correlation. At the same time, inspection of the the left hand panel in Figure 5 shows that the data is actually not incompatible with a linear or inverse rise time-amplitude relation, especially if the anomalous cycle 19 is ignored as an outlier. (Indeed, a logarithmic representation is found not to improve the correlation coefficient - its only advantage is that cycle 19 ceases to be an outlier.) All this indicates that nonlinear dynamo models may have the potential to provide a satisfactory quantitative explanation of the Waldmeier effect, but more extensive comparisons will need to be done, using various models and various representations of the relation.
2 Precursor Methods
“Jeder Fleckenzyklus muß als ein abgeschlossenes Ganzes, als ein Phänomen für sich, aufgefaßt werden, und es reiht sich einfach Zyklus an Zyklus.”
(Gleissberg, 1952)
In the most general sense, precursor methods rely on the value of some measure of solar activity or magnetism at a specified time to predict the amplitude of the following solar maximum. The precursor may be any proxy of solar activity or other indicator of solar and interplanetary magnetism. Specifically, the precursor may also be the value of the sunspot number at a given time.
In principle, precursors might also herald the activity level at other phases of the sunspot cycle, in particular the minimum. Yet the fact that practically all the good precursors found need to be evaluated at around the time of the minimum and refer to the next maximum is not simply due to the obvious greater interest in predicting maxima than predicting minima. Correlations between minimum parameters and previous values of solar indices have been looked for, but the results were overwhelmingly negative (e.g., Tlatov, 2009). This indicates that the sunspot number series is not homogeneous and Rudolf Wolf’s instinctive choice to start new cycles with the minimum rather than the maximum in his numbering system is not arbitrary - for which even more obvious evidence is provided by the butterfly diagram. Each numbered solar cycle is a consistent unit in itself, while solar activity seems to consist of a series of much less tightly intercorrelated individual cycles, as suggested by Wolfgang Gleissberg in the motto of this section.
In Section 1.3.2 we have seen that there is significant evidence for a long-term memory underlying solar activity. In addition to the evidence reviewed there, systematic long-term statistical trends and periods of solar activity, such as the secular and supersecular cycles (to be discussed in Section 3.2), also attest to a secular mechanism underlying solar activity variations and ensuring some degree of long-term coherence in activity indicators. However, as we noted, this long-term memory is of limited importance for cycle prediction due to the large, apparently haphazard decadal variations superimposed on it. What the precursor methods promise is just to find a system in those haphazard decadal variations - which clearly implies a different type of memory. As we already mentioned in Section 1.3.2, there is obvious evidence for an intracycle memory operating within a single cycle, so that forecasting of activity in an ongoing cycle is currently a much more successful enterprise than cycle-to-cycle forecasting. As we will see, this intracycle memory is one candidate mechanism upon which precursor techniques may be founded, via the Waldmeier effect.
The controversial issue is whether, in addition to the intracycle memory, there is also an intercycle memory at work, i.e., whether behind the apparent stochasticity of the cycle-to-cycle variations there is some predictable pattern, whether some imprint of these variations is somehow inherited from one cycle to the next, or individual cycles are essentially independent. The latter is known as the “outburst hypothesis”: consecutive cycles would then represent a series of “outbursts” of activity with stochastically fluctuating amplitudes (Halm, 1901; Waldmeier, 1935; Vitinsky, 1973; see also de Meyer, 1981 who calls this “impulse model”). Note that cycle-to-cycle predictions in the strict temporal sense may be possible even in the outburst case, as solar cycles are known to overlap. Active regions belonging to the old and new cycles may coexist for up to three years or so around sunspot minima; and high latitude ephemeral active regions oriented according to the next cycle appear as early as 2 – 3 years after the maximum (Tlatov et al., 2010 — the so-called extended solar cycle).
In any case, it is undeniable that for cycle-to-cycle predictions, which are our main concern here, the precursor approach seems to have been the relatively most successful, so its inherent basic assumption must contain an element of truth - whether its predictive skill is due to a “real” cycle-to-cycle memory (intercycle memory) or just to the overlap effect (intracycle memory).
The two precursor types that have received most attention are polar field precursors and geomagnetic precursors. A link between these two categories is forged by a third group, characterizing the interplanetary magnetic field strength or “open flux”. But before considering these approaches, we start by discussing the most obvious precursor type: the level of solar activity at some epoch before the next maximum.
2.1 Cycle parameters as precursors and the Waldmeier effect
The simplest weather forecast method is saying that “tomorrow the weather will be just like today” (works in about 2/3 of the cases). Similarly, a simple approach of sunspot cycle prediction is correlating the amplitudes of consecutive cycles. There is indeed a marginal correlation, but the correlation coefficient is quite low (0.35). The existence of the correlation is related to secular variations in solar activity, while its weakness is due to the significant cycle-to-cycle variations.
A significantly better correlation exists between the minimum activity level and the amplitude of the next maximum (Figure 6). The relation is linear (Brown, 1976), with a correlation coefficient of 0.72 (if the anomalous cycle 19 is ignored — Brajša et al., 2009; see also Pishkalo, 2008). The best fit is
Using the observed value 1.7 for the SSN in the recent minimum, the next maximum is predicted by this “minimax” method to reach values around 80, with a 1 σ error of about ± 25.
Cameron and Schüssler (2007) point out that the activity level three years before the minimum is an even better predictor of the next maximum. Indeed, playing with the value of time shift we find that the best correlation coefficient corresponds to a time shift of 2.5 years, as shown in the right hand panel of Figure 6 (but this may depend on the particular time period considered, so we will refer to this method in Table 1 as “minimax3” for brevity). The linear regression is
For cycle 24 the value of the predictor is 16.3, so this indicates an amplitude of 69, suggesting that the upcoming cycle may be comparable in strength to those during the Gleissberg minimum at the turn of the 19th and 20th centuries.
Monthly smoothed sunspot number R at cycle maximum plotted against the values of R at the previous minimum (left) and 2.5 years before the minimum (right). Cycles are labeled with their numbers. The blue solid line is a linear regression to the data; corresponding correlation coefficients are shown. In the left hand panel, cycle 19 was considered an outlier.
As the epoch of the minimum of R cannot be known with certainty until about a year after the minimum, the practical use of these methods is rather limited: a prediction will only become available 2 – 3 years before the maximum, and even then with the rather low reliability reflected in the correlation coefficients quoted above. In addition, as convincingly demonstrated by Cameron and Schüssler (2007) in a Monte Carlo simulation, these methods do not constitute real cycle-to-cycle prediction in the physical sense: instead, they are due to a combination of the overlap of solar cycles with the Waldmeier effect. As stronger cycles are characterized by a steeper rise phase, the minimum before such cycles will take place earlier, when the activity from the previous cycle has not yet reached very low levels.
The same overlap readily explains the Rmax - tcycle;n correlations discussed in Section 1.3.3. These relationships may also be used for solar cycle prediction purposes (e.g., Kane, 2008) but they lack robustness. For cycle 24 the Rmax – tcycle;−1 correlation, as formulated by Hathaway (2010b) predicts Rmax = 80 while the methods used by Solanki et al. (2002) yield values ranging from 86 to about 110, depending on the relative weights of tcycle;−1 and tcycle;−3. The forecast is not only sensitive to the value of n used but also to the data set (relative or group sunspot numbers) (Vaquero and Trigo, 2008).
2.2 Polar precursors
Direct measurements of the magnetic field in the polar areas of the Sun have been available from Wilcox Observatory since 1976 (Svalgaard et al., 1978; Hoeksema, 1995). Even before a significant amount of data had been available for statistical analysis, solely on the basis of the Babcock-Leighton scenario of the origin of the solar cycle, Schatten et al. (1978) suggested that the polar field measurements may be used to predict the amplitude of the next solar cycle. Data collected in the four subsequent solar cycles have indeed confirmed this suggestion. As it was originally motivated by theoretical considerations, this polar field precursor method might also be a considered a model-based prediction technique. As, however, no particular detailed mathematical model is underlying the method, numerical predictions must still be based on empirical correlations - hence our categorization of this technique as a precursor method.
The shortness of the available direct measurement series represents a difficulty when it comes to finding empirical correlations to solar activity. This problem can to some extent be circumvented by the use of proxy data. For instance, Obridko and Shelting (2008) use Hα synoptic maps to reconstruct the polar field strength at the source surface back to 1915. Spherical harmonic expansions of global photospheric magnetic measurements can also be used to deduce the field strength near the poles. The use of such proxy techniques permits a forecast with a sufficiently restricted error bar to be made, despite the shortness of the direct polar field data set.
The polar fields reach their maximal amplitude near minima of the sunspot cycle. In its most commonly used form, the polar field precursor method employs the value of the polar magnetic field strength (typically, the absolute value of the mean field strength poleward of 55° latitudes, averaged for the two hemispheres) at the time of sunspot minimum. It is indeed remarkable that despite the very limited available experience, forecasts using the polar field method have proven to be consistently in the right range for cycles 21, 22, and 23 (Schatten and Sofia, 1987; Schatten et al., 1996).
By virtue of the definition (2), the time of the minimum of R cannot be known earlier than 6 months after the minimum - indeed, to make sure that the perceived minimum was more than just a local dip in R, at least a year or so needs to elapse. This would suggest that the predictive value of polar field measurements is limited, the prediction becoming available 2 – 3 years before the upcoming maximum only.
To remedy this situation, Schatten and Pesnell (1993) introduced a new activity index, the “Solar Dynamo Amplitude” (SoDA) index, combining the polar field strength with a traditional activity indicator (the 10.7 cm radio flux F10.7). Around minimum, SoDA is basically proportional to the polar precursor and its value yields the prediction for F10.7 at the next maximum; however, it was constructed so that its 11-year modulation is minimized, so theoretically it should be rather stable, making predictions possible well before the minimum. That is the theory, anyway — in reality, SoDA based forecasts made more than 2 – 3 years before the minimum usually proved unreliable. It is then questionable to what extent SoDA improves the prediction skill of the polar precursor, to which it is more or less equivalent in those late phases of the solar cycle when forecasts start to become reliable.
Fortunately, however, the maxima of the polar field curves are often rather flat (see Figure 7), so approximate forecasts are feasible several years before the actual minimum. Using the current, rather flat and low maximum in polar field strength, Svalgaard et al. (2005) have been able to predict a relatively weak cycle 24 (peak R value 75 ± 8) as early as 4 years before the sunspot minimum took place in December 2008! Such an early prediction is not always possible: early polar field predictions of cycles 22 and 23 had to be corrected later and only forecasts made shortly before the actual minimum did finally converge. Nevertheless, even the moderate success rate of such early predictions seems to indicate that the suggested physical link between the precursor and the cycle amplitude is real.
Magnetic field strength in the Sun’s polar regions as a function of time. Blue solid: North; red dashed: (−1) South; thin black solid: average; heavy black solid: smoothed average. Strong annual modulations in the hemispheric data are due to the tilt of the solar equator to the Ecliptic. Data and figure courtesy of Wilcox Solar Observatory (see http://wso.stanford.edu/gifs/Polar.gif for updated version).
In addition to their above mentioned use in reconstructing the polar field strength, various proxies or alternative indices of the global solar magnetic field during the activity minimum may also be used directly as activity cycle precursors. Hα synoptic charts are now available from various observatories from as early as 1870. As Hα filaments lie on the magnetic neutral lines, these maps can be used to reconstruct the overall topology, if not the detailed map, of the large-scale solar magnetic field. Tlatov (2009) has shown that several indices of the polar magnetic field during the activity minimum, determined from these charts, correlate well with the amplitude of the incipient cycle.
High resolution Hinode observations have now demonstrated that the polar magnetic field has a strongly intermittent structure, being concentrated in intense unipolar tubes that coincide with polar faculae (Tsuneta et al., 2008). The number of polar faculae should then also be a plausible proxy of the polar magnetic field strength and a good precursor of the incipient solar cycle around the minimum. This conclusion was indeed confirmed by Li et al. (2002) and, more recently, by Tlatov (2009).
These methods offer a prediction over a time span of 3 – 4 years, comparable to the rise time of the next cycle. A significantly earlier prediction possibility was, however, suggested by Makarov et al. (1989) and Makarov and Makarova (1996) based on the number of polar faculae observed at Kislovodsk, which was found to predict the next sunspot cycle with a time lag of 5 – 6 years; even short term annual variations or “surges” of sunspot activity were claimed to be discernible in the polar facular record. This surprising result may be partly due to the fact that Makarov et al. considered all faculae poleward of 50° latitude. Bona fide polar faculae, seen on Hinode images to be knots of the unipolar field around the poles, are limited to higher latitudes, so the wider sample may consist of a mix of such “real” polar faculae and small bipolar ephemeral active regions. These latter are known to obey an extended butterfly diagram, as recently confirmed by Tlatov et al. (2010): the first bipoles of the new cycle appear at higher latitudes about 4 years after the activity maximum. It is not impossible that these early ephemeral active regions may be used for prediction purposes (cf. also Badalyan et al., 2001); but whether or not the result of Makarov et al. (1989) may be attributed to this is doubtful, as Li et al. (2002) find that even using all polar faculae poleward of 50° from the Mitaka data base, the best autocorrelation still results with a time shift of about 4 years only.
Finally, trying to correlate various solar activity parameters, Tlatov (2009) finds this surprising relation:
where t (n)rev is the epoch of the polarity reversal in cycle n (typically, about a year after t (n)max ). The origin of this curious relationship is unclear. In any case, the good correlation coefficient (r = 0:86, based on 12 cycles) and the time lag of ∼ 10 years make this relationship quite remarkable. For cycle 24 this formula predicts R (24)max = 94 ± 14.
2.3 Geomagnetic and interplanetary precursors
Relations between the cycle related variations of geomagnetic indices and solar activity were noted long ago. It is, however, important to realize that the overall correlation between geomagnetic indices and solar activity, even after 13-month smoothing, is generally far from perfect. This is due to the fact that the Sun can generate geomagnetic disturbances in two ways:
-
(a)
By material ejections (such as CMEs or flare particles) hitting the terrestrial magnetosphere. This effect is obviously well correlated with solar activity, with no time delay, so this contribution to geomagnetic disturbances peaks near, or a few years after, sunspot maximum. (Note that the occurrence of the largest flares and CMEs is known to peak some years after the sunspot maximum — see Figure 6 in Hathaway, 2010b.)
-
(b)
By a variation of the strength of the general interplanetary magnetic field and of solar wind speed. Geomagnetic disturbances may be triggered by the alternation of the Earth’s crossing of interplanetary sector boundaries (slow solar wind regime) and its crossing of high speed solar wind streams while well within a sector. The amplitude of such disturbances will clearly be higher for stronger magnetic fields. The overall strength of the interplanetary magnetic field, in turn, depends mainly on the total flux present in coronal holes, as calculated from potential field source surface models of the coronal magnetic field. At times of low solar activity the dominant contribution to this flux comes from the two extended polar coronal holes, hence, in a simplistic formulation this interplanetary contribution may be considered linked to the polar magnetic fields of the Sun, which in turn is a plausible precursor candidate as we have seen in the previous subsection. As the polar field reverses shortly after sunspot maximum, this second contribution often introduces a characteristic secondary minimum in the cycle variation of geomagnetic indices, somewhere around the maximum of the curve.
The component (a) of the geomagnetic variations actually follows sunspot activity with a variable time delay. Thus a geomagnetic precursor based on features of the cycle dominated by this component has relatively little practical utility. This would seem to be the case, e.g., with the forecast method first proposed by Ohl (1966), who noticed that the minimum amplitudes of the smoothed geomagnetic aa index are correlated to the amplitude of the next sunspot cycle (see also Du et al., 2009).
An indication that the total geomagnetic activity, resulting from both mechanisms does contain useful information on the expected amplitude of the next solar cycle was given by Thompson (1993), who found that the total number of disturbed days in the geomagnetic field in cycle n is related to the sum of the amplitudes of cycles n and n+1 (see also Dabas et al., 2008).
A method for separating component (b) was proposed by Feynman (1982) who correlated the annual aa index with the annual mean sunspot number and found a linear relationship between R and the minimal value of aa for years with such R values. She interpreted this linear relationship as representing the component (a) discussed above, while the amount by which aa in a given year actually exceeds the value predicted by the linear relation would be the contribution of type (b) (the “interplanetary component”). The interplanetary component usually peaks well ahead of the sunspot minimum and the amplitude of the peak seemed to be a good predictor of the next sunspot maximum. However, it is to be noted that the assumption that the “surplus” contribution to aa originates from the interplanetary component only is likely to be erroneous, especially for stronger cycles. It is known that the number of large solar eruptions shows no unique relation to R: in particular, for R > 100 their frequency may vary by a factor of 3 (see Figure 15 in Hathaway, 2010b), so in some years they may well yield a contribution to aa that greatly exceeds the minimum contribution. A case in point was the “Halloween events” of 2003, that very likely resulted in a large false contribution to the derived “interplanetary” aa index (Hathaway, 2010a). As a result, the geomagnetic precursor method based on the separation of the interplanetary component predicts an unusually strong cycle 24 (Rm ∼ 150), in contrast to most other methods, including Ohl’s method and the polar field precursor, which suggest a weaker than average cycle (Rm ∼ 80 – 90).
In addition to the problem of neatly separating the interplanetary contribution to geomagnetic disturbances, it is also wrong to assume that this interplanetary contribution is dominated by the effect of polar magnetic fields at all times during the cycle. Indeed, Wang and Sheeley Jr (2009) point out that the interplanetary magnetic field amplitude at the Ecliptic is related to the equatorial dipole moment of the Sun that does not survive into the next cycle, so despite its more limited practical use, Ohl’s original method, based on the minima of the aa index is physically better founded, as the polar dipole dominates around the minimum. The total amount of open interplanetary flux, more closely linked to polar fields, could still be determined from geomagnetic activity if the interplanetary contribution to it is further split into:
-
(b1)
A contribution due to the varying solar wind speed (or to the interplanetary magnetic field strength anticorrelated with it), which in turn reflects the strength of the equatorial dipole.
-
(b2)
Another contribution due to the overall interplanetary field strength or open magnetic flux, which ultimately reflects the axial dipole.
Clearly, if the solar wind speed contribution (b1) could also subtracted, a physically better founded prediction method should result. While in situ spacecraft measurements for the solar wind speed and the interplanetary magnetic field strength do not have the necessary time coverage, Svalgaard and Cliver (2005, 2007) and Rouillard et al. (2007) devised a method to reconstruct the variations of both variables from geomagnetic measurements alone. Building on their results, Wang and Sheeley Jr (2009) arrive at a prediction of Rm = 97 ± 25 for the maximum amplitude of solar cycle 24. To what extent the effect of the Halloween 2003 events has been removed from this analysis is unclear. In any case, the prediction agrees fairly well with that of Bhatt et al. (2009) who, assuming a preliminary minimum time of August 2008 and applying a modified form of Ohl’s method, predict a cycle maximum in late 2012, with an amplitude of 93 ± 20.
The actual run of cycle 24 will be certainly most revealing from the point of view of these complex interrelationships.
The open magnetic flux can also be derived from the extrapolation of solar magnetograms using a potential field source surface model. The magnetograms applied for this purpose may be actual observations or the output from surface flux transport models, using the sunspot distribution (butterfly diagram) and the meridional flow as input. Such models indicate that the observed latitude independence of the interplanetary field strength (“split monopole” structure) is only reproduced if the source surface is far enough (> 10R⊙) and the potential field model is modified to take into account the heliospheric current sheet (current sheet source surface model, Schüssler and Baumann, 2006; Jiang et al., 2010a). The extrapolations are generally found to agree well with in situ measurements where these are available.
2.4 Flows in the photosphere
In the currently widely popular flux transport dynamo models the strong polar fields prevalent around sunspot minimum are formed by the advection of following polarity flux from active regions by the poleward meridional flow. Changes in this flow may thus influence the would-be polar fields and thereby may serve as precursors of the upcoming cycle.
Such changes, on the other hand, are also associated with the normal course of the solar activity cycle, the overall flow at mid-latitudes being slower before and during maxima and faster during the decay phase. Therefore, it is just the cycle-to-cycle variation in this normal pattern that may be associated with the activity variations between cycles. In this respect it is of interest to note that the poleward flow in the late phases of cycle 23 seems to have had an excess speed relative to the previous cycle (Hathaway and Rightmire, 2010). If this were a latitude-independent amplitude modulation of the flow, then most flux transport dynamo models would predict a stronger than average polar field at the minimum, contrary to observations. On the other hand, in the surface flux transport model of Wang et al. (2009) an increased poleward flow actually results in weaker polar fields, as it lets less leading polarity flux to diffuse across the equator and cancel there. As the recent analysis by Muñoz-Jaramillo et al. (2010) has shown, the discrepancy resulted from the neglect of leading polarity flux in the Babcock-Leighton source term in flux transport dynamo models, and it can be remedied by substituting a pair of opposite polarity flux rings as source term instead of the α-term. With this correction, 2D flux transport and surface flux transport models agree in predicting a weaker polar field for faster meridional flow.
It is known from helioseismology that meridional flow speed fluctuations follow a characteristic latitudinal pattern associated with torsional oscillations and the butterfly diagram, consisting of a pair of axisymmetric bands of latitudinal flows converging towards the activity belts, migrating towards the equator, and accompanied by similar high-latitude poleward branches. This suggests interpreting the unusual meridional flow speeds observed during cycle 23 as an increased amplitude of this migrating modulation, rather than a change in the large-scale flow speed (Cameron and Schüssler, 2010). In this case, the flows converging on the activity belts tend to inhibit the transport of following polarities to the poles, again resulting in a lower than usual polar field, as observed (Jiang et al., 2010b; note, however, that Švanda et al., 2007 find no change in the flux transport in areas with increased flows). It is interesting to note that the torsional oscillation pattern, and thus presumably the associated meridional flow modulation pattern, was shown to be fairly well reproduced by a microquenching mechanism due to magnetic flux emerging in the active belts (Petrovay and Forgács-Dajka, 2002). Observational support for this notion has been provided by the seismic detection of locally increased flow modulation near active regions (Švanda et al., 2007). This suggests that stronger cycles may be associated with a stronger modulation pattern, introducing a nonlinearity into the flux transport dynamo model, as suggested by Jiang et al. (2010b).
In addition to a variation in the amplitude of migrating flow modulations, their migration speed may also influence the cycle. Howe et al. (2009) point out that in the current minimum the equatorward drift of the torsional oscillation shear belt corresponding to the active latitude of the cycle has been slower than in the previous minimum. They suggest that this slowing may explain the belated start of cycle 24.
3 Extrapolation Methods
In contrast to precursor methods, extrapolation methods only use the time series of sunspot numbers (or whichever solar activity indicator is considered) but they generally rely on more than one previous point to identify trends that can be used to extrapolate the data into the future. They are therefore also known as time series analysis or, for historic reasons, regression methods.
A cornerstone of time series analysis is the assumption that the time series is homogeneous, i.e., the mathematical regularities underlying its variations are the same at any point of time. This implies that a forecast for, say, three years ahead has equal chance of success in the rising or decaying phase of the sunspot cycle, across the maximum or, in particular, across the minimum. In this case, distinguishing intracycle and intercycle memory effects, as we did in Sections 1.3.2 and 2, would be meaningless. This concept of solar activity variations as a continuous process stands in contrast to that underlying precursor methods, where solar cycles are thought of as individual units lasting essentially from minimum to minimum, correlations within a cycle being considerably stronger than from one cycle to the next. While, as we have seen, there is significant empirical evidence for the latter view, the possibility of time homogeneity cannot be discarded out of hand. Firstly, if we consider the time series of global parameters (e.g., amplitudes) of cycles, homogeneity may indeed be assumed fairly safely. This approach has rarely been used for the directly observed solar cycles as their number is probably too low for meaningful inferences - but the long data sets from cosmogenic radionuclides are excellent candidates for time series analysis.
In addition, there may be good reasons to consider the option of homogeneity of solar activity data even on the scale of the solar cycle. Indeed, in dynamo models the solar magnetic field simply oscillates between (weak) poloidal and (strong) toroidal configuration: there is nothing inherently special about either of the two, i.e., there is no a priori reason to attribute a special significance to solar minimum. While at first glance the butterfly diagram suggests that starting a new cycle at the minimum is the only meaningful way to do it, there may be equally good arguments for starting a new cycle at the time of polar reversal. There is, therefore, plenty of motivation to try and apply standard methods of time series analysis to sunspot data.
Indeed, as the sunspot number series is a uniquely homogeneous and long data set, collected over centuries and generated in a fairly carefully controlled manner, it has become a favorite testbed of time series analysis methods and is routinely used in textbooks and monographs for illustration purposes (Box et al., 2008; Wei, 2005; Tong, 1990). This section will summarize the various approaches, proceeding, by and large, from the simplest towards the most complex.
3.1 Linear regression
Linear (auto)regression means representing the value of a time series at time t by a linear combination of values at times t — Δt, t — 2Δt, ..., t — pΔt. Admitting some random error ∈n, the value of R in point n is
where p is the order of the autoregression and the ci’s are weight parameters. A further twist on the model admits a propagation of errors from the previous q points:
This is known as the ARMA (AutoRegressive Moving Average) model.
Linear regression techniques have been widely used for solar activity prediction during the course of an ongoing cycle. Their application for cycle-to-cycle prediction has been less common and successful (Lomb and Andersen, 1980; Box et al., 2008; Wei, 2005).
Brajša et al. (2009) applied an ARMA model to the series of annual values of R. A successful fit was found for p = 6, q = 6. Using this fit, the next solar maximum was predicted to take place around 2012.0 with an amplitude 90 ± 27, and the following minimum occurring in 2017.
Instead of applying an autoregression model directly to SSN data, Hiremath (2008) applied it to a forced and damped harmonic oscillator model claimed to well represent the SSN series. This resulted in a predicted amplitude of 110 ± 10 for solar cycle 24, with the cycle starting in mid-2008 and lasting 9.34 years.
3.2 Spectral methods
“...the use of any mathematical algorithm to derive hidden periodicities from the data always entails the question as to whether the resulting cycles are not introduced either by the particular numerical method used or by the time interval analyzed.”
(de Meyer, 1981)
Spectral analysis of the sunspot number record is used for prediction under the assumption that the main reason of variability in the solar cycle is a long-term modulation due to one or more periods.
The usual approach to the problem is the purely formal one of representing the sunspot record with the superposition of eigenfunctions forming an orthogonal basis. From a technical point of view, spectral methods are a complicated form of linear regression. The analysis can be performed by any of the widely used means of harmonic analysis:
(1) Least squares (LS) frequency analysis (sometimes called “Lomb-Scargle periodogram”) consists in finding by trial and error the best fitting sine curve to the data using the least squares method, subtracting it (“prewhitening”), then repeating the procedure until the residuals become indistinguishable from white noise. The first serious attempt at sunspot cycle prediction, due to Kimura (1913), belonged to this group. The analysis resulted in a large number of peaks with dubious physical significance. The prediction given for the upcoming cycle 15 failed, the forecasted amplitude being ∼ 60 while the cycle actually peaked at 105. However, it is interesting to note that Kimura correctly predicted the long term strengthening of solar activity during the first half of the 20th century! LS frequency analysis on sunspot data was also performed by Lomb and Andersen (1980), with similar results for the spectrum.
(2) Fourier analysis is probably the most commonly used method of spectral decomposition in science. It has been applied to sunspot data from the beginning of the 20th century (Turner, 1913a,b; Michelson, 1913). Vitinsky (1973) judges Fourier-based forecasts even less reliable than LS periodogram methods. Indeed, for instance Cole (1973) predicted cycle 21 to have a peak amplitude of 60, while the real value proved to be nearly twice that.
(3) The maximum entropy method (MEM) relies on the Wiener-Khinchin theorem that the power spectrum is the Fourier transform of the autocorrelation function. Calculating the autocorrelation of a time series for M ≪ N points and extrapolating it further in time in a particular way to ensure maximal entropy can yield a spectrum that extends to arbitrarily low frequencies despite the shortness of the data segment considered, and also has the property of being able to reproduce sharp spectral features (if such are present in the data in the first place). A good description of the method is given by Ables (1974), accompanied with some propaganda for it - see Press et al. (1992) for a more balanced account of its pros and cons. The use of MEM for sunspot number prediction was pioneered by Currie (1973). Using maximum entropy method combined with multiple regression analysis (MRA) to estimate the amplitudes and phases, Kane (2007) arrived at a prediction of 80 to 101 for the maximum amplitude of cycle 24. It should be noted that the same method yielded a prediction (Kane, 1999) for cycle 23 that was far off the mark.
(4) Singular spectrum analysis (SSA) is a relatively novel method for the orthogonal decomposition of a time series. While in the methods discussed above the base was fixed (the trigonometric functions), SSA allows for the identification of a set of othogonal eigenfunctions that are most suitable for the problem. This is done by a principal component analysis of the covariance matrix rik = 〈RiRi+k〉. SSA was first applied to the sunspot record by Rangarajan (1998) who only used this method for pre-filtering before the application of MEM. Loskutov et al. (2001) who also give a good description of the method, already made a prediction for cycle 24: a peak amplitude of 117. More recently, the forecast has been corrected slightly downwards to 106 (Kuzanyan et al., 2008).
The dismal performance of spectral predictions with the methods (1) – (3) indicates that the sunpot number series cannot be well represented by the superposition of a limited number of fixed periodic components. Instead,
-
the periods may be time dependent,
-
the system may be quasiperiodic, with a significant finite width of the periodic peaks (esp. the 11-year peak),
-
there may be non-periodic (i.e., chaotic or stochastic) components in the behaviour of the system, manifested as a continuous background in the spectrum.
In practice, all three effects suggested above may play some part. The first mentioned effect, time dependence, may in fact be studied within the framework of spectral analysis. MEM and SSA are intrinsically capable of detecting or representing time dependence in the spectrum, while LS and Fourier analysis can study time dependence by sliding an appropriate data window across the period covered by observations. If the window is Gaussian with a width proportional to the frequency we arrive at the popular wavelet analysis. This method was applied to the sunspot number series by Ochadlick Jr et al. (1993), Vigouroux and Delachie (1994), Frick et al. (1997), Fligge et al. (1999), and Li et al. (2005) who could confirm the existence and slight variation of the 11-year cycle and the Gleissberg-cycle. Recently, Kolláth and Oláh (2009) called attention to a variety of other generalized time dependent spectral analysis methods, of which the pseudo-Wigner transform yields especially clear details (see Figure 9). The time varying character of the basic periods makes it difficult to use these results for prediction purposes but they are able to shed some light on the variation as well as the presistent or intermittent nature of the periods determining solar activity.
Pseudo-Wigner power distribution in the sunspot number record, with time on the abscissa and frequency on the ordinate. The three horizontal bands of high power correspond, from bottom to top, to the Gleissberg cycle, the 11-year cycle and its first harmonic. The sunspot number curve is shown on top for guidance (figure courtesy of Z. Kolláth).
In summary, it is fair to say that forecasts based on harmonic analysis are notoriously unreliable. The secular variation of the basic periods, obeying as yet unknown rules, would render harmonic analysis practically useless for the prediction of solar cycles even if solar activity could indeed be described by a superposition of periodic functions. Although they may be potentially useful for very long term prediction (on centennial scales), when it comes to cycle-to-cycle forecasts the best we can hope from spectral studies is apparently an indirect contribution, by constraining dynamo models with the inambiguously detected periodicities.
In what remains from this subsection, we briefly review what these apparently physically real periods are and what impact they may have on solar cycle prediction.
3.2.1 The 11-year cycle and its harmonics
As an example of the period spectrum obtained by these methods, in Figure 8 we present the FFT based power spectrum estimate of the smoothed sunspot number record. Three main features are immediately noticed:
-
The dominant 11-year peak, with its sidelobes and its 5.5-year harmonic.
-
The 22-year subharmonic, representing the even-odd rule.
-
The significant power present at periods longer than 50 years, associated with the Gleissberg cycle.
The dominant peak in the power spectrum is at ∼ 11 years. Significant power is also present at the first harmonic of this period, at 5.5 years. This is hardly surprising as the sunspot number cycles, as presented in Figure 3, have a markedly asymmetrical profile. It is a characteristic of Fourier decomposition that in any periodic series of cycles where the profiles of individual cycles are non-sinusoidal, all harmonics of the base period will appear in the spectrum.
Indeed, were it not for the 13-month smoothing, higher harmonics could also be expected to appear in the power spectrum. It has been proposed (Krivova and Solanki, 2002) that these harmonics are detected in the sunspot record and that they may be related to the periodicities of ∼ 1.3 years intermittently observed in solar wind speed (Richardson et al., 1994; Paularena et al., 1995; Szabo et al., 1995; Mursula and Zieger, 2000; Lockwood, 2001) and in the internal rotation velocity of the Sun (Howe, 2009, Sect. 10.1). An analoguous intermittent 2.5 year variation in the solar neutrino flux (Shirai, 2004) may also belong to this group of phenomena. It may be worth noting that, from the other end of the period spectrum, the 154-day Rieger period in solar flare occurrence (Rieger et al., 1984; Bai and Cliver, 1990) has also been tentatively linked to the 1.3-year periodicity. Unusually strong excitation of such high harmonics of the Schwabe cycle may possibly be explained by excitation due to unstable Rossby waves in the tachocline (Zaqarashvili et al., 2010).
The 11-year peak in the power spectrum has substantial width, related to the rather wide variation in cycle lengths in the range 9 – 13 years. Yet Figure 8 seems to suggest the presence of a well detached second peak in the spectrum at a period of ∼ 14 years. The presence of a distinct peak at the first harmonic and even at the subharmonic of this period seems to support its reality. Indeed, peaks at around 14 and 7 years were already found by other researchers (e.g., Kimura, 1913; Currie, 1973) who suggested that these may be real secondary periods of sunspot activity.
The situation is, however, more prosaic. Constraining the time interval considered to data more recent than 1850, from which time the sunspot number series is considered to be more reliable, the 14.5-year secondary peak and its harmonics completely disappear. On the other hand, the power spectrum for the years 1783 – 1835 indicates that the appearance of the 14.5-year secondary peak in the complete series is almost entirely due to the strong predominance of this period (and its harmonic) in that interval. This interval covers the unusually long cycle 4 and the Dalton minimum, consisting of three consecutive unusually weak cycles, when the “normal” 11-year mode of operation was completely suppressed.
As pointed out by Petrovay (2010), this probably does not imply that the Sun was operating in a different mode during the Dalton minimum, the cycle length being 14.5 years instead of the usual 11 years. Instead, the effect may be explained by the well known inverse correlation between cycle length and amplitude, which in turn is the consequence of the strong inverse correlation between rise rate and cycle amplitude (Waldmeier effect), combined with a much weaker or nonexistent correlation between decay rate and amplitude (see Section 1.3.3). The cycles around the Dalton minimum, then, seem to lie at the low amplitude (or long period) end of a continuum representing the well known cycle length-amplitude relation, ultimately explained by the Waldmeier effect.
A major consequence of this is that the detailed distribution of peaks varies significantly depending on the interval of time considered. Indeed, Kolláth and Oláh (2009) recently applied time dependent harmonic analysis to the sunspot number series and found that the dominant periods have shown systematic secular changes during the past 300 years (Figure 9). For instance, the basic period seems to have shortened from 11 years to 10 years between 1850 and 1950, with some moderate increase in the last 50 years. (This is consistent with the known anticorrelation between cycle length and amplitude, cf. Section 1.3.3.)
3.2.2 The even-odd (a.k.a. Gnevyshev-Ohl) rule
A cursory look at Figure 3 shows that solar cycles often follow an alternating pattern of higher and lower maxima. In this apparent pattern, already noticed by the early observers (e.g, Turner, 1913c), odd cycles have been typically stronger than even cycles in the last two centuries.
This even-odd rule can be given two interpretations: a “weak” one of a general tendency of alternation between even and odd cycles in amplitude, or a “strong” one of a specific numerical relation between the amplitudes of consecutive cycles.
Let us first consider the rule in its weak interpretation. At first sight the rule admits many exceptions, but the amplitude of solar cycles depends on the particular measuring method used. Exceptions from the even-odd alternation rule become less common if a long term trend (calculated by applying a 12221 or 121 filter, see Section 1.3.1) is subtracted from the data (Charbonneau, 2001), or if integrated cycle amplitudes (sums of annual mean sunspot numbers during the cycle) are used (Gnevyshev and Ohl, 1948).
In fact, as evident from, e.g., the work of Mursula et al. (2001) where cycle amplitudes are based on group sunspot numbers and the amplitude of a cycle is defined as the sum of the annual GSN value over the course of the cycle, the odd-even alternation may be considered as strictly valid with only four exceptions:
-
In the pairs 7 – 8 and 17 – 18, odd cycles are followed by stronger even cycles at the end of Dalton minimum and at the beginning of the Modern Maximum. These exceptions could be made to disappear by the subtraction of the long term trend as suggested by Charbonneau (2001).
-
The pair 22 – 23 represents another apparent break of the weak even-odd rule which is not easily explained away, even though the relative difference is smaller if the Kislovodsk sunspot number series is used (Nagovitsyn et al., 2009). The possibility is obviously there that the subtraction of the long term trend may resolve the problem but we have no way to tell in the near future.
-
Prior to cycle 5, the phase of the alternation was opposite, even cycles being stronger than odd cycles. As cycle 4 is known to have been anomalously long anyway (the so-called “phase catastrophe” in the solar cycle, Vitinsky et al., 1986) and its decaying phase is not well covered by observations (Vaquero, 2007), this gave rise to the suggestion of a “lost solar cycle” between cycles 4 and 5 (Usoskin et al., 2001; Usoskin and Mursula, 2003). This cycle, however, would have been even more anomalous than cycle 4 and despite intensive searches in historic data the evidence is still not quite conclusive (Krivova et al., 2002; see, however, Usoskin et al., 2009a).
The issue whether the even-odd rule can go through phase jumps or not is important with respect to its possible origin. One plausible possibility is that the alternation is due to the superposition of a steady primordial magnetic field component on the oscillatory magnetic field generated by the dynamo (Levy and Boyer, 1982). In this case, any phase jump in the Gnevyshev-Ohl rule should imply a phase jump in Hale’s polarity rules, too. Alternatively, persistent even-odd alternation may also arise in nonlinear dynamos as a period-2 limit cycle (Durney, 2000); with a stochastic forcing occasional phase jumps are also possible (Charbonneau, 2001; Charbonneau et al., 2007).
While we have no information on this from the 18th century phase jump, we can be certain that there was no such phase jump in polarities in the last two decades, even though the even-odd rule seems to have been broken again. It will be interesting to see when (and if) the even-odd rule settles in again, whether it will have done so with a phase jump or not. For instance, if cycle 25 will again exceed cycle 24 it would seem that no phase jump occurred and both theoretical options are still open. But if cycle 25 will represent a further weakening from cycle 24, followed by a stronger cycle 26, a phase jump will have occurred, which may exclude the primordial field origin of the rule if Hale’s polarity rules remain unchanged.
Let us now discuss the stronger interpretation of the even-odd rule. In the first quantitative study of the relative amplitudes of consecutive cycles, Gnevyshev and Ohl (1948) found a rather tight correlation between the time integrated amplitudes of even and subsequent odd cycles, while the correlation between odd cycles and subsequent even cycles was found to be much less strong. This gave rise to the notion that solar cycles come in “two-packs” as even-odd pairs. Nagovitsyn et al. (2009) confirmed this puzzling finding on the basis of data covering the whole period of telescopic observations (and renumbering cycles before 1790 in accordance with the lost cycle hypothesis); they also argue that cycle pair 22 – 23 does not deviate strongly from the even-odd correlation curve so it should not be considered a “real” exception to the even-odd rule.
The fact that shortly after its formulation by Gnevyshev and Ohl (1948), the (strong) even-odd rule was used by Kopecký (1950) to successfully predict the unusually strong cycle 19 made this method particularly popular for forecast purposes. However, forecasts based on the even-odd rule completely failed for cycle 23, overpredicting the amplitude by > 50% (see review by Li et al., 2001). Taken together with the implausibility of the suggested two-pack system, this shows that it is probably wiser to take the position that “extraordinary claims need extraordinary evidence” - which is yet to be provided in the case of the “strong” even-odd rule.
Finally, in the context of the even-odd rule, it is also worth mentioning the three-cycle regularity proposed by Ahluwalia (1998). Even though the evidence presented for the alleged triadic pattern is not overwhelming, this method resulted in one of the few successful predictions for the amplitude of cycle 23.
3.2.3 The Gleissberg cycle
Besides the changes in the length of the 11-year cycle related to the amplitude-cycle length correlation, even more significant are the variations in the period of the so-called Gleissberg cycle (Gleissberg, 1939). This “cycle”, corresponding to the 60 – 120 year “plateau” in Figure 8 was actually first noticed by Wolf, who placed it in the range 55 – 80 years (see Richard, 2004, for a discussion of the history of the studies of the Gleissberg cycle). Researchers in the middle of the 20th century characterized it as an 80 – 100 year variation. Figure 9 explains why so widely differing periods were found in different studies: the period has in fact shown a secular increase in the past 300 years, from about 50 years in the early 18th century, to a current value exceeding 140 years. This increased length of the Gleissberg cycle also agrees with the results of Forgács-Dajka and Borkovits (2007).
The detection of ∼ 100 year periods in a data set of 300 years is of course always questionable, especially if the period is even claimed to be varying. However, the very clear and, most importantly, nearly linear secular trend seen in Figure 9 argues convincingly for the reality of the period in question. This clear appearance of the period is due to the carefully optimized choice of the kernel function in the time-frequency analysis, a method resulting in a so-called pseudo-Wigner distribution (PWD). In addition, in their study Kolláth and Oláh (2009) present an extremely conscientious test of the reliability of their methods, effectively proving that the most salient features in their PWD are not artefacts. (The method was subsequently also applied to stellar activity, Oláh et al., 2009.) This is the most compelling evidence for the reality of the Gleissberg cycle yet presented.
3.2.4 Supersecular cycles
For the 210-year Suess cycle, McCracken and Beer (2008) present further evidence for the temporally intermittent nature of this marked peak in the spectrum of solar proxies. The Suess cycle seems to have a role in regulating the recurrence rate of grand minima. Grand minima, in turn, only seem to occur during < 1 kiloyear intervals (“Spörer events”) around the minimum of the ∼ 2400-year Hallstatt cycle.
For further discussion of long term variations in solar activity we refer the reader to the reviews by Beer et al. (2006) and Usoskin (2008).
3.3 Nonlinear methods
“...every complicated question has a simple answer which is wrong. Analyzing a time series with a nonlinear approach is definitely a complicated problem. Simple answers have been repeatedly offered in the literature, quoting numerical values for attractor dimensions for any conceivable system.”
(Hegger et al., 1999)
The nonlinearities in the dynamo equations readily give rise to chaotic behaviour of the solutions. The long term behaviour of solar activity, with phenomena like grand minima and grand maxima, is also suggestive of a chaotic system. While chaotic systems are inherently unpredictable on long enough time scales, their deterministic nature does admit forecast within a limited range. It is therefore natural to explore this possibility from the point of view of solar cycle prediction.
3.3.1 Attractor analysis and phase space reconstruction: the pros ...
Assuming that the previous (M — 1) values of the sunspot number do in some way determine the current expected value, our problem becomes restricted to an M-dimensional phase space, the dimensions being the current value and the (M — 1) previous values. With a time series of length N, we have N — M + 1 points fixed in the phase space, consecutive points being connected by a line. This phase space trajectory is a sampling of the attractor of the physical system underlying the solar cycle (with some random noise added to it). The attractor represents a mapping in phase space which maps each point into the one the system occupies in the next time step: if this mapping is known to a good approximation, it can be used to extend the trajectory towards the future.
For the mapping to be known, M needs to be high enough to avoid self-crossings in the phase space trajectory (otherwise the mapping is not unique) but low enough so that the trajectory still yields a good sampling of the attractor. The lowest integer dimension satisfying these conditions is the embedding dimension D of the attractor (which may have a fractal dimension itself).
Once the attractor has been identified, its mathematical description may be done in two ways.
(1) Parametric fitting of the attractor mapping in phase space. The simplest method is the piecewise linear fit suggested by Farmer and Sidorowich (1987) and applied in several solar prediction attempts, e.g., Kurths and Ruzmaikin (1990). Using a method belonging to this group, for cycle 24 Kilcik et al. (2009) predict a peak amplitude of 87 to be reached in late 2012. Alternatively, a global nonlinear fit can also be used: this is the method applied by Serre and Nesme-Ribes (2000) as the first step in their global flow reconstruction (GFR) approach.
(2) Nonparametric fitting. The simplest nonparametric fit is to find the closest known attractor point to ours (in the (M — 1)-dimensional subspace excluding the last value) and then using this for a prediction, as done by Jensen (1993). (This resulted in so large random forecast errors that it is practically unsuitable for prediction.) Neural networks, discussed in more detail in Section 3.3.4 below, are a much more sophisticated nonparametric fitting device.
(3) Indirectly, one may try to find a set of differential equations describing a system that gives rise to an attractor with properties similar to the observed. In this case there is no guarantee that the derived equations will be unique, as an alternative, completely different set may also give rise to a very similar attractor. This arbitrariness of the choice is not necessarily a problem from the point of view of prediction as it is only the mapping (the attractor structure) that matters. Such phase space reconstruction by a set of governing equations was performed, e.g., by Serre and Nesme-Ribes (2000) or Aguirre et al. (2008); for cycle 24 the latter authors predict a peak amplitude of 65 ± 16. On the other hand, instead of putting up with any arbitrary set of equations correctly reproducing the phase space, one might make an effort to find a set with a structure reasonably similar to the dynamo equations so they can be given a meaningful physical interpretation. Methods following this latter approach will be discussed in Sections 4.4 and 4.5.
3.3.2 ... the cons ...
Finding the embedding dimension and the attractor structure is not a trivial task, as shown by the widely diverging results different researchers arrived at. One way to find the correct embedding dimension is the false nearest neighbours method (Kennel et al., 1992), essentially designed to identify self-crossing in the phase space trajectory, in which case the dimension M needs to be increased. But self-crossings are to some extent inevitable, due to the stochastic component superimposed on the deterministic skeleton of the system.
As a result, the determination of the minimal necessary embedding dimension is usually done indirectly. One indirect method fairly popular in the solar community is the approach proposed by Sugihara and May (1990) where the correct dimension is basically figured out on the basis of how successfully the model, fit to the first part of the data set, can “predict” the second part (using a piecewise linear mapping).
Another widely used approach, due to Grassberger and Procaccia (1983), starts by determining the correlation dimension of the attractor, by simply counting how the number of neighbours in an embedding space of dimension M ≫ 1 increases with the distance from a point. If the attractor is a lower dimensional manifold in the embedding space and it is sufficiently densely sampled by our data then the logarithmic steepness d of this function should be constant over a considerable stretch of the curve: this is the correlation dimension d. Now, we can increase M gradually and see at what value d saturates: that value determines the attractor dimension, while the value of M where saturation is reached yields the embedding dimension.
The first nonlinear time series studies of solar activity indicators suggested a time series spacing of 2 – 5 years, an attractor dimension ∼ 2 – 3 and an embedding dimension of 3 – 4 (Kurths and Ruzmaikin, 1990; Gizzatullina et al., 1990). Other researchers, however, were unable to confirm these results, either reporting very different values or not finding any evidence for a low dimensional attractor at all (Calvo et al., 1995; Price et al., 1992; Carbonell et al., 1994; Kilcik et al., 2009; Hanslmeier and Brajša, 2010). In particular, I would like to call attention to the paper by Jensen (1993), which, according to ADS and WoS, has received a grand total of zero citations (!) up to 2010, yet it displays an exemplary no-nonsense approach to the problem of sunspot number prediction by nonlinear time series methods. Unlike so many other researchers, the author of that paper does not fool himself into believing to see a linear segment on the logarithmic correlation integral curve (his Figure 4); instead, he demonstrates on a simple example that the actual curve can be perfectly well reproduced by a simple stochastic process.
These contradictory results obviously do not imply that the mechanism generating solar activity is not chaotic. For a reliable determination a long time series is desirable to ensure a sufficiently large number of neighbours in a phase space volume small enough compared to the global scale of the attractor. Solar data sets (even the cosmogenic radionuclide proxies extending over millennia but providing only a decadal sampling) are typically too short and sparse for this. In addition, clearly distinguishing between the phase space fingerprints of chaotic and stochastic processes is an unsolved problem of nonlinear dynamics which is not unique to solar physics. A number of methods have been suggested to identify chaos unambiguously in a time series but none of them has been generally accepted and this topic is currently a subject of ongoing research - see, e.g., the work of Freitas et al. (2009) which demonstrates that the method of “noise titration”, somewhat akin to the Sugihara-May algorithm, is uncapable of distinguishing superimposed coloured noise from intrinsically chaotic systems.
3.3.3 ... and the upshot
Starting from the 1980s many researchers jumped on the chaos bandwagon, applying nonlinear time series methods designed for the study of chaotic systems to a wide variety of empirical data, including solar activity parameters. From the 1990s, however, especially after the publication of the influential book by Kantz and Schreiber (1997), it was increasingly realized that the applicability of these nonlinear algorithms does not in itself prove the predominantly chaotic nature of the system considered. In particular, stochastic noise superposed on a simple, regular, deterministic skeleton can also give rise to phase space characteristics that are hard to tell from low dimensional chaos, especially if strong smoothing is applied to the data. As a result, the pendulum has swung in the opposite direction and currently the prevailing view is that there is no clear cut evidence for chaos in solar activity data (Panchev and Tsekov, 2007).
One might take the position that any forecast based on attractor analysis is only as good as the underlying assumption of a chaotic system is: if that assumption is unverifiable from the data, prediction attempts are pointless. This, however, is probably a too hasty judgment. As we will see, the potentially most useful product of phase space reconstruction attempts is the inferences they allow regarding the nature of the underlying physical system (chaotic or not), even offering a chance to constrain the form of the dynamo equations relevant for the Sun. As discussed in the next section, such truncated models may be used for forecast directly, or alternatively, the insight they yield into the mechanisms of the dynamo may be used to construct more sophisticated dynamo models.
3.3.4 Neural networks
Neural networks are algorithms built up from a large number of small interconnected units (“neurons” or “threshold logic units”), each of which is only capable of performing a simple nonlinear operation on an input signal, essentially described by a step function or its generalized (rounded) version, a sigmoid function. To identify the optimal values of thresholds and weights parameterizing the sigmoid functions of each neuron, an algorithm called “back propagation rule” is employed which minimizes (with or without human guidance) the error between the predicted and observed values in a process called “training” of the network. Once the network has been correctly trained, it is capable of further predictions.
The point is that any arbitrary multidimensional nonlinear mapping may be approximated by a combination of stepfunctions to a good degree - so, as mentioned in Section 3.3.1 above, the neural network can be used to find the nonlinear mapping corresponding to the attractor of the given time series.
More detailed introductions to the method are given by Blais and Mertz (2001) and by Calvo et al. (1995); the latter authors were also the first to apply a neural network for sunspot number prediction. Unfortunately, despite their claim of being able to “predict” (i.e., postdict) some earlier cycles correctly, their prediction for cycle 23 was off by a wide margin (predicted peak amplitude of 166 as opposed to 121 observed). One of the neural network forecasts for cycle 24 (Maris and Oncica, 2006) was equally far off, predicting a maximum of 145 as early as December 2009, while another one (Uwamahoro et al., 2009) yields a more conservative value of 117.5 ± 8.5 for 2012.
4 Model-Based Predictions
“Progress in dynamo theory is extremely difficult, as it can be made only by understanding the interaction of turbulent plasma motions with magnetic fields. Indeed, the extreme conditions within the solar interior make this a formidable task. ... Any predictions made with such models should be treated with extreme caution (or perhaps disregarded), as they lack solid physical underpinnings.”
(Tobias et al., 2006)
While attempts to predict future solar cycles on the basis of the empirical sunspot number record have a century-old history, predictions based on physical models of solar activity only started a few years ago. The background of this new trend is, however, not some significant improvement in our understanding of the solar dynamo. Rather, it is the availability of increasingly fast new computers that made it possible to fine-tune the parameters of certain dynamo models to reproduce the available sunspot record to a good degree of accuracy and to apply data assimilation methods (such as those used in terrestrial weather prediction) to these models. This is not without perils. On the one hand, the capability of multiparametric models to fit a multitude of observational data does not prove the conceptual correctness of the underlying model. On the other hand, in chaotic or stochastic systems such as the solar dynamo, fitting a model to existing data will not lead to a good prediction beyond a certain time span, the extent of which can only be objectively assessed by “postdiction” tests, i.e., checking the models predictive skill by trying to “predict” previous solar cycles and comparing those predictions to available data. Apparently successful postdiction tests have led some groups to claim a breakthrough in solar cycle prediction owing to the model-based approach (Dikpati and Gilman, 2006; Kitiashvili and Kosovichev, 2008). Yet, as we will see in the following discussion, a closer inspection of these claims raises many questions regarding the role that the reliance on a particular physical dynamo model plays in the success of their predictions.
4.1 The solar dynamo: a brief summary of current models
Extensive summaries of the current standing of solar dynamo theory are given in the reviews by Petrovay (2000), Ossendrijver (2003), Charbonneau (2010), and Solanki et al. (2006). As explained in detail in those reviews, all current models are based on the mean-field theory approach wherein a coupled system of partial differential equations governs the evolution of the toroidal and poloidal components of the large-scale magnetic field. The large-scale field is assumed to be axially symmetric in practically all current models. In some nonlinear models the averaged equation of motion, governing large-scale flows is also coupled into the system.
In the simplest case of homogeneous and isotropic turbulence, where the scale l of turbulence is small compared to the scale L of the mean variables (scale separation hypothesis), the dynamo equations have the form
Here B and U are the large-scale mean magnetic field and flow speed, respectively; ηT is the magnetic diffusivity (dominated by the turbulent contribution for the highly conductive solar plasma), while α is a parameter related to the non-mirror symmetric character of the magnetized plasma flow.
In the case of axial symmetry the mean flow U may be split into a meridional circulation Uc and a differential rotation characterized by the angular velocity profile Ω0(r; θ):
where r, θ, ϕ are spherical coordinates and eϕ is the azimuthal unit vector. Now introducing the shear
assuming α ≪ ΩL and ignoring spatial derivatives of α and ηT, Equation (13) simplifies to the pair
where B and A are the toroidal (azimuthal) components of the magnetic field and of the vector potential, respectively, and \(\frac{{\partial A}} {{\partial x}}\) is to be evaluated in the direction 90° clockwards of \(\vec \Omega\) (along the isorotation surface) in the meridional plane. These are the classic αΩ dynamo equations, including a meridional flow.
In the more mainstream solar dynamo models the strong toroidal field is now generally thought to reside near the bottom of the solar convective zone. Indeed, it is known that a variety of flux transport mechanisms such as pumping (Petrovay, 1994) remove magnetic flux from the solar convective zone on a timescale short compared to the solar cycle. Following earlier simpler numerical experiments, recent MHD numerical simulations have indeed demonstrated this pumping of large scale magnetic flux from the convective zone into the tachocline below, where it forms strong coherent toroidal fields (Browning et al., 2006). As this layer is also where rotational shear is maximal, it is plausible that the strong toroidal fields are not just stored but also generated here, by the winding up of poloidal field. The two main groups of dynamo models, interface dynamos and flux transport dynamos, differ mainly in their assumptions about the site and mechanism of the α-effect responsible for the generation of a new poloidal field from the toroidal field.
In interface dynamos α is assumed to be concentrated near the bottom of the convective zone, in a region adjacent to the tachocline, so that the dynamo operates as a wave propagating along the interface between these two layers. While these models may be roughly consistent and convincing from the physical point of view, they have only had limited success in reproducing the observed characteristics of the solar cycle, such as the butterfly diagram.
Flux transport dynamos, in contrast, rely on the Babcock-Leighton mechanism for α, arising due to the action of the Coriolis force on emerging flux loops, and they assume that the corresponding α-effect is concentrated near the surface. They keep this surface layer incommunicado with the tachocline by introducing some arbitrary unphysical assumptions (such as very low diffusivities in the bulk of the convective zone). The poloidal fields generated by this surface α-effect are then advected to the poles and there down to the tachocline by the meridional circulation - which, accordingly, has key importance in these models. The equatorward deep return flow of the meridional circulation is assumed to have a significant overlap with the tachocline (another controversial point), and it keeps transporting the toroidal field generated by the rotational shear towards the equator. By the time it reaches lower latitudes, it is amplified sufficiently for the flux emergence process to start, resulting in the formation of active regions and, as a result of the Babcock-Leighton mechanism, in the reconstruction of a poloidal field near the surface with a polarity opposed to that in the previous 11-year cycle. While flux transport models may be questionable from the point of view of their physical consistency, they can be readily fine-tuned to reproduce the observed butterfly diagram quite well.
It should be noted that while the terms “interface dynamo” and “flux transport dynamo” are now very widely used to describe the two main approaches, the more generic terms “advectiondominated” and “diffusion-dominated” would be preferable in several respects. This classification allows for a continuous spectrum of models depending on the numerical ratio of advective and diffusive timescales (for communication between surface and tachocline). In addition, even at the two extremes, classic interface dynamos and circulation-driven dynamos are just particular examples of advection or diffusion dominated systems with different geometrical structures.
4.2 Is model-based cycle prediction feasible?
As it can be seen even from the very brief and sketchy presentation given above, all current solar dynamo models are based on a number of quite arbitrary assumptions and depend on a number of free parameters, the functional form and amplitude of which is far from being well constrained. For this reason, Bushby and Tobias (2007) rightfully say that all current solar dynamo models are only of “an illustrative nature”. This would suggest that as far as solar cycle prediction is concerned, the best we should expect from dynamo models is also an “illustrative” reproduction of a series of solar cycles with the same kind of long-term variations (qualitatively and, in the statistical sense, quantitatively) as seen in solar data. Indeed, Bushby and Tobias (2007) demonstrated that even a minuscule stochastic variation in the parameters of a particular flux transport model can lead to large, unpredictable variations in the cycle amplitudes. And even in the absence of stochastic effects, the chaotic nature of nonlinear dynamo solutions seriously limits the possibilities of prediction, as the authors find in a particular interface dynamo model: even if the very same model is used to reproduce the results of one particular run, the impossibility of setting initial conditions exactly representing the system implies that predictions are impossible even for the next cycle. Somewhat better results are achieved by an alternative method, based on the phase space reconstruction of the attractor of the nonlinear system - this is, however, a purely empirical time series analysis technique for which no knowledge of the detailed underlying physics is needed. (Cf. Section 3.3 above.)
Despite these very legitimate doubts regarding the feasibility of model-based prediction of solar cycles, in recent years several groups have claimed to be able to predict solar cycle 24 on the basis of dynamo models with a high confidence. So let us consider these claims.
4.3 Explicit models
The current buzz in the field of model-based solar cycle prediction was started by the work of the solar dynamo group in Boulder (Dikpati et al., 2006; Dikpati and Gilman, 2006). Their model is a flux transport dynamo, advection-dominated to the extreme. The strong suppression of diffusive effects is assured by the very low value (less than 20 km2 s-1) assumed for the turbulent magnetic diffusivity in the bulk of the convective zone. As a result, the poloidal fields generated near the surface by the Babcock-Leighton mechanism are only transported to the tachocline on the very long, decadal time scale of meridional circulation. The strong toroidal flux residing in the low-latitude tachocline, producing solar activity in a given cycle is thus the product of the shear amplification of poloidal fields formed near the surface about 2 – 3 solar cycles earlier, i.e., the model has a “memory” extending to several cycles. The mechanism responsible for cycle-to-cycle variation is assumed to be the stochastic nature of the flux emergence process. In order to represent this variability realistically, the model drops the surface α-term completely (a separate, smaller α term is retained in the tachocline); instead, the generation of poloidal field near the surface is represented by a source term, the amplitude of which is based on the sunspot record, while its detailed functional form remains fixed.
Dikpati and Gilman (2006) find that, starting off their calculation by fixing the source term amplitudes of sunspot cycles 12 to 15, they can predict the amplitudes of each subsequent cycle with a reasonable accuracy, provided that the relation between the relative sunspot numbers and the toroidal flux in the tachocline is linear, and that the observed amplitudes of all previous cycles are incorporated in the source term for the prediction of any given cycle. For the upcoming cycle 24 the model predicts peak smoothed annual relative sunspot numbers of 150 or more. Elaborating on their model, they proceeded to apply it separately to the northern and southern hemispheres, to find that the model can also be used to correctly forecast the hemispheric asymmetry of solar activity (Dikpati et al., 2007).
The extraordinary claims of this pioneering research have prompted a hot debate in the dynamo community. Besides the more general, fundamental doubt regarding the feasibility of model-based predictions (see Section 3.2 above), more technical concerns arose, to be discussed below.
Another flux transport dynamo code, the Surya code, originally developed by A. Choudhuri and coworkers in Bangalore, has also been utilized for prediction purposes. The crucial difference between the two models is in the value of the turbulent diffusivity assumed in the convective zone: in the Bangalore model this value is 240 km2 s-1, 1 – 2 orders of magnitude higher than in the Boulder model, and within the physically plausible range (Chatterjee et al., 2004). As a result of the shorter diffusive timescale, the model has a shorter memory, not exceeding one solar cycle. As a consequence of this relatively rapid diffusive communication between surface and tachocline, the poloidal fields forming near the surface at low latitudes due to the Babcock-Leighton mechanism diffuse down to the tachocline in about the same time as they reach the poles due to the advection by the meridional circulation. In these models, then, polar magnetic fields are not a true physical precursor of the low-latitude toroidal flux, and their correlation is just due to their common source. In the version of the code adapted for cycle prediction (Choudhuri et al., 2007; Jiang et al., 2007), the “surface” poloidal field (i.e., the poloidal field throughout the outer half of the convection zone) is rescaled at each minimum by a factor reflecting the observed amplitude of the Sun’s dipole field. The model shows reasonable predictive skill for the last three cycles for which data are available, and can even tackle hemispheric asymmetry (Goel and Choudhuri, 2009). For cycle 24, the predicted amplitude is 30 – 35% lower than cycle 23.
4.4 Truncated models
The “illustrative” nature of solar dynamo models is nowhere more clearly on display than in truncated or reduced models where some or all of the detailed spatial structure of the system is completely disregarded, and only temporal variations are explicitly considered. This is sometimes rationalised as a truncation or spatial integration of the equations of a more realistic inhomogenous system; in other cases, no such rationalisation is provided, representing the solar dynamo by an infinite, homogeneous or periodic turbulent medium where the amplitude of the periodic large-scale magnetic field varies with time only.
In the present subsection we deal with models that do keep one spatial variable (typically, the latitude), so growing wave solutions are still possible - these models, then, are still dynamos even though their spatial structure is not in a good correspondence with that of the solar dynamo.
This approach in fact goes back to the classic migratory dynamo model of Parker (1955) who radially truncated (i.e., integrated) his equations to simplify the problem. Parker seems to have been the first to employ a heuristic relaxation term of the form -Br/τd in the poloidal field equation to represent the effect of radial diffusion; here, τd = d2/ghT is the diffusive timescale across the thickness d of the convective zone. His model was recently generalized by Moss et al. (2008) and Usoskin et al. (2009b) to the case when the α-effect includes an additive stochastic noise, and nonlinear saturation of the dynamo is achieved by α-quenching. These authors do not make an attempt to predict solar activity with their model but they can reasonably well reproduce some features of the very long term solar activity record, as seen from cosmogenic isotope studies.
Another radially truncated model, this time formulated in a Cartesian system, is that of Kitiashvili and Kosovichev (2009). In this model stochastic effects are not considered and, in addition to using an α-quenching recipe, further nonlinearity is introduced by coupling in the Kleeorin-Ruzmaikin equation (Zel’dovich et al., 1983) governing the evolution of magnetic helicity, which in the hydromagnetic case contributes to α. Converting the toroidal field strength to relative sunspot number using the Bracewell transform, Equation (3), the solutions reproduce the asymmetric profile of the sunspot number cycle. For sufficiently high dynamo numbers the solutions become chaotic, cycle amplitudes show an irregular variation. Cycle amplitudes and minimum-maximum time delays are found to be related in a way reminiscent of the Waldmeier relation.
Building on these results, Kitiashvili and Kosovichev (2008) attempt to predict solar cycles using a data assimilation method. The approach used is the so-called Ensemble Kalman Filter method. Applying the model for a “postdiction” of the last 8 solar cycles yielded astonishingly good results, considering the truncated and arbitrary nature of the model and the fundamental obstacles in the way of reliable prediction discussed above. While the presently available brief preliminary publication leaves several details of the method unclear, the question may arise whether the actual physics of the model considered has any significant role in this prediction, or we are dealing with something like the phase space reconstruction approach discussed in Section 3.3 above where basically any model with an attractor that looks reasonably similar to that of the actual solar dynamo would do. Either way, the method is remarkable, and the prediction for cycle 24 of a maximal smoothed annual sunspot number of 80, to be reached in 2013, will be worth comparing to the actual value.
In order to understand the origin of the predictive skill of the Boulder model, Cameron and Schüssler (2007) studied a radially truncated version of the model, wherein only the equation for the radial field component is solved as a function of time and latitude. The equation includes a source term similar to the one used in the Boulder model. As the toroidal flux does not figure in this simple model, the authors use the transequatorial flux Φ as a proxy, arguing that this may be more closely linked to the amplitude of the toroidal field in the upcoming cycle than the polar field. They find that Φ indeed correlates quite well (correlation coefficients r ∼ 0.8 – 0:9, depending on model details) with the amplitude of the next cycle, as long as the form of the latitude dependence of the source term is prescribed and only its amplitude is modulated with the observed sunspot number series (“idealized model”). But surprisingly, the predictive skill of the model is completely lost if the prescribed form of the source function is dropped and the actually observed latitude distribution of sunspots is used instead (“realistic model”). Cameron and Schüssler (2007) interpret this by pointing out that Φ is mainly determined by the amount of very low latitude flux emergence, which in turn occurs mainly in the last few years of the cycle in the idealized model, while it has a wider temporal distribution in the realistic model. The conclusion is that the root of the apparently good predictive skill of the truncated model (and, by inference, of the Boulder model it is purported to represent) is actually just the good empirical correlation between latephase activity and the amplitude of the next cycle, discussed in Section 2.1 above. This correlation is implicitly “imported” into the idealized flux transport model by assuming that the late-phase activity is concentrated at low latitudes, and therefore gives rise to cross-equatorial flux which then serves as a seed for the toroidal field in the next cycle. So if Cameron and Schüssler (2007) are correct, the predictive skill of the Boulder model is due to an empirical precursor and is thus ultimately explained by the good old Waldmeier effect (cf. Section 1.3.3)
The fact that the truncated model of Cameron and Schüssler (2007) is not identical to the Boulder model obviously leaves room for doubt regarding this conclusion. In particular, the effective diffusivity represented by the sink term in the truncated model is ∼ km2 s-1, significantly higher than in the Boulder model; consequently, the truncated model will have a more limited memory, cf. Yeates et al. (2008). The argument that the cross-equatorial flux is a valid proxy of the amplitude of the next cycle may be correct in such a short-memory model with no radial structure, but it is dubious whether it remains valid for flux transport models in general. In an attempt to appreciate the importance of the cross-equatorial flux in their model, Dikpati et al. (2008a) find that while this flux does indeed correlate fairly well (r = 0:76) with the next cycle amplitude, the toroidal flux is a much better predictor (r = 0:96). At first sight this seems to make it unlikely that the former can explain the latter; however, part of the difference in the predictive skill may be due to the fact that Φ shows much more short-term variability than the toroidal flux.
In any case, the obvious way to address the concerns raised by Cameron and Schüssler (2007) and further by Schüssler (2007) in relation to the Boulder model would be to run that model with a modified source function incorporating the realistic latitudinal distribution of sunspots in each cycle. The results of such a test are not yet available at the time of writing this review.
4.5 The Sun as an oscillator
An even more radical simplification of the solar dynamo problem ignores any spatial dependence in the solutions completely, concentrating on the time dependence only. Spatial derivatives appearing in Equations (14) and (15) are estimated as ∇ ∼ 1/L and the resulting terms Uc/L and ηT/L2 as 1/gt where τ is a characteristic time scale. This results in the pair
which can be combined to yield
where D = αΩτ2/L is the dynamo number. For D < 1, Equation (18) clearly describes a damped linear oscillator. For D > 1, solutions have a non-oscillatory character. The system described by Equation (18), then, is not only not a true dynamo (missing the spatial dependence) but it does not even display growing oscillatory solutions that would be the closest counterpart of dynamolike behaviour in such a system. Nevertheless, there are a number of ways to extend the oscillator model to allow for persistent oscillatory solutions, i.e., to turn it into a relaxation oscillator:
(1) The most straightforward approach is to add a forcing term + sin(ω0t) to the r.h.s. of Equations (18). Damping would cause the system to relax to the driving period 2π/gw0 if there were no stochastic disturbances to this equilibrium. Hiremath (2006) fitted the parameters of the forced and damped oscillator model to each observed solar cycle individually; then in a later work (Hiremath, 2008) he applied linear regression to the resulting series to provide a forecast (see Section 3.1 above).
(2) Another trick is to account for the π/2 phase difference between poloidal and toroidal field components in a dynamo wave by introducing a phase factor i into the first term on the r.h.s. of Equation (17). This can also be given a more formal derivation as equations of this form result from the substitution of solutions of the form A ∝ eikx, B ∝ ei(kx+π=2) into the 1D dynamo equations. This route, combined with a nonlinearity due to magnetic modulation of differential rotation described by a coupled third equation, was taken by Weiss et al. (1984). Their model displayed chaotic behaviour with intermittent episodes of low activity similar to grand minima.
(3) Wilmot-Smith et al. (2006) showed that another case where dynamo-like behaviour can be found in an equation like (18) is if the missing effects of finite communication time between parts of a spatially extended system are reintroduced by using a time delay δt, evaluating the first term on the r.h.s. at time t — Δt to get the value for the l.h.s. at time t.
(4) Yet another possibility is to introduce a nonlinearity into the model by assuming D = D0[1 — f(B)] where f(B = 0) = 0 and f ≥ 0 everywhere. (Note that any arbitrary form of α- or Ω-quenching can be cast in the above form by series expansion.) The governing equation then becomes one of a nonlinear oscillator:
In the most commonly assumed quenching mechanisms the leading term in f(B) is quadratic; in this case Equation (19) describes a Duffing oscillator (Kanamaru, 2008). For large positive dynamo numbers, D0 ≫ 1, then, the large nonlinear term dominates for high values of B, its negative sign imposing oscillatory behaviour; yet the origin is a repeller so the oscillation will never be damped out. The Duffing oscillator was first considered in the solar context by Paluš and Novotná (1999). Under certain conditions on the parameters, it can be reduced to a van der Pol oscillator (Adomian, 1989; Mininni et al., 2002; Kanamaru, 2007):
with μ > 0. From this form it is evident that the problem is equivalent to that of an oscillator with a damping that increases with amplitude; in fact, for small amplitudes the damping is negative, i.e., the oscillation is self-excited.
These simple nonlinear oscillators were among the first physical systems where chaotic behaviour was detected (when a periodic forcing was added). Yet, curiously, they first emerged in the solar context precisely as an alternative to chaotic behaviour. Considering the mapping of the solar cycle in the differential phase space {B; dB/dt}, Mininni et al. (2000) got the impression that, rather than showing signs of a strange attractor. The SSN series is adequately modelled by a van der Pol oscillator with stochastic fluctuations. This concept was further developed by Lopes and Passos (2009) who fitted the parameters of the oscillator to each individual sunspot cycle. The parameter μ is related to the meridional flow speed and the fit indicates that a slower meridional flow may have been responsible for the Dalton minimum. This was also corroborated in an explicit dynamo model (the Surya code) — however, as we discussed in Section 2.4, this result of flux transport dynamo models is spurious and the actual effect of a slower meridional flow is likely to be opposite to that suggested by the van der Pol oscillator model.
In an alternative approach to the problem, Nagovitsyn (1997) attempted to constrain the properties of the solar oscillator from its amplitude-frequency diagram, suggesting a Duffing oscillator driven at two secular periods. While his empirical reconstruction of the amplitude-frequency plot may be subject to many uncertainties, the basic idea is certainly noteworthy.
In summary: despite its simplicity, the oscillator representation of the solar cycle is a relatively new development in dynamo theory, and its obvious potential for forecasting purposes has barely been exploited.
5 Summary Evaluation
The performance of various forecast methods in cycles 21 – 23 was discussed by Li et al. (2001) and Kane (2001).
Precursor methods stand out with their internally consistent forecasts for these cycles which for cycles 21 and 22 proved to be correct. For cycle 23 these methods were still internally consistent in their prediction, mostly scattering in a narrow range between 150 and 170; however, the cycle amplitude proved to be considerably lower (Rmax = 121). It should be noted, however, that one precursor based prediction, that of Schatten et al. (1996) was significantly lower than the rest (138 ± 30) and within 0:6 σ of the actual value. Indeed, the method of Schatten and Sofia (1987) and Schatten et al. (1996) has consistently proven its skill in all cycles. As discussed in Section 2.2, this method is essentially based on the polar magnetic field strength as precursor.
Extrapolation methods as a whole have shown a much less impressive performance. Overall, the statistical distribution of maximum amplitude values predicted by “real” forecasts made using these methods (i.e., forecasts made at or before the minimum epoch) for any given cycle does not seem to significantly differ from the long term climatological average of the solar cycle quoted in Section 1.3 above (100 ± 35). It would of course be a hasty judgement to dismiss each of the widely differing individual approaches comprised in this class simply due to the poor overall performance of the group. In particular, some novel methods suggested in the last 20 years, such as SSA or neural networks have hardly had a chance to debut, so their further performance will be worth monitoring in upcoming cycles.
One group of extrapolation methods that stands apart from the rest are those based on the even-odd rule. These methods enjoyed a relatively high prestige until cycle 23, when they coherently predicted a peak amplitude around 200, i.e., ∼ 70% higher than the actual peak. This can only be qualified as a miserable failure, independently of the debate as to whether cycle 23 is truly at odds with the even-odd rule or not.
In this context it may be worth noting that the double peaked character and long duration of cycle 23 implies that its integrated amplitude (sum of annual sunspot numbers during the cycle) is much less below that of cycle 22 than the peak amplitude alone would indicate. This suggests that forecasts of the integrated amplitude (rarely attempted) could be more robust than forecasts of the peak. Nevertheless, one has to live with the fact that for most practical applications (space weather) it is the peak amplitude that matters most, so this is where the interest of forecasters is naturally focused.
Finally, model based methods are a new development that have had no occasion yet to prove their skill. As discussed above, current dynamo models do not seem to be at a stage of development where such forecasts could be attempted with any confidence, especially before the time of the minimum. (The method of Choudhuri et al., 2007, using polar fields as input near the minimum, would seem to be akin to a version of the polar field based precursor method with some extra machinery built into it.) The claimed good prediction skills of models based on data assimilation will need to be tested in future cycles and the roots of their apparent success need to be understood.
Table 1 presents a collection of forecasts for the amplitude of cycle 24, without claiming completeness. (See, e.g., Pesnell, 2008, for a more exhaustive list.) The objective was to include one or two representative forecasts from each category.
The incipient cycle 24 may be a milestone for solar cycle forecasting. Current evidence indicates that we are at the end of the Modern Maximum when the Sun is about to switch to a state of less intense long term activity. The appearance of a number of novel prediction methods, in particular the model based approach, as well as the unusually large discrepancy between forecasts based on the precursor approach imply that, whichever course solar activity will take in the coming years, we have a lot to learn from the experience.
6 Epilogue
Throughout the ages, mankind felt and tried to answer the urge to predict events to come. Omens were carefully collected and categorized on Mesopotamian clay tablets; omen-based prediction was developed into an industry in the form of hepatoscopy (analyzing the shape of the liver of a sacrificed animal) and, in later Roman times, of auspicium (watching the flight of the birds). Ancient Greeks often turned to oracles like the Pythia of Delphi. By the late antiquity, the astrological world view was widespread throughout the civilized world, implying that cosmic and terrestrial events were subject to cosmic cycles governed by a variety of (planetary) periods.
Today we tend to smile at these “superstitious” early attempts. Yet, ironically, many of the “advanced” methods we have for the prediction of solar activity are based on principles that hardly differ from those listed above: just substitute “precursor” for “omen”, “neural network” for “oracle” or “harmonic analysis” for “cosmic cycles”. . .
But in parallel with the often naïve phenomenological or empirical prediction attempts, already in the Hellenistic world, a handful of enlightened scientists started the development of physical models, based on logic and experience, that would lead to the advanced predictive skills of many models of modern science (Russo, 2004). Extending the analogy, we can see that the real importance of the recent debut of model-based solar cycles predictions is not their still dubious success rate but the conceptual leap they represent.
Despite the rather poor overall performance of solar cycle prediction attempts, the extensive efforts invested in this endeavour were not in vain as they have contributed and keep contributing to a better understanding of the physical processes governing the solar cycle and to constraining the dynamo.
Notes
1 The more precise condition defining ϕ is that ϕ =±π/2 at each maximum and ϕ is quadratically related to the time since the last minimum.
References
Ables, J.G., 1974, “Maximum Entropy Spectral Analysis”, Astron. Astrophys. Suppl., 15, 383–393. [ADS] (Cited on page 26.)
Adomian, G., 1989, Nonlinear Stochastic Systems Theory and Applications to Physics, Kluwer, Dordrecht; Boston. [Google Books] (Cited on page 42.)
Aguirre, L.A., Letellier, C. and Maquet, J., 2008, “Forecasting the Time Series of Sunspot Numbers”, Solar Phys., 249, 103–120. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 33 and 44.)
Ahluwalia, H.S., 1998, “The predicted size of cycle 23 based on the inferred three-cycle quasiperiodicity of the planetary index Ap”, J. Geophys. Res., 103(A6), 12,103–12,109. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 31.)
Ahluwalia, H.S. and Ygbuhay, R.C., 2009, “Preliminary forecast for the peak of solar activity cycle 24”, Adv. Space Res., 44, 611–614. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 44.)
Badalyan, O.G., Obridko, V.N. and Sýkora, J., 2001, “Brightness of the Coronal Green Line and Prediction for Activity Cycles 23 and 24”, Solar Phys., 199, 421–435. [ADS] (Cited on page 22.)
Bai, T. and Cliver, E.W., 1990, “A 154 day periodicity in the occurrence rate of proton flares”, Astrophys. J., 363, 299–309. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 28.)
Beer, J., Vonmoos, M. and Muscheler, R., 2006, “Solar Variability Over the Past Several Millennia”, Space Sci. Rev., 125, 67–79. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 32.)
Berggren, A.-M., Beer, J., Possnert, G., Aldahan, A., Kubik, P., Christl, M., Johnsen, S.J., Abreu, J. and Vinther, B.M., 2009, “A 600-year annual 10Be record from the NGRIP ice core, Greenland”, Geophys. Res. Lett., 36, L11801. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 9.)
Bhatt, N.J., Jain, R. and Aggarwal, M., 2009, “Prediction of the Maximum Amplitude and Timing of Sunspot Cycle 24”, Solar Phys., 260, 225–232. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 23 and 44.)
Blais, A. and Mertz, D., 2001, “An introduction to neural networks: Pattern learning with the back-propagation algorithm”, online resource, IBM developerWorks. URL (accessed 17 August 2010): http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/library/l-neural/ (Cited on page 35.)
Box, G.E.P., Jenkins, G.M. and Reinsel, G.C., 2008,Time Series Analysis: Forecasting and Control, Wiley, Hoboken, NJ, 4th edn. (Cited on pages 25 and 26.)
Bracewell, R.N., 1953, “The Sunspot Number Series”, Nature, 171, 649–650. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 7.)
Bracewell, R.N., 1988, “Three-halves law in sunspot cycle shape”, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 230, 535–550. [ADS] (Cited on page 7.)
Brajša, R., Wöhl, H., Hanslmeier, A., Verbanac, G., Ruždjak, D., Cliver, E., Svalgaard, L. and Roth, M., 2009, “On solar cycle predictions and reconstructions”, Astron. Astrophys., 496, 855–861. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 18, 26, and 44.)
Brown, G.M., 1976, “What determines sunspot maximum?”, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 174, 185–189. [ADS] (Cited on pages 18 and 44.)
Browning, M.K., Miesch, M.S., Brun, A.S. and Toomre, J., 2006, “Dynamo Action in the Solar Convection Zone and Tachocline: Pumping and Organization of Toroidal Fields”, Astrophys. J. Lett., 648, L157–L160. [DOI], [ADS], [arXiv:astro-ph/0609153] (Cited on page 37.)
Bushby, P.J. and Tobias, S.M., 2007, “On Predicting the Solar Cycle Using Mean-Field Models”, Astrophys. J., 661, 1289–1296. [DOI], [ADS], [arXiv:0704.2345] (Cited on page 38.)
Calvo, R.A., Ceccato, H.A. and Piacentini, R.D., 1995, “Neural network prediction of solar activity”, Astrophys. J., 444, 916–921. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 34 and 35.)
Cameron, R. and Schüssler, M., 2007, “Solar Cycle Prediction Using Precursors and Flux Transport Models”, Astrophys. J., 659, 801–811. [DOI], [ADS], [arXiv:astro-ph/0612693] (Cited on pages 15, 18, 19, 40, 41, and 44.)
Cameron, R. and Schüssler, M., 2008, “A Robust Correlation between Growth Rate and Amplitude of Solar Cycles: Consequences for Prediction Methods”, Astrophys. J., 685, 1291–1296. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 14.)
Cameron, R.H. and Schüssler, M., 2010, “Changes of the Solar Meridional Velocity Profile During Cycle 23 Explained by Flows Toward the Activity Belts”, Astrophys. J., 720, 1030–1032. [DOI], [ADS], [arXiv:1007.2548 [astro-ph.SR]] (Cited on page 24.)
Carbonell, M., Oliver, R. and Ballester, J.L., 1994, “A search for chaotic behaviour in solar activity.”, Astron. Astrophys., 290, 983–994. [ADS] (Cited on page 34.)
Charbonneau, P., 2001, “Multiperiodicity, Chaos, and Intermittency in a Reduced Model of the Solar Cycle”, Solar Phys., 199, 385–404. [ADS] (Cited on pages 30 and 31.)
Charbonneau, P., 2010, “Dynamo Models of the Solar Cycle”, Living Rev. Solar Phys., 7, lrsp–2010–3. URL (accessed 9 December 2010): {rshttp://www.livingreviews.org/lrsp-2010-3 URL } (Cited on page 36.)
Charbonneau, P. and Dikpati, M., 2000, “Stochastic Fluctuations in a Babcock-Leighton Model of the Solar Cycle”, Astrophys. J., 543, 1027–1043. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 15.)
Charbonneau, P., Beaubien, G. and St-Jean, C., 2007, “Fluctuations in Babcock-Leighton Dynamos. II. Revisiting the Gnevyshev-Ohl Rule”, Astrophys. J., 658, 657–662. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 31.)
Chatterjee, P., Nandy, D. and Choudhuri, A.R., 2004, “Full-sphere simulations of a circulationdominated solar dynamo: Exploring the parity issue”, Astron. Astrophys., 427, 1019–1030. [DOI], [ADS], [arXiv:astro-ph/0405027] (Cited on page 39.)
Choudhuri, A.R., Chatterjee, P. and Jiang, J., 2007, “Predicting Solar Cycle 24 With a Solar Dynamo Model”, Phys. Rev. Lett., 98, 131103. [DOI], [ADS], [arXiv:astro-ph/0701527] (Cited on pages 39, 43, and 44.)
Cole, T.W., 1973, “Periodicities in Solar Activity”, Solar Phys., 30, 103–110. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 26.)
Crosson, I.J. and Binder, P.-M., 2009, “Chaos-based forecast of sunspot cycle 24”, J. Geophys. Res., 114, A01108. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 44.)
Currie, R.G., 1973, “Fine Structure in the Sunspot Spectrum - 2 to 70 Years”, Astrophys. Space Sci., 20, 509–518. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 27 and 29.)
Dabas, R.S., Sharma, K., Das, R.M., Pillai, K.G.M., Chopra, P. and Sethi, N.K., 2008, “A Prediction of Solar Cycle 24 Using a Modified Precursor Method”, Solar Phys., 250, 171–181. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 22.)
de Meyer, F., 1981, “Mathematical modelling of the sunspot cycle”, Solar Phys., .70, 259–272. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 17 and 26.)
Dikpati, M. and Gilman, P.A., 2006, “Simulating and Predicting Solar Cycles Using a Flux-Transport Dynamo”, Astrophys. J., .649, 498–514. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 36, 38, and 44.)
Dikpati, M., de Toma, G. and Gilman, P.A., 2006, “Predicting the strength of solar cycle 24 using a flux-transport dynamo-based tool”, Geophys. Res. Lett., 33, L05102. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 38.)
Dikpati, M., Gilman, P.A., de Toma, G. and Ghosh, S.S., 2007, “Simulating Solar Cycles in Northern and Southern Hemispheres by Assimilating Magnetic Data into a Calibrated Flux-Transport Dynamo”, Solar Phys., 245, 1–17. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 39.)
Dikpati, M., de Toma, G. and Gilman, P.A., 2008a, “Polar Flux, Cross-equatorial Flux, and Dynamo-generated Tachocline Toroidal Flux as Predictors of Solar Cycles”, Astrophys. J., 675, 920–930. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 40.)
Dikpati, M., Gilman, P.A. and de Toma, G., 2008b, “The Waldmeier Effect: An Artifact of the Definition of Wolf Sunspot Number?”, Astrophys. J. Lett., 673, L99–L101. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 14.)
Dmitrieva, I.V., Kuzanyan, K.M. and Obridko, V.N., 2000, “Amplitude and period of the dynamo wave and prediction of the solar cycle”, Solar Phys., 195, 209–218. [ADS] (Cited on page 16.)
Du, Z.L., Li, R. and Wang, H.N., 2009, “The Predictive Power of Ohl’s Precursor Method”, Astron. J., 138, 1998–2001. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 22.)
Durney, B.R., 2000, “On the Differences Between Odd and Even Solar Cycles”, Solar Phys., 196, 421–426. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 31.)
Farmer, J.D. and Sidorowich, J.J., 1987, “Predicting chaotic time series”, Phys. Rev. Lett., 59, 845–848. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 33.)
Feynman, J., 1982, “Geomagnetic and solar wind cycles, 1900-1975”, J. Geophys. Res., 87(A8), 6153–6162. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 23.)
Fligge, M., Solanki, S.K. and Beer, J., 1999, “Determination of solar cycle length variations using the continuous wavelet transform”, Astron. Astrophys., 346, 313–321. [ADS] (Cited on page 27.)
Forgács-Dajka, E. and Borkovits, T., 2007, “Searching for mid-term variations in different aspects of solar activity - looking for probable common origins and studying temporal variations of magnetic polarities”, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 374, 282–291. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 31.)
Freitas, U.S., Letellier, C. and Aguirre, L.A., 2009, “Failure in distinguishing colored noise from chaos using the ‘noise titration’ technique”, Phys. Rev. E, 79(3), 035201. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 34.)
Frick, P., Galyagin, D., Hoyt, D.V., Nesme-Ribes, E., Schatten, K.H., Sokoloff, D. and Zakharov, V., 1997, “Wavelet analysis of solar activity recorded by sunspot groups”, Astron. Astrophys., 328, 670–681. [ADS] (Cited on page 27.)
Gizzatullina, S.M., Rukavishnikov, V.D., Ruzmaikin, A.A. and Tavastsherna, K.S., 1990, “Radiocarbon evidence of the global stochasticity of solar activity”, Solar Phys., 127, 281–288. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 34.)
Gleissberg, W., 1939, “A long-periodic fluctuation of the sun-spot numbers”, Observatory, 62, 158–159. [ADS] (Cited on page 31.)
Gleissberg, W., 1952, Die Häufigkeit der Sonnenflecken, Akademie-Verlag, Berlin (Cited on page 17.)
Gleissberg, W., 1967, “Secularly Smoothed Data on the Minima and Maxima of Sunspot Frequency”, Solar Phys., 2, 231–233. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 11.)
Gnevyshev, M.N. and Ohl, A.I., 1948, “On the 22-year cycle of solar activity”, Astron. Zh., 25, 18–20 (Cited on pages 30 and 31.)
Goel, A. and Choudhuri, A.R., 2009, “The hemispheric asymmetry of solar activity during the last century and the solar dynamo”, Res. Astron. Astrophys., 9, 115–126. [DOI], [ADS], [arXiv:0712.3988] (Cited on page 39.)
Grassberger, P. and Procaccia, I., 1983, “Characterization of strange attractors”, Phys. Rev. Lett., 50, 346–349. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 34.)
Halm, J., 1901, “Über eine neue Theorie zur Erklärung der Periodicität der solaren Erscheinungen”, Astron. Nachr., 156, 33–50. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 17.)
Hanslmeier, A. and Brajša, R., 2010, “The chaotic solar cycle. I. Analysis of cosmogenic 14C-data”, Astron. Astrophys., 509, A5. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 34.)
Hathaway, D.H., 2009, “Solar Cycle Forecasting”, Space Sci. Rev., 144, 401–412. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 5.)
Hathaway, D.H., 2010a, “Does the Current Minimum Validate (or Invalidate) Cycle Prediction Methods?”, in SOHO-23: Understanding a Peculiar Solar Minimum, Northeast Harbor, Maine, USA, 21 - 25 September 2009, (Eds.) Cranmer, S.R., Hoeksema, J.T., Kohl, J.L., vol. 428 of ASP Conference Series, p. 307, Astronomical Society of the Pacific, San Francisco. [ADS], [arXiv:1003.4208] (Cited on page 23.)
Hathaway, D.H., 2010b, “The Solar Cycle”, Living Rev. Solar Phys., 7, lrsp–2010–1. [ADS]. URL (accessed 17 August 2010): {rshttp://www.livingreviews.org/lrsp-2010-1 URL } (Cited on pages 6, 19, 22, and 23.)
Hathaway, D.H. and Rightmire, L., 2010, “Variations in the Sun’s Meridional Flow over a Solar Cycle”, Science, 327, 1350. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 24.)
Hathaway, D.H. and Wilson, R.M., 2006, “Geomagnetic activity indicates large amplitude for sunspot cycle 24”, Geophys.Res. Lett.}, 33, L18101. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 44.)
Hathaway, D.H., Wilson, R.M. and Reichmann, E.J., 1994, “The shape of the sunspot cycle”, Solar Phys., 151, 177–190. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 12 and 15.)
Hegger, R., Kantz, H. and Schreiber, T., 1999, “Practical implementation of nonlinear time series methods: The TISEAN package”, Chaos, 9, 413–435. [DOI], [chao-dyn/9810005] (Cited on page 33.)
Henwood, R., Chapman, S.C. and Willis, D.M., 2010, “Increasing Lifetime of Recurrent Sunspot Groups Within the Greenwich Photoheliographic Results”, Solar Phys., 262, 299–313. [DOI], [ADS], [arXiv:0907.4274 [astro-ph.SR]] (Cited on page 7.)
Hiremath, K.M., 2006, “The solar cycle as a forced and damped harmonic oscillator: long-term variations of the amplitudes, frequencies and phases”, Astron. Astrophys., 452, 591–595. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 41.)
Hiremath, K.M., 2008, “Prediction of solar cycle 24 and beyond”, Astrophys. Space Sci., 314, 45–49. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 26, 41, and 44.)
Hoeksema, J.T., 1995, “The Large-Scale Structure of the Heliospheric Current Sheet During the ULYSSES Epoch”, Space Sci. Rev., 72, 137–148. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 19.)
Howe, R., 2009, “Solar Interior Rotation and its Variation”, Living Rev. Solar Phys., 6, lrsp–2009–1. [ADS], [arXiv:0902.2406]. URL (accessed 17 August 2010): {rshttp://www.livingreviews.org/lrsp-2009-1 URL } (Cited on page 28.)
Howe, R., Christensen-Dalsgaard, J., Hill, F., Komm, R., Schou, J. and Thompson, M.J., 2009, “A Note on the Torsional Oscillation at Solar Minimum”, Astrophys. J. Lett., 701, L87–L90. [DOI], [ADS], [arXiv:0907.2965] (Cited on page 24.)
Hoyt, D.V. and Schatten, K.H., 1998, “Group Sunspot Numbers: A New Solar Activity Reconstruction”, Solar Phys., 181, 491–512. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 6 and 8.)
Jensen, J.L., 1993, “Comments on nonparametric predictions of sunspot numbers”, Astron. J., 105, 350–352. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 33 and 34.)
Jiang, J., Chatterjee, P. and Choudhuri, A.R., 2007, “Solar activity forecast with a dynamo model”, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 381, 1527–1542. [DOI], [ADS], [arXiv:0707.2258] (Cited on pages 39 and 44.)
Jiang, J., Cameron, R., Schmitt, D. and Schüssler, M., 2010a, “Modeling the Sun’s Open Magnetic Flux and the Heliospheric Current Sheet”, Astrophys. J., 709, 301–307. [DOI], [ADS], [arXiv:0912.0108] (Cited on page 24.)
Jiang, J., Ičsik, E., Cameron, R.H., Schmitt, D. and Schüssler, M., 2010b, “The Effect of Activityrelated Meridional Flow Modulation on the Strength of the Solar Polar Magnetic Field”, Astrophys. J., 717, 597–602. [DOI], [ADS], [arXiv:1005.5317] (Cited on page 24.)
Kanamaru, T., 2007, “Van der Pol oscillator”, Scholarpedia, 2(1), 2202. [DOI]. URL (accessed 17 August 2010): http://www.scholarpedia.org/article/Duffing_oscillator (Cited on page 42.)
Kanamaru, T., 2008, “Duffing oscillator”, Scholarpedia, 3(3), 6327}. [DOI]. URL (accessed 17 August 2010): http://www.scholarpedia.org/article/Van_der_Pol_oscillator (Cited on page 41.)
Kane, R.P., 1999, “Prediction of the sunspot maximum of solar cycle 23 by extrapolation of spectral components”, Solar Phys., 189, 217–224. [ADS] (Cited on page 27.)
Kane, R.P., 2001, “Did Predictions of the Maximum Sunspot Number for Solar Cycle 23 Come True?”, Solar Phys., 202, 395–406. [ADS] (Cited on pages 5 and 43.)
Kane, R.P., 2007, “Solar Cycle Predictions Based on Extrapolation of Spectral Components: An Update”, Solar Phys., 246, 487–493. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 27 and 44.)
Kane, R.P., 2008, “Prediction of Solar Cycle Maximum Using Solar Cycle Lengths”, Solar Phys., 248, 203–209. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 19.)
Kantz, H. and Schreiber, T., 1997, Nonlinear Time Series Analysis, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge; New York. [Google Books] (Cited on page 35.)
Kennel, M.B., Brown, R. and Abarbanel, H.D.I., 1992, “Determining embedding dimension for phase-space reconstruction using a geometrical construction”, Phys. Rev. A, 45, 3403–3411. [DOI] (Cited on page 34.)
Kilcik, A., Anderson, C.N.K., Rozelot, J.P., Ye, H., Sugihara, G. and Ozguc, A., 2009, “Nonlinear Prediction of Solar Cycle 24”, Astrophys. J., 693, 1173–1177. [DOI], [ADS], [arXiv:0811.1708] (Cited on pages 13, 33, 34, and 44.)
Kimura, H., 1913, “Sun-Spots and Facula, On the harmonic analysis of sun-spot relative numbers”, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 73, 543–548B. [ADS] (Cited on pages 26 and 29.)
Kitiashvili, I.N. and Kosovichev, A.G., 2008, “Application of Data Assimilation Method for Predicting Solar Cycles”, Astrophys. J. Lett., 688, L49–L52. [DOI], [ADS], [arXiv:0807.3284] (Cited on pages 36, 40, and 44.)
Kitiashvili, I.N. and Kosovichev, A.G., 2009, “Nonlinear dynamical modeling of solar cycles using dynamo formulation with turbulent magnetic helicity”, Geophys. Astrophys. Fluid Dyn., 103, 53–68. [DOI], [ADS], [arXiv:0807.3192] (Cited on pages 15 and 39.)
Kolláth, Z. and Oláh, K., 2009, “Multiple and changing cycles of active stars. I. Methods of analysis and application to the solar cycles”, Astron. Astrophys., 501, 695–702. [DOI], [ADS], [arXiv:0904.1725 [astro-ph.SR]] (Cited on pages 27, 30, and 32.)
Komm, R.W., 1995, “Hurst analysis of Mt. Wilson rotation measurements”, Solar Phys., 156, 17–28. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 13.)
Kopecký, M., 1950, “Cycle de 22 ans de l’activité solaire”, Bull. Astron. Inst. Czech., 2, 14. [ADS] (Cited on page 31.)
Kopecký, M., Ružičková-Topolová, B. and Kuklin, G.V., 1980, “On the relative inhomogeneity of long-term series of sunspot indices”, Bull. Astron. Inst. Czech., 31, 267–283. [ADS] (Cited on page 6.)
Krivova, N.A. and Solanki, S.K., 2002, “The 1.3-year and 156-day periodicities in sunspot data: Wavelet analysis suggests a common origin”, Astron. Astrophys., 394, 701–706. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 28.)
Krivova, N.A., Solanki, S.K. and Beer, J., 2002, “Was one sunspot cycle in the 18th century really lost?”, Astron. Astrophys., 396, 235–242. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 30.)
Kuklin, G.V., 1986, “A classification of cycle pairs according to the ‘cycle height-ascending branch length’ relationship type and reconstruction of the solar activity level variation in the 16th and 17th centuries”, Contrib. Astron. Obs. Skalnate Pleso, 15, 607–615. [ADS] (Cited on page 15.)
Kurths, J. and Ruzmaikin, A.A., 1990, “On forecasting the sunspot numbers”, Solar Phys., 126, 407–410. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 33 and 34.)
Kuzanyan, K., Obridko, V.N., Kotlyarov, O.L., Loskutov, A.Y. and Istomin, I.A., 2008, “Predictions of the Magnitude of the Forthcoming Solar Cycles using Knowledge on the Solar Dynamo and Singular Spectrum Analysis”, in 12th European Solar Physics Meeting (ESPM-12), 8 - 12 September 2008, Freiburg, Germany, (Ed.) Peter, H., vol. 12, KIS, Freiburg. [ADS]. URL (accessed 13 December 2010): http://espm.kis.uni-freiburg.de (Cited on pages 27 and 44.)
Lantos, P., 2000, “Prediction of the Maximum Amplitude of Solar Cycles Using the Ascending Inflexion Point”, Solar Phys., 196, 221–225. [ADS] (Cited on page 14.)
Levy, E.H. and Boyer, D., 1982, “Oscillating dynamo in the presence of a fossil magnetic field. The solar cycle”, Astrophys. J. Lett., 254, L19–L22. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 30.)
Li, K.J., Yun, H.S. and Gu, X.M., 2001, “On long-term predictions of the maximum sunspot numbers of solar cycles 21 to 23”, Astron. Astrophys., 368, 285–291. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 31 and 43.)
Li, K.J., Irie, M., Wang, J., Xiong, S., Yun, H., Liang, H., Zhan, L. and Zhao, H., 2002, “Activity Cycle of Polar Faculae”, Publ. Astron. Soc. Japan, 54, 787–792. [ADS] (Cited on pages 21 and 22.)
Li, K.J., Gao, P.X. and Su, T.W., 2005, “The Schwabe and Gleissberg Periods in the Wolf Sunspot Numbers and the Group Sunspot Numbers”, Solar Phys., 229, 181–198. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 27.)
Lockwood, M., 2001, “Long-term variations in the magnetic fields of the Sun and the heliosphere: Their origin, effects, and implications”, J. Geophys. Res., 106(A8), 16,021–16,038. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 28.)
Lomb, N.R. and Andersen, A.P., 1980, “The analysis and forecasting of theWolf sunspot numbers”, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 190, 723–732. [ADS] (Cited on page 26.)
Lopes, I. and Passos, D., 2009, “Solar Variability Induced in a Dynamo Code by Realistic Meridional Circulation Variations”, Solar Phys., 257, 1–12. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 42.)
Loskutov, A.Y., Istomin, I.A., Kotlyarov, O.L. and Kuzanyan, K.M., 2001, “A Study of the Regularities in Solar Magnetic Activity by Singular Spectral Analysis”, Astron. Lett., 27, 745–753. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 27 and 44.)
Makarov, V.I. and Makarova, V.V., 1996, “Polar Faculae and Sunspot Cycles”, Solar Phys., 163, 267–289. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 21.)
Makarov, V.I., Makarova, V.V. and Sivaraman, K.R., 1989, “Do polar faculae on the sun predict a sunspot cycle?”, Solar Phys., 119, 45–54. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 21 and 22.)
Mandelbrot, B.B. and Wallis, J.R., 1969, “Some long-run properties of geophysical records”, Water Resour. Res., 5(2), 321–340. [DOI] (Cited on page 13.)
Maris, G. and Oncica, A., 2006, “Solar Cycle 24 Forecasts”, Sun and Geosphere, 1(1), 8–11. [ADS] (Cited on pages 35 and 44.)
McCracken, K.G. and Beer, J., 2008, “The 2300 year Modulation in the Galactic Cosmic Radiation”, in Proceedings of the 30th International Cosmic Ray Conference, Vol. 1 (SH), July 3 - 11, 2007, Mérida, Yucatán, Mexico, (Eds.) Caballero, R., D’Olivo, J.C., Medina-Tanco, G., Nellen, L., Sánchez, F.A., Valdés-Galicia, J.F., pp. 549–552, UNAM, Mexico City. [ADS]. Online version (accessed 10 December 2010): http://indico.nucleares.unam.mx/contributionDisplay.py?contribId=1248&confId=4 (Cited on page 32.)
Michelson, A.A., 1913, “Determination of Periodicities by the Harmonic Analyzer with an Application to the Sun-Spot Cycle”, Astrophys. J., 38, 268. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 26.)
Mininni, P.D., Gómez, D.O. and Mindlin, G.B., 2000, “Stochastic Relaxation Oscillator Model for the Solar Cycle”, Phys. Rev. Lett., 85, 5476–5479. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 15 and 42.)
Mininni, P.D., Gómez, D.O. and Mindlin, G.B., 2002, “Instantaneous Phase and Amplitude Correlation in the Solar Cycle”, Solar Phys., 208, 167–179. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 15 and 42.)
Moss, D., Sokoloff, D., Usoskin, I. and Tutubalin, V., 2008, “Solar Grand Minima and Random Fluctuations in Dynamo Parameters”, Solar Phys., 250, 221–234. [DOI], [ADS], [arXiv:0806.3331] (Cited on pages 12 and 39.)
“Solar Cycle 24 Prediction”, project homepage, NASA Marshall Space Flight Center. URL (accessed 12 February 2010): http://solarscience.msfc.nasa.gov/predict.shtml (Cited on page 5.)
Muńoz-Jaramillo, A., Nandy, D., Martens, P.C.H. and Yeates, A.R., 2010, “A Double-ring Algorithm for Modeling Solar Active Regions: Unifying Kinematic Dynamo Models and Surface Flux-transport Simulations”, Astrophys. J. Lett., 720, L20–L25. [DOI], [ADS], [arXiv:1006.4346 [astro-ph.SR]] (Cited on page 24.)
Mursula, K. and Zieger, B., 2000, “The 1.3-Year Variation in Solar Wind Speed and Geomagnetic Activity”, Adv. Space Res., 25, 1939–1942. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 28.)
Mursula, K., Usoskin, I.G. and Kovaltsov, G.A., 2001, “Persistent 22-year cycle in sunspot activity: Evidence for a relic solar magnetic field”, Solar Phys., 198, 51–56. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 30.)
Nagovitsyn, Y.A., 1997, “A nonlinear mathematical model for the solar cyclicity and prospects for reconstructing the solar activity in the past”, Astron. Lett., 23, 742–748. [ADS] (Cited on pages 9, 15, and 42.)
Nagovitsyn, Y.A., Nagovitsyna, E.Y. and Makarova, V.V., 2009, “The Gnevyshev-Ohl rule for physical parameters of the solar magnetic field: The 400-year interval”, Astron. Lett., 35, 564–571. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 30 and 31.)
Obridko, V.N. and Shelting, B.D., 2008, “On Prediction of the Strength of the 11-Year Solar Cycle No. 24”, Solar Phys., 248, 191–202. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 19.)
Ochadlick Jr, A.R., Kritikos, H.N. and Giegengack, R., 1993, “Variations in the period of the sunspot cycle”, Geophys. Res. Lett., 20, 1471–1474. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 27.)
Ogurtsov, M.G., 2004, “New Evidence for Long-Term Persistence in the Sun’s Activity”, Solar Phys., 220, 93–105. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 13.)
Ohl, A.I., 1966, “Forecast of sunspot maximum number of cycle 20”, Soln. Dannye, (12), 84 (Cited on page 22.)
Oláh, K., Kolláth, Z., Granzer, T., Strassmeier, K.G., Lanza, A.F., Järvinen, S., Korhonen, H., Baliunas, S.L., Soon, W., Messina, S. and Cutispoto, G., 2009, “Multiple and changing cycles of active stars. II. Results”, Astron. Astrophys., 501, 703–713. [DOI], [ADS], [arXiv:0904.1747 [astro-ph.SR]] (Cited on page 32.)
Oliver, R. and Ballester, J.L., 1996, “Rescaled Range Analysis of the Asymmetry of Solar Activity”, Solar Phys., 169, 215–224. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 13.)
Oliver, R. and Ballester, J.L., 1998, “Is there memory in solar activity?”, Phys. Rev. E, 58, 5650–5654. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 13.)
Ossendrijver, A.J.H., Hoyng, P. and Schmitt, D., 1996, “Stochastic excitation and memory of the solar dynamo”, Astron. Astrophys., 313, 938–948. [ADS] (Cited on page 15.)
Ossendrijver, M., 2003, “The solar dynamo”, Astron. Astrophys. Rev., 11, 287–367. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 36.)
Paluš, M. and Novotná, D., 1999, “Sunspot Cycle: A Driven Nonlinear Oscillator?”, Phys. Rev. Lett., 83, 3406–3409. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 15 and 42.)
Panchev, S. and Tsekov, M., 2007, “Empirical evidences of persistence and dynamical chaos in solar terrestrial phenomena”, J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys., 69, 2391–2404. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 35.)
Parker, E.N., 1955, “Hydromagnetic Dynamo Models”, Astrophys. J., 122, 293–314. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 39.)
Paularena, K.I., Szabo, A. and Richardson, J.D., 1995, “Coincident 1.3-year periodicities in the ap geomagnetic index and the solar wind”, Geophys. Res. Lett., 22, 3001–3004. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 28.)
Pesnell, W.D., 2008, “Predictions of Solar Cycle 24”, Solar Phys., 252, 209–220. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 5 and 43.)
Petrovay, K., 1994, “Theory of Passive Magnetic Field Transport”, in Solar Surface Magnetism, Proceedings of the NATO Advanced ResearchWorkshop, Soesterberg, The Netherlands, November 1–5, 1993, (Eds.) Rutten, R.J, Schrijver, C.J., vol. 433 of NATO ASI Series C, pp. 415–440, Kluwer, Dordrecht; Boston (Cited on page 37.)
Petrovay, K., 2000, “What Makes the Sun Tick? The Origin of the Solar Cycle”, in The Solar Cycle and Terrestrial Climate, Solar and Space Weather, Proceedings of the 1st Solar and Space Weather Euroconference: 25–29 September 2000, Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, Santa Cruz de Tenerife, Tenerife, Spain, (Ed.) Wilson, A., vol. SP-463 of ESA Special Publication, p. 3, ESA Publications Division, Noordwijk. [ADS], [arXiv:astro-ph/0010096] (Cited on page 36.)
Petrovay, K., 2007, “On the possibility of a bimodal solar dynamo”, Astron. Nachr., 328, 777–780. [DOI], [ADS], [arXiv:0708.2131] (Cited on page 12.)
Petrovay, K., 2010, “Harmonic analysis approach to solar cycle prediction and the Waldmeier effect”, in Solar and Stellar Variability: Impact on Earth and Planets, 3 - 7 August 2009, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, (Eds.) Kosovichev, A., Andrei, A.H., Rozelot, J.-P., vol. 264 of IAU Symposia, pp. 150–154, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge; New York. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 29.)
Petrovay, K. and Forgács-Dajka, E., 2002, “The Role of Active Regions in the Generation of Torsional Oscillations”, Solar Phys., 205, 39–52. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 24.)
Petrovay, K. and van Driel-Gesztelyi, L., 1997, “Making Sense of Sunspot Decay I: Parabolic Decay Law and Gnevyshev-Waldmeier Relation”, Solar Phys., 176, 249–266 (Cited on page 7.)
Petrovay, K., Martínez Pillet, V. and van Driel-Gesztelyi, L., 1999, “Making sense of sunspot decay - II. Deviations from the Mean Law and Plage Effects”, Solar Phys., 188, 315–330. [ADS], [arXiv:astro-ph/9906258] (Cited on page 9.)
Pishkalo, M.I., 2008, “Preliminary prediction of solar cycles 24 and 25 based on the correlation between cycle parameters”, Kinemat. Phys. Celest. Bodies, 24, 242–247. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 18.)
Press, W.H., Teukolsky, S.A., Vetterling, W.T. and Flannery, B.P., 1992, Numerical Recipes in FORTRAN: The Art of Scientific Computing, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge; New York, 2nd edn. [ADS] (Cited on page 26.)
Price, C.P., Prichard, D. and Hogenson, E.A., 1992, “Do the sunspot numbers form a ‘chaotic’ set?”, J. Geophys. Res., 97, 19,113–19,120. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 34.)
Qian, B. and Rasheed, K., 2004, “Hurst exponent and financial market predictability”, in Financial Engineering and Applications (FEA 2004), Proceedings of the IASTED International Conference, November 8–10, 2004, Cambridge, MA, USA, (Ed.) Hamza, M.H., ACTA Press, Anaheim; Calgary (Cited on page 13.)
Rangarajan, G.K., 1998, “Sunspot variability and an attempt to predict solar cycle 23 by adaptive filtering”, Earth Planets Space, 50, 91–100. [ADS] (Cited on page 27.)
Richard, J.-G., 2004, “The eight-Schwabe-cycle pulsation”, Solar Phys., 223, 319–333. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 31.)
Richardson, J.D., Paularena, K.I., Belcher, J.W. and Lazarus, A.J., 1994, “Solar wind oscillations with a 1.3 year period”, Geophys. Res. Lett., 21, 1559–1560. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 28.)
Rieger, E., Kanbach, G., Reppin, C., Share, G.H., Forrest, D.J. and Chupp, E.L., 1984, “A 154-day periodicity in the occurrence of hard solar flares?”, Nature, 312, 623–625. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 28.)
Rouillard, A.P., Lockwood, M. and Finch, I., 2007, “Centennial changes in the solar wind speed and in the open solar flux”, J. Geophys. Res., 112, A05103. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 23.)
Russo, L., 2004, The Forgotten Revolution: How Science Was Born in 300 BC and Why It Had to Be Reborn, Springer, Berlin; New York. [Google Books] (Cited on page 45.)
Ruzmaikin, A., 1997, “On the origin of sunspots”, Astron. Astrophys., 319, L13–L16. [ADS] (Cited on page 7.)
Ruzmaikin, A., Feynman, J. and Robinson, P., 1994, “Long-term persistence of solar activity”, Solar Phys., 149, 395–403. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 13.)
Schatten, K., 2005, “Fair space weather for solar cycle 24”, Geophys. Res. Lett., 32, L21106. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 44.)
Schatten, K., Myers, D.J. and Sofia, S., 1996, “Solar activity forecast for solar cycle 23”, Geophys. Res. Lett., 23, 605–608. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 19 and 43.)
Schatten, K.H. and Pesnell, W.D., 1993, “An early solar dynamo prediction: Cycle 23 is approximately cycle 22”, Geophys. Res. Lett., 20, 2275–2278. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 21.)
Schatten, K.H. and Sofia, S., 1987, “Forecast of an exceptionally large even-numbered solar cycle”, Geophys. Res. Lett., 14, 632–635. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 19 and 43.)
Schatten, K.H., Scherrer, P.H., Svalgaard, L. and Wilcox, J.M., 1978, “Using dynamo theory to predict the sunspot number during solar cycle 21”, Geophys. Res. Lett., 5, 411–414. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 19.)
Schüssler, M., 2007, “Are solar cycles predictable?”, Astron. Nachr., 328, 1087. [DOI], [ADS], [arXiv:0712.1917] (Cited on page 41.)
Schüssler, M. and Baumann, I., 2006, “Modeling the Sun’s open magnetic flux”, Astron. Astrophys., 459, 945–953. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 24.)
Serre, T. and Nesme-Ribes, E., 2000, “Nonlinear analysis of solar cycles”, Astron. Astrophys., 360, 319–330. [ADS] (Cited on page 33.)
Shirai, T., 2004, “Time variation of the solar neutrino fluxes from Super-Kamiokande data”, Solar Phys., 222, 199–201. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 28.)
Solanki, S., Inhester, B. and Schüssler, M., 2006, “The solar magnetic field”, Rep. Prog. Phys., 69, 563–668. [DOI] (Cited on page 36.)
Solanki, S.K., Krivova, N.A., Schüssler, M. and Fligge, M., 2002, “Search for a relationship between solar cycle amplitude and length”, Astron. Astrophys., 396, 1029–1035. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 15 and 19.)
Stephenson, F.R. and Wolfendale, A.W. (Eds.), 1988, Secular Solar and Geomagnetic Variations in the Last 10,000 Years, Proceedings at the NATO Advanced Research Workshop, held at Durham, England, 6 - 10 April 1987, vol. 236 of NATO ASI Series C, Kluwer, Dordrecht. [ADS] (Cited on page 9.)
Stix, M., 1972, “Non-Linear DynamoWaves”, Astron. Astrophys., 20, 9. [ADS] (Cited on page 15.)
Sugihara, G. and May, R.M., 1990, “Nonlinear forecasting as a way of distinguishing chaos from measurement error in time series”, Nature, 344, 734–741. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 34.)
Svalgaard, L. and Cliver, E.W., 2005, “The IDV index: Its derivation and use in inferring longterm variations of the interplanetary magnetic field strength”, J. Geophys. Res., 110(A9), 12 103. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 23.)
Svalgaard, L. and Cliver, E.W., 2007, “Interhourly variability index of geomagnetic activity and its use in deriving the long-term variation of solar wind speed”, J. Geophys. Res., 112, A10111. [DOI], [ADS], [arXiv:0706.0961] (Cited on page 23.)
Svalgaard, L., Duvall Jr, T.L. and Scherrer, P.H., 1978, “The strength of the Sun’s polar fields”, Solar Phys., 58, 225–239. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 19.)
Svalgaard, L., Cliver, E.W. and Kamide, Y., 2005, “Sunspot cycle 24: Smallest cycle in 100 years?”, Geophys. Res. Lett., 32, L01104. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 21 and 44.)
Švanda, M., Kosovichev, A.G. and Zhao, J., 2007, “Speed of Meridional Flows and Magnetic Flux Transport on the Sun”, Astrophys. J. Lett., 670, L69–L72. [DOI], [ADS], [arXiv:0710.0590] (Cited on page 24.)
“Solar Cycle 24 Prediction”, project homepage, Space Weather Prediction Center. URL (accessed 12 February 2010): http://www.swpc.noaa.gov/SolarCycle/SC24/ (Cited on page 5.)
Szabo, A., Lepping, R.P. and King, J.H., 1995, “Magnetic field observations of the 1.3-year solar wind oscillations”, Geophys. Res. Lett., 22, 1845–1848. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 28.)
Thompson, R.J., 1993, “A Technique for Predicting the Amplitude of the Solar Cycle”, Solar Phys., 148, 383–388. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 22.)
Tlatov, A.G., 2009, “The Minimum Activity Epoch as a Precursor of the Solar Activity”, Solar Phys., 260, 465–477. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 17, 21, 22, and 44.)
Tlatov, A.G., Vasil’eva, V.V. and Pevtsov, A.A., 2010, “Distribution of Magnetic Bipoles on the Sun over Three Solar Cycles”, Astrophys. J., 717, 357–362. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 17 and 21.)
Tobias, S., Hughes, D. and Weiss, N., 2006, “Unpredictable Sun leaves researchers in the dark”, Nature, 442, 26. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 36.)
Tong, H., 1990, Non-linear Time Series: A Dynamical System Approach, vol. 6 of Oxford Statistical Science Series, Oxford University Press, Oxford; New York. [Google Books] (Cited on page 25.)
Tritakis, B.P., 1982, “Evidence of interdependence within 22-year solar cycles”, Astrophys. Space Sci., 82, 463–471. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 14.)
Tsuneta, S., Ichimoto, K., Katsukawa, Y., Lites, B.W., Matsuzaki, K., Nagata, S., Orozco Suárez, D., Shimizu, T., Shimojo, M., Shine, R.A., Suematsu, Y., Suzuki, T.K., Tarbell, T.D. and Title, A.M., 2008, “The Magnetic Landscape of the Sun’s Polar Region”, Astrophys. J., 688, 1374–1381. [DOI], [ADS], [arXiv:0807.4631] (Cited on page 21.)
Turner, H.H., 1913a, “On the harmonic analysis of Wolf’s sun-spot numbers, with special reference to Mr. Kimura’s paper”, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 73, 549–552. [ADS] (Cited on page 26.)
Turner, H.H., 1913b, “On the expression of sun-spot periodicity as a Fourier sequence, and on the general use of a Fourier sequence in similar problems”, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 73, 714–732. [ADS] (Cited on page 26.)
Turner, H.H., 1913c, “On a simple method of detecting discontinuities in a series of recorded observations, with an application to sun-spots, suggesting that they are caused by a meteor swarm”, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 74, 82–109. [ADS] (Cited on page 30.)
Usoskin, I.G., 2008, “A History of Solar Activity over Millennia”, Living Rev. Solar Phys., 5, lrsp–2008–3. [ADS], [arXiv:0810.3972]. URL (accessed 17 August 2010): http://www.livingreviews.org/lrsp-2008-3 (Cited on page 32.)
Usoskin, I.G. and Mursula, K., 2003, “Long-Term Solar Cycle Evolution: Review of Recent Developments”, Solar Phys., 218, 319–343. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 30.)
Usoskin, I.G., Mursula, K. and Kovaltsov, G.A., 2001, “Was one sunspot cycle lost in late XVIII century?”, Astron. Astrophys., 370, L31–L34. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 30.)
Usoskin, I.G., Solanki, S.K. and Kovaltsov, G.A., 2007, “Grand minima and maxima of solar activity: new observational constraints”, Astron. Astrophys., 471, 301–309. [DOI], [ADS], [arXiv:0706.0385] (Cited on page 12.)
Usoskin, I.G., Mursula, K., Arlt, R. and Kovaltsov, G.A., 2009a, “A Solar Cycle Lost in 1793-1800: Early Sunspot Observations Resolve the Old Mystery”, Astrophys. J. Lett., 700, L154–L157. [DOI], [ADS], [arXiv:0907.0063 [astro-ph.SR]] (Cited on page 30.)
Usoskin, I.G., Sokoloff, D. and Moss, D., 2009b, “Grand Minima of Solar Activity and the Mean-Field Dynamo”, Solar Phys., 254, 345–355. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 12 and 39.)
Uwamahoro, J., McKinnell, L.-A. and Cilliers, P.J., 2009, “Forecasting solar cycle 24 using neural networks”, J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys., 71, 569–574. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 35 and 44.)
Vaquero, J.M., 2007, “Historical sunspot observations: A review”, Adv. Space Res., 40, 929–941. [DOI], [ADS], [arXiv:astro-ph/0702068] (Cited on page 30.)
Vaquero, J.M. and Trigo, R.M., 2008, “Can the Solar Cycle Amplitude Be Predicted Using the Preceding Solar Cycle Length?”, Solar Phys., 250, 199–206. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 19.)
Vigouroux, A. and Delachie, P., 1994, “Sunspot numbers uncertainties and parametric representations of solar activity variations”, Solar Phys., 152, 267–274. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 27.)
Vitinsky, Y.I., 1963, Prognozi solnechnoi aktivnosti, Nauka, Leningrad (Cited on page 5.)
Vitinsky, Y.I., 1973, Tsiklichnost i prognozi solnechnoi aktivnosti, Nauka, Leningrad (Cited on pages 5, 17, and 26.)
Vitinsky, Y.I., Kopecký, M. and Kuklin, G.V., 1986, Statistika Pyatnoobrazovatel’noy Deyatel’nosti Solntsa, Nauka, Moscow (Cited on page 30.)
Waldmeier, M., 1935, “Neue Eigenschaften der Sonnenfleckenkurve”, Astron. Mitt. Zurich, 14 (133), 105–130. [ADS] (Cited on pages 14 and 17.)
Waldmeier, M., 1961, The Sunspot-Activity in the Years 1610-1960, Schulthess u. Co. / Swiss Federal Observatory, Zürich. [ADS] (Cited on page 6.)
Wang, Y.-M. and Sheeley Jr, N.R., 2009, “Understanding the Geomagnetic Precursor of the Solar Cycle”, Astrophys. J. Lett., 694, L11–L15. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 23 and 44.)
Wang, Y.-M., Robbrecht, E. and Sheeley Jr, N.R., 2009, “On the Weakening of the Polar Magnetic Fields during Solar Cycle 23”, Astrophys. J., 707, 1372–1386. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 24.)
Wei, W.W.S., 2005, Time Series Analysis: Univariate and Multivariate Methods, Addison Wesley, Reading, MA, 2nd edn. (Cited on pages 25 and 26.)
Weiss, N.O., Cattaneo, F. and Jones, C.A., 1984, “Periodic and aperiodic dynamo waves”, Geophys. Astrophys. Fluid Dyn., .30, 305–341. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 11 and 41.)
Wilmot-Smith, A.L., Nandy, D., Hornig, G. and Martens, P.C.H., 2006, “A Time Delay Model for Solar and Stellar Dynamos”, Astrophys. J., 652, 696–708. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 41.)
Wolf, R., 1859, “Mittheilungen über die Sonnenflecken. I”, Astron. Mitt. Zurich, 1, 3–13. [ADS] (Cited on page 6
Wolf, R., 1861, “Abstract of his latest Results”, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 21, 77–78. [ADS] (Cited on pages 6, 14, and 15.)
Yeates, A.R., Nandy, D. and Mackay, D.H., 2008, “Exploring the Physical Basis of Solar Cycle Predictions: Flux Transport Dynamics and Persistence of Memory in Advection-versus Diffusiondominated Solar Convection Zones”, Astrophys. J., 673, 544–556. [DOI], [ADS], [arXiv:0709.1046] (Cited on page 40.)
Zaqarashvili, T.V., Carbonell, M., Oliver, R. and Ballester, J.L., 2010, “Magnetic Rossby Waves in the Solar Tachocline and Rieger-Type Periodicities”, Astrophys. J., 709, 749–758. [DOI], [ADS], [arXiv:0911.4591] (Cited on page 28.)
Zel’dovich, Y.B., Ruzmaikin, A.A. and Sokoloff, D.D., 1983, Magnetic Fields in Astrophysics, vol. 3 of Fluid Mechanics of Astrophysics and Geophysics, Gordon and Breach, New York (Cited on page 39.)
Acknowledgements
Support by the Hungarian Science Research Fund (OTKA grant no. K67746), by the European Commission’s 6th Framework Programme (SOLAIRE Network, MTRN-CT-2006-035484) as well as by the European Union with the co-financing of the European Social Fund (grant no. TÁMOP-4.2.1/B-09/1/KMR-2010-0003) is gratefully acknowledged.
Wilcox Solar Observatory data used in this study was obtained via the web site http://wso. stanford.edu/, courtesy of J.T. Hoeksema. The Wilcox Solar Observatory is currently supported by NASA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0), which permits use, duplication, adaptation, distribution, and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Petrovay, K. Solar Cycle Prediction. Living Reviews in Solar Physics 7, 6 (2010). https://doi.org/10.12942/lrsp-2010-6
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12942/lrsp-2010-6
Keywords
Article history
Latest
Solar cycle prediction- Published:
- 23 March 2020
- Received:
- 02 July 2019
- Accepted:
- 17 January 2020
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41116-020-0022-z
Original
Solar Cycle Prediction- Published:
- 01 December 2010
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12942/lrsp-2010-6