Abstract
Background
The application of the free radical nitric oxide (NO) donors (arginine and sodium nitroprusside) have protective effects on plants in alleviating salinity stress throughout improving the enzymatic activities of antioxidant enzymes and osmotic adjustment which induced plant antioxidative defense system. This experiment carried out to study the effect of soaking seeds of sunflower plant in different concentrations of arginine or sodium nitroprusside (SNP) on growth, some physiological parameters, yield and chemical composition of the yielded seeds of sunflower under salinity stress.
Results
Growth parameters (shoot length, stem diameter, no. of leaves, shoot fresh, and dry weights) decreased significantly with salinity stress and such effect ameliorated using the two levels of both arginine and SNP. Photosynthetic pigments significantly increased in the arginine and SNP treated plants under salinity stress or not stressed ones. Phenol and indole acetic acid as well as compatible solutes as total soluble sugar and proline showed highly significant increase with arginine and SNP treatments either in unstressed plants or those under salinity stress conditions. Free amino acids showed significant increase in both unstressed and stressed sunflower plants treated with either arginine or SNP. High level of arginine recorded the highest values of TSS, proline, free AA, phenol, and IAA in both unstressed and salinity stressed plants. Arginine and SNP with salinity levels showed a highly significant increase in various antioxidant enzymes compared to the control plants. Arginine or SNP at all tested concentrations decreased significantly plant content of Na, while K and P highly significantly increased and Ca, Mg, and N non-significantly increased. The yield parameters showed in general highly significant increase in head diameter, 100-seed weight, seed yield/plant, and oil% with arginine or SNP with the superiority of the higher concentration of both treatment materials. Both arginine and SNP increased markedly total unsaturated (TU) fatty acids as well as TU/TS with superiority of high concentration of SNP treatment in that domain.
Conclusion
Soaking seeds of sunflower plant with arginine and SNP improved yield parameters of sunflower. High level of SNP under salinity stress conditions proved to be the most effective.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Throughout the world, more than 800 million ha of land are salt-affected (FAO 2008). In arid and semi-arid regions, limited water and hot dry climates cause salinity problem that adversely affects crop growth and production. At low concentrations, salt suppresses plant growth and at higher concentration can cause death throughout imbalance of the cellular ions resulting in ion toxicity (Michael et al. 2004). Morphological, physiological, and metabolic disorders in plants, e.g., decrease in seed germination, shoot and root length, alterations in the integrity of cell membranes, inhibition of different enzymatic activities, photosynthesis, and even plant death by NaCl (Sairam and Tyagi 2004). Khan et al. (2012) reported that higher concentration of sodium chloride as the prevailing salt in the soil induces osmotic and ionic changes in plants, since it lowers its osmotic potential resulting in decreased availability of water and minerals to root cells. Hashem et al. (2014) explained the reduction in physiological and biochemical activities of plants by causing toxic effects on cell membranes and accordingly electrolyte leakage, as well as constrains the metabolic processes in the cytosol with excessive accumulation of Na+ in the cytosol.
Under stressful conditions reactive oxygen species (ROS) which known as signaling intermediates during biotic and abiotic stresses overproduced and cause oxidative stress in plants (Abdel Latef and Chaoxing 2014). Throughout lipid peroxidation and ability to damage DNA, proteins, and chlorophyll, these compounds are responsible for damage cellular membranes (Mittova et al. 2002). Sharma and Dubey (2007) found that the lifetime of active oxygen species within the cellular environment is determined by the antioxidant system which provides vital protection against oxidative damage. According to Evelin and Kapoor (2014), the ROS scavenging enzymes involves superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), ascorbate peroxidase (APX), and glutathione reductase (GR). Proline, glycine betaine (GB), soluble proteins, and soluble sugars accumulation to beat osmotic stress caused by salinity is another strategy (Abdel Latef and Chaoxing 2014).
In the past few years, nitric oxide (NO) as a water and lipid soluble gas endogenous plant bioactive signaling molecule had been tested in salt stress tolerance (Mostofa et al. 2015). The NO has attracted much attention because of its pivotal role in stress tolerance exerted by oxidative stress in various processes of plant growth, development, metabolism, and cell death (Manai et al. 2014). Moreover, the NO can mediate plant growth regulators and ROS metabolism and focuses which NO involves in signal transduction and responses to biotic and abiotic stresses (Fan et al. 2007).
l-arginine (arg.) is one of the most functionally diverse amino acids and a precursor for the biosynthesis of polyamines (PAs) and the cell signaling molecule nitric oxide (NO). It seems that some positive effects of arg. are related to the production of nitric oxide, polyamines, or proline (Liu et al. 2006). The PAs modulate several biological activities in plants, throughout participation in cellular defense against oxidative damage via the inhibition of lipid peroxidation and scavenge of free radicals (Velikova et al. 2000).
Pre-sowing seed treatment is an easy and low, and both cost and risk technique were used to cope with salinity stress among different strategies which have recently been used to overcome the salinity problem in saline agricultural lands. The present study was conducted to evaluate and compare the effects of seed priming with arginine and SNP on growth, yield, and alleviation of oxidative damages in sunflower plant under salt stress.
Materials and methods
This experiment carried out to study the effect of soaking sunflower plant seeds in different concentrations of arginine or sodium nitroprusside (SNP) on growth, some physiological parameters, yield, and chemical composition of the yielded seeds under salinity stress.
Experiment management
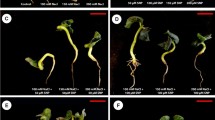
A pot experiment using sunflower (Helianthus annuus, L.) cultivar Sakha 53 was carried out in two successive seasons 2016 and 2017 in the greenhouse of National Research Centre, Dokki, Giza, Egypt. Seeds of sunflower were obtained from the Agricultural Research Centre, Giza, Egypt. Arginine or SNP used in the present work was supplied from Sigma-Aldrich. Seeds were planted in pots (50 cm3) with the soil of silt and sand soil of 1:1 ratio to reduce compaction and improve drainage. Seeds were previously sterilized after washing several times with distilled water. The pots were divided into two main groups according to irrigation with fresh water and saline solution (0 and 5000 mg/L equal to EC of 0.03 and 5.10 dSm−1) by using Stroganov (1962) nutrient solutions (Tables 1 and 2). Each of the two main groups was divided into five subgroups one of them without treatment (control) and the other four subgroups were soaked for 12 h in two concentrations of both arginine (10 and 20 mM) or SNP (0.25 and 0.50 mM). Every treatment consisted of three replicates distributed in a completely randomized design system. Sunflower seeds were sown in May in both seasons. The seedlings were irrigated with an equal volume (half liter/pot) of salt solution three times, whereas tap water was used for the fourth one to prevent the accumulation of salts around the root system. Thinning was carried out at 15 days after sowing, and five plants were left in each pot. Fertilization applied with the recommended doses of superphosphate, potassium sulfate, and urea in each pot.
Growth measurements
Samples were taken after 40 days from sowing to determine the morphological measurements and chemical analysis. One plant/pot has been left for yield determination. The morphological measurements were plant height (cm), number of leaves/plant, stem circumference (cm), fresh and dry weight of shoot (gm/plant).
Yield measurements
When signs of full maturity stage showed, measurements for yield and its components (head diameter (cm), seeds weight/head (gm), 100-seeds weight (gm), oil %, and fatty acids profile) were also recorded.
Chemical analysis
Some biochemical aspects were determined including photosynthetic pigments (chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, carotenoids, and total pigments) in fresh leaves which were estimated using the method of Lichtenthaler and Buschmann (2001). Indole acetic acid content was extracted and analyzed by the method of Larsen et al. (1962). Phenolic content was measured as described by Danil and George (1972). Free amino acids (free AA) was extracted according to Vartainan et al. (1992) and determined with the ninhydrin reagent method (Yemm and Cocking 1955). Proline content was extracted and calculated according to Bates et al. (1973). Total soluble sugars (TSS) were extracted according to Homme et al. (1992) and assayed according to Yemm and Willis (1954). Enzyme extracts were prepared according to the method of Chen and Wang (2006). Catalase (CAT) and superoxide dismutase (SOD, EC 1.12.1.1) activity was calculated by nitro-blue-tetrazolium reduction method (Chen and Wang 2006). Peroxidase (POX, EC 1.11.1.7) activity was evaluated according to Kumar and Khan (1982).
Macro element contents of sunflower plants were determined according to Chapman and Pratt (1978). Phosphorus was determined using Spekol Spectrocolorimeter VEB Carl Zeiss. Plant contents of Ca, K, and Na were estimated by using the flame photometer. The Mg contents were estimated using atomic absorption spectrophotometer. Total N was determined by using micro-Kjeldahl method (A.O.A.C. 1970).
The oil content of sunflower seeds was determined according to the procedure reported by A.O.A.C. (1990). As the quality of the oil depends on the proportion of different fatty acids, their composition was determined quantitatively by gas-liquid chromatography according to the method described by Fedak and De La Roche (1977).
Statistical analysis
The data were statistically analyzed on complete randomized design system according to Snedecor and Cochran (1980). Combined analysis of the two growing seasons was carried out. Means were compared by using the least significant difference (LSD) at 1 and 5% levels of probability.
Results
Changes in growth parameters
Data in Table 3 showed clearly that shoot length and stem diameter (cm) decreased significantly (P≤0.05 and 0.01, respectively) with salinity stress.
Such reduced effect was ameliorated using arginine at the rate of 10 and 20 mM and SNP at the rate of 0.25 and 0.50 mM. While, although number of leaves showed a non-significant decrease by about 17.4% due to salinity stress, it showed improvement reached 15.8%, 20.9%, 39.5%, and 31.6% using the low and high levels of either arginine or SNP, respectively as compared with the corresponding controls. The same trend recorded with number of leaves also found in shoot fresh and dry weights (gm). It is interesting to note that the most obvious effect for the studied growth parameters found with the use of high concentration of both arginine and SNP.
Changes in photosynthetic pigments
The presented data (Table 4) showed that chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, and total pigments significantly (P < 0.05) decreased in sunflower leaves due to salinity stress. Data in the same table showed generally that chlorophyll a, carotenoids, and total pigments significantly (P < 0.01) increased in treated plants with arginine and SNP either under salinity stress or not stressed ones. The highest increase (22.2%) and (21.8%) in total pigment content was obtained with both high concentrations of arginine and SNP respectively with salinity stressed sunflower plants. Although chl. B presented no significant effect of the interaction between the tested materials and their concentrations with both levels of salinity, the treatment improved its values.
Changes in compatible solutes
Generally, data in Table 5 showed that salinity induced significant changes in tested plants’ compatible solutes (TSS, proline, and free AA). TSS and proline showed a highly significant increase (P < 0.01) with all the experimental treatments either in unstressed plants or those under salinity stress conditions. Free AA showed only significant increase (P < 0.05) in both salinity unstressed or stressed sunflower plants. Arginine treatment at the rate of 20 mM recorded the highest values of the previously studied parameters with both unstressed or salinity stressed plants.
Changes in phenol and IAA content
It is obvious in Table 5 that phenol increased significantly, but IAA decreased significantly (P ≤ 0.05 and 0.01) with salinity stressed sunflower plants. In either unstressed or salinity-stressed plant, arginine, and Sod. nitroprusside at the two tested levels increased significantly the contents of both phenols and IAA in sunflower leaves.
Changes in antioxidant enzymes
Data in Table 6 indicated that salinity caused a significant increase in antioxidant enzymes (CAT, SOD, and POX) of tested plants. Pretreatment of sunflower seeds with arginine (10 and 20 mM) and SNP (0.25 and 0.50 mM) with both salinity levels 0 and 5000 mg/L showed highly significant increase (P < 0.01) in various antioxidant enzymes compared to the control plants. Both treatments levels of SNP recorded the highest (P < 0.01) values of antioxidant enzymes in plants either unstressed or salinity stressed ones. The magnitude of these enzymes’ enhancement increased with increasing salinity level and the treatment of sunflower seeds with arginine or SNP improved stress tolerance by increasing CAT, SOD, and POX activities with corresponding salinity level as compared to the control.
Changes in some mineral contents
Some macro-element content of sunflower plants (either unstressed or salinity stressed) resulted from seeds treated with either arginine or SNP at the two levels of both materials before sowing are listed in Table 7. The results showed clearly that salinity significantly decreased all measured elements except Na which increased significantly with increasing salinity level. Arginine or SNP at the two levels each decreased significantly (P < 0.05) Na, while the same treatments highly significantly increased (P < 0.01) K and P content of the tested plants. On the other hand, the interaction showed no significant effect on Ca, Mg, and N contents of resulted plants due to the experimental treatments.
Changes in yield parameters
The yield parameters (Table 8) of treated sunflower plants showed a remarkable decrease in general due to salinity stress. Highly significant increase (P < 0.01) in head diameter, 100-seed weight, and oil% of resultant seeds with either arginine or SNP with the superiority of the higher concentration of both treatment materials. On the other hand, although there is marked differences in seed yield/plant showed no significant response due to the interaction among the experimental factors (salinity levels, treatment materials, and tested concentrations of treatment materials).
Changes in fatty acids contents
Gas chromatographic analysis results of the methyl esters for fatty acids of yielded sunflower seeds are presented in (Table 9). The present data showed that under salinity stress, the unsaturated fatty acids (TU), palmitolic (C16:1), oleic (C18:1), linoleic (C18:2), and linolenic (C18:3) showed a marked decrease of the yielded seeds. Meanwhile, the opposite result was observed in the saturated fatty acids (TS); palmitic (C16:0), steraic (C18:0), and archidic (C20:0).
In either unstressed or salinity-stressed plant, arginine and Sod. nitroprusside at the two tested levels increased remarkably all the unsaturated fatty acids. The most effective increase recorded with SNP at the highest concentration (0.50 mM) at stressed yielded seeds, while all the saturated fatty acids induced a remarkable reduction. Total unsaturated fatty acids (TU) content as well as TU/TS increased markedly with SNP treatment more than arginine treatment with the superiority of high concentration for both treatments.
Discussion
Changes in growth parameters
Regarding growth parameters of sunflower plants treated with arginine and SNP grown under unstressed and stressed conditions, data in Table 3 showed clearly that all growth parameters decreased significantly with salinity stress. This result is in harmony with results on different crops obtained by Abdel Latef and Chaoxing (2014) on pepper (Capsicum annuum) and Mostofa et al. (2015) on rice (Oryza sativa).
The reduction effect of salinity stress on plant growth parameters (Table 3) may be due to the toxic effect of Na and Cl ions excessive accumulation around the root system and accordingly in plant cells. Kosová et al. (2011) explained that these ions reduced the uptake of water by plants resulted from the increased osmotic pressure of soil solution. The plants overcome salinity toxic effect via mechanisms of osmotic adjustment (increases the compatible solutes), improve stomata closure, and decreased photosynthesis rate.
The reduction effect was ameliorated using arginine at the rate of 10 and 20 mM and SNP at the rate of 0.25 and 0.50 mM. It is of interest to note that the most obvious effect recorded for the studied growth parameters with the use of high concentration of both of arginine (20 mM) and SNP (0.50 mM). The obtained results came in line with findings of Nejadalimoradi et al. (2014) who found that pretreatment of sunflower plants with arginine and SNP increased the length of shoot and root of the salinity stressed plants. The SNP effect on purple coneflower studied by Asadi-Sanam et al. (2018) proved that fresh and dry weights of roots and leaves increased compared to the plants under salinity stress.
Exogenous application of NO sources (arginine and SNP) protected sunflower plants against salt stress-induced oxidative damage via promoting the biosynthesis of antioxidant enzymes and accordingly improving plant growth under salinity stress conditions. The present results supported with findings of Ahmad et al. (2016) who reported that exogenous application of NO to salinized plants enhanced the growth parameters. They attributed this effect to the NO capability to mitigate the adverse effects of high salinity on chickpea plants by improving leaf relative water content (LRWC), photosynthetic pigment biosynthesis, osmolyte accumulation, and antioxidative defense system. Also, Mostafa et al. (2010) found that foliar application of arginine enhanced the growth rate and yield of wheat plants. They attributed this stimulatory effect to arginine as a precursor of polyamines which increased vegetative growth, growth promoters, antioxidant enzymes, endogenous amino acids, and their translocation to the produced grains under normal or stress condition.
Changes in photosynthetic pigments
All photosynthetic pigments (chl. a, chl. b, carotenoids) as well as total pigments (Table 4) data recorded a significant decrease generally in sunflower plants under salinity stress. Suppression of photosynthetic activity forms took place through different means, e.g., stomatal closure (Kosová et al. 2011), an increase in free radicals in chloroplasts and destruction of chlorophyll molecules by ROS (Dolatabadian and Saleh Jouneghani 2009) and inhibition of its biosynthesis processes and activation of enzymatic degradation (Rady et al. 2015). Gururani et al. (2015) stated that involved carotenoids in mechanisms regulating photoprotection against auto-oxidation is a key role in photosynthetic reaction center. Ahmad et al. (2016) noted that the synthesis of carotenoids increased under salinity stress due to the antioxidants action of these compounds to minimize the oxidative damage induced in chickpea by salinity stress
Such reduced effect of photosynthetic activity was ameliorated using arginine and SNP which increased in treated plants either under salinity stress or not stressed ones. The obtained results in the present study can be explained by the potent role of NO in scavenging the ROS and thus decreased the oxidative damage in photosynthetic apparatus and increased the chlorophyll content (Lei et al. 2007). Moreover, Kausar et al. (2013) reported that NO was found to promote the improvement of photosynthetic pigments likely by defending the membrane of the cell organelle containing Chl. against salt-induced ion toxicity in chickpea plants.
Similar results to the present investigation were obtained by Nejadalimoradi et al. (2014) who showed that chl. a decreased under saline condition, while chl. b and total Chl. did not change in comparison with control plants of sunflower. They added that carotenoid content increased in plants under salt stress and pretreatment of plants with arginine and SNP increased chlorophyll content in plants under salinity stress. Moreover, Asadi-Sanam et al. (2018) found that chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, and total chlorophyll followed the same mentioned trend when purple cornflower exposed to salinity stress conditions. They obtained the highest amount of chlorophyll when they treated plants with 0.4 mM of SNP.
Changes in compatible solutes
In the present work, salinity stress caused significant increases in TSS, proline, and free amino acids (Table 5). Increasing the compatible solutes (TSS, proline, and free amino acids) improves plant cells tolerance to salinity stress via increasing osmotic pressure in the cytoplasm as well as relative water contents essential for plant growth (Tawfik et al. 2017). In addition, Hosseini et al. (2014) stated that improve membrane stabilization due to soluble sugars which may act as ROS scavengers. Proline has vital roles from damaging effects of osmotic stresses as an osmotic adjustment as well as stabilization and protection of enzymes, proteins, and membranes (Ashraf and Foolad 2007).
Table 5 showed that pretreatment sunflower seeds with arginine (10 and 20 mM) and Sod. nitroprusside (0.25 and 0.50 mM) with both salinity levels 0 and 5000 mg/L enhanced all the previous parameters in sunflower leaves. The same trend recorded herein is in harmony with Liu et al. (2006) who reported that some positive effects of arginine are related to production of nitric oxide (NO), polyamines, or proline. The trend obtained herein can be explained by the fact that proline and TSS accumulated in plant tissues under saline stress conditions are suspected to contribute to osmotic adjustment. On the same line, Rasool et al. (2013) documented that plants are self-defensed with well-regulated antioxidant machinery that capable of protecting biomolecules from further damages to overcome the adverse effects of oxidative stress. Moreover, plants under salinity stress conditions followed another strategy of accumulation for both soluble proteins and sugars to overcome osmotic stress since cellular defense against oxidative damage via the inhibition of lipid peroxidation and scavenge of free radicals (Ahmad et al. 2016)
Changes in phenols and IAA contents
The phenolic contents of sunflower leaves (Table 5) were significantly increased due to salinity and/or exogenous application of NO donor (arginine and SNP). This increase in phenol contents can mitigate the harmful effect of salinity. In this domain, Huang et al. (2005) stated that phenol considered as antioxidants defense system scavenging free radicals resulted from their high reactivity as hydrogen or electron donors. This process leads to stabilize and delocalize the unpaired electron (chain-breaking function) and from their ability to chelate transition metal ions.
The decreases in IAA in shoot tissues due to salinity stress cause a reduction in growth rate (Table 3). These results are in agreement with those obtained by Jasim et al. (2016). This effect diminished using arginine and SNP which increased IAA content in treated plants either under salinity stress or not stressed ones. This increase in IAA resulted in stimulation of cell division and/or cell enlargement and consequently improved the growth rate (Mostafa et al. 2010).
Changes in antioxidant enzymes
The activities of antioxidant enzymes, such as CAT, SOD, and POX in the shoot of sunflower plants increased significantly under salinity stress (Table 6). Khattab (2007) reported that these antioxidant enzymes considered a preservation system that minimizes oxidative damage due to increasing production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) resulted from salinity stress. At stress conditions, higher content of hydrogen peroxide is detoxified by catalase and glutathione peroxidase (Dat et al. 2000). Jin et al. (2006) found that SOD is the first defense enzyme converts superoxide to H2O2, which can be scavenged by CAT and different classes of POX and ascorbate peroxidase. These results are in agreement with those observed by El-Bassiouny and Sadak (2015) and Ahmad et al. (2016).
Pretreatment sunflower seeds with arginine and SNP improved stress tolerance by increasing CAT, SOD, and POX activities with corresponding salinity level as compared to the control. In this concern, Sharma and Dubey (2007) reported that this antioxidant system produces viable protection against oxidative damage which found to enhance the lifetime of active oxygen species within the cellular environment.
Nejadalimoradi et al. (2014) on sunflower plants explained the protective effects of arginine in salt-stressed plants may be due to NO releasing from arginine, either directly or indirectly. Since, under normal conditions, the total amount of ROS formed in the plants is controlled by the balance between the multiple ROS producing pathways and the ability of the enzymatic and non-enzymatic mechanism to deal with them. While, under stress conditions, ROS formation is higher than the ability of plants to remove them and this could result in oxidative damages (Laspina et al. 2005). In this concern, data recorded by Zheng et al. (2009) indicated that nitric oxide (NO) serves as a signal inducing salt tolerance by increasing the activities of SOD and CAT generation rate in the mitochondria. Under stressful of NaCl conditions, the signaling intermediates, e.g., ROS overproduced and accumulate causing oxidative stress in plants in a step of adaptation and this is associated with the antioxidant enzyme system of plants (Abdel Latef and Chaoxing 2014). Nejadalimoradi et al. (2014) found that SNP pretreatment could increase the activity of CAT, GPX, and APX enzymes in root and leaves, while arginine pretreatment increased the activity of CAT and APX in roots and leaves of sunflower-stressed plants.
Moreover, Kaya et al. (2015) reported that the main action of NO is the induction of plant antioxidative defense system by improving the enzymatic activities of antioxidant enzymes of SOD, CAT, APX, POD, and glutathione reductase. Qiao et al. (2014) said that throughout decreasing the levels of ROS, by scavenging O2 and free radicals (R), NO inhibits oxidative damage in stressed plants by regulating redox homeostasis, increasing the enzymatic activities of H2O2-scavenging enzymes.
Changes in some minerals content
The data obtained in this work (Table 7) showed that under salinity stress the content of essential mineral nutrients (N, P, K, Ca, and Mg) of sunflower plants were significantly decreased and the toxic ion (Na+) increased.
As reviewed and discussed by Farooq et al. (2017), salt stress disrupts the availability, competitive uptake, and translocation of nutrients to the aboveground plant parts. The presence of excessive concentrations of Na and Cl ions in the soil will cause imbalanced nutrition in legumes due to the interference of these ions with other elements. Such kind of results can be contradicted to others on the base that higher concentrations of sodium chloride (NaCl) as the prevailing salt in the soil induces osmotic and ionic effects on plants since it lowers its osmotic potential, resulting in decreased availability of water and minerals to root cells (Khan et al. 2012). Higher salt concentrations and prolonged exposure to NaCl stress resulted in oxidative stress in plants accompanied with a reduction in physiological and biochemical activities of plants causing toxic effects on cell membranes (Rasool et al. 2013). Poor et al. (2015) reported that administration of low molecular weight NO donors under high salinity conditions improves plant ability to equilibrate ion homeostasis. The SNP at 100 μM as a NO donor significantly increased K+ and decreased Na+ levels in mangrove species (Kanadelia obovate).
The used experimental treatments in the present study (arginine or SNP) as NO donors showed an amelioration effect throughout preventing the salinity stress conditions in forms of improving the tested elements with decreasing Na+ content. This protective effect can be declared by the electrolyte leakage as well as constrains the metabolic processes in the cytosol explained by Hashem et al. (2014) with excessive accumulation of Na+ in the cytosol.
Kaya et al. (2015) recorded that alleviation the adverse effects of salinity by decreasing Na+ content and increasing Ca2+, K+, N, and P levels maintained the ion homeostasis of salt-stressed maize cultivars plants by exogenous administration of SNP. They added that SNP reduced toxic levels of malondialdehyde (MDA) and H2O2 and increased the content of photosynthetic pigments in salt-stressed plants. Moreover, Jamali et al. (2015) treated strawberry (Fragaria ananassa) plants, 1 week before the start of salinity stress, with 75 μM SNP and found that the K+/Na+ ratio increased in treated plants compared with non-SNP treated ones.
Changes in yield parameters
Exposure of sunflower plants to salinity stress resulted in a severe reduction in yield parameters in forms of head diameter, 100-seed weight, seed yield/plant, and oil% (Table 8). These results were in agreement with those obtained by El Sebai et al. (2016) who found that increasing salinity level resulted in a gradual reduction of yield (shoot length, number of branches, shoot weight, and seed weight/plant) and also the oil content of quinoa plants. The reduction in yield parameters may be attributed to the inhibitory effect of salinity on growth parameters (Table 3) and chemical composition of plants, which therefore reflected in the produced yield. Furthermore, the reduction of sunflower yield/plant due to salinity stress might be due to the harmful effect of salt on growth as well as the disturbance in mineral uptake (Table 7). In this concern, El Sayed 2011 mentioned different reasons for yield reduction due to salinity stress, e.g., reduced carbon fixation, disturbed hormonal regulation, nutritional imbalances, specific ion, and osmotic effects. Ahmad et al. (2016) reported that the decrease in chlorophyll content might partially cause a decrease in growth and biomass yield on chickpea plants. Khan et al. (2016) found that such a reduction in yield associated with delayed flowering reduced flower numbers and pod set. More recently, Farooq et al. (2017) mentioned that reductions in grain yield due to salinity can be attributed to reduced pollen viability, stigma receptivity, and the supply of photo-assimilates during grain filling.
Data showed clearly that the application of different treatments with arginine and SNP increased significantly yield and its components either under salinity stress or not stressed ones. The most pronounced increase observed with both the highest concentration of arginine in unstressed plant and SNP under stress conditions. The obtained results are in harmony with those recorded by Mohamed et al. (2015) on faba bean plants grown in sandy soils. They found that significant increases in faba bean yield and yield components (mean pod weight, mean seed weight/pod, 100-seed weight, seeds, straw, and mean average biological yield/feddan) by foliar spraying with arginine at the rate of 300 ppm. Such effect was not significant when plants sprayed with 200 ppm arginine.
Ali et al. (2017), working on different wheat varieties, found that both SNP levels (0.1 and 0.2 mM) had the same effect in reducing the adverse effects of salt stress on a number of tillers. Pre-sowing wheat seed treatment with both SNP levels effectively reduced the adverse effects of salt stress on hundred-grain weight and grain yield. They concluded that exogenous SNP application could effectively increase the growth and grain yield of wheat plants under salt stress conditions.
Changes in fatty acids contents
The reduction in the content of unsaturated fatty acids of the sunflower plants yielded seeds and increase in the content of saturated fatty acids due to salinity stress (Table 9) are in harmony with the data obtained by Bybordi et al. (2010) who found that salt treatment reduced significantly the total fatty acids (TFA) content by 25% at 200 mM NaCl of canola. Hajlaoui et al. (2009) explained that the adaptive feature to salinity expressed in forms of possible reduction of the desaturase activity in Schizochytrium limacinum. In addition, Malkit et al. (2002) worked on Alga dunaliella salina, and reported that some plants could be protected against the oxidative effects of salt ions through restructuring membranes with less polyunsaturated fatty acids. Moreover, this low unsaturation degree limited the membrane fluidity (Zhao and Qin 2005 and Upchurch 2008) and restricted permeability to Na and Cl ions (Konova et al. 2009).
These positive results of increased unsaturated fatty acids content as well as TU/TS (Table 9) may be explained as a result of cellular defense against oxidative damage via the inhibition of lipid peroxidation and scavenge of free radicals (Velikova et al. 2000). This is considered one of the good results from the consumer health point of view, since the increase in unsaturated fatty acids content means an increase Ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. The production of such kind of oils rich in Omega-3-polyunsaturated fatty acids (Ω-3-PUFA) would be of benefit to overcome human health problems since in recent decades human health concern took place because of the century diseases spread all over the world. The demand increased on producing healthy product with low saturated fatty acids “FAs” and high-unsaturated fatty acid levels, since the latter plays a vital role in human nutrition since they help to reduce the incidence of coronary artery diseases, hypertension, and diabetes and certain inflammatory diseases as arthritis and dermatitis (Simopoulos 2000). Conclusively, the obtained results under the present experimental conditions suggested that SNP proved to be better than arginine in most cases of the studied parameters under salinity stress conditions.
Conclusion
Soaking the seeds of sunflower plant with arginine and SNP improved the yield parameters of sunflower. High level of SNP under salinity stress conditions proved to be the most effective.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- CAT:
-
Catalase
- Free AA:
-
Free amino acids
- IAA:
-
Indole acetic acid
- POX:
-
Peroxidase
- SNP:
-
Sodium nitroprusside
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- TSS:
-
Total soluble sugar
References
A.O.A.C (1970) Official methods of analysis of association agriculture chemists, 11th edn. Assoc Off. Agric. Chemists, Washington, p 777
A.O.A.C (1990) Official Methods of Analysis, 20th edn. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Arlington
Abdel Latef AA, Chaoxing H (2014) Does the inoculation with Glomus mosseae improves salt tolerance in pepper plants? J Plant Growth Regul. 33:644–653
Ahmad P, Latef AAA, Hashem A (2016) Nitric oxide mitigates salt stress by regulating levels of osmolytes and antioxidant enzymes in chickpea. Front Plant Sci. 7:347
Ali Q, Daud MK, Haider MZ, Ali S, Rizwan M, Aslam N, Noman A, Iqbal N, Shahzad F, Deeba F, Ali I, Zhu SJ (2017) Seed priming by sodium nitroprusside improves salt tolerance in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) by enhancing physiological and biochemical parameters. Plant Physiol Biochem 119:50–59
Asadi-Sanam S, Mohammadi SM, Rameeh S, Gerami M, Khoshrooz M (2018) Effect of sodium nitroprusside (SNP) on some of biochemical characteristics of purple coneflower (Echinacea purpurea (L) Moench) under salinity stress. J Plant Process Funct Iran Soc Plant Physiol 7(23):123–138
Ashraf M, Foolad MR (2007) Roles of glycine betaine and proline in improving plant abiotic stress tolerance. Environ Exp Bot 59:206–216
Bates LS, Waldan RP, Teare LD (1973) Rapid determination of free proline under water stress studies. Plant Soil. 39:205–207
Bybordi A, Jalal Tabatabaei S, Ahmedov A (2010) Effects of salinity on fatty acid composition of canola (Brassica napus, L.). J Food Agric Environ 8(1):113–115
Chapman HD, Pratt PF (1978) Methods of analysis for soils, plant and water, vol 4034. Division Agriculture Science, California Univ, pp 50–169
Chen JX, Wang XF (2006) Plant physiology experimental guide. Higher Education Press, Beijing, pp 24–25 55–56
Danil AD, George CM (1972) Peach seed dormancy in relation to endogenous inhibitors and applied growth substances. J Amer Soc Hort Sci 17:621–624
Dat J, Vandenabeele S, Vranova E, Van Montagu M, Inzé D, Van Breusegem F (2000) Dual action of the active oxygen species during plant stress responses. Cell Mol Life Sci 57:779–795
Dolatabadian A, Saleh Jouneghani RJ (2009) Impact of exogenous ascorbic acid on antioxidant activity and some physiological traits of common been subjected to salinity stress. Notulae Botanicae Horti Agrobotanici Cluj-Napoca 37(2):165–172
El Sayed HESA (2011) Influence of salinity stress on growth parameters, photosynthetic activity and cytological studies of Zea mays, L. plant using hydrogel polymer. AgricBiol J N Am 2:907–920
El Sebai TN, Abdallah MMS, El-Bassiouny HMS, Ibrahim FM (2016) Amelioration of the adverse effects of salinity stress by using compost, Nigella Sativa extract or ascorbic acid in quinoa plants. Int J Pharm Tech Res 9(6):127–144
El-Bassiouny HMS, Sadak MS (2015) Impact of foliar application of ascorbic acid and α-tocopherol on antioxidant activity and some biochemical aspects of flax cultivars under salinity stress. Acta Biol Colomb 20(2):209–222
Evelin H, Kapoor R (2014) Arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis modulates antioxidant response in salt-stressed Trigonella foenum-graecum plants. Mycorrhiza 24:197–208
Fan HF, Guo SR, Li J, Du CX, Huang BJ (2007) Effects if exogenous nitric oxide on Cucumis sativus seedlings growth and osmotic adjustment substances contents under NaCl stress. J Chem Ecol 26:2045–2050
FAO (2008). Land and Plant Nutrition Management Service. Retrieved from: http://www.fao.org/ag/agl/agll/spush.
Farooq M, Gogoi N, Barthakur S, Baroowa B, Bharadwaj N, Alghamdi SS, Siddique KHM (2017) Draught stress in grain legume during reproduction and grain filling. J Agron Crop Sci 203:81–102
Fedak G, De La Roche I (1977) Lipid and fatty acid composition of barley kernels. Canad J Plant Sci 57:257
Gururani MA, Venkatesh J, Tran LSP (2015) Regulation of photosynthesis during abiotic stress-induced photoinhibition. Mol Plant 8:1304–1320
Hajlaoui H, Denden M, El-Ayeb N (2009) Changes in fatty acids composition, hydrogen peroxide generation and lipid peroxidation of salt stressed corn (Zea mays L.) roots. Acta Physiol Plant 31:787–797
Hashem A, Abd Allah EF, El-Didamony G, Alwhibi MS, Egamberdieva D, Ahmad P (2014) Alleviation of adverse impact of salinity on faba bean (Vicia faba, L.) by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Pak J Bot 46:2003–2013
Homme PM, Gonzalez B, Billard J (1992) Carbohydrate content, frutane and sucrose enzyme activities in roots, stubble and leaves of rye grass (Lolium perenne L.) as affected by sources / link modification after cutting. J Plant Physiol 140:282–291
Hosseini SM, Hasanloo T, Mohammadi S (2014) Physiological characteristics, antioxidant enzyme activities, and gene expression in 2 spring canola (Brassica napus, L.) cultivars under drought stress conditions. Turk J Agric For 38:1–8
Huang C, He W, Guo J, Chang X, Su P, Zhang L (2005) Increased sensitivity to salt stress in ascorbate-deficient Arabidopsis mutant. J Exp Bot 56:3041–3049
Jamali B, Eshghi S, Tafazoli E (2015) Mineral composition of ‘selva’ strawberry as affected by time of application of nitric oxide under saline conditions. Hort Environ Biotechnol 56:273–279
Jasim AH, Abo Al Timmen WM, Abid AS (2016) Effect of salt stress on plant growth and free endogenous hormones of primed radish (Raphanus Sativus, L.) seeds with salicylic acid. Int J Chem Tech Res CODEN (USA): 0974-4290. ISSN(Online) 9(06):339–346
Jin J, Shan N, Ma N, Bai J, Gao J (2006) Regulation of ascorbate peroxidase at the transcript level is involved in tolerance to postharvest drought stress in the cut rose (Rosa hybrida, L.) cv. Samantha. Postharvest Biol Tec 40:236–243
Kausar F, Shahbaz M, Ashraf M (2013) Protective role of foliar-applied nitric oxide in Triticum aestivum under saline stress. Turk J Bot 37:1155–1165
Kaya C, Ashraf M, Sonmez O (2015) Exogenously applied nitric oxide confers tolerance to salinity-induced oxidative stress in two maize (Zea mays, L.) cultivars differing in salinity tolerance. Turk J Agric For 39:909–919
Khan HA, Siddique KHM, Colmer TD (2016) Vegetative and reproductive growth of salt-stressed chickpea are carbon-limited: sucrose infusion at the reproductive stage improves salt tolerance. J Exp Bot 68(8):2001–2011
Khan MN, Siddiqui MH, Mohammad F, Naeem M (2012) Interactive role of nitric oxide and calcium chloride in enhancing tolerance to salt stress. Nitric Oxide 27:210–218
Khattab H (2007) Role of glutathione and polyadenylic acid on the oxidative defense systems of two different cultivars of canola seedlings grown under saline conditions. Aust J Basic Appl Sci 1(3):323–334
Konova IV, Sergeeva YE, Galanina LA, Kochkina GA, Ivanuskina NE, Ozerskaya SM (2009) Lipid synthesis by Geomyces pannorum under the impact of stress factors. Microbiol. 78(1):42–47
Kosová K, Vítámvás P, Prášil IT, Renaut J (2011) Plant proteome changes under abiotic stress contribution of proteomics studies to understanding plant stress response. J Proteomics 74:1301–1322
Kumar KB, Khan PA (1982) Peroxidase and polyphenol oxidase in excised ragi (Eleusine coracana cv. PR 202) leaves during senescence. Indian J Exp Bot 20:412–416
Larsen P, Harbo A, Klungron S, Ashein TA (1962) On the biosynthesis of some indole compounds in Acetobacter Xylinum. Physiologia Plantarum 15:552–565
Laspina NV, Groppa MD, Tomaro ML, Benavides MP (2005) Nitric oxide protects sunflower leaves against Cd-induced oxidative stress. J Plant Sci 169:323–330
Lei Y, Yin C, Ren J, Li C (2007) Effect of osmotic stress and sodium nitroprusside pretreatment on proline metabolism of wheat seedlings. J Plant Biol 516:386–390
Lichtenthaler HK, Buschmann C (2001) Chlorophylls and carotenoids: measurement and characterization by UV-VIS spectroscopy. In: Wrolstad RE, Acree TE, An H, Decker EA, Penner MH, Reid DS, Schwartz SJ, Shoemaker CF, Sporns P (eds) Current protocols in food analytical chemistry (CPFA). Wiley, New York, pp F4.3.1–F4.3.8
Liu JH, Nada K, Honda C, Kitashiba H, Wen XP (2006) Polyamine biosynthesis of apple callus under salt stress. Importance of the arginine decarboxylase pathway in stress responses. J Exp Bot 57:2589–2599
Malkit A, Sadka A, Fisher M, Goldshlag P, Gokhman I, Zamir A (2002) Salt induction of fatty acid elongase and membranes lipid modifications in the extreme halotolerant Alga dunaliella salina. Plant Physiol. 129:1320–1329
Manai J, Kalai T, Gouia H, Corpas FJ (2014) Exogenous nitric oxide (NO) ameliorates salinity-induced oxidative stress in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) plants. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 14(2):433
Michael D, Peel B, Waldron L, Kevin B (2004) Screening for salinity tolerance in Alfalfa. Crop Sci. 44:2049–2053
Mittova V, Tal M, Volokita M, Guy M (2002) Salt stress induces up-regulation of an efficient chloroplast antioxidant system in the salt tolerant wild tomato species Lycopersicon pennellii but not in the cultivated species. J Plant Physiol 115:393–400
Mohamed MF, Maha MSA, Khalifa RKM, Ahmed AG, Hozayn M (2015) Effect of arginine and GA3 on growth, yield, mineral nutrient content and chemical constituents of Faba bean plants grown in sandy soil conditions. Int J Chem Tech Res 8(12):187–195
Mostafa HAM, Hassanein RA, Khalil SI, El-Khawas SA, El-Bassiouny HMS, Abd El-Monem AA (2010) Effect of arginine or putrescine on growth, yield and yield components of late sowing Wheat. J Appl Sci Res 6(2):177–183
Mostofa MG, Fujita M, Tran LSP (2015) Nitric oxide mediates hydrogen peroxide- and salicylic acid induced salt tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings. Plant Growth Regul 77:265–277
Nejadalimoradi H, Nasibi F, Kalantari KM, Zanganeh R (2014) Effect of seed priming with L-arginine and sodium nitroprusside on some physiological parameters and antioxidant enzymes of sunflower plants exposed to salt stress. Agric Commun 2(1):23–30
Poor P, Laskay G, Tari I (2015) Role of nitric oxide in salt stress-induced programmed cell death and defense mechanisms. In: Khan MN, Mobin M, Mohammad F, Corpas FJ (eds) Nitric Oxide Action in Abiotic Stress Responses in Plants. Springer International Publishing Switzerlans, 2015, Charm, pp 193–219
Qiao W, Li C, Fan LM (2014) Cross-talk between nitric oxide and hydrogen peroxide in plant responses to abiotic stresses. Environ Exp Bot 100:84–93
Rady MM, Sadak MS, El-Lethy SR, Abd El-Hamid EM, Abdelhamid MT (2015) Exogenous α-tocopherol has a beneficial effect on Glycine max (L.) plants irrigated with diluted sea water. J Hortic Sci Biotech 90(2):195–202
Rasool S, Ahmad A, Siddiqi TO, Ahmad P (2013) Changes in growth, lipid peroxidation and some key antioxidant enzymes in chickpea genotypes under salt stress. Acta Physiol Plant 35:1039–1050
Sairam RK, Tyagi A (2004) Physiology and molecular biology of salinity stress tolerance in plants. J Curr Sci 86:407–421
Sharma P, Dubey RS (2007) Involvement of oxidative stress and role of antioxidative defense system in growing rice seedlings exposed to toxic concentrations of aluminum. J Plant Cell Rep 26:2027–2038
Simopoulos AP (2000) Human requirement for Ω-3-polyunsaturated fatty acids. Symposium: role of poultry products in enriching the human diet with n-3 PUFA. Poult Sci 79:961–970
Snedecor GW, Cochran WG (1980) Statistical Methods, 7th edn. The Iowa State Univ, Press, Ames
Stroganov BP (1962) Physiological basis of the salt tolerance of plants (under different types of soil salinization). Izd. Akad. Nauk. USSR, Moscow
Tawfik MM, Badr EA, Ibrahim OM, Abd Elhamid EM, Sadak MS (2017) Biomass and some physiological aspects of Spartina patens grown under salt affected environment in South Sinai, inter. J Agric Res 12(1):17–26
Upchurch RG (2008) Fatty acid unsaturation, mobilization and regulation in the response of plants to stress. Biotechnol Lett 30:967–977
Vartainan N, Hervochon P, Marcotte L, Larher F (1992) Proline accumulation during drought rhizogenesis in Brassica napus var. Oleifera Plant Physiol. 140:623–628
Velikova V, Yordanov I, Edreva A (2000) Oxidative stress and some antioxidant systems in acid rain-treated bean plants. Protective role of exogenous polyamines. J Plant Sci 151:59–66
Yemm EW, Cocking EC (1955) The determination of amino acids with ninhydrin. Analyst 80:209–213
Yemm EW, Willis AJ (1954) The respiration of barley plants. IX. The metabolism of roots during assimilation of nitrogen. New Phytotol 55:229–234
Zhao FG, Qin P (2005) Protective effects of exogeous fatty acids on root tonoplast function against salt stress in barley seedlings. Environ Exp Bot 53:215–223
Zheng C, Jiang D, Liu F, Dai T, Liu W, Jing Q, Cao W (2009) Exogenous nitric oxide improves seed germination in wheat against mitochondrial oxidative damage induced by high salinity. Environ Exp Bot 67:222–227
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors share in every step of this work, and all of them contribute to writing the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Ramadan, A.A., Abd Elhamid, E.M. & Sadak, M.S. Comparative study for the effect of arginine and sodium nitroprusside on sunflower plants grown under salinity stress conditions. Bull Natl Res Cent 43, 118 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s42269-019-0156-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s42269-019-0156-0